568678be2fe8d74a974c9886da71d774.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Intermediate Mechanics Physics 321 Richard Sonnenfeld New Mexico Tech : 00
Intermediate Mechanics Physics 321 Richard Sonnenfeld New Mexico Tech : 00
 Lecture #1 of 25 Course goals n Physics Concepts / Mathematical Methods Class background / interests / class photo Course Motivation n “Why you will learn it” Course outline (hand-out) Course “mechanics” (hand-outs) Basic Vector Relationships Newton’s Laws Worked problems Inertia of brick and ketchup III-3, 4 2 : 02
Lecture #1 of 25 Course goals n Physics Concepts / Mathematical Methods Class background / interests / class photo Course Motivation n “Why you will learn it” Course outline (hand-out) Course “mechanics” (hand-outs) Basic Vector Relationships Newton’s Laws Worked problems Inertia of brick and ketchup III-3, 4 2 : 02
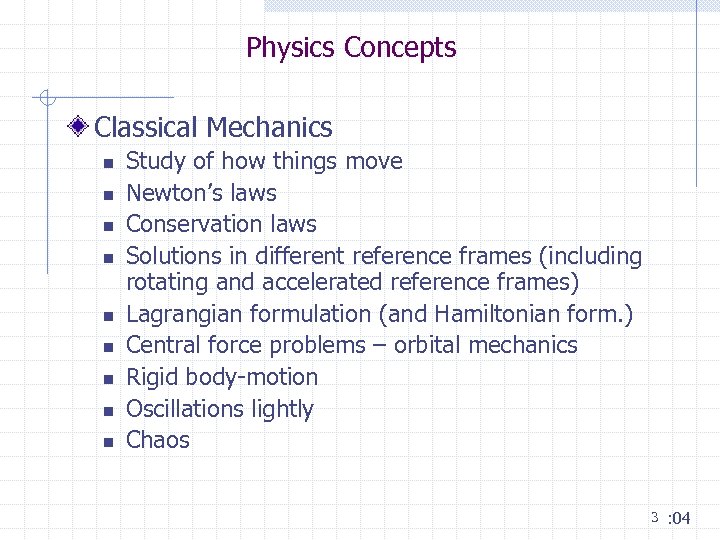 Physics Concepts Classical Mechanics n n n n n Study of how things move Newton’s laws Conservation laws Solutions in different reference frames (including rotating and accelerated reference frames) Lagrangian formulation (and Hamiltonian form. ) Central force problems – orbital mechanics Rigid body-motion Oscillations lightly Chaos 3 : 04
Physics Concepts Classical Mechanics n n n n n Study of how things move Newton’s laws Conservation laws Solutions in different reference frames (including rotating and accelerated reference frames) Lagrangian formulation (and Hamiltonian form. ) Central force problems – orbital mechanics Rigid body-motion Oscillations lightly Chaos 3 : 04
 Mathematical Methods Vector Calculus n n n Differential equations of vector quantities Partial differential equations More tricks w/ cross product and dot product Stokes Theorem “Div, grad, curl and all that” Matrices n n Coordinate change / rotations Diagonalization / eigenvalues / principal axes Lagrangian formulation n Calculus of variations “Functionals” and operators Lagrange multipliers for constraints General Mathematical competence 4 : 06
Mathematical Methods Vector Calculus n n n Differential equations of vector quantities Partial differential equations More tricks w/ cross product and dot product Stokes Theorem “Div, grad, curl and all that” Matrices n n Coordinate change / rotations Diagonalization / eigenvalues / principal axes Lagrangian formulation n Calculus of variations “Functionals” and operators Lagrange multipliers for constraints General Mathematical competence 4 : 06
 Class Background and Interests Majors n Physics? EE? CS? Other? Preparation n n Assume Math 231 (Vector Calc) Phys 242 (Waves) Math 335 (Diff. Eq) concurrent Phys 333 (E&M) concurrent Year at tech n 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th Graduate school? Greatest area of interest in mechanics 5 : 08
Class Background and Interests Majors n Physics? EE? CS? Other? Preparation n n Assume Math 231 (Vector Calc) Phys 242 (Waves) Math 335 (Diff. Eq) concurrent Phys 333 (E&M) concurrent Year at tech n 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th Graduate school? Greatest area of interest in mechanics 5 : 08
 Physics Motivation Physics component n Classical mechanics is incredibly useful w Applies to everything bigger than an atom and slower than about 100, 000 miles/sec n n Lagrangian method allows “automatic” generation of correct differential equations for complex mechanical systems, in generalized coordinates, with constraints Machines and structures / Electron beams / atmospheric phenomena / stellar-planetary motions / vehicles / fluids in pipes 6 : 10
Physics Motivation Physics component n Classical mechanics is incredibly useful w Applies to everything bigger than an atom and slower than about 100, 000 miles/sec n n Lagrangian method allows “automatic” generation of correct differential equations for complex mechanical systems, in generalized coordinates, with constraints Machines and structures / Electron beams / atmospheric phenomena / stellar-planetary motions / vehicles / fluids in pipes 6 : 10
 Mathematics Motivation Mathematics component n n Hamiltonian formulation transfers DIRECTLY to quantum mechanics Matrix approaches also critical for quantum Differential equations and vector calculus completely relevant for advanced E&M and wave propagation classes Functionals, partial derivatives, vector calculus. “Real math”. Good grad-school preparation. 7 : 12
Mathematics Motivation Mathematics component n n Hamiltonian formulation transfers DIRECTLY to quantum mechanics Matrix approaches also critical for quantum Differential equations and vector calculus completely relevant for advanced E&M and wave propagation classes Functionals, partial derivatives, vector calculus. “Real math”. Good grad-school preparation. 7 : 12
 About instructor 15 years post-doctoral industry experience n n n Materials studies (tribology) for hard-drives Automated mechanical and magnetic measurements of hard-drives Bringing a 20 -million unit/year product to market Likes engineering applications of physics n Will endeavor to provide interesting problems that correspond to the real world 8 : 16
About instructor 15 years post-doctoral industry experience n n n Materials studies (tribology) for hard-drives Automated mechanical and magnetic measurements of hard-drives Bringing a 20 -million unit/year product to market Likes engineering applications of physics n Will endeavor to provide interesting problems that correspond to the real world 8 : 16
 Course “Mechanics” Web. CT / Syllabus and Homework Office hours, Testing and Grading 9 : 26
Course “Mechanics” Web. CT / Syllabus and Homework Office hours, Testing and Grading 9 : 26
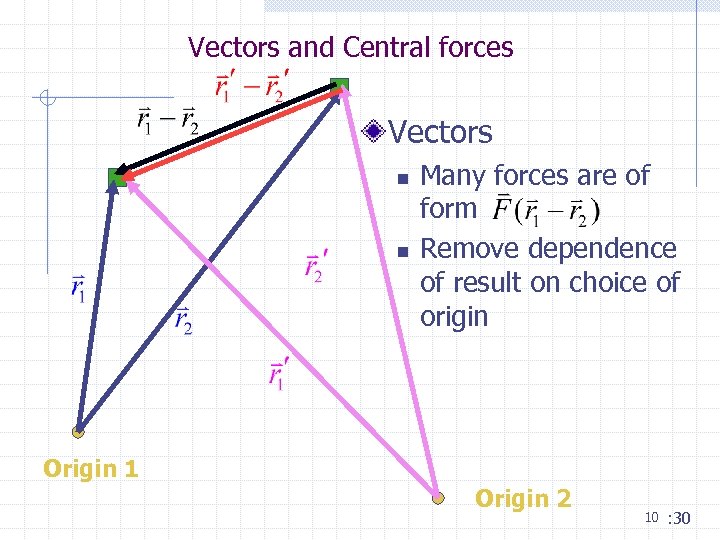 Vectors and Central forces Vectors n n Many forces are of form Remove dependence of result on choice of origin Origin 1 Origin 2 10 : 30
Vectors and Central forces Vectors n n Many forces are of form Remove dependence of result on choice of origin Origin 1 Origin 2 10 : 30
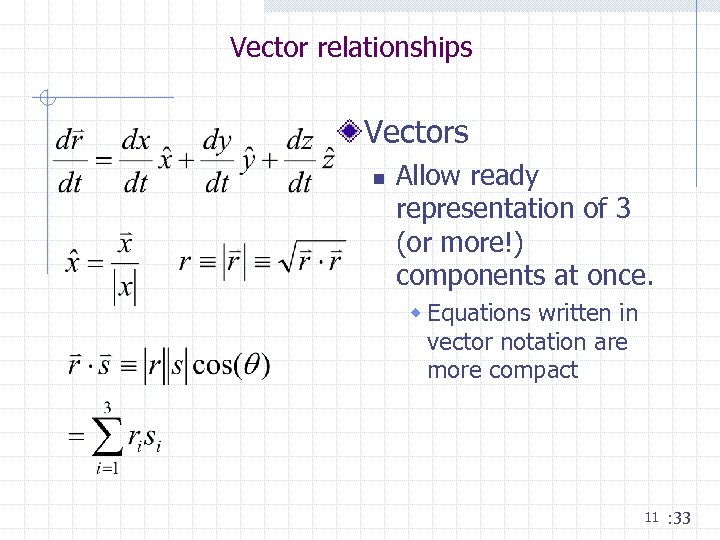 Vector relationships Vectors n Allow ready representation of 3 (or more!) components at once. w Equations written in vector notation are more compact 11 : 33
Vector relationships Vectors n Allow ready representation of 3 (or more!) components at once. w Equations written in vector notation are more compact 11 : 33
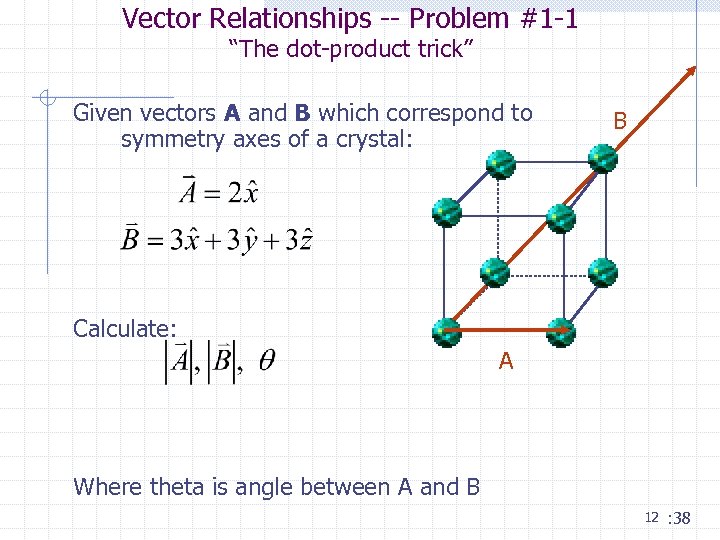 Vector Relationships -- Problem #1 -1 “The dot-product trick” Given vectors A and B which correspond to symmetry axes of a crystal: B Calculate: A Where theta is angle between A and B 12 : 38
Vector Relationships -- Problem #1 -1 “The dot-product trick” Given vectors A and B which correspond to symmetry axes of a crystal: B Calculate: A Where theta is angle between A and B 12 : 38
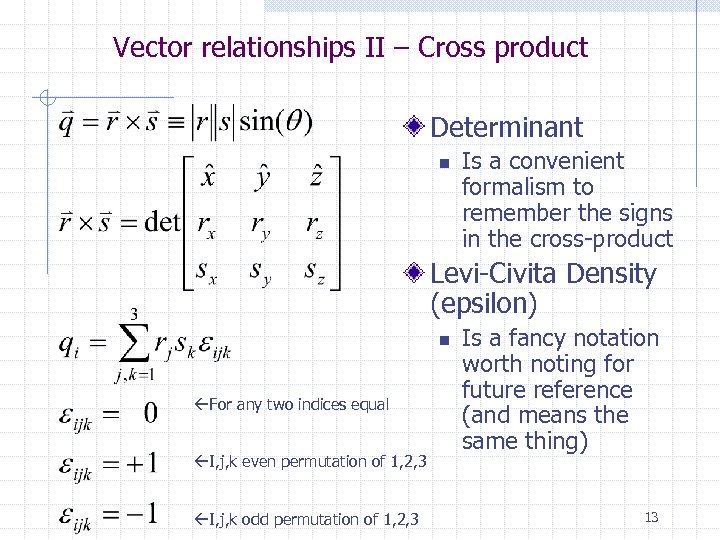 Vector relationships II – Cross product Determinant n Is a convenient formalism to remember the signs in the cross-product Levi-Civita Density (epsilon) n For any two indices equal I, j, k even permutation of 1, 2, 3 I, j, k odd permutation of 1, 2, 3 Is a fancy notation worth noting for future reference (and means the same thing) 13
Vector relationships II – Cross product Determinant n Is a convenient formalism to remember the signs in the cross-product Levi-Civita Density (epsilon) n For any two indices equal I, j, k even permutation of 1, 2, 3 I, j, k odd permutation of 1, 2, 3 Is a fancy notation worth noting for future reference (and means the same thing) 13
 Newton’s Laws 1. A Body at rest remains at rest, while a body in motion at constant velocity remains in motion Unless acted on by an external force 2. The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the applied forc 3. Two bodies exert equal and opposite forces on each other <--- Using 2 and 3 Together 14 : 42
Newton’s Laws 1. A Body at rest remains at rest, while a body in motion at constant velocity remains in motion Unless acted on by an external force 2. The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the applied forc 3. Two bodies exert equal and opposite forces on each other <--- Using 2 and 3 Together 14 : 42
 Newton’s Laws imply momentum conservation In absence of external force, momentum change is equal and opposite in two-body system. Regroup terms Integrate. Q. E. D. Newton’s laws are valid in all inertial (i. e. constant velocity) reference frames 15 : 45
Newton’s Laws imply momentum conservation In absence of external force, momentum change is equal and opposite in two-body system. Regroup terms Integrate. Q. E. D. Newton’s laws are valid in all inertial (i. e. constant velocity) reference frames 15 : 45
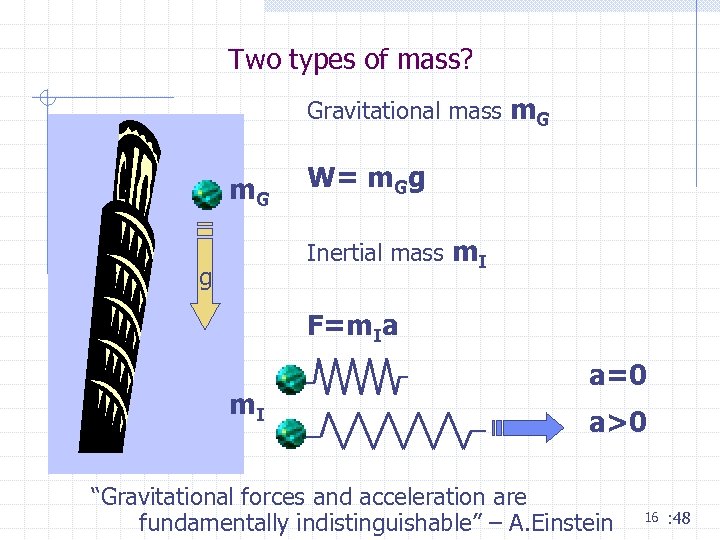 Two types of mass? Gravitational mass m. G W= m. Gg Inertial mass m. I g F=m. Ia m. I a=0 a>0 “Gravitational forces and acceleration are fundamentally indistinguishable” – A. Einstein 16 : 48
Two types of mass? Gravitational mass m. G W= m. Gg Inertial mass m. I g F=m. Ia m. I a=0 a>0 “Gravitational forces and acceleration are fundamentally indistinguishable” – A. Einstein 16 : 48
 Momentum Conservation -- Problem #1 -2 “A car crash” James and Joan were drinking straight tequila while driving two cars of mass 1000 kg and 2000 kg with velocity vectors and Their vehicles collide “perfectly inelastically” (i. e. they stick together) Assume that the resultant wreck slides with velocity vector Friction has not had time to work yet. Calculate 17 : 55
Momentum Conservation -- Problem #1 -2 “A car crash” James and Joan were drinking straight tequila while driving two cars of mass 1000 kg and 2000 kg with velocity vectors and Their vehicles collide “perfectly inelastically” (i. e. they stick together) Assume that the resultant wreck slides with velocity vector Friction has not had time to work yet. Calculate 17 : 55
 Two types of mass -- Problem #1 -3 a-b “Galileo in an alternate universe” A cannonball (m. G = 10 kg) and a golf-ball (m. G = 0. 1 kg) are simultaneously dropped from a 98 m tall leaning tower in Italy. Neglect air-resistance How long does each ball take to hit the ground if: a) m. I=m. G b) m. I =m. G * m. G 18 : 65
Two types of mass -- Problem #1 -3 a-b “Galileo in an alternate universe” A cannonball (m. G = 10 kg) and a golf-ball (m. G = 0. 1 kg) are simultaneously dropped from a 98 m tall leaning tower in Italy. Neglect air-resistance How long does each ball take to hit the ground if: a) m. I=m. G b) m. I =m. G * m. G 18 : 65
 Lecture #1 Wind-up. Buy the book!! First homework due in class Thursday 8/29 Office hours today 3 -5 Get on Web. CT 19
Lecture #1 Wind-up. Buy the book!! First homework due in class Thursday 8/29 Office hours today 3 -5 Get on Web. CT 19


