b70fefc652e7cecbc34623a0f83d8d05.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8
Interfacing External Sensors to Telosb Motes April 06, 2005 Raghul Gunasekaran

Telosb Motes Low power consuming Capable of operating in large clusters 8 MHz MSP 430 with 10 KB RAM 250 Kbps data rate IEEE 802. 15. 4 Compliant Operating in 2. 4 to 2. 483 GHz Virtual USB programming Serial UART communication Programmable Flash Memory 48 K 1 MB external flash for data logging On board Sensors (Temperature, Humidity and Light Sensor)
Telosb Motes Open source operating System – Tiny. OS Programmed in NESC - a modular programming language - an extension to C Built in 12 -bit ADC Supports 8 channels Capable of interfacing with external Sensors
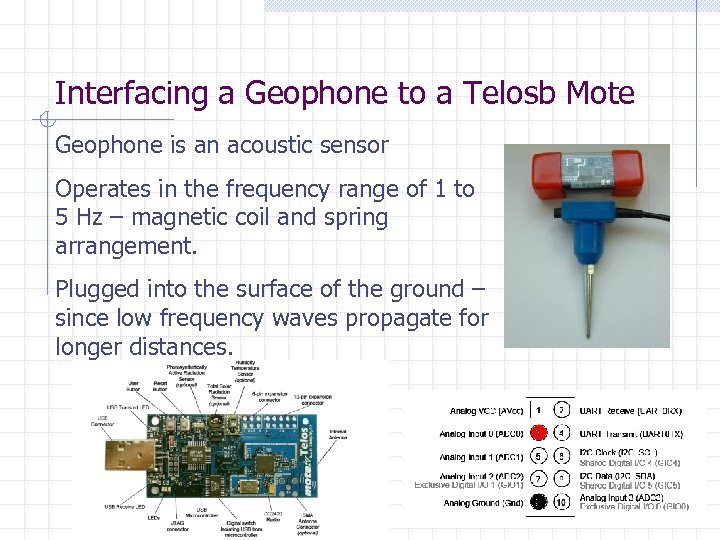
Interfacing a Geophone to a Telosb Mote Geophone is an acoustic sensor Operates in the frequency range of 1 to 5 Hz – magnetic coil and spring arrangement. Plugged into the surface of the ground – since low frequency waves propagate for longer distances.

Exploratory Seismographs Works using acoustic sensors, buy measuring wave velocities through different materials www. geometrics. com/Smart. Seis. Cropped. jpg Few Applications • Oil exploration • Underground Imaging • Mineral Exploration • Landslide studies & Earthquakes www. geometrics. com/SMARTPATTY. jpg
Implementation Issues Synchronization - triggered data collection (most important for the application discussed ) Compression of data - Data collected is stored in the flash memory - data sizes would be in the order of 10 k. B + header information. Example: 12 bit ADC (2 byte storage space in the memory) sampled for every 1 ms (or 0. 5 ms) time interval for a period of 2 (or 3) seconds would result in a data size of 6 KB) - Reduced data size results in energy saving over transmitting high data

Implementation Issues Routing – Store and Forward - since the motes have a fixed arrangement - no complex algorithm required - moreover the programming space on the mote needs to be small for we have enough space for data logging.

Thanks
b70fefc652e7cecbc34623a0f83d8d05.ppt