0615c16a5e40e02dc81b0c7e8016b39d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Interim Reports for PEEC April 3, 2003 } } Sustainable Schools CO-SEED Community Mapping Program A Forest For Every Classroom
Interim Reports for PEEC April 3, 2003 } } Sustainable Schools CO-SEED Community Mapping Program A Forest For Every Classroom
 Sustainable Schools Project “I’ve seen kids in the lunchroom looking at labels, wondering if their food is local, and what’s in it. They never did that before. And I’ve gotten excellent feedback from parents, saying ‘I’ve been trying to talk to my children about nutrition and where food comes from and they were not listening…but now they are interested!’” --Champlain Principal
Sustainable Schools Project “I’ve seen kids in the lunchroom looking at labels, wondering if their food is local, and what’s in it. They never did that before. And I’ve gotten excellent feedback from parents, saying ‘I’ve been trying to talk to my children about nutrition and where food comes from and they were not listening…but now they are interested!’” --Champlain Principal
 Sustainable Schools Overview } Evaluation Focus: § First year process implementation § First year outcomes Change in teacher practice } Key Methods: § § § § Teacher pre-post interviews Teacher pre-post surveys Workshop, classroom and meeting observations Staff and community advisor interviews Internal process watching by SSP staff and faculty Document review Trial of pre-post student assessment activity
Sustainable Schools Overview } Evaluation Focus: § First year process implementation § First year outcomes Change in teacher practice } Key Methods: § § § § Teacher pre-post interviews Teacher pre-post surveys Workshop, classroom and meeting observations Staff and community advisor interviews Internal process watching by SSP staff and faculty Document review Trial of pre-post student assessment activity
 Sustainable Schools Interim Report (Teachers set up the Living Machine with Community Partner)
Sustainable Schools Interim Report (Teachers set up the Living Machine with Community Partner)
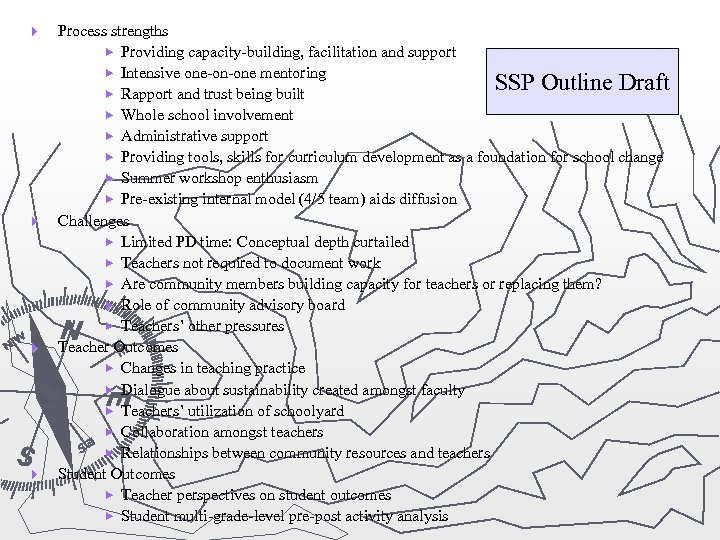 } } Process strengths Providing capacity-building, facilitation and support Intensive one-on-one mentoring SSP Outline Draft Rapport and trust being built Whole school involvement Administrative support Providing tools, skills for curriculum development as a foundation for school change Summer workshop enthusiasm Pre-existing internal model (4/5 team) aids diffusion Challenges Limited PD time: Conceptual depth curtailed Teachers not required to document work Are community members building capacity for teachers or replacing them? Role of community advisory board Teachers’ other pressures Teacher Outcomes Changes in teaching practice Dialogue about sustainability created amongst faculty Teachers’ utilization of schoolyard Collaboration amongst teachers Relationships between community resources and teachers Student Outcomes Teacher perspectives on student outcomes Student multi-grade-level pre-post activity analysis
} } Process strengths Providing capacity-building, facilitation and support Intensive one-on-one mentoring SSP Outline Draft Rapport and trust being built Whole school involvement Administrative support Providing tools, skills for curriculum development as a foundation for school change Summer workshop enthusiasm Pre-existing internal model (4/5 team) aids diffusion Challenges Limited PD time: Conceptual depth curtailed Teachers not required to document work Are community members building capacity for teachers or replacing them? Role of community advisory board Teachers’ other pressures Teacher Outcomes Changes in teaching practice Dialogue about sustainability created amongst faculty Teachers’ utilization of schoolyard Collaboration amongst teachers Relationships between community resources and teachers Student Outcomes Teacher perspectives on student outcomes Student multi-grade-level pre-post activity analysis
 The CO-SEED Project “The attitude toward education and kids has changed in a positive manner in Littleton because of the increased interaction between students and Joe Blow on the street. ” -Littleton High School Principal
The CO-SEED Project “The attitude toward education and kids has changed in a positive manner in Littleton because of the increased interaction between students and Joe Blow on the street. ” -Littleton High School Principal
 } Evaluation Focus: § Process: Sustainability beyond ANE involvement § Civic engagement, schoolcommunity relations: survey process development § Student achievement: Student writing assessment § Teacher practice change } Key Methods: § Site visits § Staff, teacher, administrator, community partner interviews § Surveys: three groups § Classroom and meeting observations § Creation of internal monitoring system: ELCs, SEED Team § Document review CO-SEED Overview
} Evaluation Focus: § Process: Sustainability beyond ANE involvement § Civic engagement, schoolcommunity relations: survey process development § Student achievement: Student writing assessment § Teacher practice change } Key Methods: § Site visits § Staff, teacher, administrator, community partner interviews § Surveys: three groups § Classroom and meeting observations § Creation of internal monitoring system: ELCs, SEED Team § Document review CO-SEED Overview
 Bradford Seed Team CO-SEED Interim Report
Bradford Seed Team CO-SEED Interim Report
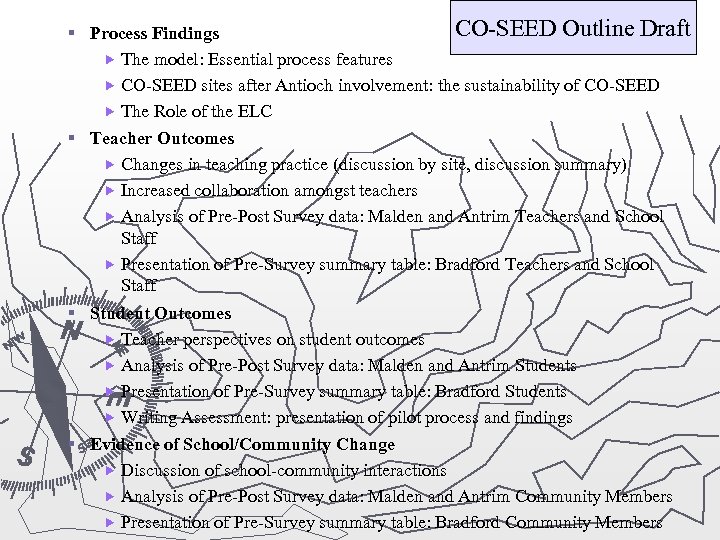 CO-SEED Outline Draft § Process Findings The model: Essential process features CO-SEED sites after Antioch involvement: the sustainability of CO-SEED The Role of the ELC § Teacher Outcomes Changes in teaching practice (discussion by site, discussion summary) Increased collaboration amongst teachers Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Teachers and School Staff Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Teachers and School Staff § Student Outcomes Teacher perspectives on student outcomes Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Students Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Students Writing Assessment: presentation of pilot process and findings § Evidence of School/Community Change Discussion of school-community interactions Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Community Members Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Community Members
CO-SEED Outline Draft § Process Findings The model: Essential process features CO-SEED sites after Antioch involvement: the sustainability of CO-SEED The Role of the ELC § Teacher Outcomes Changes in teaching practice (discussion by site, discussion summary) Increased collaboration amongst teachers Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Teachers and School Staff Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Teachers and School Staff § Student Outcomes Teacher perspectives on student outcomes Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Students Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Students Writing Assessment: presentation of pilot process and findings § Evidence of School/Community Change Discussion of school-community interactions Analysis of Pre-Post Survey data: Malden and Antrim Community Members Presentation of Pre-Survey summary table: Bradford Community Members
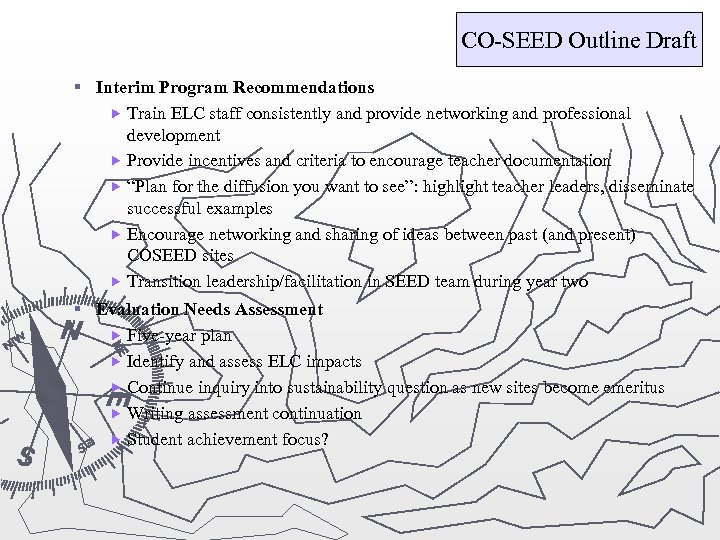 CO-SEED Outline Draft § Interim Program Recommendations Train ELC staff consistently and provide networking and professional development Provide incentives and criteria to encourage teacher documentation “Plan for the diffusion you want to see”: highlight teacher leaders, disseminate successful examples Encourage networking and sharing of ideas between past (and present) COSEED sites Transition leadership/facilitation in SEED team during year two § Evaluation Needs Assessment Five-year plan Identify and assess ELC impacts Continue inquiry into sustainability question as new sites become emeritus Writing assessment continuation Student achievement focus?
CO-SEED Outline Draft § Interim Program Recommendations Train ELC staff consistently and provide networking and professional development Provide incentives and criteria to encourage teacher documentation “Plan for the diffusion you want to see”: highlight teacher leaders, disseminate successful examples Encourage networking and sharing of ideas between past (and present) COSEED sites Transition leadership/facilitation in SEED team during year two § Evaluation Needs Assessment Five-year plan Identify and assess ELC impacts Continue inquiry into sustainability question as new sites become emeritus Writing assessment continuation Student achievement focus?
 Assessment of Student Writing What is the impact of CO-SEED on students’ writing abilities?
Assessment of Student Writing What is the impact of CO-SEED on students’ writing abilities?
 The Community Mapping Program
The Community Mapping Program
 CMP Overview } Evaluation Focus: § Process § Teacher Outcomes § Community and Student Outcomes § Colorado: Student Achievement pilots } Key Methods: § Site visits § Staff, teacher, student and community partner interviews § Teacher and student pre and post surveys § Classroom, institute and meeting observations § Document review
CMP Overview } Evaluation Focus: § Process § Teacher Outcomes § Community and Student Outcomes § Colorado: Student Achievement pilots } Key Methods: § Site visits § Staff, teacher, student and community partner interviews § Teacher and student pre and post surveys § Classroom, institute and meeting observations § Document review
 CMP Interim Report “I think that when you see a large scale map you don’t think about the actual land that’s there. But when you actually go out there it’s different…you see what’s there. Now I have something real to associate with the maps. It makes it more meaningful. ” --7 th grade student
CMP Interim Report “I think that when you see a large scale map you don’t think about the actual land that’s there. But when you actually go out there it’s different…you see what’s there. Now I have something real to associate with the maps. It makes it more meaningful. ” --7 th grade student
 Interim Teacher Outcomes Educators Discover Community Resources CMP Educators Stimulate Colleagues to do Place-based Education CMP Provides Positive Public Relations for Schools CMP Helps Educators Provide Service-Learning Opportunities A Catalyst for Interdisciplinary Teaching Technology at Work in the Field and in the Classroom Maps: A Powerful Tool Educators Remain Enthusiastic about CMP after Year One
Interim Teacher Outcomes Educators Discover Community Resources CMP Educators Stimulate Colleagues to do Place-based Education CMP Provides Positive Public Relations for Schools CMP Helps Educators Provide Service-Learning Opportunities A Catalyst for Interdisciplinary Teaching Technology at Work in the Field and in the Classroom Maps: A Powerful Tool Educators Remain Enthusiastic about CMP after Year One
 Interim Community Partner Outcomes The Community Partner Relationship: A Challenging but Rewarding Endeavor Increased connection with the school Working with Adolescents and Schools: Dispelling the Myth The Value of Final Products Introduction to Technology
Interim Community Partner Outcomes The Community Partner Relationship: A Challenging but Rewarding Endeavor Increased connection with the school Working with Adolescents and Schools: Dispelling the Myth The Value of Final Products Introduction to Technology
 Student Outcomes and Process Report } Interim Student Outcomes An Affinity for Real World Learning Inter-disciplinary Learning Mimics Real Life Increased citizenship skills and pride Increased “sense of place” Environmental knowledge
Student Outcomes and Process Report } Interim Student Outcomes An Affinity for Real World Learning Inter-disciplinary Learning Mimics Real Life Increased citizenship skills and pride Increased “sense of place” Environmental knowledge
 Program Processes Program Strengths · · } } Staff availability, communication Trainings Flexibility CMP as a “toolbox” Service-learning Community partner model Programmatic Challenges } } } Technology as a barrier Lack of planning time for educators Teacher expectations vs staff expectations CMP staff underused or used primarily for tech support and chaperones Weak Community Partner relationships Teacher comfort taking kids outside
Program Processes Program Strengths · · } } Staff availability, communication Trainings Flexibility CMP as a “toolbox” Service-learning Community partner model Programmatic Challenges } } } Technology as a barrier Lack of planning time for educators Teacher expectations vs staff expectations CMP staff underused or used primarily for tech support and chaperones Weak Community Partner relationships Teacher comfort taking kids outside
 A Forest for Every Classroom
A Forest for Every Classroom
 “Being part of this model and connecting with other teachers and the partners has given me the tools and the courage to put out my teaching philosophy to colleagues at my school. This has enabled us to actually make some significant movement towards change in the science content at my school. ” --FFEC Teacher
“Being part of this model and connecting with other teachers and the partners has given me the tools and the courage to put out my teaching philosophy to colleagues at my school. This has enabled us to actually make some significant movement towards change in the science content at my school. ” --FFEC Teacher
 FFEC Overview } Evaluation Focus: § Process implementation Partnership functioning § Teacher practice change § Student outcomes } Key Methods: § § § Site visits Teacher and staff focus groups Student Surveys Informal student interviews Classroom and institute observations § Document review
FFEC Overview } Evaluation Focus: § Process implementation Partnership functioning § Teacher practice change § Student outcomes } Key Methods: § § § Site visits Teacher and staff focus groups Student Surveys Informal student interviews Classroom and institute observations § Document review
 FFEC Interim Report (National Park Ranger with 7 th graders)
FFEC Interim Report (National Park Ranger with 7 th graders)
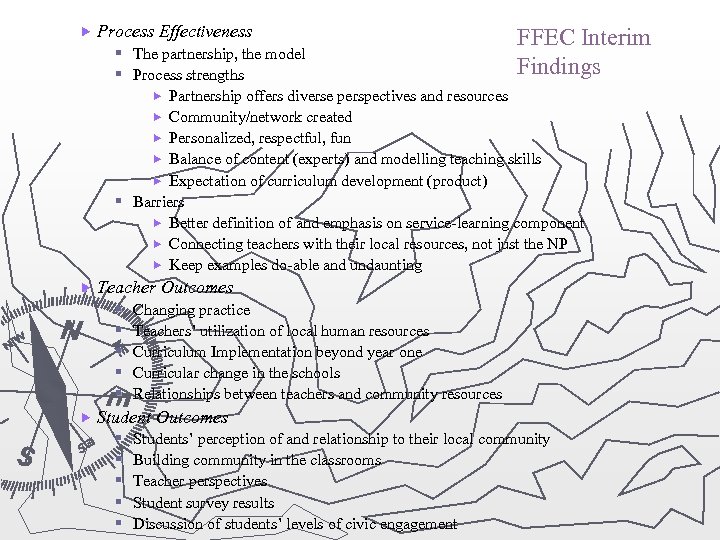 Process Effectiveness FFEC Interim § The partnership, the model Findings § Process strengths Partnership offers diverse perspectives and resources Community/network created Personalized, respectful, fun Balance of content (experts) and modelling teaching skills Expectation of curriculum development (product) § Barriers Better definition of and emphasis on service-learning component Connecting teachers with their local resources, not just the NP Keep examples do-able and undaunting Teacher Outcomes § § § Changing practice Teachers’ utilization of local human resources Curriculum Implementation beyond year one Curricular change in the schools Relationships between teachers and community resources Student Outcomes § § § Students’ perception of and relationship to their local community Building community in the classrooms Teacher perspectives Student survey results Discussion of students’ levels of civic engagement
Process Effectiveness FFEC Interim § The partnership, the model Findings § Process strengths Partnership offers diverse perspectives and resources Community/network created Personalized, respectful, fun Balance of content (experts) and modelling teaching skills Expectation of curriculum development (product) § Barriers Better definition of and emphasis on service-learning component Connecting teachers with their local resources, not just the NP Keep examples do-able and undaunting Teacher Outcomes § § § Changing practice Teachers’ utilization of local human resources Curriculum Implementation beyond year one Curricular change in the schools Relationships between teachers and community resources Student Outcomes § § § Students’ perception of and relationship to their local community Building community in the classrooms Teacher perspectives Student survey results Discussion of students’ levels of civic engagement
 FFEC translated from teachers to students Summer Institute for Teachers at MABI Fall Math Class for Middle School Students at MABI
FFEC translated from teachers to students Summer Institute for Teachers at MABI Fall Math Class for Middle School Students at MABI
 Cross Program Report Thoughts
Cross Program Report Thoughts
 Cross Program Report Contents Introduction } Place-based Education Evaluation Collaborative (PEEC) § Brief overview of each program } Context § Place-based Education § Service-learning § School Change and Professional Development Methods } Teacher Question defined, Student Question defined } Cross program common methods under development Discussion } Common impacts on teachers } Discussion of civic engagement in students } Process: Greatest strengths and challenges of each program CO-SEED SSP FFEC CMP Conclusions and Recommendations } Recommendations for all programs, and place-based education } Plans for future PEEC research
Cross Program Report Contents Introduction } Place-based Education Evaluation Collaborative (PEEC) § Brief overview of each program } Context § Place-based Education § Service-learning § School Change and Professional Development Methods } Teacher Question defined, Student Question defined } Cross program common methods under development Discussion } Common impacts on teachers } Discussion of civic engagement in students } Process: Greatest strengths and challenges of each program CO-SEED SSP FFEC CMP Conclusions and Recommendations } Recommendations for all programs, and place-based education } Plans for future PEEC research
 Cross Program Questions teacher practice: How does participation in one of these place-based education programs change teachers’ teaching practices? Cross program objectives: § Teachers/schools implement/adopt place-based education beyond project/program intervention § Teachers understand that program is related to standards, a tool for teaching, not an add-on curriculum § Students are more engaged in learning through service OR teachers encourage service learning
Cross Program Questions teacher practice: How does participation in one of these place-based education programs change teachers’ teaching practices? Cross program objectives: § Teachers/schools implement/adopt place-based education beyond project/program intervention § Teachers understand that program is related to standards, a tool for teaching, not an add-on curriculum § Students are more engaged in learning through service OR teachers encourage service learning
 Cross Program Questions student civic engagement: How does participation in one of these place-based education programs affect students’ levels of civic engagement? Cross-program objectives: § Student learning occurs out in the community OR teachers use community in their teaching § Students are more engaged in learning through service OR teachers encourage service learning § Students will have knowledge/motivation/skills for stewardship/citizenship behavior community question: Cross-program objective: § Forging connections between school and community (formation of partnerships)
Cross Program Questions student civic engagement: How does participation in one of these place-based education programs affect students’ levels of civic engagement? Cross-program objectives: § Student learning occurs out in the community OR teachers use community in their teaching § Students are more engaged in learning through service OR teachers encourage service learning § Students will have knowledge/motivation/skills for stewardship/citizenship behavior community question: Cross-program objective: § Forging connections between school and community (formation of partnerships)
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs } Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (COSEED)
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs } Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (COSEED)
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) }
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) }
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) }
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) }
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model)
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model)
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § } => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § } => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams } Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for communitybased, place-based, service-learning curriculum. }
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams } Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for communitybased, place-based, service-learning curriculum. }
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § } => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for communitybased, place-based, service-learning curriculum. } Involve teachers, administrators, community members in program evaluation from the start of contact so that they: } § § Know what to expect and are cooperative. Can provide insight into place-specific evaluation indicators that might be especially useful.
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) } Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) } Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect servicelearning to be specific and useful (CMP) } Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school --a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) } § } => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for communitybased, place-based, service-learning curriculum. } Involve teachers, administrators, community members in program evaluation from the start of contact so that they: } § § Know what to expect and are cooperative. Can provide insight into place-specific evaluation indicators that might be especially useful.
 Interim Recommendations for Four Programs } } Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect service-learning to be specific and useful (CMP) Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school--a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) } Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams } Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for community-based, place-based, service-learning curriculum. Involve teachers, administrators, community members in program evaluation from the start of contact so that they: } § § } Know what to expect and are cooperative. Can provide insight into place-specific evaluation indicators that might be especially useful. Distinguish between place-based ed. and service-learning and prepare schools, teachers, staff accordingly.
Interim Recommendations for Four Programs } } Involve community partners early in process, and as integrally as possible, and provide community partners your organizational support as well as educators/schools (CO-SEED) Create a culture of respect, communication, support and rapport with participants to promote buy-in (FFEC) Offer resources or training in specific, useful skills if you expect service-learning to be specific and useful (CMP) Before intervention, help establish or locate one good model in a school--a successful teacher/team completing an example project--to encourage ‘spread of effect’ (SSP) § => either seek out schools with this model in place, or create this scenario in the first year of working with a school (example of how PD-focused program complements the whole-school change model) } Encourage (or require) teachers to participate in teams } Lead teachers in learning new assessment techniques for community-based, place-based, service-learning curriculum. Involve teachers, administrators, community members in program evaluation from the start of contact so that they: } § § } Know what to expect and are cooperative. Can provide insight into place-specific evaluation indicators that might be especially useful. Distinguish between place-based ed. and service-learning and prepare schools, teachers, staff accordingly.
 Text about PEEC on each report Antioch New England Institute is part of the Place-based Education Evaluation Collaborative (PEEC), a unique partnership of organizations whose aim is to strengthen and deepen the practice and evaluation of place-based education initiatives. Other PEEC members are: Shelburne Farms, Vermont Institute of Natural Science, Orton Family Foundation, Upper Valley Community Foundation, Vermont Education for Sustainability Project, National Wildlife Federation, the National Park Service and the US Forest Service. This year, in addition to the Co-SEED Project, three other place-based education programs were evaluated: The Community Mapping Program; The Sustainable Schools Project; and The Forest For Every Classroom Program.
Text about PEEC on each report Antioch New England Institute is part of the Place-based Education Evaluation Collaborative (PEEC), a unique partnership of organizations whose aim is to strengthen and deepen the practice and evaluation of place-based education initiatives. Other PEEC members are: Shelburne Farms, Vermont Institute of Natural Science, Orton Family Foundation, Upper Valley Community Foundation, Vermont Education for Sustainability Project, National Wildlife Federation, the National Park Service and the US Forest Service. This year, in addition to the Co-SEED Project, three other place-based education programs were evaluated: The Community Mapping Program; The Sustainable Schools Project; and The Forest For Every Classroom Program.




