13239fb6893fa735b54f3e729f4bbb64.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

INTERNAL CONTROL PROGRAM Presented to President’s Cabinet

What Is Internal Control INTERNAL CONTROLS are the integration of the activities, plans, attitudes, policies and efforts of the people of an organization working together to provide reasonable assurance that the organization will achieve its mission. Simply put -

What is Internal Controls are actions taken to make sure the right things happen --- -- and the wrong things don’t.
What is the Purpose of Internal Controls Promote efficient and effective operations and produce quality products and services Ensure adherence to laws, regulations, contracts and management directives Safeguard resources against loss due to waste, abuse, mismanagement, errors and fraud Develop and maintain reliable data, and accurately present the data in timely reports

Who is Responsible for Internal Control Everyone in an organization has responsibility for internal control. Senior Management sets the “tone at the top” that affects integrity, ethics and other factors of a positive control environment.

What is the Purpose of Internal Controls Compliance with laws and policies Accomplishment of mission Relevant and reliable data Economical and efficient use of resources Safeguard assets
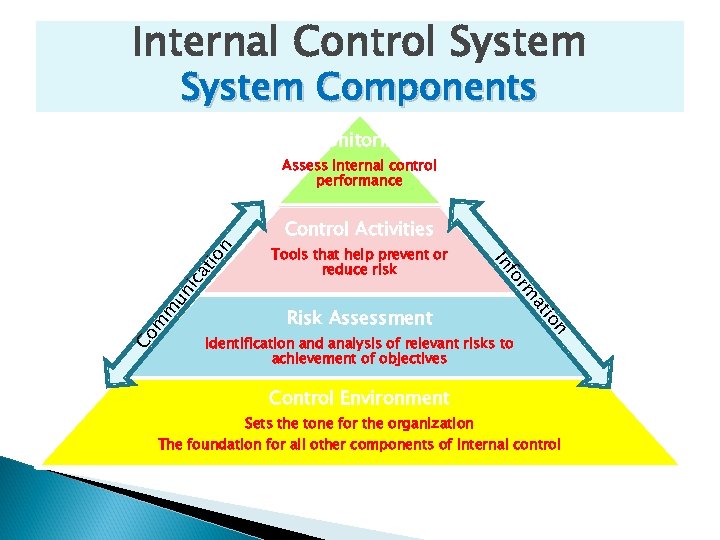
Internal Control System Components Monitoring Assess internal control performance at ic un m m n Identification and analysis of relevant risks to achievement of objectives io Risk Assessment at Co m r fo Tools that help prevent or reduce risk In io n Control Activities Control Environment Sets the tone for the organization The foundation for all other components of internal control

Components of the Control Environment Component Management Responsibilities ØEstablish the overall management style, philosophy and “tone” ØApprove and monitor the organization’s mission and strategic plan ØEnsure and provide accountability ØRecognize and respond to risks – both internal and external ØAccept regulatory control imposed by others ØSupport and be responsive to internal and external audits and evaluations

Components of the Control Environment Component Management Responsibilities ØEstablish and communicate a code of conduct ØComply with the organization’s values and code of conduct ØEstablish methods for reporting ethical violations ØEnforce disciplinary practices for all ethical violations ØEstablish levels of knowledge and skill required for every position ØVerify qualifications of job candidates ØProvide training programs that help employees increase their knowledge and skills

Components of the Control Environment Component Management Responsibilities ØEmploy minimal and guarded use of control overrides ØDemonstrate responsiveness to issues raised as the result of the evaluations and audits ØEnsure employees’ opinions and contributions are welcomed, valued and recognized ØSupport and participate in ongoing education to ensure everyone understands the system of internal control and their role in it

Control Environment Setting the proper control environment is crucial to the effective implementation of all the other elements of internal control. Staff will take their cue from the attitude and example displayed by management.

Risk and Risk Assessment RISKS are events that threaten the accomplishment of objectives and can be either internal or external. They ultimately impact an organization’s ability to accomplish its mission. Examples of risks include: ØHuman error ØFraud ØSystem breakdowns ØNatural disasters

Risk Assessment Ø Identify each risk in terms of: Likelihood The probability that an unfavorable event would occur if there were no internal controls in place Significance or Impact The magnitude of the effect on the organization if the unfavorable event were to occur Cause The reason why the unfavorable event may occur

Managing Risk ØRisk assumption – impact and likelihood low (do not establish control activities) ØRisk control – take action to lower the probability or eliminate the risk (establish control activities) ØRisk avoidance – abandon plan; risks uncontrollable and unacceptable (do not carry out the function)

Managing Risk COSTS BENEFITS The cost of internal control should not exceed the benefit derived

What are Control Activities? Control activities are tools – both manual and automated – that help identify, prevent or reduce the risks that can impede accomplishment of the unit’s objectives. Directive Controls (Laws, Regulations) Detective Controls (Reconciliations, Audits) Preventive Controls (Approvals, Authorizations) Corrective Controls (Training, Supervision)

Commonly Used Control Activities Documentation – preserving evidence to substantiate a decision, event, transaction or system Approval and Authorization Verification – determination of the completeness, accuracy, authenticity and/or validity of transactions, events or information Supervision Separation of Duties – division of key tasks and responsibilities among various employees Safeguarding Assets – restricting access to resources and information to help reduce the risk of unauthorized use or loss Reporting – helps promote accountability for actions and decisions

Conclusion All Employees Have Responsibility for Internal Controls ◦ Senior Management sets the “tone at the top” that affects integrity, ethics and other factors of a positive control environment. Management should consider risks to achieving established objectives and strategies and manage appropriately (accept, control or avoid). Communication must occur up, down and across an organization. An Internal Control Program is a good idea and IT’S THE LAW

References Standards for Internal Control in New York State Government, Office of the State Comptroller. Control Environment – Tone at the Top, New York State Internal Control Association
13239fb6893fa735b54f3e729f4bbb64.ppt