26032015.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
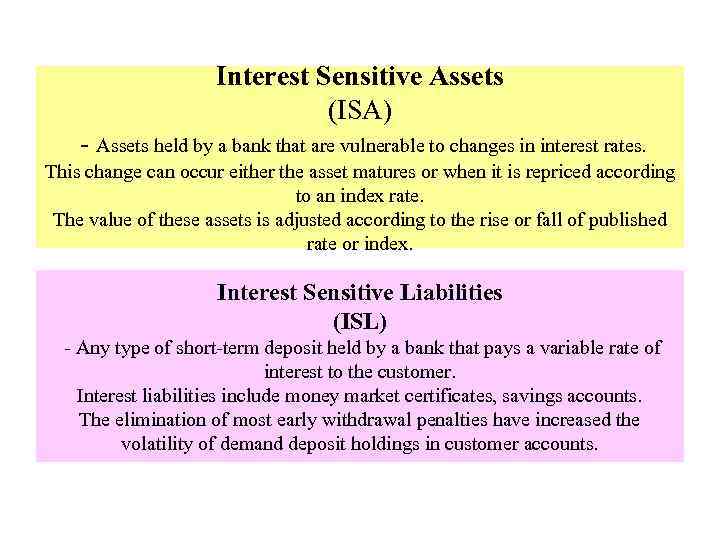
Interest Sensitive Assets (ISA) - Assets held by a bank that are vulnerable to changes in interest rates. This change can occur either the asset matures or when it is repriced according to an index rate. The value of these assets is adjusted according to the rise or fall of published rate or index. Interest Sensitive Liabilities (ISL) - Any type of short-term deposit held by a bank that pays a variable rate of interest to the customer. Interest liabilities include money market certificates, savings accounts. The elimination of most early withdrawal penalties have increased the volatility of demand deposit holdings in customer accounts.
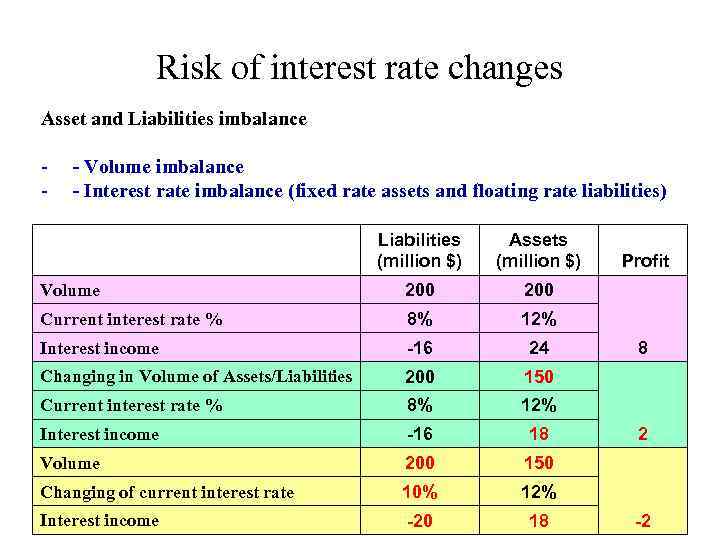
Risk of interest rate changes Asset and Liabilities imbalance - - Volume imbalance - - Interest rate imbalance (fixed rate assets and floating rate liabilities) Liabilities (million $) Assets (million $) Profit Volume 200 Current interest rate % 8% 12% Interest income -16 24 8 Changing in Volume of Assets/Liabilities 200 150 Current interest rate % 8% 12% Interest income -16 18 2 Volume 200 150 Changing of current interest rate 10% 12% Interest income -20 18 -2
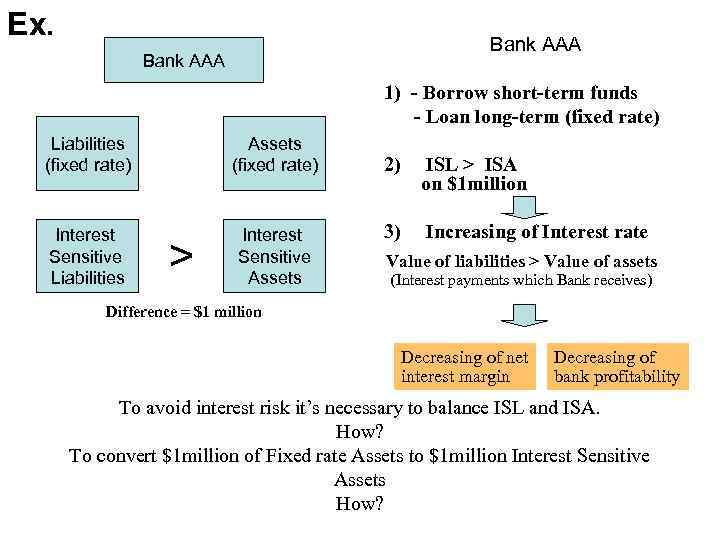
Ex. Bank AAA 1) - Borrow short-term funds - Loan long-term (fixed rate) Liabilities (fixed rate) Assets (fixed rate) Interest Sensitive Liabilities Interest Sensitive Assets > 2) ISL > ISA on $1 million 3) Increasing of Interest rate Value of liabilities > Value of assets (Interest payments which Bank receives) Difference = $1 million Decreasing of net interest margin Decreasing of bank profitability To avoid interest risk it’s necessary to balance ISL and ISA. How? To convert $1 million of Fixed rate Assets to $1 million Interest Sensitive Assets How?
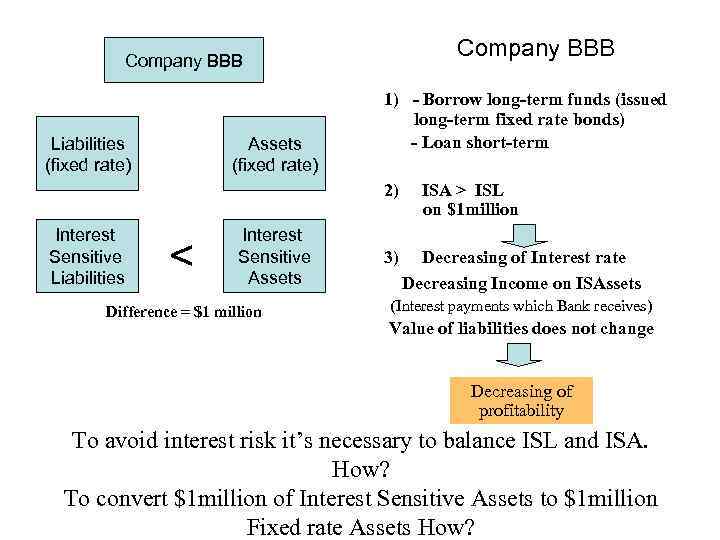
Company BBB Liabilities (fixed rate) Assets (fixed rate) Company BBB 1) - Borrow long-term funds (issued long-term fixed rate bonds) - Loan short-term 2) ISA > ISL on $1 million Interest Sensitive Liabilities < Interest Sensitive Assets Difference = $1 million 3) Decreasing of Interest rate Decreasing Income on ISAssets (Interest payments which Bank receives) Value of liabilities does not change Decreasing of profitability To avoid interest risk it’s necessary to balance ISL and ISA. How? To convert $1 million of Interest Sensitive Assets to $1 million Fixed rate Assets How?
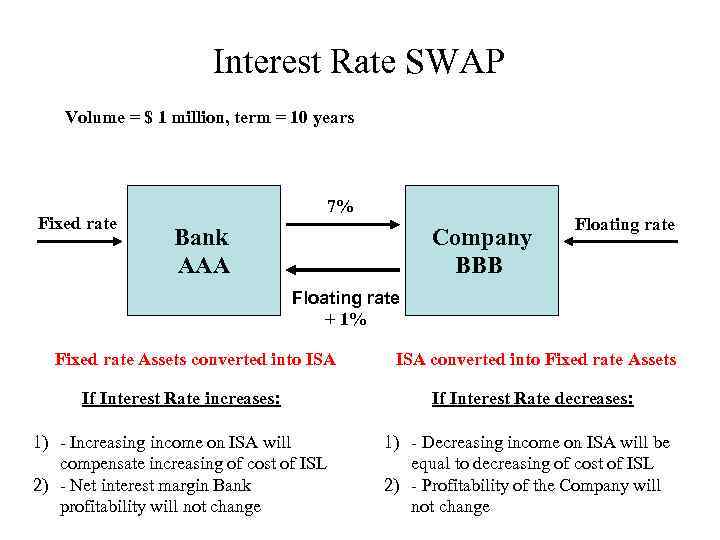
Interest Rate SWAP Volume = $ 1 million, term = 10 years Fixed rate 7% Bank AAA Company BBB Floating rate + 1% Fixed rate Assets converted into ISA converted into Fixed rate Assets If Interest Rate increases: If Interest Rate decreases: 1) - Increasing income on ISA will compensate increasing of cost of ISL 2) - Net interest margin Bank profitability will not change 1) - Decreasing income on ISA will be equal to decreasing of cost of ISL 2) - Profitability of the Company will not change

Ex. Using Swap to transform Liabilities Development company Building association 1) Start the construction of building zone. 1) Attract the capital by issuing fixed rate eurobonds – Volume of issuing - $ 5 million, with 2 years maturity. 2) To finance operating assets Company makes a loan in a bank - $2 million on the Floating rate base. 2) To give morgtgage credits on floating rate base. 3) If the Interest rate will increase significantly the Company may not get expected Profit. 4) Term of construction – 2 years. 5) Swap agreement with a bank of changing floating rate liabilities to fixed rate liabilities. 3) If the Interest rate will decrease significantly the Association may not meet liabilities (fixed rate). Interest income of floating rate mortgage credits will not enough. 4) Swap agreement with a bank of changing fixed rate liabilities to floating rate liabilities.

Equity swap A swap in which the cash flows that are exchanged are based on the total return on some stock market index and an interest rate (either a fixed rate or floating rate). Hedge fund – a flexible investment company for small number of large investors (usually the minimum investment is $1 million); can use high-risk techniques (not allowed for mutual funds) such as short-selling and heavy leveraging. It’s usual for fund managers to use investment strategy which is based on following the Stock Index. The mechanism of such type investment means that you buy the whole stock basket instead of selecting individual stocks to create portfolio which would mimic the structure of market or some market segment. In result your costs are less compare with common investing in stocks. Michael Lewis The Big Short Inside the Doomsday Machine

Ex. • • Large international Hedge Fund wishes to invest in USA stock market. And decided to use investment strategy “follow the Index”. Suppose, that HF promises to its shareholders to get payments from the changing of S&P 500 Index. HF has 3 alternatives: • • • 1) Buying individual stocks which enter into S&P 500 Index in Index proportions. 2) Buying FC on S&P 500 Index. 3) Make SWAP agreement on S&P 500 Index. According to Swap contract HF will pay floating/fixed interest payments instead of receiving payments from changing S&P 500 Index. So, HF would realize his investment strategy “follow the Index”.

Ex. HF makes Equity Swap agreement with Investment Bank: - Term of agreement – 1 year; - HF receives the income from changing S&P 500 Index (increasing or decreasing value); - Volume of investment - $100 million; - HF pays to IB annual payment = LIBOR * $100 million; - At the beginning of the year S&P 500 Index = 1853; FC on S&P 500 Index = 1853; - a) At the end of the year S&P 500 Index = 2061; FC on S&P 500 Index = 2061; - b) At the end of the year S&P 500 Index = 1650; FC on S&P 500 Index = 1650; - FC size = $250* S&P 500 - Dividend yield on stocks = 1% of investment volume; - LIBOR is constant = 2% per year Calculate the results of this investment strategy for HF and IB.
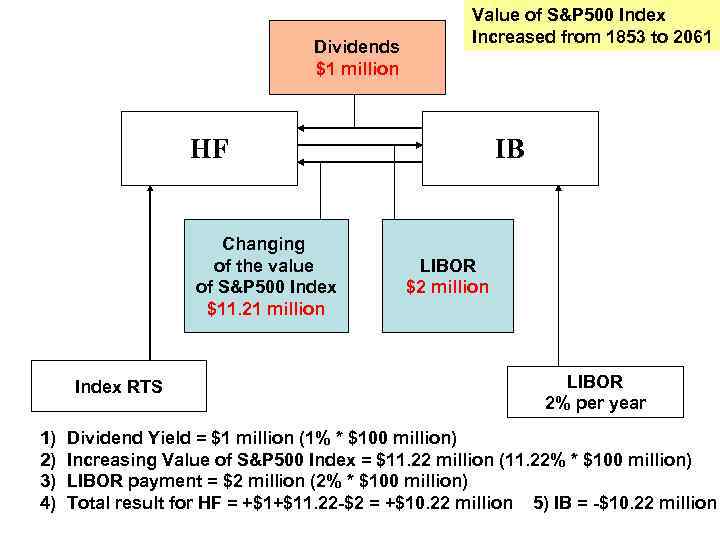
Dividends $1 million Value of S&P 500 Index Increased from 1853 to 2061 HF Changing of the value of S&P 500 Index $11. 21 million Index RTS 1) 2) 3) 4) IB LIBOR $2 million LIBOR 2% per year Dividend Yield = $1 million (1% * $100 million) Increasing Value of S&P 500 Index = $11. 22 million (11. 22% * $100 million) LIBOR payment = $2 million (2% * $100 million) Total result for HF = +$1+$11. 22 -$2 = +$10. 22 million 5) IB = -$10. 22 million
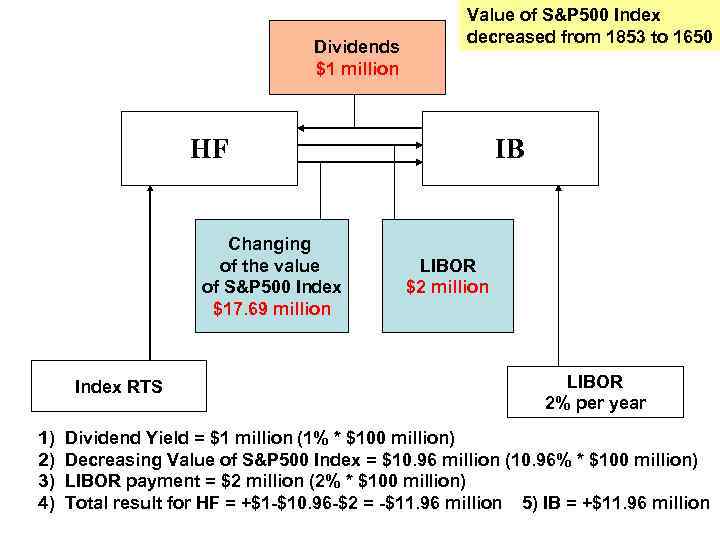
Dividends $1 million Value of S&P 500 Index decreased from 1853 to 1650 HF Changing of the value of S&P 500 Index $17. 69 million Index RTS 1) 2) 3) 4) IB LIBOR $2 million LIBOR 2% per year Dividend Yield = $1 million (1% * $100 million) Decreasing Value of S&P 500 Index = $10. 96 million (10. 96% * $100 million) LIBOR payment = $2 million (2% * $100 million) Total result for HF = +$1 -$10. 96 -$2 = -$11. 96 million 5) IB = +$11. 96 million

Total result for IB Hedging: - At the beginning: Buy S&P 500 Index FC. (100 000/ 250*1853) = 216 contracts - At the end: Sell 216 S&P 500 Index FC. a 1) Result from Swap agreement: 2) Result in Futures market: -$1 -$11. 22+$2 = -$10. 22 million (2061 -1853) * 250*216 = $11 232 000 Total result for IB: -$10. 22+$11. 232 = $ 1. 012 million b 1) Result from Swap agreement: 2) Result in Futures market -$1+$10. 96+$2 = $11. 96 million (1650 -1853) *250*216 = -$10 962 000 Total result for IB: $11. 96 -$10. 962 = $ 0. 988 million

Currency Swap Currency swap – an agreement under which two parties agree to exchange or swap specific amounts of two different currencies and repay over time with payments based on fixed interest rates in each currency. Currency pair – the relationship between the value of two different currencies which are being bought and sold on a foreign exchange market. Base currency is the first currency in a currency pair. The second currency is named quote currency (counter currency, terms currency). Base currency can also mean the accounting currency or domestic currency. When you go into long/short position – you buy/sell base currency and make reverse transaction with the equivalent amount in quote currency. If the open position of currency pair is transported to the next day (period) it is used Deposit/Lending Rates for each currency.

Currency Swap – The currency hierarchy for the "majors" is as follows: * Euro * Pound sterling * Australian dollar * New Zealand Dollar * United States dollar * Canadian Dollar * Swiss franc * Japanese Yen Other currencies (the “minors”) are generally quoted against one of the major currencies.

Swap Transaction on AUD/USD • Volume 1 lot (100 000 AUD) • Current exchange rate 0. 92 Current date: • Australian Dollar Overnight Deposit Rate: 2. 7% • Australian Dollar Overnight Lending Rate: 2. 5% • US Dollar Lending Rate: 0. 12% • US Dollar Deposit Rate: 0. 00%

Long position Going into long position and transporting it to the next day the client: • gets 2. 5% from buying 100 000 AUD, that is 2500 AUD per year or 6. 94 AUD per day (6. 38 USD). • pays 0. 12% per year for selling (borrowing) 92 000 USD (100 000 AUD*0. 92 = 92 000 USD), that is 110. 4 USD per year or 0. 31 USD per day. • Net difference is 6. 07 USD (6. 38 USD-0. 31 USD), in swap points 0. 61 point

• Short position • Going into short position and transporting it to the next day the client: • pays 2. 70% per year for selling (borrowing)100 000 AUD, that is 2722 AUD per year or 7. 5 AUD (6. 9 USD)per day. • gets 0% from buying 92 000 USD (100 000 AUD = 92 000 USD), that is 0 USD. • Net difference is -6. 9 USD, in swap points 0. 69 point

Currency swap types 1) Spot – Forward: • Date of the first leg – Spot • Date of second leg – Forward 2) Forward-Forward: 2 outright transactions. • Date of the first leg – Forward (later than Spot) • Date of second leg – Forward (later than first Forward) 3) Short Forward: Tom/Next • Date of the first leg – Tomorrow • Date of second leg – Next working day after Tomorrow Outright Forward – a forward currency contract with a locked-in exchange rate and delivery date.

Currency swap types 1) Buy and sell Swap – • First leg – buying curency (base as usual) • Second leg – selling currency 2) Sell and Buy Swap – • First leg – selling curency (base as usual) • Second leg – buying currency

Question 1 • January 5 2014 Investor wishes to invest $100 000 to bonds, denominated in USD. In a year after debt repayment he plans to get $100 000 and $5 000 of income, Total $105 000. • At current moment Investor has cash resources in euro. • To realize investment strategy it’s necessary to have USD, which he will able to repay in a year (after bonds repayment). • Current exchange rate for EUR/USD = 1. 365 • Offered banking exchange rate for swap: 1. 365 with settlement day January 5 2014. 1. 370 with settlement day January 5 2015. Recognize and analyze all possibilities of Investor, calculate results.
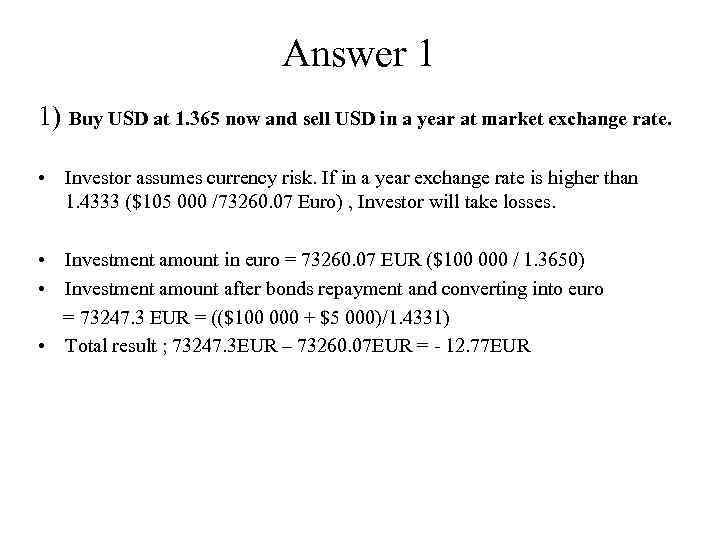
Answer 1 1) Buy USD at 1. 365 now and sell USD in a year at market exchange rate. • Investor assumes currency risk. If in a year exchange rate is higher than 1. 4333 ($105 000 /73260. 07 Euro) , Investor will take losses. • Investment amount in euro = 73260. 07 EUR ($100 000 / 1. 3650) • Investment amount after bonds repayment and converting into euro = 73247. 3 EUR = (($100 000 + $5 000)/1. 4331) • Total result ; 73247. 3 EUR – 73260. 07 EUR = - 12. 77 EUR

Answer 1 2) Borrow USD for 1 year. • It may take additional resources and collateral.

Answer 1 3) Make swap agreement: • Buy 100 000 USD with EUR at 1. 365 with settlement date day January 5 2014 • Sell 100 000 USD with EUR at 1. 370 with settlement date day January 5 2015 • Investor declines the possibility of taking a loss as a result of negative currency rate changing. • At the same time Investor declines the possibility of taking additional profit as a result of positive currency rate changing • Investment amount in euro = 73260. 07 EUR ($100 000 / 1. 3650) • Investment amount after bonds repayment and converting into euro = 76642. 34 EUR = (($100 000 + $5 000)/1. 370) • Total result : 76642. 343 EUR – 73260. 07 EUR = 3 382. 27 EUR
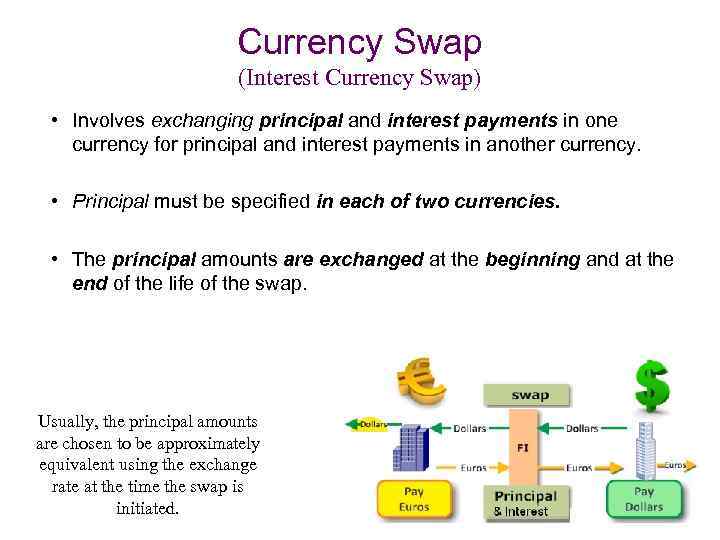
Currency Swap (Interest Currency Swap) • Involves exchanging principal and interest payments in one currency for principal and interest payments in another currency. • Principal must be specified in each of two currencies. • The principal amounts are exchanged at the beginning and at the end of the life of the swap. Usually, the principal amounts are chosen to be approximately equivalent using the exchange rate at the time the swap is initiated.
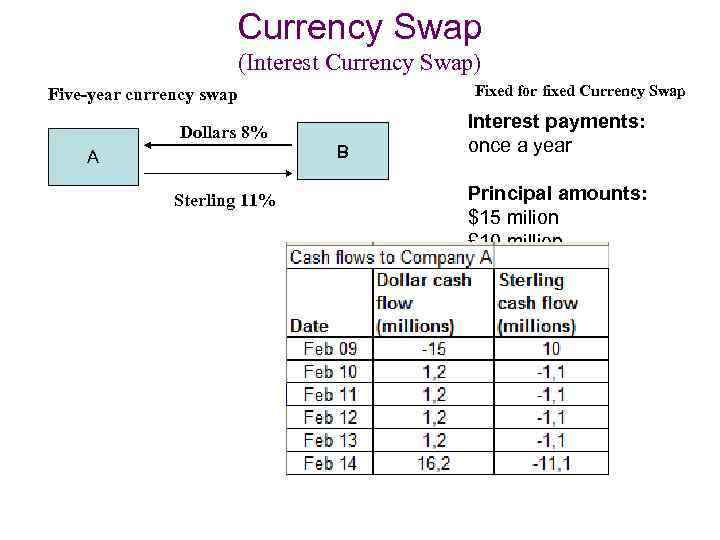
Currency Swap (Interest Currency Swap) Fixed for fixed Currency Swap Five-year currency swap Dollars 8% A Sterling 11% B Interest payments: once a year Principal amounts: $15 milion £ 10 million

• A Swap can be used to transform borrowings in one currency to borrowings in another. • A Swap can be used to transform the nature of assets

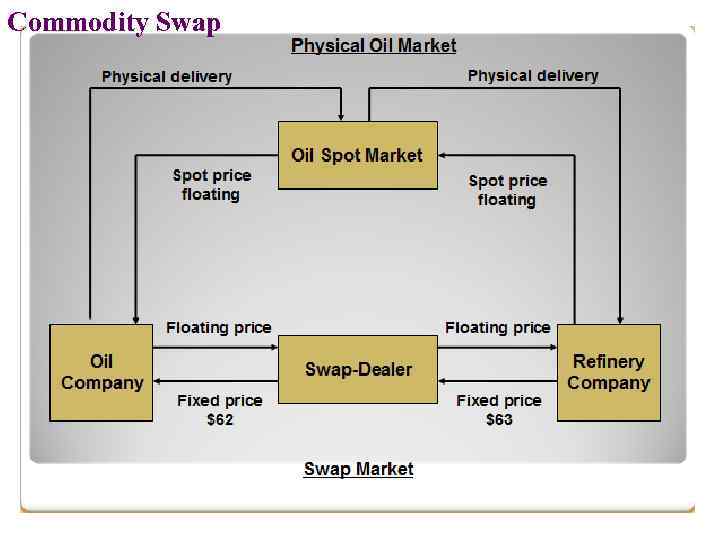
Commodity Swap • A commodity swap is an agreement whereby a floating (or market or spot) price based on an underlying commodity is exchanged for a fixed price over a specified period. • A Commodity swap is similar to a Fixed-Floating Interest rate swap. • The difference is that in an Interest rate swap the floating leg is based on standard Interest rates such as LIBOR, EURIBOR etc. but in a commodity swap the floating leg is based on the price of underlying commodity like Oil, Sugar etc. User of a commodity would secure a maximum price and agree to pay a financial institution this fixed price; • would get payments based on the market price for the commodity involved. Producer of a commodity Fixed price Market price • wishes to fix his income and would agree to pay the market price to a financial institution, in return for receiving fixed payments for the commodity; • receives fixed payments for the commodity. No Commodities are exchanged during the trade.

Commodity Swap • It is a swap in which exchanged cash flows are dependent on the price of an underlying commodity. • • The swap is accomplished through a series of payments made through a bank or other intermediary. • The purpose of the commodity swap is to allow commodity producers and users to predict more accurately their revenue or raw material costs.
Commodity Swap

Question 1 1. Refinery Company would secure a maximum price and agree to pay a financial institution $63 per barrel instead of receiving payments based on the market price for the Oil. 2. Oil Company wishes to fix his income and would agree to pay the market price to a financial institution, in return receiving $62 per barrel for the Oil. 3. Spot Oil prices, $ 1 per. 55 2 per. 60 3 per. 65 4 per. 70 5 per. 52 6 per. 49 4. Swap Dealer makes swap agreements with each company on presented conditions. 5. Calculate Total financial results for Oil Company, Refinery Company and Swap Dealer from using Swap contract.
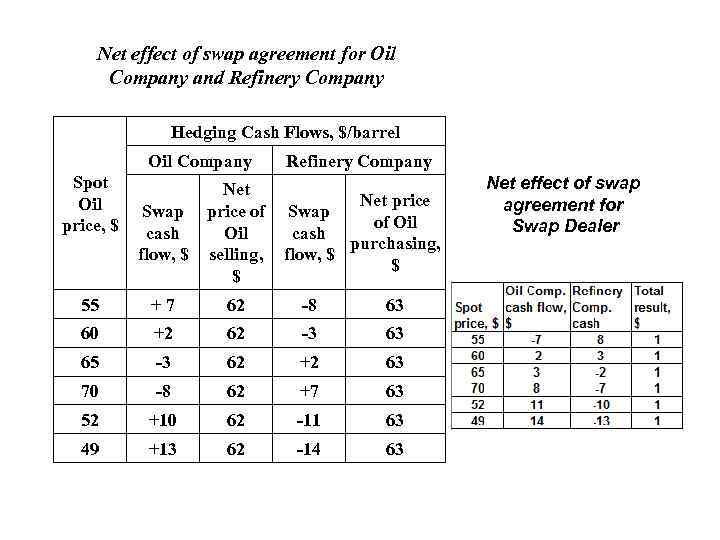
Net effect of swap agreement for Oil Company and Refinery Company Hedging Cash Flows, $/barrel Oil Company Spot Oil price, $ Swap cash flow, $ Refinery Company Net price of Swap of Oil cash Oil purchasing, selling, flow, $ $ $ 55 + 7 62 -8 63 60 +2 62 -3 63 65 -3 62 +2 63 70 -8 62 +7 63 52 +10 62 -11 63 49 +13 62 -14 63 Net effect of swap agreement for Swap Dealer
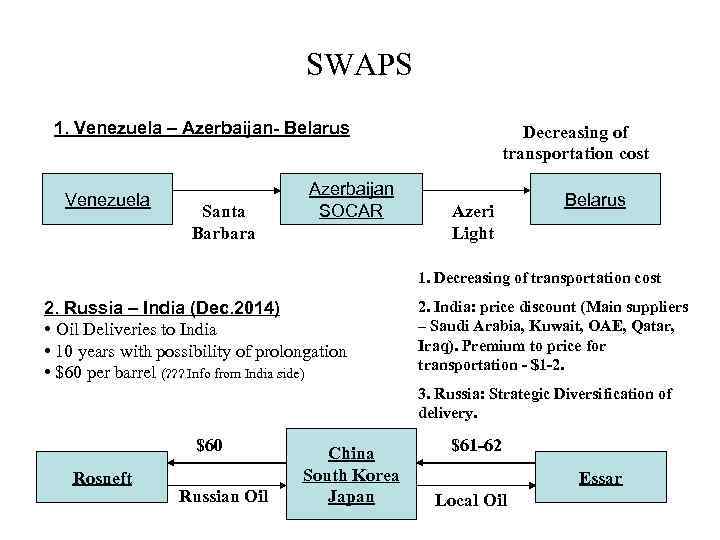
SWAPS 1. Venezuela – Azerbaijan- Belarus Venezuela Santa Barbara Azerbaijan SOCAR Decreasing of transportation cost Azeri Light Belarus 1. Decreasing of transportation cost 2. Russia – India (Dec. 2014) • Oil Deliveries to India • 10 years with possibility of prolongation • $60 per barrel (? ? ? Info from India side) 2. India: price discount (Main suppliers – Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, OAE, Qatar, Iraq). Premium to price for transportation - $1 -2. 3. Russia: Strategic Diversification of delivery. $60 Rosneft Russian Oil China South Korea Japan $61 -62 Essar Local Oil
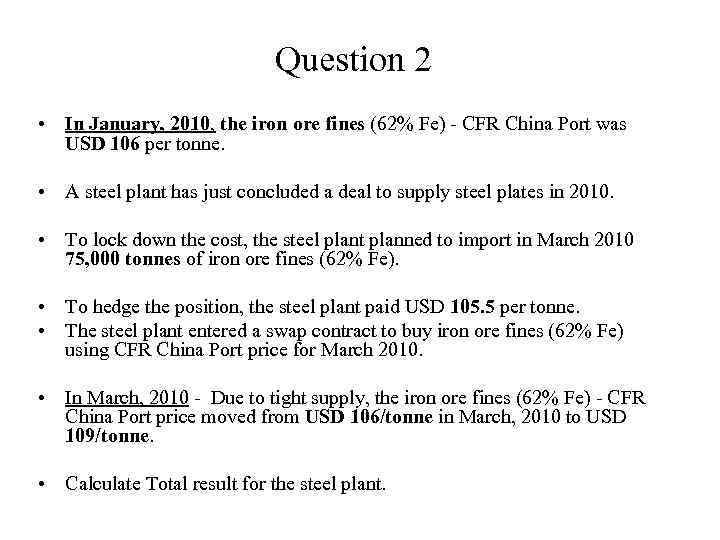
Question 2 • In January, 2010, the iron ore fines (62% Fe) - CFR China Port was USD 106 per tonne. • A steel plant has just concluded a deal to supply steel plates in 2010. • To lock down the cost, the steel plant planned to import in March 2010 75, 000 tonnes of iron ore fines (62% Fe). • To hedge the position, the steel plant paid USD 105. 5 per tonne. • The steel plant entered a swap contract to buy iron ore fines (62% Fe) using CFR China Port price for March 2010. • In March, 2010 - Due to tight supply, the iron ore fines (62% Fe) - CFR China Port price moved from USD 106/tonne in March, 2010 to USD 109/tonne. • Calculate Total result for the steel plant.
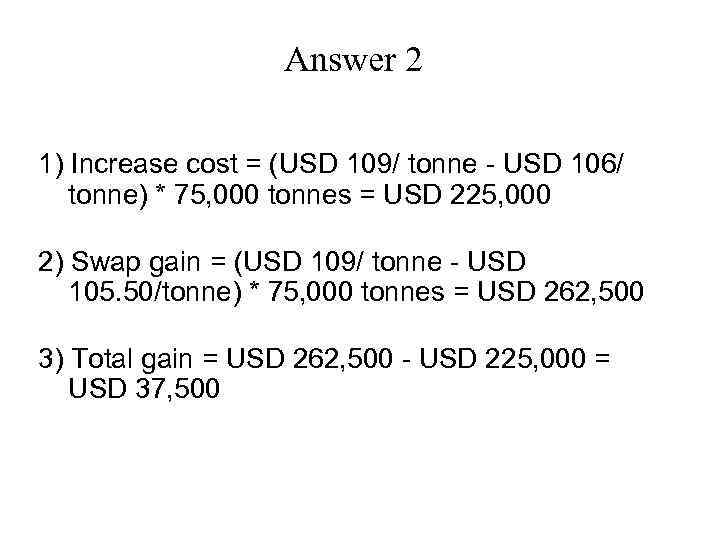
Answer 2 1) Increase cost = (USD 109/ tonne - USD 106/ tonne) * 75, 000 tonnes = USD 225, 000 2) Swap gain = (USD 109/ tonne - USD 105. 50/tonne) * 75, 000 tonnes = USD 262, 500 3) Total gain = USD 262, 500 - USD 225, 000 = USD 37, 500

26032015.ppt