1c994c964393148065336d375bddd8f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 Internal energy: total amount of the energy of the particles that compose matter
Internal energy: total amount of the energy of the particles that compose matter
 What is the difference between heat, temperature and thermal energy? • Temperature: the measure of the average kinetic energy of the vibrating particles that compose an object • Heat: the quantity of thermal energy transferred from a hotter to a colder object • Internal Energy: the total amount of internal energy possessed by the particles that compose matter
What is the difference between heat, temperature and thermal energy? • Temperature: the measure of the average kinetic energy of the vibrating particles that compose an object • Heat: the quantity of thermal energy transferred from a hotter to a colder object • Internal Energy: the total amount of internal energy possessed by the particles that compose matter
 When matter gets warmer, the atoms or molecules in the matter move faster.
When matter gets warmer, the atoms or molecules in the matter move faster.
 All matter—solid, liquid, and gas—is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules, which have KE.
All matter—solid, liquid, and gas—is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules, which have KE.
 21. 1 Temperature The higher the temperature of a substance, the faster the motion of its molecules. This is also referred to as the Kinetic Theory— a) all matter is made of atoms and molecules that are moving. b) The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move. c) Given the same temperature, heavier particles move slower than lighter particles.
21. 1 Temperature The higher the temperature of a substance, the faster the motion of its molecules. This is also referred to as the Kinetic Theory— a) all matter is made of atoms and molecules that are moving. b) The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move. c) Given the same temperature, heavier particles move slower than lighter particles.
 21. 1 Temperature Measure temperature by showing expansion and contraction of a liquid in a glass tube. Three Scales (, Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin) • Fahrenheit (32 -212 F) • Celsius (0 -100 C) • Kelvin is a universal scale with no upper limit. (0 K or absolute zero to …)
21. 1 Temperature Measure temperature by showing expansion and contraction of a liquid in a glass tube. Three Scales (, Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin) • Fahrenheit (32 -212 F) • Celsius (0 -100 C) • Kelvin is a universal scale with no upper limit. (0 K or absolute zero to …)
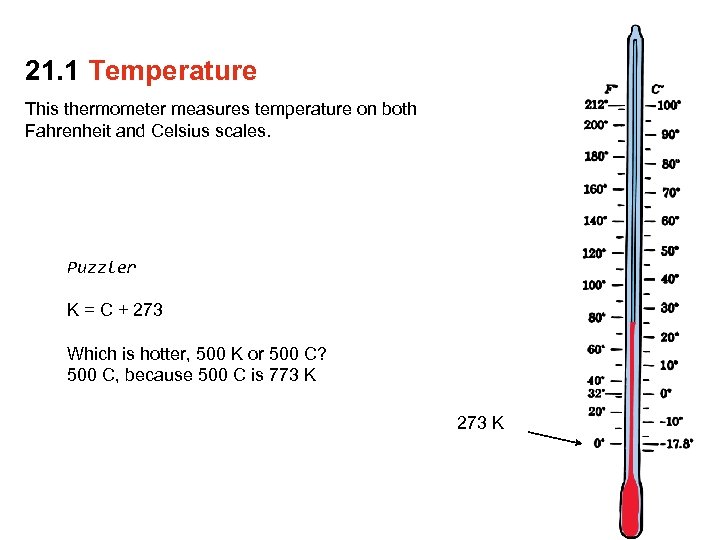 21. 1 Temperature This thermometer measures temperature on both Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Puzzler K = C + 273 Which is hotter, 500 K or 500 C? 500 C, because 500 C is 773 K 273 K
21. 1 Temperature This thermometer measures temperature on both Fahrenheit and Celsius scales. Puzzler K = C + 273 Which is hotter, 500 K or 500 C? 500 C, because 500 C is 773 K 273 K
 21. 1 Temperature • Which has more thermal energy, a cup of boiling water or Lake Michigan in winter? Lake Michigan! The water molecules are moving faster in the boiling cup of water, but there are vastly more water molecules in Lake Michigan. Are the water molecules in an ice cube moving? Yes. Motion of molecules stops at absolute zero.
21. 1 Temperature • Which has more thermal energy, a cup of boiling water or Lake Michigan in winter? Lake Michigan! The water molecules are moving faster in the boiling cup of water, but there are vastly more water molecules in Lake Michigan. Are the water molecules in an ice cube moving? Yes. Motion of molecules stops at absolute zero.
 21. 1 Temperature What is the relationship between the temperature of a substance and the speed of its molecules? The higher the temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules and the greater their average KE.
21. 1 Temperature What is the relationship between the temperature of a substance and the speed of its molecules? The higher the temperature of a substance, the faster is the motion of its molecules and the greater their average KE.
 Physics and Particles • Particle is a general term used to describe molecules, atoms and sub-atomic particles
Physics and Particles • Particle is a general term used to describe molecules, atoms and sub-atomic particles
 Starter Questions • 1. How does a thermometer work
Starter Questions • 1. How does a thermometer work
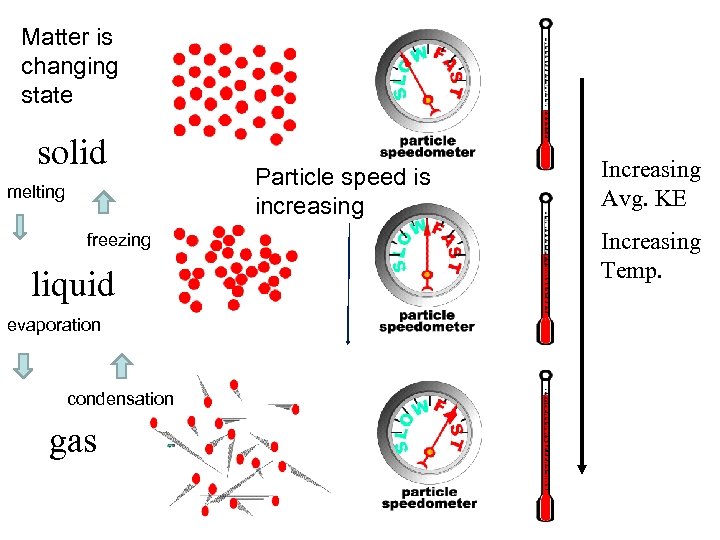 Matter is changing state solid melting freezing liquid evaporation condensation gas Particle speed is increasing Increasing Avg. KE Increasing Temp.
Matter is changing state solid melting freezing liquid evaporation condensation gas Particle speed is increasing Increasing Avg. KE Increasing Temp.
 21. 1 Temperature and Kinetic Energy Temperature is related to the average kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance. The faster the molecules move, the _______ greater the temperature and the _______ the average greater kinetic energy and the _____ the particle greater speed.
21. 1 Temperature and Kinetic Energy Temperature is related to the average kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in a substance. The faster the molecules move, the _______ greater the temperature and the _______ the average greater kinetic energy and the _____ the particle greater speed.
 21. 2 Heat is the quantity of thermal energy transferred from a hotter to a colder substance. 1. Heat always flows from a substance with a higher temperature to a substance with a lower temperature. 2. Heat flows only when there is a difference in temperature. 3. Heat units are calories or joules.
21. 2 Heat is the quantity of thermal energy transferred from a hotter to a colder substance. 1. Heat always flows from a substance with a higher temperature to a substance with a lower temperature. 2. Heat flows only when there is a difference in temperature. 3. Heat units are calories or joules.
 21. 2 Heat Just as water will not flow uphill by itself, regardless of the relative amounts of water in the reservoirs, heat will not flow from a cooler substance into a hotter substance by itself. hotter Entropy! Flow from higher to lower energy state. colder
21. 2 Heat Just as water will not flow uphill by itself, regardless of the relative amounts of water in the reservoirs, heat will not flow from a cooler substance into a hotter substance by itself. hotter Entropy! Flow from higher to lower energy state. colder
 21. 2 Heat What causes heat to flow? A difference in temperature between objects in thermal contact.
21. 2 Heat What causes heat to flow? A difference in temperature between objects in thermal contact.
 21. 4 Internal Energy When a substance takes in or gives off heat, its internal energy changes.
21. 4 Internal Energy When a substance takes in or gives off heat, its internal energy changes.
 21. 3 Thermal Equilibrium What happens when a warmer substance comes in contact with a cooler substance? • Heat flows between two objects of different temperature until they have the same temperature. (2 nd law of thermodyamics) • The loss of thermal energy from the warmer object equals the gain of thermal energy for the cooler object
21. 3 Thermal Equilibrium What happens when a warmer substance comes in contact with a cooler substance? • Heat flows between two objects of different temperature until they have the same temperature. (2 nd law of thermodyamics) • The loss of thermal energy from the warmer object equals the gain of thermal energy for the cooler object
 21. 8 Thermal Expansion Most forms of matter—solids, liquids, and gases— expand when they are heated and contract when they are cooled.
21. 8 Thermal Expansion Most forms of matter—solids, liquids, and gases— expand when they are heated and contract when they are cooled.
 21. 8 Thermal Expansion When the temperature of a substance is increased, its molecules jiggle faster and normally tend to move farther apart. This results in an expansion of the substance. • Gases generally expand or contract much more than liquids. • Liquids generally expand or contract more than solids.
21. 8 Thermal Expansion When the temperature of a substance is increased, its molecules jiggle faster and normally tend to move farther apart. This results in an expansion of the substance. • Gases generally expand or contract much more than liquids. • Liquids generally expand or contract more than solids.
 Starter Question #2 How does a thermometer work? The kinetic theory be used to explain expansion and contraction of materials when the temperature of the material changes. As the temperature rises, heat is transferred from the surroundings to the liquid inside thermometer and the molecules that compose the liquid vibrate faster. This causes the liquid to expand rise. As the temperature falls, heat is transferred away from the liquid inside to the surroundings and the molecules that compose this liquid slow down. This causes the liquid to contract.
Starter Question #2 How does a thermometer work? The kinetic theory be used to explain expansion and contraction of materials when the temperature of the material changes. As the temperature rises, heat is transferred from the surroundings to the liquid inside thermometer and the molecules that compose the liquid vibrate faster. This causes the liquid to expand rise. As the temperature falls, heat is transferred away from the liquid inside to the surroundings and the molecules that compose this liquid slow down. This causes the liquid to contract.
 • The liquid in thermometer stops rising or falling when thermal equilibrium is reached (no more heat flow!) Air temperature = Liquid temperature
• The liquid in thermometer stops rising or falling when thermal equilibrium is reached (no more heat flow!) Air temperature = Liquid temperature
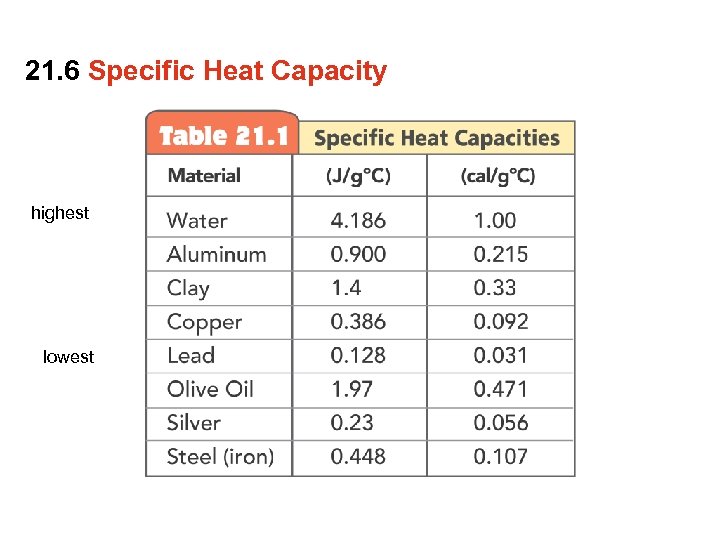
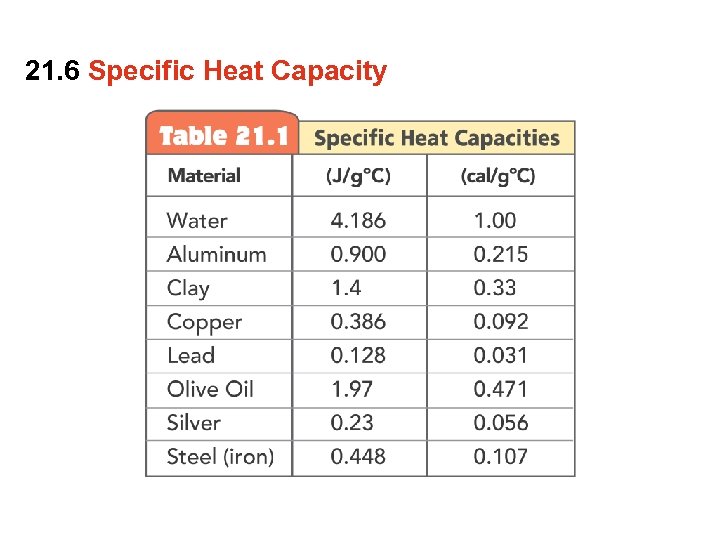
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity Do copper, clay and water have the same chemical composition? • No. Copper is composed of Cu atoms and water is composed of H 2 O molecules. Clay is a complex silicate. • The difference in chemical composition influences how copper, clay and water respond when heat is transferred.
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity Do copper, clay and water have the same chemical composition? • No. Copper is composed of Cu atoms and water is composed of H 2 O molecules. Clay is a complex silicate. • The difference in chemical composition influences how copper, clay and water respond when heat is transferred.
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity The specific heat capacity of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise 1 g of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity The specific heat capacity of a substance is the quantity of heat required to raise 1 g of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity A substance with a high specific heat capacity can absorb a large quantity of heat before it will raise in temperature (water has a high specific heat). A substance with a low specific heat requires relatively little heat to raise its temperature (copper has a low specific heat).
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity A substance with a high specific heat capacity can absorb a large quantity of heat before it will raise in temperature (water has a high specific heat). A substance with a low specific heat requires relatively little heat to raise its temperature (copper has a low specific heat).
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity highest lowest
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity highest lowest
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity think! Which has a higher specific heat capacity—water or sand? Explain.
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity think! Which has a higher specific heat capacity—water or sand? Explain.
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity think! Which has a higher specific heat capacity—water or sand? Explain. Answer: Water has a greater heat capacity than sand. Water is much slower to warm in the hot sun and slower to cool at night. Sand’s low heat capacity, shown by how quickly it warms in the morning and how quickly it cools at night, affects local climates. Good conductors have a low specific heat capacity!
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity think! Which has a higher specific heat capacity—water or sand? Explain. Answer: Water has a greater heat capacity than sand. Water is much slower to warm in the hot sun and slower to cool at night. Sand’s low heat capacity, shown by how quickly it warms in the morning and how quickly it cools at night, affects local climates. Good conductors have a low specific heat capacity!
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity A gram of water requires 1 calorie of energy to raise the temperature 1°C. It takes only about one eighth as much energy to raise the temperature of a gram of iron by the same amount. The capacity of a substance to store heat depends on its chemical composition.
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity A gram of water requires 1 calorie of energy to raise the temperature 1°C. It takes only about one eighth as much energy to raise the temperature of a gram of iron by the same amount. The capacity of a substance to store heat depends on its chemical composition.
 21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity
21. 6 Specific Heat Capacity
 6. What is the difference between a substance with a high specific heat and a low specific heat capacity?
6. What is the difference between a substance with a high specific heat and a low specific heat capacity?
 • Substances with a low specific heat (e. g. , metals) need very little heat to raise temperature – Good conductors, not good absorbers, do not hold onto heat well • Substances with a high specific heat need a large quantity of heat to raise temperature. – Poor conductors, good absorbers, store and hold onto heat well
• Substances with a low specific heat (e. g. , metals) need very little heat to raise temperature – Good conductors, not good absorbers, do not hold onto heat well • Substances with a high specific heat need a large quantity of heat to raise temperature. – Poor conductors, good absorbers, store and hold onto heat well
 7. How does the specific heat of water help to moderate climate?
7. How does the specific heat of water help to moderate climate?
 Friday 1. Heat Flow Examples—Home Heating and Cooling a) Summer time flow b) Winter time flow 2. Water and Specific Heat a) Sea Breezes b) Moderating effect of water (Edmonton vs. Cork) 3. Reason for the seasons a) Tilt of Earth’s Rotational Axis (23. 5 o) b) Insolation Angle (same radiation, different area) c) Absorption vs. Reflection
Friday 1. Heat Flow Examples—Home Heating and Cooling a) Summer time flow b) Winter time flow 2. Water and Specific Heat a) Sea Breezes b) Moderating effect of water (Edmonton vs. Cork) 3. Reason for the seasons a) Tilt of Earth’s Rotational Axis (23. 5 o) b) Insolation Angle (same radiation, different area) c) Absorption vs. Reflection
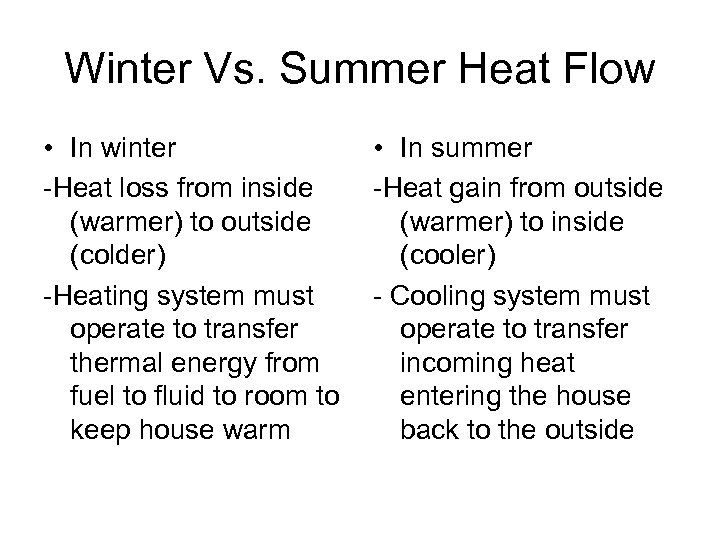 Winter Vs. Summer Heat Flow • In winter -Heat loss from inside (warmer) to outside (colder) -Heating system must operate to transfer thermal energy from fuel to fluid to room to keep house warm • In summer -Heat gain from outside (warmer) to inside (cooler) - Cooling system must operate to transfer incoming heat entering the house back to the outside
Winter Vs. Summer Heat Flow • In winter -Heat loss from inside (warmer) to outside (colder) -Heating system must operate to transfer thermal energy from fuel to fluid to room to keep house warm • In summer -Heat gain from outside (warmer) to inside (cooler) - Cooling system must operate to transfer incoming heat entering the house back to the outside
 Why do we need heating systems? • What do the green arrows represent? • How does this heat flow affect the temperature of the air inside the home? • Where does the energy come from that increases the temperature of the air inside the home?
Why do we need heating systems? • What do the green arrows represent? • How does this heat flow affect the temperature of the air inside the home? • Where does the energy come from that increases the temperature of the air inside the home?
 Explain why the heat flow for a home is different in the winter vs. the summer.
Explain why the heat flow for a home is different in the winter vs. the summer.
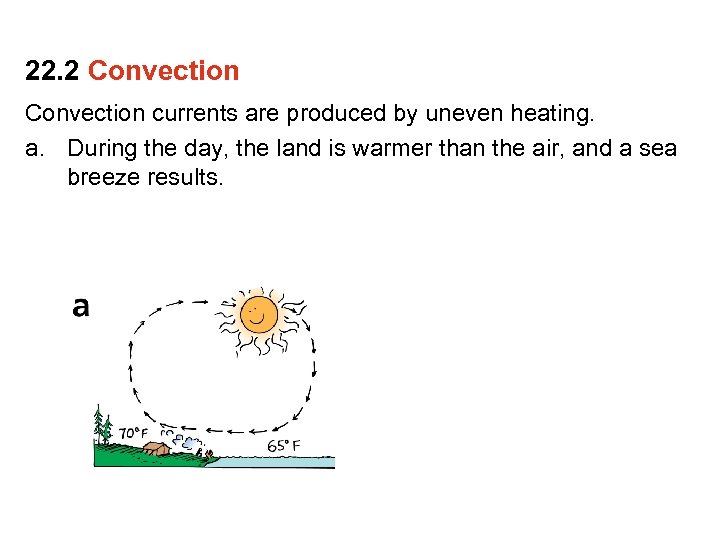 22. 2 Convection currents are produced by uneven heating. a. During the day, the land is warmer than the air, and a sea breeze results.
22. 2 Convection currents are produced by uneven heating. a. During the day, the land is warmer than the air, and a sea breeze results.
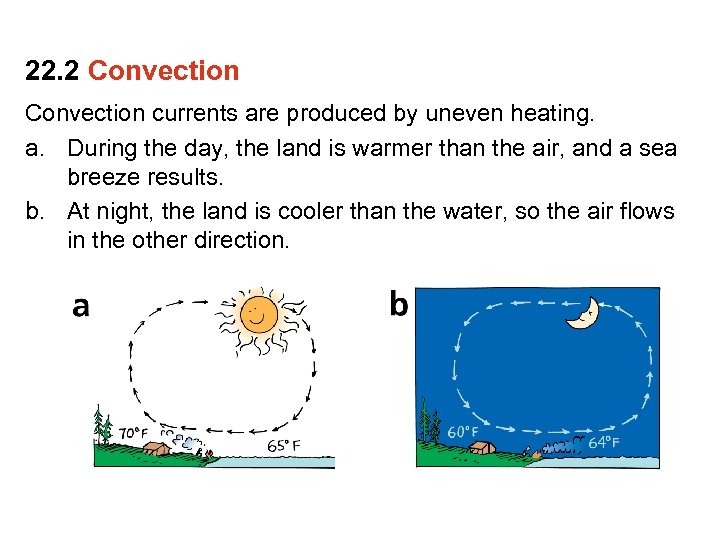 22. 2 Convection currents are produced by uneven heating. a. During the day, the land is warmer than the air, and a sea breeze results. b. At night, the land is cooler than the water, so the air flows in the other direction.
22. 2 Convection currents are produced by uneven heating. a. During the day, the land is warmer than the air, and a sea breeze results. b. At night, the land is cooler than the water, so the air flows in the other direction.
 Generation of Sea Breezes Day Convection Air above the land heats more rapidly and rises Sea breeze Land • low specific heat • heat and cools rapidly • less resistant to temperature change Air above the sea remains cooler and moves on land to replace the land air that rose Sea • high specific heat • heats and cools slowly • more resistant to temperature change
Generation of Sea Breezes Day Convection Air above the land heats more rapidly and rises Sea breeze Land • low specific heat • heat and cools rapidly • less resistant to temperature change Air above the sea remains cooler and moves on land to replace the land air that rose Sea • high specific heat • heats and cools slowly • more resistant to temperature change
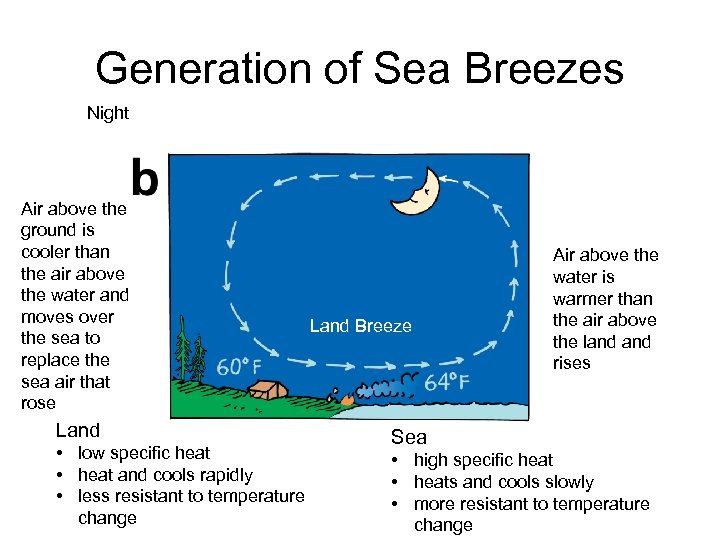 Generation of Sea Breezes Night Air above the ground is cooler than the air above the water and moves over the sea to replace the sea air that rose Land • low specific heat • heat and cools rapidly • less resistant to temperature change Land Breeze Air above the water is warmer than the air above the land rises Sea • high specific heat • heats and cools slowly • more resistant to temperature change
Generation of Sea Breezes Night Air above the ground is cooler than the air above the water and moves over the sea to replace the sea air that rose Land • low specific heat • heat and cools rapidly • less resistant to temperature change Land Breeze Air above the water is warmer than the air above the land rises Sea • high specific heat • heats and cools slowly • more resistant to temperature change
 Generation of Sea Breezes
Generation of Sea Breezes
 21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places.
21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water The property of water to resist changes in temperature improves the climate in many places.
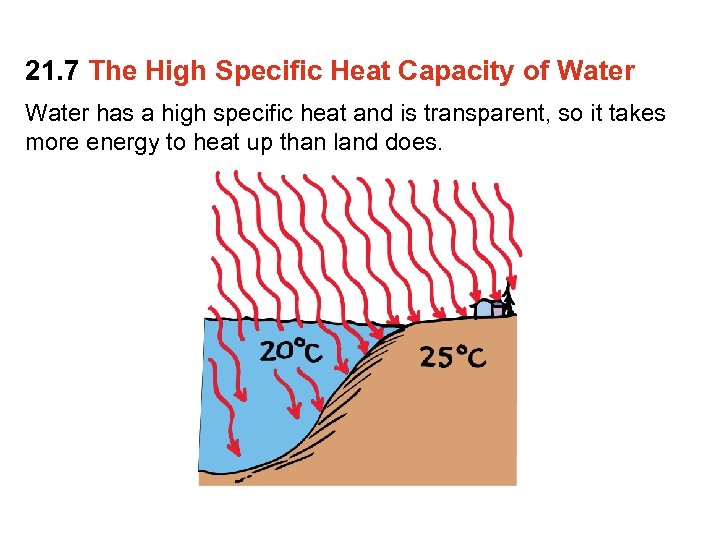 21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water has a high specific heat and is transparent, so it takes more energy to heat up than land does.
21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water has a high specific heat and is transparent, so it takes more energy to heat up than land does.
 Moderating Effect of Water • During the summer, surrounding air is cooled by the water and keeps the coast cooler than the intercontinental locations. • During the winter, the surrounding air is warmed by the water and keeps the coast warmer than the intercontinental locations.
Moderating Effect of Water • During the summer, surrounding air is cooled by the water and keeps the coast cooler than the intercontinental locations. • During the winter, the surrounding air is warmed by the water and keeps the coast warmer than the intercontinental locations.
 21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water’s capacity to store heat affects the global climate. Water stores and hold heat well because of its high specific heat. Gulf Stream brings warm water northeast from the Caribbean.
21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water’s capacity to store heat affects the global climate. Water stores and hold heat well because of its high specific heat. Gulf Stream brings warm water northeast from the Caribbean.

 Thermal Front The Gulf Stream (warm water from equator) meets The Labrador Current (cold water from polar region) Labrador Current Gulf Stream
Thermal Front The Gulf Stream (warm water from equator) meets The Labrador Current (cold water from polar region) Labrador Current Gulf Stream
 21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water Climate of Europe Look at a world globe and notice the high latitude of Europe. Both Europe and Canada get about the same amount of the sun’s energy per square kilometer.
21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water Climate of Europe Look at a world globe and notice the high latitude of Europe. Both Europe and Canada get about the same amount of the sun’s energy per square kilometer.
 Marine Climate Continental Climate Cork Edmonton Same insolation angle, different climate due to proximity to water and the warming effect from the Gulf Stream http: //www. sampleireland. com/weather-in-ireland-year-round. html
Marine Climate Continental Climate Cork Edmonton Same insolation angle, different climate due to proximity to water and the warming effect from the Gulf Stream http: //www. sampleireland. com/weather-in-ireland-year-round. html
 The Gulf Stream brings warm winters to Ireland the prevailing winds off the Atlantic carry with them rain. It means grass can grow almost all year round — creating the lush sweeping pastures of the Emerald Isle. Today they make up 93 percent of all farmland. No other country in Europe has quite as much grass as Ireland.
The Gulf Stream brings warm winters to Ireland the prevailing winds off the Atlantic carry with them rain. It means grass can grow almost all year round — creating the lush sweeping pastures of the Emerald Isle. Today they make up 93 percent of all farmland. No other country in Europe has quite as much grass as Ireland.

 21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water Climate of America On the west coast, air moves from the Pacific Ocean to the land. • In winter, the water warms the air that moves over it and warms the western coastal regions of North America. • In summer, the water cools the air and the western coastal regions are cooled. The central interior of a large continent usually experiences extremes of temperature. Land, with a lower specific heat capacity, gets hot in summer but cools rapidly in winter.
21. 7 The High Specific Heat Capacity of Water Climate of America On the west coast, air moves from the Pacific Ocean to the land. • In winter, the water warms the air that moves over it and warms the western coastal regions of North America. • In summer, the water cools the air and the western coastal regions are cooled. The central interior of a large continent usually experiences extremes of temperature. Land, with a lower specific heat capacity, gets hot in summer but cools rapidly in winter.
 Reason for the Seasons 2 Changing Angle of Sunlight • The hemisphere tilted toward the Sun receives sunlight at higher angles than the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun. • Higher insolation angle means greater intensity of radiant energy (the sun shines more directly on a smaller area). Summer in Northern Hemisphere
Reason for the Seasons 2 Changing Angle of Sunlight • The hemisphere tilted toward the Sun receives sunlight at higher angles than the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun. • Higher insolation angle means greater intensity of radiant energy (the sun shines more directly on a smaller area). Summer in Northern Hemisphere
 Identify the Seasons and the Equinox or Solstice, and comment about the number of daylight vs. night hours Season _________ Equinox or Solstice Season ____ Equinox or Solstice
Identify the Seasons and the Equinox or Solstice, and comment about the number of daylight vs. night hours Season _________ Equinox or Solstice Season ____ Equinox or Solstice
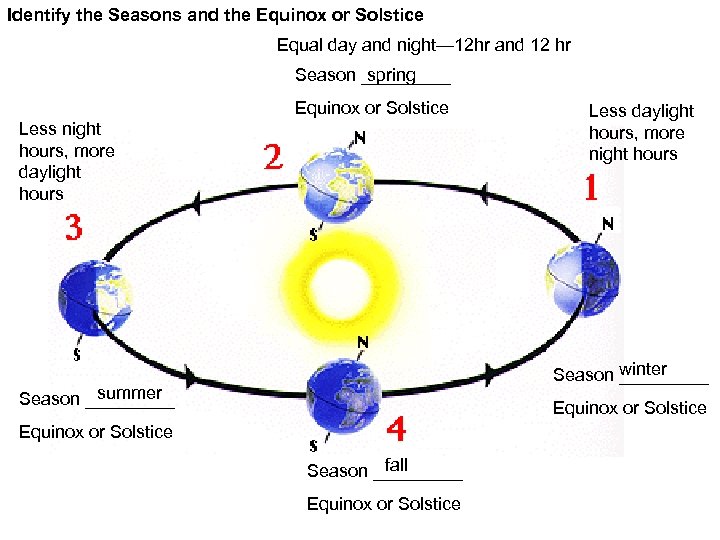 Identify the Seasons and the Equinox or Solstice Equal day and night— 12 hr and 12 hr Season _____ spring Equinox or Solstice Less night hours, more daylight hours Less daylight hours, more night hours Season winter _____ summer Season _____ Equinox or Solstice fall Season _____ Equinox or Solstice
Identify the Seasons and the Equinox or Solstice Equal day and night— 12 hr and 12 hr Season _____ spring Equinox or Solstice Less night hours, more daylight hours Less daylight hours, more night hours Season winter _____ summer Season _____ Equinox or Solstice fall Season _____ Equinox or Solstice
 Heat can be transferred by conduction, by convection, and by radiation. http: //www. nd. edu/~ysun/Yang/Physics. Ani mation/collection/transport. P. swf
Heat can be transferred by conduction, by convection, and by radiation. http: //www. nd. edu/~ysun/Yang/Physics. Ani mation/collection/transport. P. swf
 22. 1 Conduction In conduction, collisions between particles transfer thermal energy, without any overall transfer of matter.
22. 1 Conduction In conduction, collisions between particles transfer thermal energy, without any overall transfer of matter.
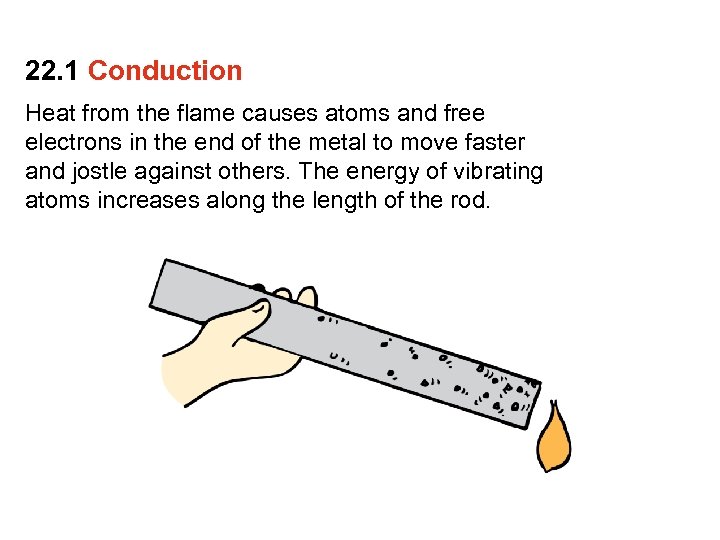 22. 1 Conduction Heat from the flame causes atoms and free electrons in the end of the metal to move faster and jostle against others. The energy of vibrating atoms increases along the length of the rod.
22. 1 Conduction Heat from the flame causes atoms and free electrons in the end of the metal to move faster and jostle against others. The energy of vibrating atoms increases along the length of the rod.
 22. 2 Convection In convection, heat is transferred by movement of the hotter substance from one place to another.
22. 2 Convection In convection, heat is transferred by movement of the hotter substance from one place to another.
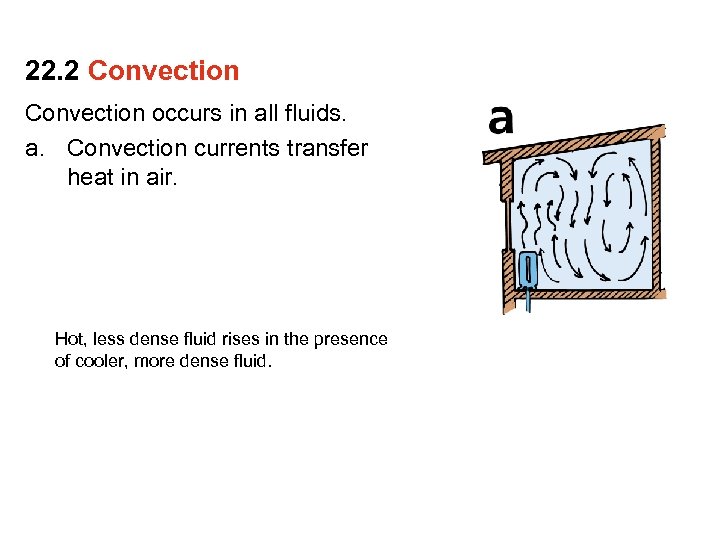 22. 2 Convection occurs in all fluids. a. Convection currents transfer heat in air. Hot, less dense fluid rises in the presence of cooler, more dense fluid.
22. 2 Convection occurs in all fluids. a. Convection currents transfer heat in air. Hot, less dense fluid rises in the presence of cooler, more dense fluid.
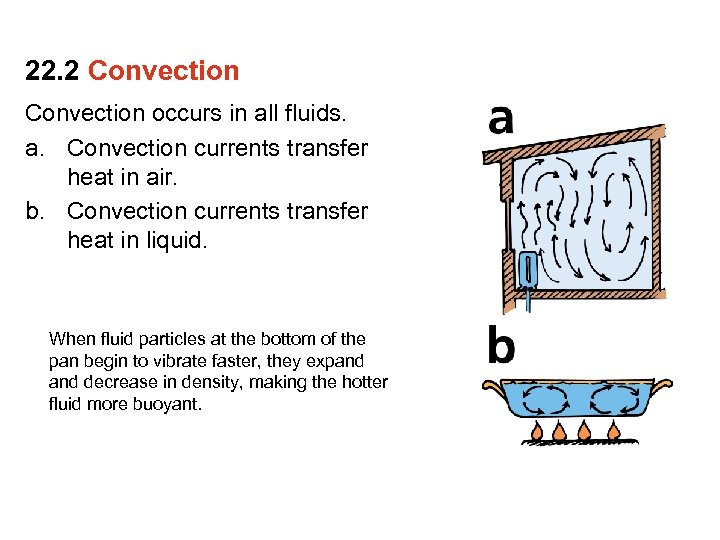 22. 2 Convection occurs in all fluids. a. Convection currents transfer heat in air. b. Convection currents transfer heat in liquid. When fluid particles at the bottom of the pan begin to vibrate faster, they expand decrease in density, making the hotter fluid more buoyant.
22. 2 Convection occurs in all fluids. a. Convection currents transfer heat in air. b. Convection currents transfer heat in liquid. When fluid particles at the bottom of the pan begin to vibrate faster, they expand decrease in density, making the hotter fluid more buoyant.
 22. 3 Radiation In radiation, heat is transmitted in the form of radiant energy, or electromagnetic waves.
22. 3 Radiation In radiation, heat is transmitted in the form of radiant energy, or electromagnetic waves.
 22. 3 Radiation Most of the heat from a fireplace goes up the chimney by convection. The heat that warms us comes to us by radiation.
22. 3 Radiation Most of the heat from a fireplace goes up the chimney by convection. The heat that warms us comes to us by radiation.
 Heat Transfer 1 • Which heat transfer occurs from particle to particle during direct contact of substances? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 1 • Which heat transfer occurs from particle to particle during direct contact of substances? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
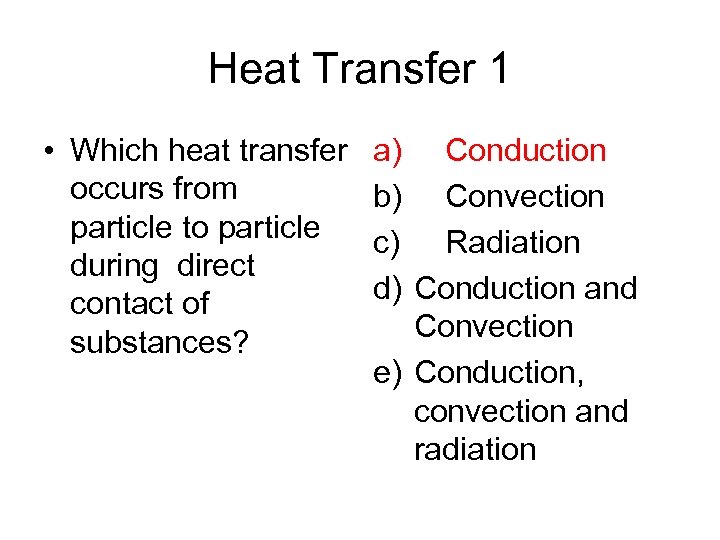 Heat Transfer 1 • Which heat transfer occurs from particle to particle during direct contact of substances? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 1 • Which heat transfer occurs from particle to particle during direct contact of substances? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 2 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction can occur through b) Convection a vacuum or c) Radiation through matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 2 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction can occur through b) Convection a vacuum or c) Radiation through matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
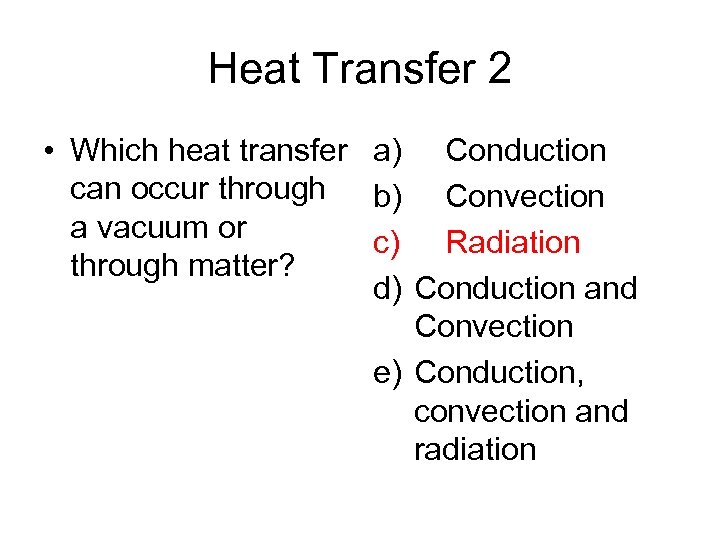 Heat Transfer 2 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction can occur through b) Convection a vacuum or c) Radiation through matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 2 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction can occur through b) Convection a vacuum or c) Radiation through matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
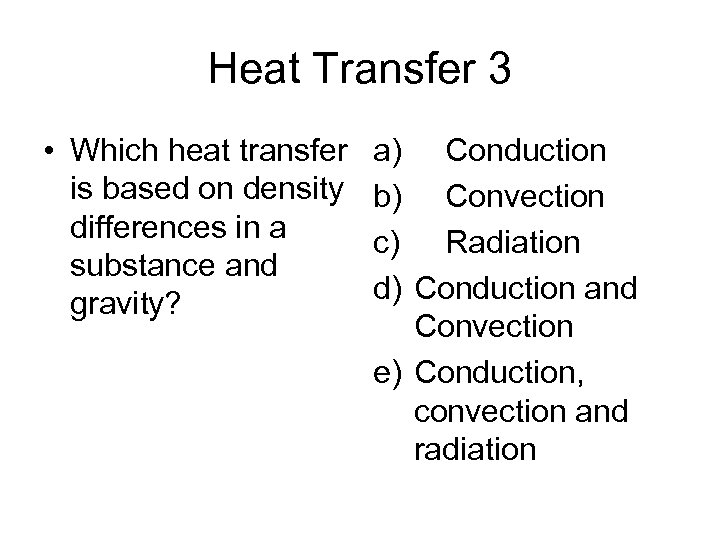 Heat Transfer 3 • Which heat transfer is based on density differences in a substance and gravity? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 3 • Which heat transfer is based on density differences in a substance and gravity? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
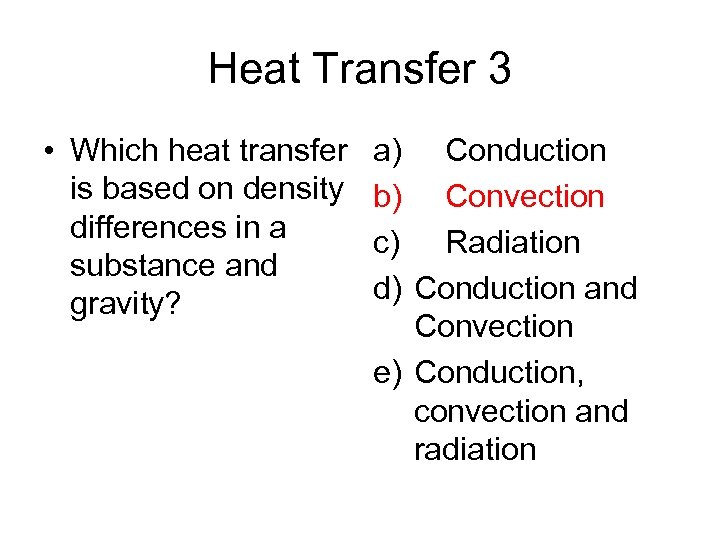 Heat Transfer 3 • Which heat transfer is based on density differences in a substance and gravity? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 3 • Which heat transfer is based on density differences in a substance and gravity? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 4 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction occurs through the b) Convection movement of the c) Radiation heated substance? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 4 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction occurs through the b) Convection movement of the c) Radiation heated substance? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 4 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction occurs through the b) Convection movement of the c) Radiation heated substance? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 4 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction occurs through the b) Convection movement of the c) Radiation heated substance? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 5 • Which heat transfer is characterized by transmission by electromagnetic waves? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 5 • Which heat transfer is characterized by transmission by electromagnetic waves? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 5 • Which heat transfer is characterized by transmission by electromagnetic waves? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 5 • Which heat transfer is characterized by transmission by electromagnetic waves? a) Conduction b) Convection c) Radiation d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 6 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction processes can only b) Convection occur through c) Radiation matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 6 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction processes can only b) Convection occur through c) Radiation matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 Heat Transfer 6 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction processes can only b) Convection occur through c) Radiation matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
Heat Transfer 6 • Which heat transfer a) Conduction processes can only b) Convection occur through c) Radiation matter? d) Conduction and Convection e) Conduction, convection and radiation
 • Radiation is caused by moving electrons or charged particles in matter. The faster the particles move, the higher the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation.
• Radiation is caused by moving electrons or charged particles in matter. The faster the particles move, the higher the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation.
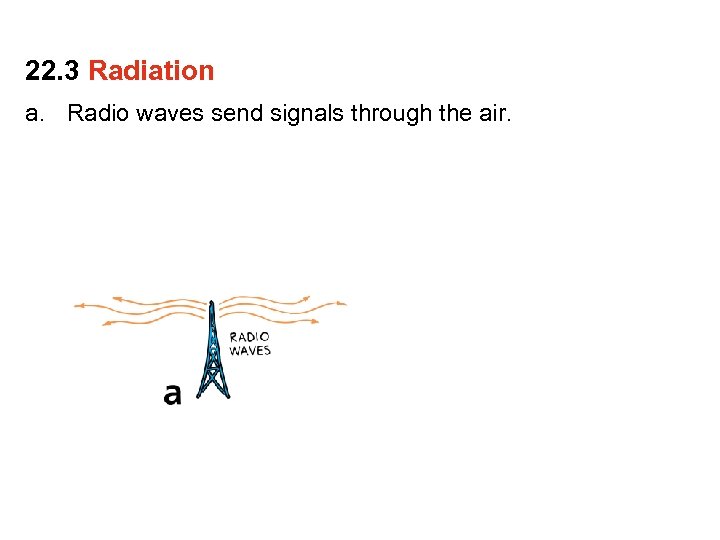 22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air.
22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air.
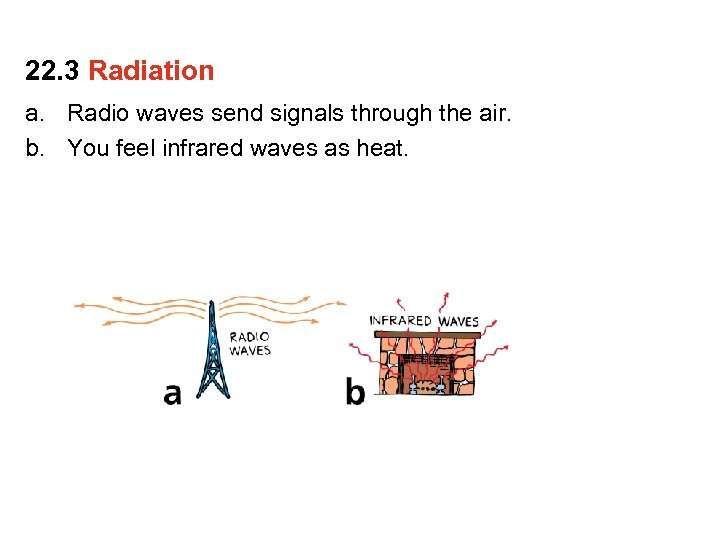 22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air. b. You feel infrared waves as heat.
22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air. b. You feel infrared waves as heat.
 22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air. b. You feel infrared waves as heat. c. A visible form of radiant energy is light waves.
22. 3 Radiation a. Radio waves send signals through the air. b. You feel infrared waves as heat. c. A visible form of radiant energy is light waves.
 11. What happens to the frequency of radiant energy as the temperature of the substance increases or decreases?
11. What happens to the frequency of radiant energy as the temperature of the substance increases or decreases?
 • The frequency of radiant energy increases as the temperature of the substance increases.
• The frequency of radiant energy increases as the temperature of the substance increases.
 http: //mail. jsd. k 12. ca. us/bf/bflibrary/images/electromagnetic-spectrum. jpg
http: //mail. jsd. k 12. ca. us/bf/bflibrary/images/electromagnetic-spectrum. jpg


