86b5e4cfbc2e8924ffa354eafa74a380.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia: Energy Security, Green Economy, and Urban Security China’s Approach to Green Development and Transformation of Economic Development Pattern Prof. WANG Yi Institute of Policy and Management, CAS Academy House, Seoul, Korea October 20, 2010 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Contents 1. Challenge and Actions since 2000 2. Achievements and Problems during 11 th FYP (2006 -2010) 3. China’s approach towards Green, Low-Carbon Development in 12 th FYP (2011 -2015) and through 2020 2 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Rapid Economic Growth and Its Impacts l New round of Rapid Growth since 2000 Ø Ø l Middle Stage of Industrialization Ø Ø l l Heavy and Chemistry Industries (about 70%) Resources, Energy and pollutant discharge intensive Rapid urbanization Ø l Growth rate: about 10% both positive and Negative Effects Growth rate over 1% Consumption pattern transition with per capita GDP over US$ 1000: auto, house, etc (as driving force) Since late 2002, overall stress of resources and energy and serious environmental pollutions 3 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
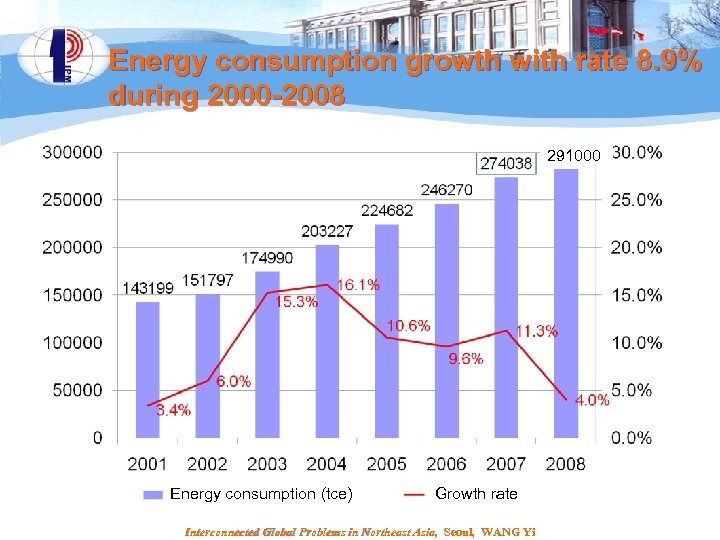
Energy consumption growth with rate 8. 9% during 2000 -2008 291000 Energy consumption (tce) Growth rate Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
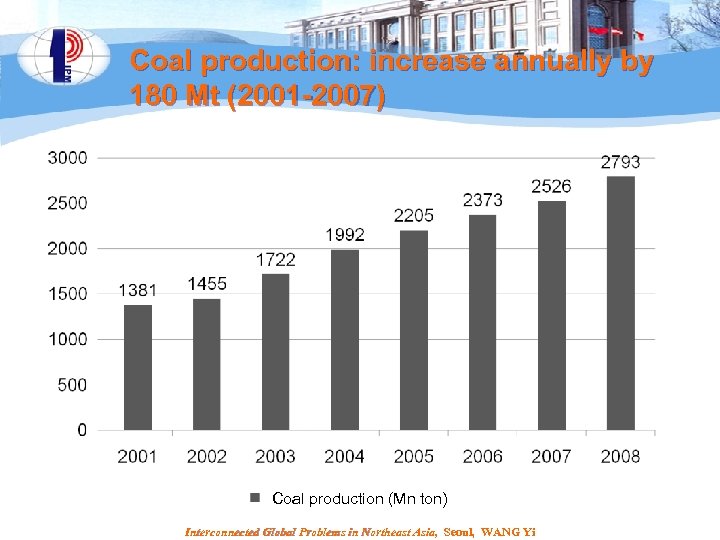
Coal production: increase annually by 180 Mt (2001 -2007) Coal production (Mn ton) Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
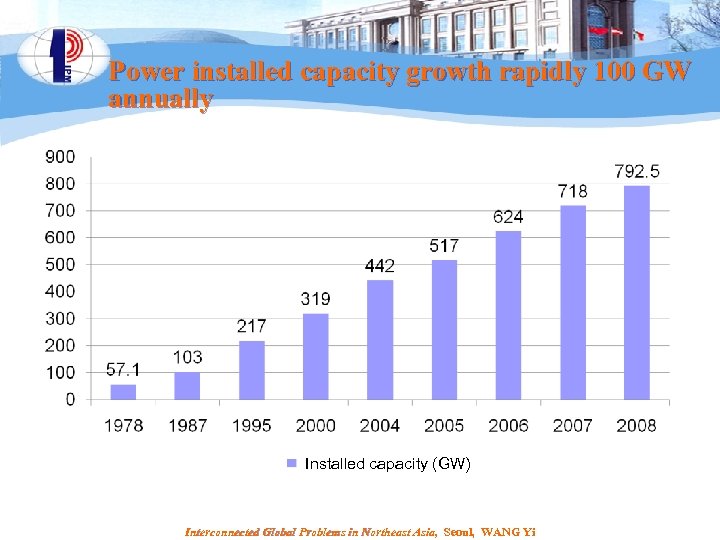
Power installed capacity growth rapidly 100 GW annually Installed capacity (GW) Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
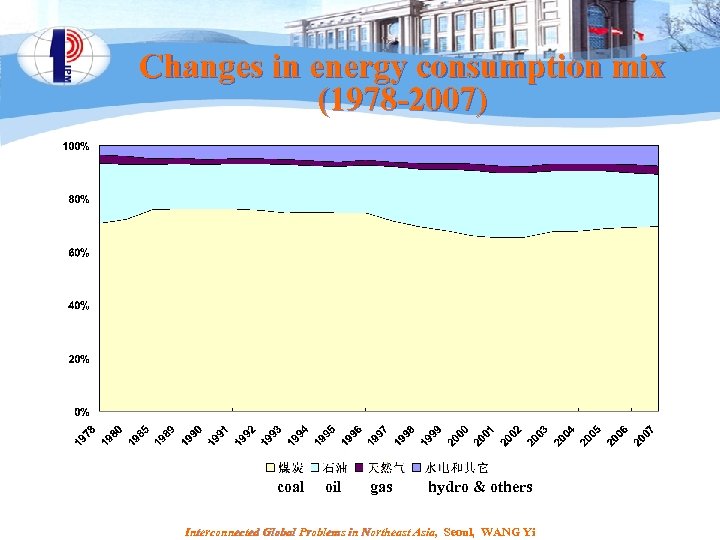
Changes in energy consumption mix (1978 -2007) coal oil gas hydro & others Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Main challenges of sustainability China will face in 5 -10 years l l l Ø Domestic resources supply security and serious environmental pollutions Impacts of financial crisis Energy security, transition and Climate change Other development issues: poverty, employment, social insurance, regional disparity, etc. Many dilemmas and conflict of policy goals Two Prospects ahead and policy implications: unsustainable way or new China’s sustainable model 8 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Government actions: new ideas of development l l l Ø 2002: Develop a New Industrialization Pathway 2003: Scientific Outlook on Development: Balanced development; people-centered, comprehensive, coordinated, and sustainable development 2004: Resource-Efficient and Environment-Friendly Society (REEFS) and Circular Economy (CE) 2005: Harmonious Society including man and nature relationship, and innovation-oriented country 2009: Green economy and low carbon development 2010: Transformation of economic development pattern Transition towards market-based, regulationoriented, and sustainable development 9 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Current Legislative Framework to Sustainability l l l Environmental Impact Assessment Law (2002) Cleaner production promoting Law (2003) Renewable energy law (2006) State Council Circular on REEFS (2006) Industrial regulations, code, standard Energy Conservation Law (amended, 2007) Plan of Renewable Energy Development in Mid- and Long-Term (2007, revising now) Circular Economy Promotion Law (2008) Regulations on E-Waste Mgt (2009) Renewable energy law (amended, 2009) Energy Law (review by NPC, hopefully in 2010) 10 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

China’s actions to address climate change l l l l l Mandatory targets of energy efficiency during 2006 -2010, increase by 20% (about 1. 5 bn t CO 2 e reduction by plan) National Climate Change Assessment Report (Dec, 2006; update 2010) National Climate Change Program (June, 2007) China’s S & T Actions on Climate Change (June, 2007) White paper: China’s Policies and Actions on Climate Change (Oct. 2008) Establish the National Leading Group on Climate Change , chaired by Premier WEN Jiabo Establish the Department of Climate Change under NDRC (2008) A new NPC Resolution on Climate Change (Aug. 27, 2009) National Energy Commission (2010, super coordinating body) 11 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Contents 1. Challenge and Actions since 2000 2. Achievements and Problems during 11 th FYP (2006 -2010) 3. China’s approach towards Green, Low-Carbon Development in 12 th FYP (2011 -2015) and through 2020 12 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Targets of the 11 th Five-Year Plan (2006 -10) l Approach: comprehensive measures Ø growth model transfer and structural adjustment Ø Innovation orientation Ø l l Main goals: energy efficiency and pollution reduction Mandatory targets in 2006 -2010: per unit GDP energy consumption: 20% ↓ Ø Main pollutants discharge (SO 2, COD): 10%↓ Ø Water use per unit industrial value-added : 30 % ↓ Ø Forest coverage rate: 1. 8 %↑ annually Ø 13 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Clear Government Vision and Strong Policy Support in 11 th FYP l 20% reduction in energy intensity below 2005 levels by 2010 Ø Ø Ø Allocation to province, Top-1000 Enterprises and sectors Energy Efficiency will contribute more to support the target Industrial restructuring (closing small, inefficient plant where possible) Cumulative reduction below BAU emissions from 2007 to 2020: 5. 6 Gt. CO 2 2005 -2009: 15. 61% cut achieved (SO 2 and COD: 13. 14%, 9. 66% achieved) l Renewable policy Ø Connection and Must-buy: pre-condition (added in 2009) ü ü Planed Mandatory Renewable Portfolio Grid coverage Ø Feed-in tariffs Ø Special Fund for R&D, Demo, Industry development, etc. l Other policies include: Ø Fuel efficiency standards for cars and vehicle excise taxes Ø Ambitious water and waste targets Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Energy intensity target distribution by provinces during 2006 -2010 l A political task l Central gov’t supervision 15 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

China’s energy efficiency (EE) priorities l Approaches: Ø Ø Ø l l l Control growth rate adjust existing stocks optimize industrial structure Implement EE objective-based responsibility system Implement “Ten key EE Programs” Top 1000 enterprises energy conservation action plan (100 mtce in 5 yrs) Improve collection of energy statistics and metrological management Improve EE in governmental agencies Further EE publicity, education, and training 16 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Economic Stimulus / Green Recovery l l l Ø Investment in environmental areas directly, 5% (of 4 Tn Yuan); plus EE, about 10% (2008 -2010) Green direct investment, 10%; plus indirect, 38%(HSBC, 2009) Development of New Strategic Industries: including EE and Environmental industries R & D investment in energy efficiency, pollution reduction and climate change, over 7 Bn Yuan Large scale of new tech application and infrastructure construction, such as RE, high speed railway Problem and side-effect: traditional industries restoring and rebound effect of EE reduction in short term; expanding domestic demand 17 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Transportation sector: Greening policies l l Policy: fuel economy; EV development; public transport Clean vehicle demo: Ø Ø l l Conventional vehicle improvement Battery EV Hybrid car Fuel cell “ 10 cities and 1000 vehicles” program, has expanded to 20 cities with new energy vehicles Subsidy Policies to Boost the Promotion of New Energy Vehicles (plug-in) in China, 1 June 2010 pilot in 5 cities highest subsidies at 50, 000 yuan for plug-in hybrid car and 60, 000 yuan for battery car l In addition, BRT demo and construction in over 20 cities l High speed rail: 6552 km in service now, over 18, 000 km in 2020 l Local Activities for Green Vehicles 18 Ø Ø Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
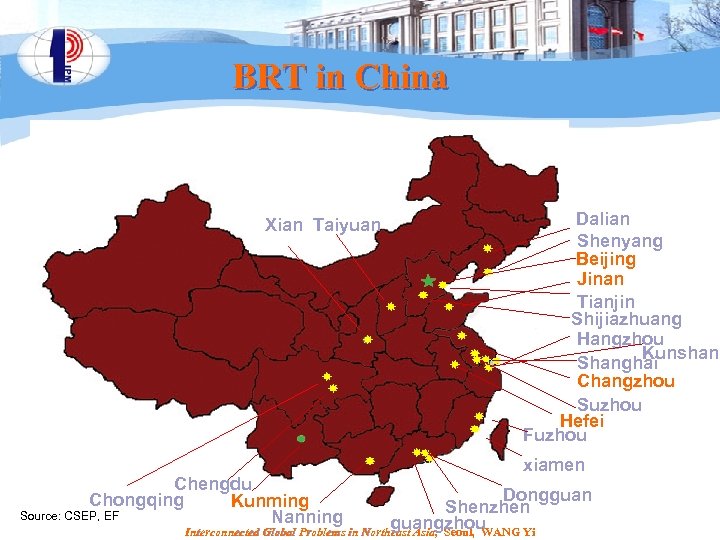
BRT in China Xian Taiyuan Chengdu Chongqing Kunming Source: CSEP, EF Nanning Dalian Shenyang Beijing Jinan Tianjin Shijiazhuang Hangzhou Kunshan Shanghai Changzhou Suzhou Hefei Fuzhou xiamen Dongguan Shenzhen guangzhou Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
Opportunity in Green Buildings l National Design Standards for Green Buildings l Green Building Development Strategy l Green Building Technology Guideline l Best Design for Demonstration Buildings l Advance building materials, windows l Renewable integrated with buildings l Central heating and cooling systems Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Opportunity in Renewable Energy l Ranked 1 st worldwide on renewable investment; World’s largest exporter of solar cells and solar water heating market Ø Renewable electricity targets by 2020 ü ü ü Ø Ø Ø 80 GW small hydro (55 GW in 2009) 200 GW wind (25. 8 in 2009) 30 GW biomass 20 GW solar PV 300 million m 2 solar water heater 24 billion m 3 biogas Energy storage technology Strong and Smart grid Distributed energy system Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Comparison of on-grid prices of de-S thermal power and costs of renewables solar thermal wind PV coal geothermal biomass Unit: RMB Yuan/k. Wh Source: ERI, 2010 22 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
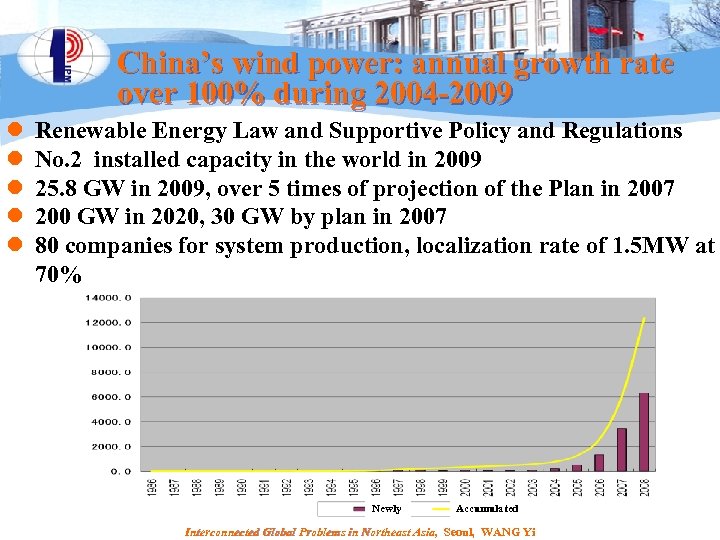
China’s wind power: annual growth rate over 100% during 2004 -2009 l l l Renewable Energy Law and Supportive Policy and Regulations No. 2 installed capacity in the world in 2009 25. 8 GW in 2009, over 5 times of projection of the Plan in 2007 200 GW in 2020, 30 GW by plan in 2007 80 companies for system production, localization rate of 1. 5 MW at 70% Newly Accumulated Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
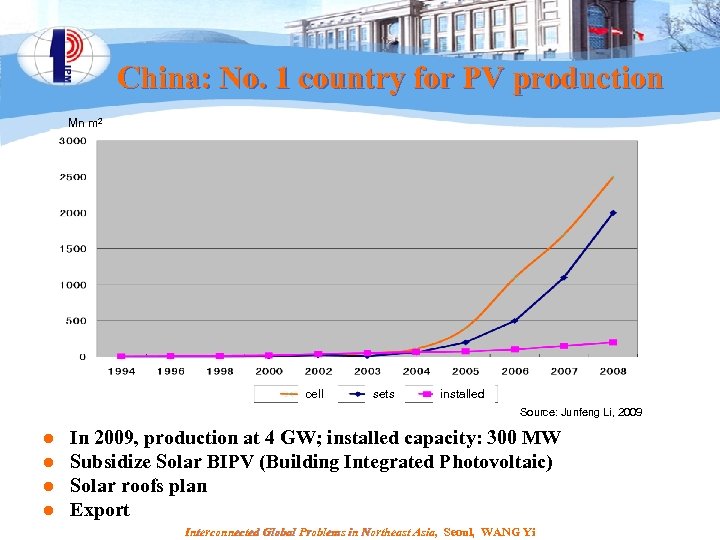
China: No. 1 country for PV production Mn m 2 cell sets installed Source: Junfeng Li, 2009 l l In 2009, production at 4 GW; installed capacity: 300 MW Subsidize Solar BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic) Solar roofs plan Export Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
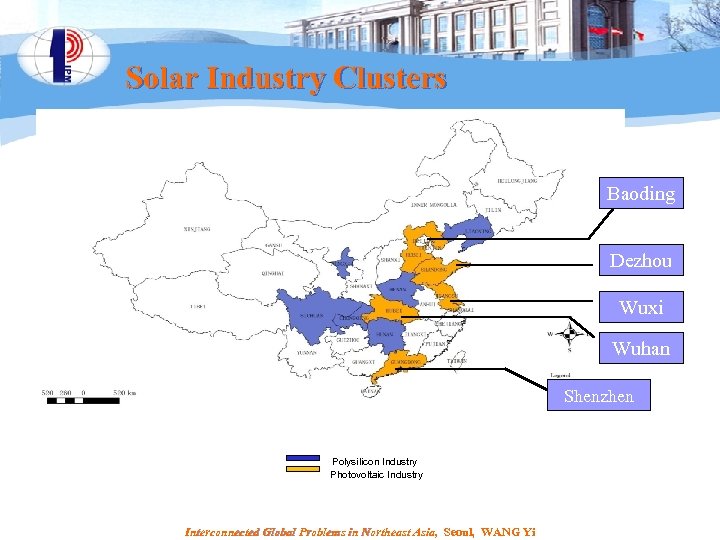
Solar Industry Clusters Baoding Dezhou Wuxi Wuhan Shenzhen Polysilicon Industry Photovoltaic Industry Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
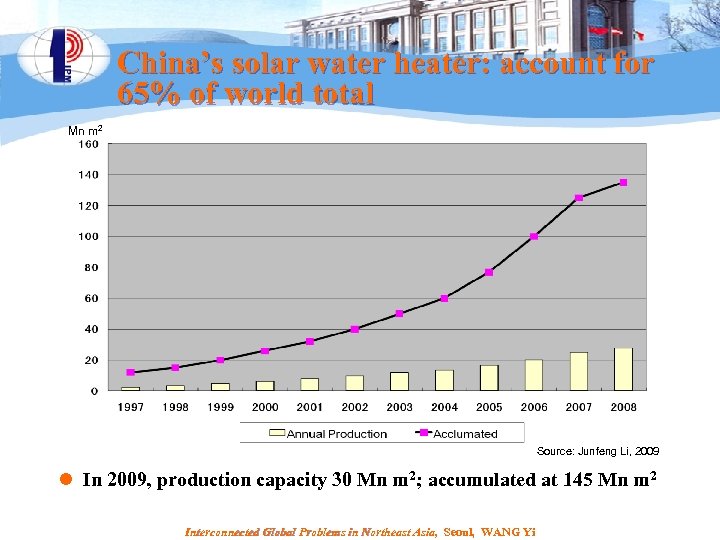
China’s solar water heater: account for 65% of world total Mn m 2 Source: Junfeng Li, 2009 l In 2009, production capacity 30 Mn m 2; accumulated at 145 Mn m 2 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Biomass Development l Diversifying sources, technology path and products l In 2009, Ø biogas production: 14 Bn m 3, supply for living fuel of 80 Mn people Ø Biomass power installed capacity: 3. 24 MW Ø Fuel ethanol production: 1. 65 Mn ton Ø Bio-diesel production: over 0. 5 Mn ton l Biomass vs. Food Security Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
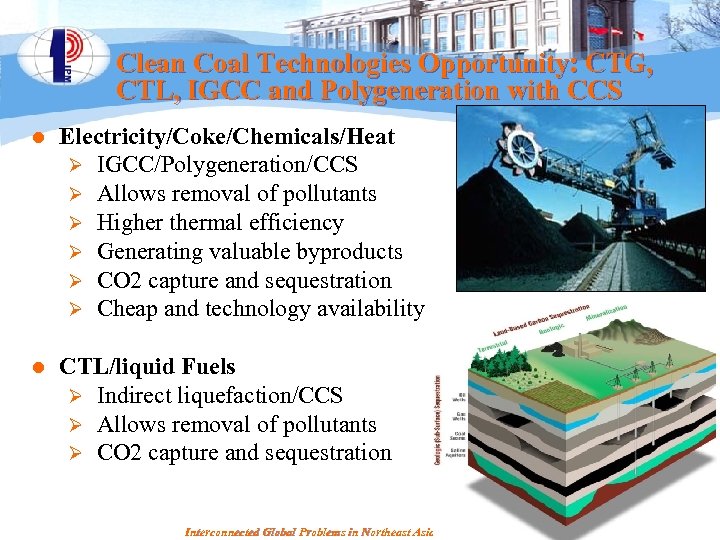
Clean Coal Technologies Opportunity: CTG, CTL, IGCC and Polygeneration with CCS l Electricity/Coke/Chemicals/Heat Ø IGCC/Polygeneration/CCS Ø Allows removal of pollutants Ø Higher thermal efficiency Ø Generating valuable byproducts Ø CO 2 capture and sequestration Ø Cheap and technology availability l CTL/liquid Fuels Ø Indirect liquefaction/CCS Ø Allows removal of pollutants Ø CO 2 capture and sequestration Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Opportunity in advanced nuclear l In 2009, 9 GW and 11 reactors in operation, about 1% of total installed capacity of power ; 30 reactors permitted (about 33 GW) and 23 under construction l Goal: 40 GW in 2015 and over 70 GW in 2020 , more then 150 million tons of CO 2 emissions reduction Ø 3 rd PWR, such as AP 1000, CAP 1400 Ø Spent fuel disposal Ø High temperature gas cooled reactor; Low temperature heat supply reactor Ø Fast Breeder Reactor, ADS, thorium reactor Ø ITER, Fusion ? Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Energy technology roadmap to 2050 Source: Energy Science & Technology in China: a roadmap to 2050, Science Press/ Springer, 2009 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi 30

Contents 1. Challenges and Actions since 2000 2. Achievements and Problems during 11 th FYP (2006 -2010) 3. China’s approach towards Sustainable Energy Development in 12 th FYP (2011 -2015) and through 2020 31 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Main tasks of the 12 th FYP and beyond l l l l General approach: Transfer the economic development pattern approach through building a Resource-Efficient and Environment-Friendly Society Develop new strategic industries, including EE, clean energy, new industries energy vehicle, environmental service, etc. Set a special plan of energy saving and environmental protection at State Council level: roadmap, priorities, action plan, demos Governmental restructuring in 2013, mega department approach, integration and coordinating mechanism relate to energy sector Policy review and mandatory targets setting including energy and carbon intensity, total energy consumption control Economic incentives: price reform and green taxation incentives Capacity building, including energy statistics and monitoring building Green innovation, eg. low cost of green, low carbon technology innovation development, such as small renewables, Biochar, etc. 32 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

China’s actions: approach to the 12 th FYP and beyond l l l Continue the approach in 11 th FYP, energy intensity cut around 18% (16 -20%) New targets on carbon intensity announced on Nov. 26, 2009, 40 -45% cut by 2020 compared with the level of 2005 New and clean energy Non Fossil Energy: 7. 5% in 2005 to 15% in 2020 Nuclear power: over 5% of total power generation in 2020 Clean coal: advanced technologies, such as SC, USC, IGCC, Polygeneration, and CCS (several demo projects available) Ø Clean vehicle: alternative fuel, hybrid, electric car, fuel cell Ø Ø Ø l Carbon sink of ecosystem Ø l Adaptation capacity Ø l Forest cover: 18. 21% during 1999 -2003 to around 23% in 2020, about 40 Mn ha. Increased Adaptation plan and capacity building More mandatory targets for pollutants: NOx, N, P, etc 33 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

How to reach the mandatory targets? l l EE first, and clean coal use crucial (with CCS? ) If energy consumption reach at 4. 6 bn tce of in 2020, contribution to 15% of non- fossil energy (ERI, 2010): Ø Ø l l Hydro power: 8 -9% (? ) Wind, 200 GW; solar, 20 GW; biomass, 30 GW; total at 4% Nuke: 70 GW, 1% (? ) Others: 2%, solar heating, 800 mn m 3; bio-diesel, 2 mn tons; bio-ethanol, 10 mn tons Technology development plays important role, but systematic barriers more serious Comprehensive solution needed such as legal, administrative and economic instruments in terms of case study in China 34 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

March policies for green and low carbon technology innovation, development and cooperation l l l Ø Technology needs assessment at MRV level, technology classification and demand list Collaboration among NICs and developing countries Joint R&D&D at bi- and multi-lateral levels Best practice sharing: tech, policy, etc Multi-lateral Green Transition Fund and relevant implementing mechanisms Systematic solution approach: including technology, policy, plan/roadmap, and practice (demo, industry development and market) 35 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi

Many thanks for your attention! wangyi@casipm. ac. cn Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, Korea October 20, 2010 Interconnected Global Problems in Northeast Asia, Seoul, WANG Yi
86b5e4cfbc2e8924ffa354eafa74a380.ppt