44b8be32a4810d0802e450b6ac727b17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Intercompany Functions for the Enterprise and Oracle’s New Intercompany Functionality – 11. 5. 9 and 11. 5. 10 Internal Sales Orders Hans Kolbe, Celantra Systems Inc. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 1
Intercompany Functions for the Enterprise and Oracle’s New Intercompany Functionality – 11. 5. 9 and 11. 5. 10 Internal Sales Orders Hans Kolbe, Celantra Systems Inc. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 1
 Goal of this Session: Help Oracle Users and Managers to achieve a basic understanding of the scope, issues, objectives for enterprise wide intercompany functions and the main intercompany tools within Oracle applications. Our detail training focus will be on internal sales orders and the resulting intercompany invoices. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 2
Goal of this Session: Help Oracle Users and Managers to achieve a basic understanding of the scope, issues, objectives for enterprise wide intercompany functions and the main intercompany tools within Oracle applications. Our detail training focus will be on internal sales orders and the resulting intercompany invoices. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 2
 Structure of the Session 1. Overview of Intercompany Challenges and Oracle Functionality 2. New Accounting for Internal Orders and IC Invoices 3. Process Steps 4. Setups Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 3
Structure of the Session 1. Overview of Intercompany Challenges and Oracle Functionality 2. New Accounting for Internal Orders and IC Invoices 3. Process Steps 4. Setups Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 3
 About Us: Celantra Systems provides international program management services with a strong focus on multi-org, inter-company, and global compliance and implementation issues. Celantra Systems also offers specialized software tools to augment application functionality in global implementations. Celantra’s consulting and technical services can add valuable impact in the integration of Oracle Apps with boundary systems such as SAP, People Soft, trade and customs compliance systems and others. Former and current clients include Xerox, Tektronix, British Telecom, Assa Abloy, Yahoo, Texas Instruments, PPG, Dionex and others. Hans Kolbe has managed and advised software implementation projects for over 15, global projects for over 8 years. His extensive knowledge on Oracle applications is combined with a formal background as a German attorney, trained in international and comparative law. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 4
About Us: Celantra Systems provides international program management services with a strong focus on multi-org, inter-company, and global compliance and implementation issues. Celantra Systems also offers specialized software tools to augment application functionality in global implementations. Celantra’s consulting and technical services can add valuable impact in the integration of Oracle Apps with boundary systems such as SAP, People Soft, trade and customs compliance systems and others. Former and current clients include Xerox, Tektronix, British Telecom, Assa Abloy, Yahoo, Texas Instruments, PPG, Dionex and others. Hans Kolbe has managed and advised software implementation projects for over 15, global projects for over 8 years. His extensive knowledge on Oracle applications is combined with a formal background as a German attorney, trained in international and comparative law. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 4
 Intercompany Transactions Overview Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 5
Intercompany Transactions Overview Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 5
 IC Transactions are a Core Part of Our Business I. Oracle application users operate in a multi-entity environment within their corporate enterprise. Intercompany relationships and transactions are core functions of those enterprises. Only through IC transactions can the organization contribute its resources efficiently. II. Correct processing of IC transactions is required for internal and external compliance and reporting. III. Intercompany transactions always need to be addressed from at least two perspectives: a) Generating correct transactions for each entity and b) Eliminating the intercompany transactions for enterprise consolidations. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 6
IC Transactions are a Core Part of Our Business I. Oracle application users operate in a multi-entity environment within their corporate enterprise. Intercompany relationships and transactions are core functions of those enterprises. Only through IC transactions can the organization contribute its resources efficiently. II. Correct processing of IC transactions is required for internal and external compliance and reporting. III. Intercompany transactions always need to be addressed from at least two perspectives: a) Generating correct transactions for each entity and b) Eliminating the intercompany transactions for enterprise consolidations. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 6
 What are these multiple entities? We need to differentiate between Legal entities, i. e. separate legal establishments and Operational entities. These are operationally separated. Operational Entities may be complex: Multiple operational entities may reside within one legal entity. However, one operational entity may also cross both legal and country boundaries and extend to corresponding parts of other legal entities. Both of these entity types have reporting and audit requirements. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 7
What are these multiple entities? We need to differentiate between Legal entities, i. e. separate legal establishments and Operational entities. These are operationally separated. Operational Entities may be complex: Multiple operational entities may reside within one legal entity. However, one operational entity may also cross both legal and country boundaries and extend to corresponding parts of other legal entities. Both of these entity types have reporting and audit requirements. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 7
 Common Types of Legal Entities • • Specialized Entities in particular lines of business or operations, such as service providers, treasury and currency trading entities, billing intermediaries, or leasing, selling, manufacturing, purchasing, payroll entities, Acquisitions – either in the process of being merged into existing entities or staying separately for management, financial or legal reasons or future divesture, Non-Operational Companies: Holding entities, entities owning intellectual property rights or real-estate, entities owning high-risk equipment (vehicles in operation, mining equipment etc. ). Associated Entities – partly owned by the enterprise. All of these entities may operate in one and the same country. In the multi-national environment we need to add Foreign subsidiaries and Foreign Branches registered in other jurisdictions in any of the categories. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 8
Common Types of Legal Entities • • Specialized Entities in particular lines of business or operations, such as service providers, treasury and currency trading entities, billing intermediaries, or leasing, selling, manufacturing, purchasing, payroll entities, Acquisitions – either in the process of being merged into existing entities or staying separately for management, financial or legal reasons or future divesture, Non-Operational Companies: Holding entities, entities owning intellectual property rights or real-estate, entities owning high-risk equipment (vehicles in operation, mining equipment etc. ). Associated Entities – partly owned by the enterprise. All of these entities may operate in one and the same country. In the multi-national environment we need to add Foreign subsidiaries and Foreign Branches registered in other jurisdictions in any of the categories. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 8
 Operational Entities • Business Groups, Divisions or Product Lines. These entities regularly have at least internal trial balance reporting requirements, sometimes these apply externally also. They often cross legal entity and country boundaries. • Shared Service Organizations – providing back office processing, collections, logistics operations, IT support etc. These entities have at least budget and performance reporting requirements. They also often cross legal entity and country boundaries. • Cost Centers with budget and performance reporting requirements. Regularly they are limited to one country and legal entity. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 9
Operational Entities • Business Groups, Divisions or Product Lines. These entities regularly have at least internal trial balance reporting requirements, sometimes these apply externally also. They often cross legal entity and country boundaries. • Shared Service Organizations – providing back office processing, collections, logistics operations, IT support etc. These entities have at least budget and performance reporting requirements. They also often cross legal entity and country boundaries. • Cost Centers with budget and performance reporting requirements. Regularly they are limited to one country and legal entity. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 9
 Examples from Industries • • • In the telecommunications industry, most of the countries stipulate mandatory domestic company partnership. Most of the steel and aluminum companies in Asia sell their entire output to another marketing company. Automobile industries are increasingly centralizing their sourcing activities globally to leverage their combined volumes for a better price from their suppliers. Trading companies are setup in tax haven nations to take advantage of bilateral and multi-lateral trade agreements to minimize the tax. Shared centers for AR Collections or AP invoice processing across 15 -20 companies with one bank account owned by treasury, while Sales and Order Management are managed independently by each company. Shared specialized technical support centers servicing products across many entities Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 10
Examples from Industries • • • In the telecommunications industry, most of the countries stipulate mandatory domestic company partnership. Most of the steel and aluminum companies in Asia sell their entire output to another marketing company. Automobile industries are increasingly centralizing their sourcing activities globally to leverage their combined volumes for a better price from their suppliers. Trading companies are setup in tax haven nations to take advantage of bilateral and multi-lateral trade agreements to minimize the tax. Shared centers for AR Collections or AP invoice processing across 15 -20 companies with one bank account owned by treasury, while Sales and Order Management are managed independently by each company. Shared specialized technical support centers servicing products across many entities Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 10
 Matching up Legal and Operational Entities for IC Transactions Legal IC Transactions: Processes involving more than one legal entity require legal IC transactions. When goods or services are provided from one to the other invoices are needed. These may be taxable under VAT, sales tax or other tax regimes. In addition, the pricing of these transactions is controlled as “Transfer Pricing”. IC documents may be required for each transaction or be summarized periodically. Operational IC Transactions: Processes involving more than one operational entity. Business structure often imposes rules on cross-charging, inter-divisional markups and other parameters. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 11
Matching up Legal and Operational Entities for IC Transactions Legal IC Transactions: Processes involving more than one legal entity require legal IC transactions. When goods or services are provided from one to the other invoices are needed. These may be taxable under VAT, sales tax or other tax regimes. In addition, the pricing of these transactions is controlled as “Transfer Pricing”. IC documents may be required for each transaction or be summarized periodically. Operational IC Transactions: Processes involving more than one operational entity. Business structure often imposes rules on cross-charging, inter-divisional markups and other parameters. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 11
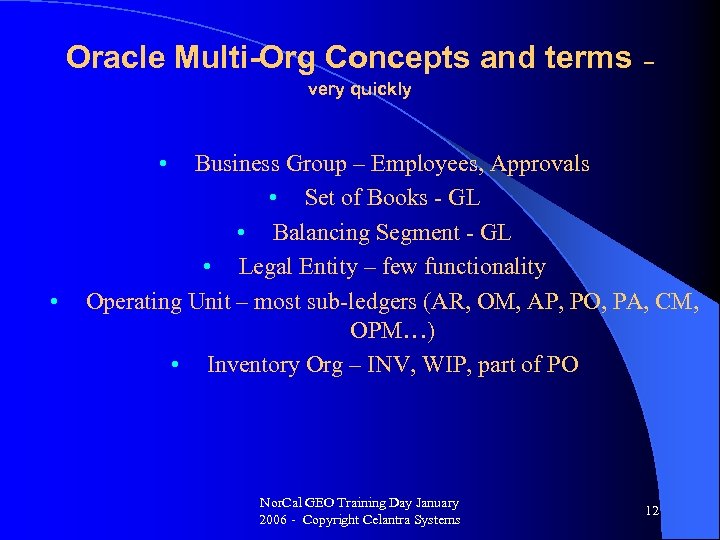 Oracle Multi-Org Concepts and terms – very quickly • • Business Group – Employees, Approvals • Set of Books - GL • Balancing Segment - GL • Legal Entity – few functionality Operating Unit – most sub-ledgers (AR, OM, AP, PO, PA, CM, OPM…) • Inventory Org – INV, WIP, part of PO Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 12
Oracle Multi-Org Concepts and terms – very quickly • • Business Group – Employees, Approvals • Set of Books - GL • Balancing Segment - GL • Legal Entity – few functionality Operating Unit – most sub-ledgers (AR, OM, AP, PO, PA, CM, OPM…) • Inventory Org – INV, WIP, part of PO Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 12
 Oracle’s IC functionality – designed for matching Legal and Operational Entities Operating Unit Driven IC Functionality: Oracle’s Operating Unit is designed to hold an operational entity and its transactions separate from others OUs. Oracle’s key IC functionality works around this structure, OM, INV, PA , AR, AP functions. Balancing Segment Driven IC Functionality: The GL Balancing Segment is designed to hold an entity’s financial information. With its automatic balancing of IC journals Oracle’s GL module provides IC functions independently from the OU concept. Oracle’s GIS functions extends these functions and supports automatic IC GL journals, cross-SOB and even crossinstance. The relationship and entries between Sender and Receiver can be defined based on the Balancing and IC Segment relationship. All is fine if the operational entity is contained within one external legal entity and one balancing segment corresponds to one OU. In other cases careful investigation and discussion is needed in order to best accommodate the business priorities. For more information, discussions, and sample solutions please join the Multi. National Interest Group of the OAUG. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 13
Oracle’s IC functionality – designed for matching Legal and Operational Entities Operating Unit Driven IC Functionality: Oracle’s Operating Unit is designed to hold an operational entity and its transactions separate from others OUs. Oracle’s key IC functionality works around this structure, OM, INV, PA , AR, AP functions. Balancing Segment Driven IC Functionality: The GL Balancing Segment is designed to hold an entity’s financial information. With its automatic balancing of IC journals Oracle’s GL module provides IC functions independently from the OU concept. Oracle’s GIS functions extends these functions and supports automatic IC GL journals, cross-SOB and even crossinstance. The relationship and entries between Sender and Receiver can be defined based on the Balancing and IC Segment relationship. All is fine if the operational entity is contained within one external legal entity and one balancing segment corresponds to one OU. In other cases careful investigation and discussion is needed in order to best accommodate the business priorities. For more information, discussions, and sample solutions please join the Multi. National Interest Group of the OAUG. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 13
 However, integrated IC functionality has not come through yet Functionality is dispersed and not yet integrated: • Product related IC transactions are the most developed (Customer drop-ship since Version 10. 7). Missing many elements of operational flexibility. OPM (Process Manufacturing not included) • GL Global Intercompany System provides facilities for GL intercompany journals with automated off-sets and predefined accounting. Missing sub-ledger integration and connection to IC pricing models as well as formal invoice transactions. • PA has its own IC transactions model • Global Accounting Engine (with Dual Posting) is not integrated with intercompany transactions • Fixed Asset transfers in separate model (some integration with OM and INV is planned) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 14
However, integrated IC functionality has not come through yet Functionality is dispersed and not yet integrated: • Product related IC transactions are the most developed (Customer drop-ship since Version 10. 7). Missing many elements of operational flexibility. OPM (Process Manufacturing not included) • GL Global Intercompany System provides facilities for GL intercompany journals with automated off-sets and predefined accounting. Missing sub-ledger integration and connection to IC pricing models as well as formal invoice transactions. • PA has its own IC transactions model • Global Accounting Engine (with Dual Posting) is not integrated with intercompany transactions • Fixed Asset transfers in separate model (some integration with OM and INV is planned) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 14
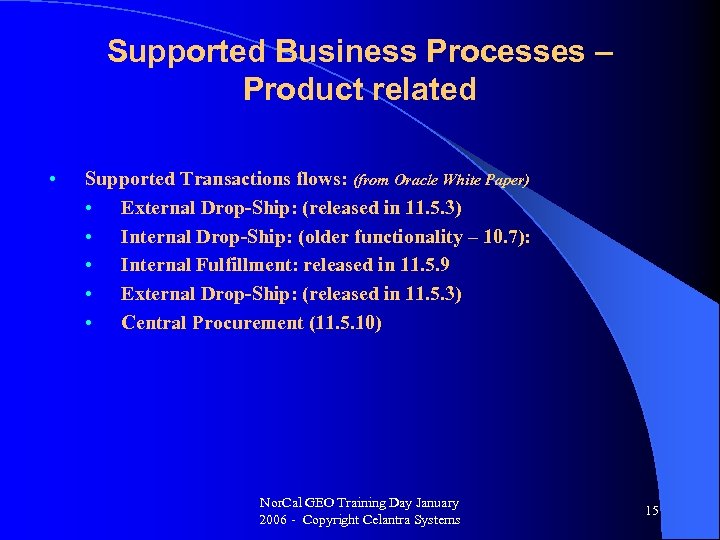 Supported Business Processes – Product related • Supported Transactions flows: (from Oracle White Paper) • External Drop-Ship: (released in 11. 5. 3) • Internal Drop-Ship: (older functionality – 10. 7): • Internal Fulfillment: released in 11. 5. 9 • External Drop-Ship: (released in 11. 5. 3) • Central Procurement (11. 5. 10) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 15
Supported Business Processes – Product related • Supported Transactions flows: (from Oracle White Paper) • External Drop-Ship: (released in 11. 5. 3) • Internal Drop-Ship: (older functionality – 10. 7): • Internal Fulfillment: released in 11. 5. 9 • External Drop-Ship: (released in 11. 5. 3) • Central Procurement (11. 5. 10) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 15
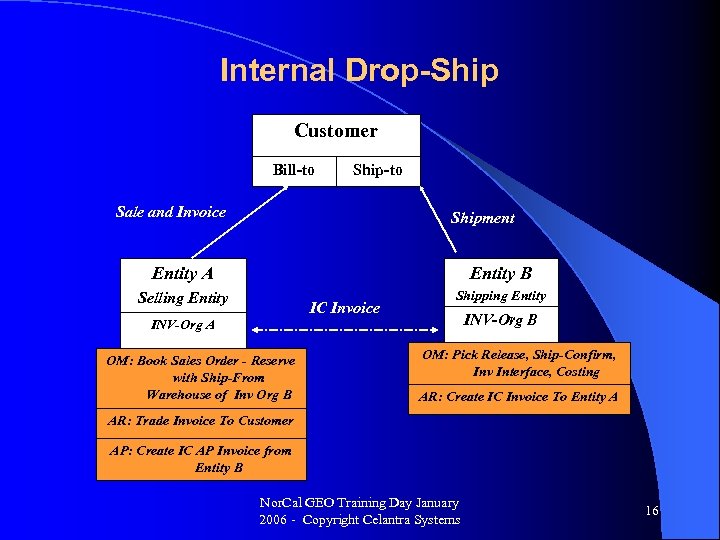 Internal Drop-Ship Customer Bill-to Ship-to Sale and Invoice Shipment Entity A Entity B Selling Entity IC Invoice Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A OM: Book Sales Order - Reserve with Ship-From Warehouse of Inv Org B OM: Pick Release, Ship-Confirm, Inv Interface, Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A AR: Trade Invoice To Customer AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 16
Internal Drop-Ship Customer Bill-to Ship-to Sale and Invoice Shipment Entity A Entity B Selling Entity IC Invoice Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A OM: Book Sales Order - Reserve with Ship-From Warehouse of Inv Org B OM: Pick Release, Ship-Confirm, Inv Interface, Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A AR: Trade Invoice To Customer AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 16
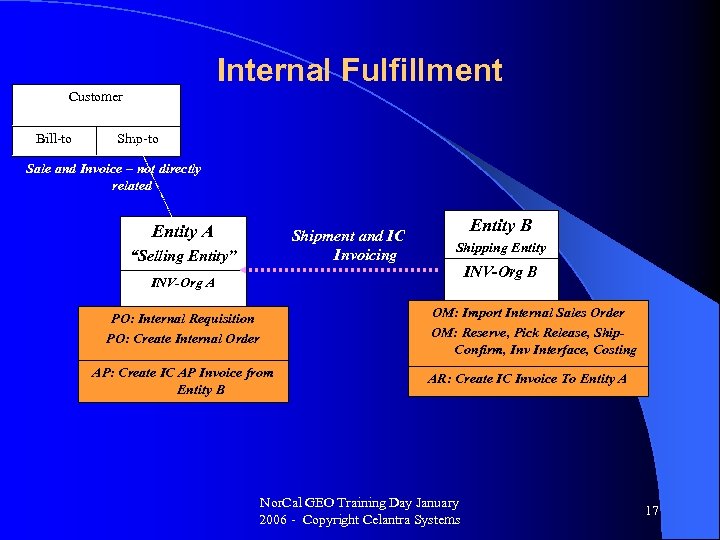 Internal Fulfillment Customer Bill-to Ship-to Sale and Invoice – not directly related Entity A Shipment and IC Invoicing “Selling Entity” Entity B Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A PO: Internal Requisition PO: Create Internal Order AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B OM: Import Internal Sales Order OM: Reserve, Pick Release, Ship. Confirm, Inv Interface, Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 17
Internal Fulfillment Customer Bill-to Ship-to Sale and Invoice – not directly related Entity A Shipment and IC Invoicing “Selling Entity” Entity B Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A PO: Internal Requisition PO: Create Internal Order AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B OM: Import Internal Sales Order OM: Reserve, Pick Release, Ship. Confirm, Inv Interface, Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 17
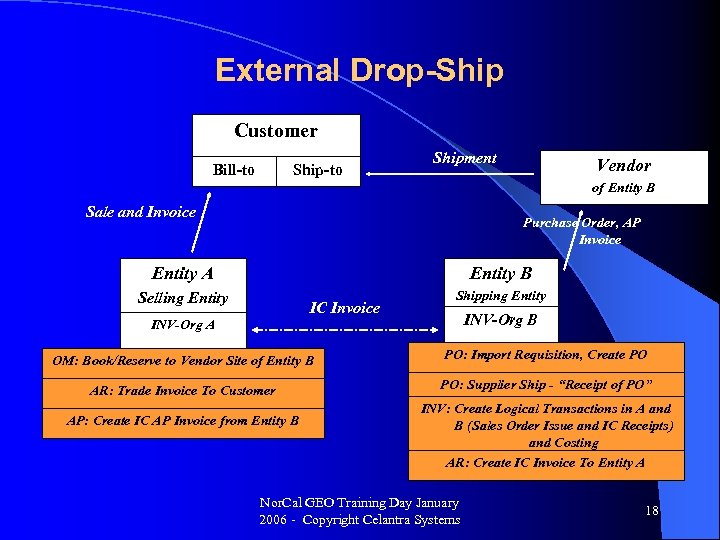 External Drop-Ship Customer Bill-to Shipment Vendor of Entity B Sale and Invoice Purchase Order, AP Invoice Entity A Entity B Selling Entity IC Invoice Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A OM: Book/Reserve to Vendor Site of Entity B PO: Import Requisition, Create PO AR: Trade Invoice To Customer PO: Supplier Ship - “Receipt of PO” AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B INV: Create Logical Transactions in A and B (Sales Order Issue and IC Receipts) and Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 18
External Drop-Ship Customer Bill-to Shipment Vendor of Entity B Sale and Invoice Purchase Order, AP Invoice Entity A Entity B Selling Entity IC Invoice Shipping Entity INV-Org B INV-Org A OM: Book/Reserve to Vendor Site of Entity B PO: Import Requisition, Create PO AR: Trade Invoice To Customer PO: Supplier Ship - “Receipt of PO” AP: Create IC AP Invoice from Entity B INV: Create Logical Transactions in A and B (Sales Order Issue and IC Receipts) and Costing AR: Create IC Invoice To Entity A Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 18
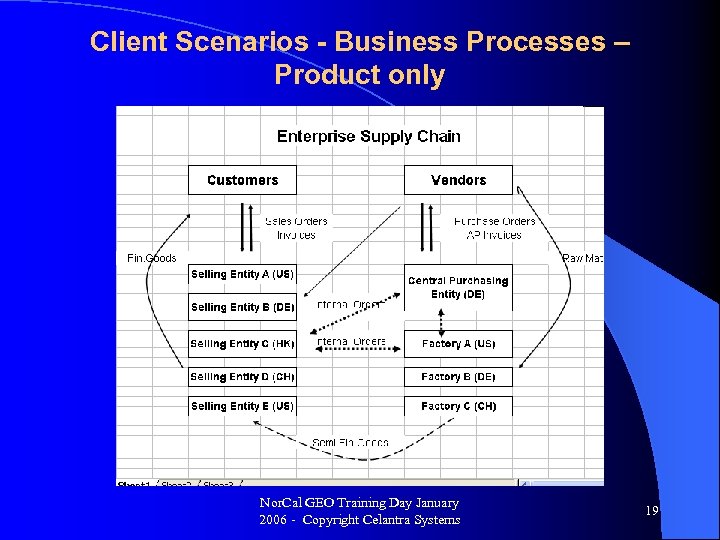 Client Scenarios - Business Processes – Product only Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 19
Client Scenarios - Business Processes – Product only Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 19
 Product Related Business Process – Issues and Challenges • Not supported transaction flows: (from Oracle White Paper) • Internal Drop-Ship to an internal organization • Non-Shippable Items • Non-Invoiced Items • Internal Fulfillment returns • Global Procurement with shop floor destinations and transfer pricing • Consigned inventory for Global Procurement flows • Retroactive pricing in Global Procurement • Advanced Sales functionality between operating units (From my own experience) • No COGS accounting on internal drop-ship • Internal requisitions and fulfillment Sales Order documents show incorrect transfer price • Transfer pricing setups are rigid • On internal fulfillments the COGS at receiving org need to be manually adjusted • No ship-to driven tax functionality Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 20
Product Related Business Process – Issues and Challenges • Not supported transaction flows: (from Oracle White Paper) • Internal Drop-Ship to an internal organization • Non-Shippable Items • Non-Invoiced Items • Internal Fulfillment returns • Global Procurement with shop floor destinations and transfer pricing • Consigned inventory for Global Procurement flows • Retroactive pricing in Global Procurement • Advanced Sales functionality between operating units (From my own experience) • No COGS accounting on internal drop-ship • Internal requisitions and fulfillment Sales Order documents show incorrect transfer price • Transfer pricing setups are rigid • On internal fulfillments the COGS at receiving org need to be manually adjusted • No ship-to driven tax functionality Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 20
 Break – Discussion Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 21
Break – Discussion Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 21
 Internal Sales Order – Intercompany Invoicing Oracle’s version 11. 5. 9 Patch Set H provides functionality to automate intercompany invoicing for internal sales order shipments. Previously Internal Sales Order shipments only generate accounting entries to balance sheet account (IC Receivable, IC Payable). No COGS or IC Revenue accounting was provided. Also invoices needed to be made manually on both sending and receiving side and reconciled. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 22
Internal Sales Order – Intercompany Invoicing Oracle’s version 11. 5. 9 Patch Set H provides functionality to automate intercompany invoicing for internal sales order shipments. Previously Internal Sales Order shipments only generate accounting entries to balance sheet account (IC Receivable, IC Payable). No COGS or IC Revenue accounting was provided. Also invoices needed to be made manually on both sending and receiving side and reconciled. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 22
 Release 11. 5. 9 Patch Set H Two new enhancements to Oracle Inventory’s Intercompany Invoicing functionality were released as part of patch set H features. The new features are : 1. Invoicing Internal Orders - Type In-Transit Shipments - as a part of Intercompany invoicing. 2. Using Advance Pricing (QP) setup and Engine to derive invoice price for items to generate Intercompany Invoices. Before patch set H of inventory, inter-company invoices were created for internal drop-ship scenarios only. Now users can set up a profile options and systems configuration to create inter company invoices for Internal Orders also. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 23
Release 11. 5. 9 Patch Set H Two new enhancements to Oracle Inventory’s Intercompany Invoicing functionality were released as part of patch set H features. The new features are : 1. Invoicing Internal Orders - Type In-Transit Shipments - as a part of Intercompany invoicing. 2. Using Advance Pricing (QP) setup and Engine to derive invoice price for items to generate Intercompany Invoices. Before patch set H of inventory, inter-company invoices were created for internal drop-ship scenarios only. Now users can set up a profile options and systems configuration to create inter company invoices for Internal Orders also. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 23
 Internal Fulfillment (Order) Intercompany Invoicing - New Accounting - Transaction Steps - Elements of Setup Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 24
Internal Fulfillment (Order) Intercompany Invoicing - New Accounting - Transaction Steps - Elements of Setup Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 24
 New Accounting Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 25
New Accounting Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 25
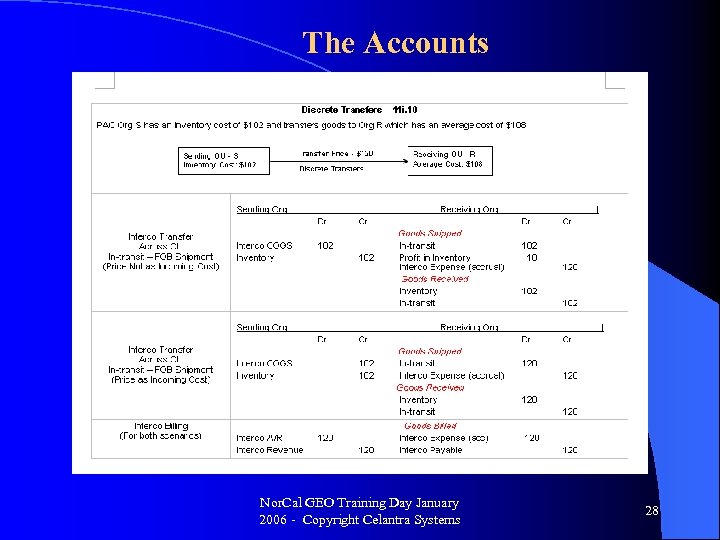
 The New Transfer Price Accounting Internal sales order shipments generate accounting on both sides – the shipping and the receiving entity. The accounting can be configured to accommodate different INCO terms, such as in-transit owned by shipped or receiver. In addition, the intercompany transfer markup can be accounted separately on the receiving side (“Profit in Inventory”). The shipment accounting is done through the INV: COGS and OM: COGS workflows, the invoicing accounting through the auto-invoice parameters. The Intercompany AR Invoice will generate the IC Receivable debit and IC Revenue credit entries. The Intercompany AP Invoice will generate the IC Payable Credit and debits to AP accrual and freight accounts. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 26
The New Transfer Price Accounting Internal sales order shipments generate accounting on both sides – the shipping and the receiving entity. The accounting can be configured to accommodate different INCO terms, such as in-transit owned by shipped or receiver. In addition, the intercompany transfer markup can be accounted separately on the receiving side (“Profit in Inventory”). The shipment accounting is done through the INV: COGS and OM: COGS workflows, the invoicing accounting through the auto-invoice parameters. The Intercompany AR Invoice will generate the IC Receivable debit and IC Revenue credit entries. The Intercompany AP Invoice will generate the IC Payable Credit and debits to AP accrual and freight accounts. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 26
 Profile Options CST: Transfer Price Option - Site Level Only Options: “Yes, Price as Incoming Cost” = complete IC price will be directly applied against cost base in receiving org, either as Purchase Price Variance (if Standard Cost) or updating the average cost. “Yes, Price not as Incoming Cost” = the intercompany markup will be booked to the new “profit-in-inventory” account on the receiving side “No” = old accounting continues INV: Intercompany Invoicing for internal orders – site level: YES/No (user option does not work? ) CST: Advanced Pricing for internal orders - Site Level, (Does user option work? ) Other important options: Tax: Invoice Freight as Revenue Tax: Inventory Item for Freight Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 27
Profile Options CST: Transfer Price Option - Site Level Only Options: “Yes, Price as Incoming Cost” = complete IC price will be directly applied against cost base in receiving org, either as Purchase Price Variance (if Standard Cost) or updating the average cost. “Yes, Price not as Incoming Cost” = the intercompany markup will be booked to the new “profit-in-inventory” account on the receiving side “No” = old accounting continues INV: Intercompany Invoicing for internal orders – site level: YES/No (user option does not work? ) CST: Advanced Pricing for internal orders - Site Level, (Does user option work? ) Other important options: Tax: Invoice Freight as Revenue Tax: Inventory Item for Freight Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 27
 The Accounts Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 28
The Accounts Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 28
 Process Steps - Rec. Org: Internal Requisition - Ship Org: Process Sales Order - Ship Org: Shipping - Ship Org: Intercompany AR - Rec. Org: Intercompany AP Invoices Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 29
Process Steps - Rec. Org: Internal Requisition - Ship Org: Process Sales Order - Ship Org: Shipping - Ship Org: Intercompany AR - Rec. Org: Intercompany AP Invoices Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 29
 Detail Process Steps Receiving org - Internal Requisition: Enter Requisition, Approve: Will show cost of shipping org as informational price of requisition, not IC price Receiving org – Create Internal Orders (request) Shipping Org: Import Sales Order – parameter by requisition (menu option) – price is informational only, not IC price. Reserve sales order and pick release (after other required steps) Ship-Confirm (add freight if needed) Run Costing Manager Shipping Org: Create intercompany AR Invoices (request) Run Auto-Invoice (request – source: internal) Receiving Org: Create intercompany AP Invoices (request) Payables Invoice Import (request) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 30
Detail Process Steps Receiving org - Internal Requisition: Enter Requisition, Approve: Will show cost of shipping org as informational price of requisition, not IC price Receiving org – Create Internal Orders (request) Shipping Org: Import Sales Order – parameter by requisition (menu option) – price is informational only, not IC price. Reserve sales order and pick release (after other required steps) Ship-Confirm (add freight if needed) Run Costing Manager Shipping Org: Create intercompany AR Invoices (request) Run Auto-Invoice (request – source: internal) Receiving Org: Create intercompany AP Invoices (request) Payables Invoice Import (request) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 30
 The Scenario: German Distributor (EUR) orders from Swiss Factory (CHF) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 31
The Scenario: German Distributor (EUR) orders from Swiss Factory (CHF) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 31
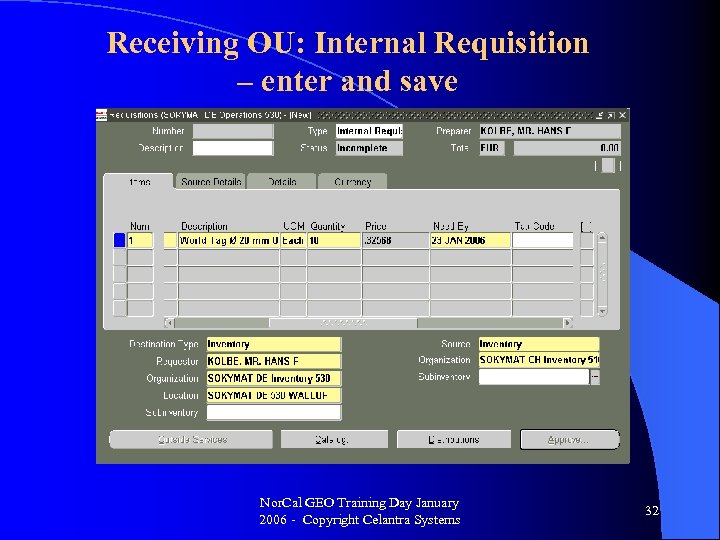 Receiving OU: Internal Requisition – enter and save Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 32
Receiving OU: Internal Requisition – enter and save Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 32
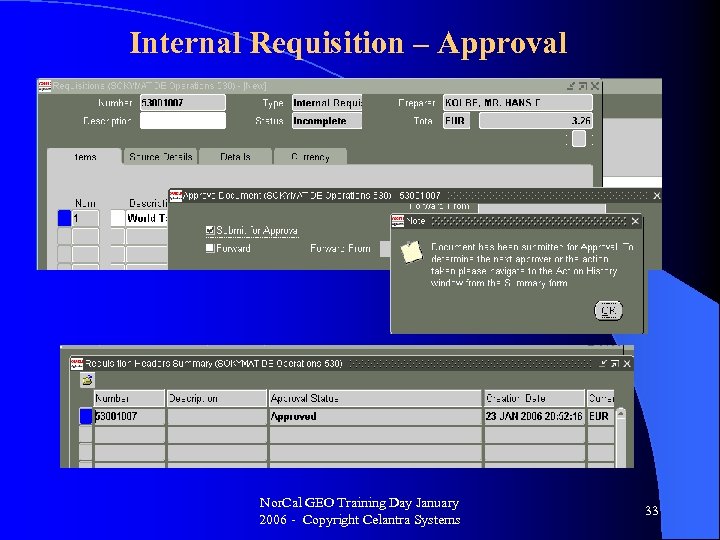 Internal Requisition – Approval Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 33
Internal Requisition – Approval Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 33
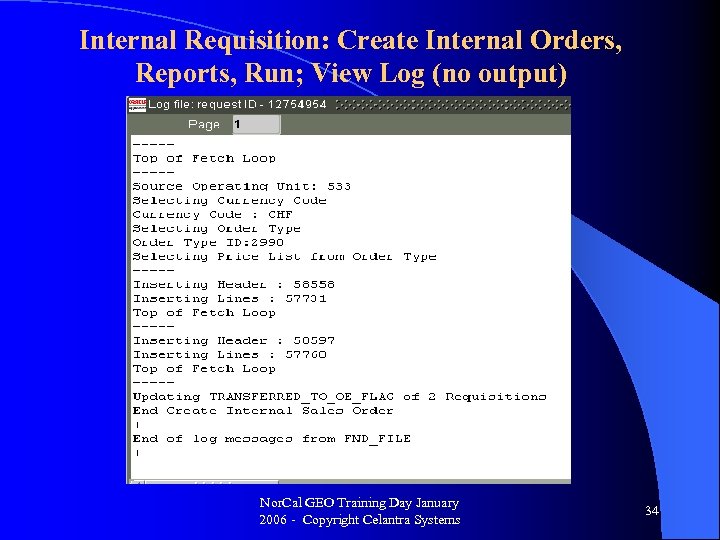 Internal Requisition: Create Internal Orders, Reports, Run; View Log (no output) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 34
Internal Requisition: Create Internal Orders, Reports, Run; View Log (no output) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 34
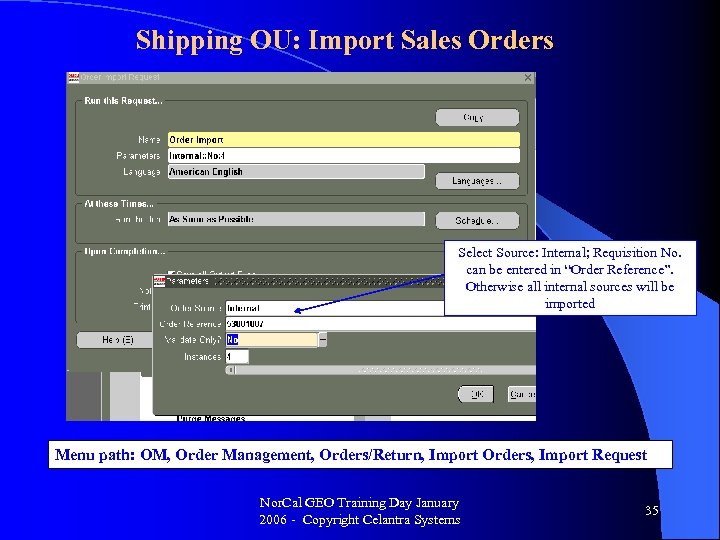 Shipping OU: Import Sales Orders Select Source: Internal; Requisition No. can be entered in “Order Reference”. Otherwise all internal sources will be imported Menu path: OM, Order Management, Orders/Return, Import Orders, Import Request Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 35
Shipping OU: Import Sales Orders Select Source: Internal; Requisition No. can be entered in “Order Reference”. Otherwise all internal sources will be imported Menu path: OM, Order Management, Orders/Return, Import Orders, Import Request Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 35
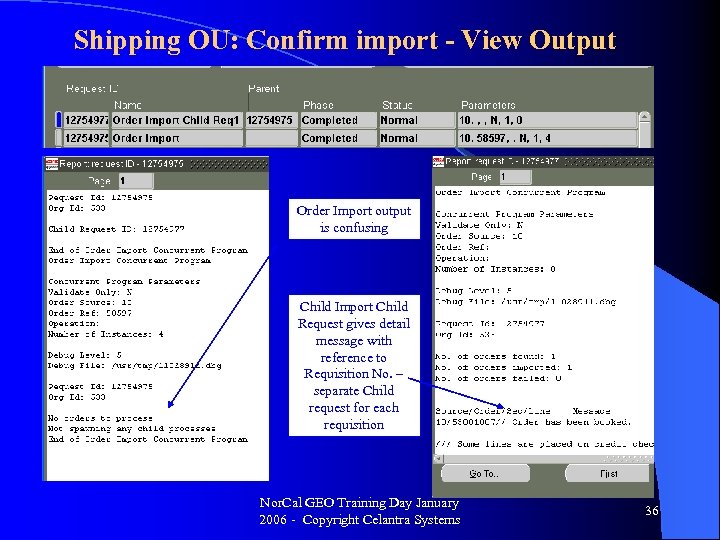 Shipping OU: Confirm import - View Output Order Import output is confusing Child Import Child Request gives detail message with reference to Requisition No. – separate Child request for each requisition Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 36
Shipping OU: Confirm import - View Output Order Import output is confusing Child Import Child Request gives detail message with reference to Requisition No. – separate Child request for each requisition Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 36
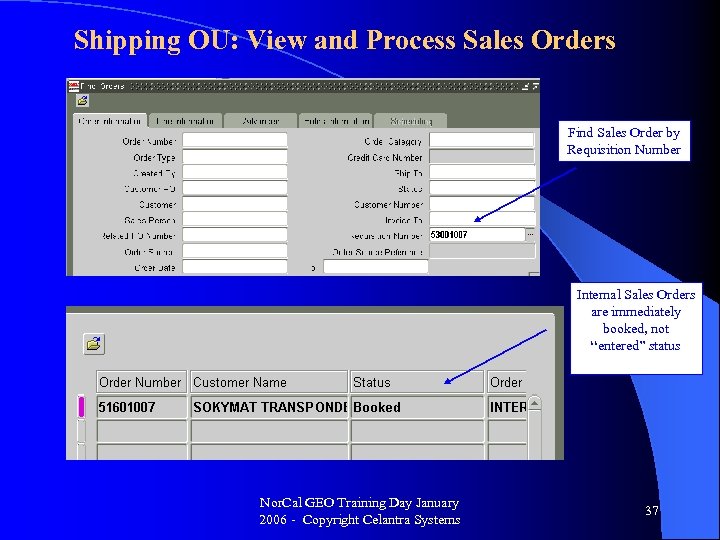 Shipping OU: View and Process Sales Orders Find Sales Order by Requisition Number Internal Sales Orders are immediately booked, not “entered” status Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 37
Shipping OU: View and Process Sales Orders Find Sales Order by Requisition Number Internal Sales Orders are immediately booked, not “entered” status Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 37
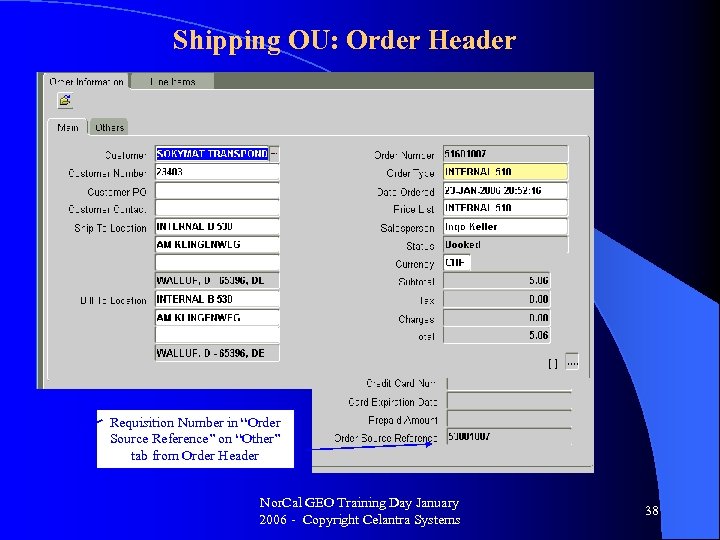 Shipping OU: Order Header Requisition Number in “Order Source Reference” on “Other” tab from Order Header Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 38
Shipping OU: Order Header Requisition Number in “Order Source Reference” on “Other” tab from Order Header Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 38
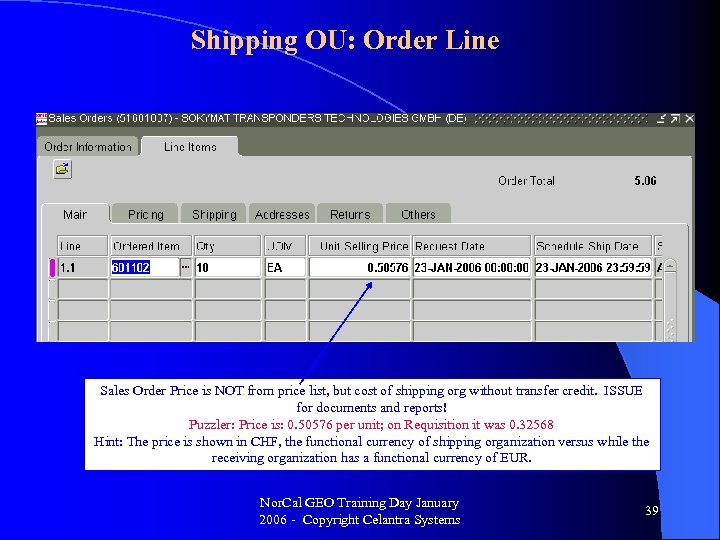 Shipping OU: Order Line Sales Order Price is NOT from price list, but cost of shipping org without transfer credit. ISSUE for documents and reports! Puzzler: Price is: 0. 50576 per unit; on Requisition it was 0. 32568 Hint: The price is shown in CHF, the functional currency of shipping organization versus while the receiving organization has a functional currency of EUR. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 39
Shipping OU: Order Line Sales Order Price is NOT from price list, but cost of shipping org without transfer credit. ISSUE for documents and reports! Puzzler: Price is: 0. 50576 per unit; on Requisition it was 0. 32568 Hint: The price is shown in CHF, the functional currency of shipping organization versus while the receiving organization has a functional currency of EUR. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 39
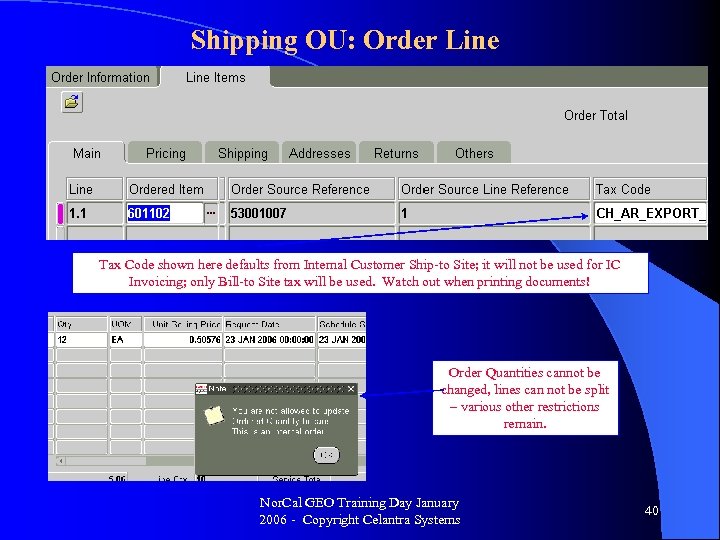 Shipping OU: Order Line Tax Code shown here defaults from Internal Customer Ship-to Site; it will not be used for IC Invoicing; only Bill-to Site tax will be used. Watch out when printing documents! Order Quantities cannot be changed, lines can not be split – various other restrictions remain. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 40
Shipping OU: Order Line Tax Code shown here defaults from Internal Customer Ship-to Site; it will not be used for IC Invoicing; only Bill-to Site tax will be used. Watch out when printing documents! Order Quantities cannot be changed, lines can not be split – various other restrictions remain. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 40
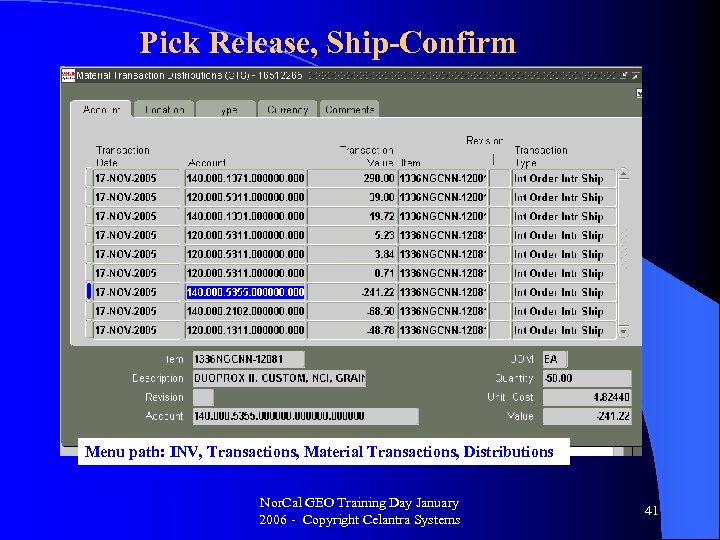 Pick Release, Ship-Confirm Menu path: INV, Transactions, Material Transactions, Distributions Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 41
Pick Release, Ship-Confirm Menu path: INV, Transactions, Material Transactions, Distributions Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 41
 Create Intercompany AR Invoices Menu path: AR, Requests, “Create Intercompany AR Invoices”, View Log Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 42
Create Intercompany AR Invoices Menu path: AR, Requests, “Create Intercompany AR Invoices”, View Log Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 42
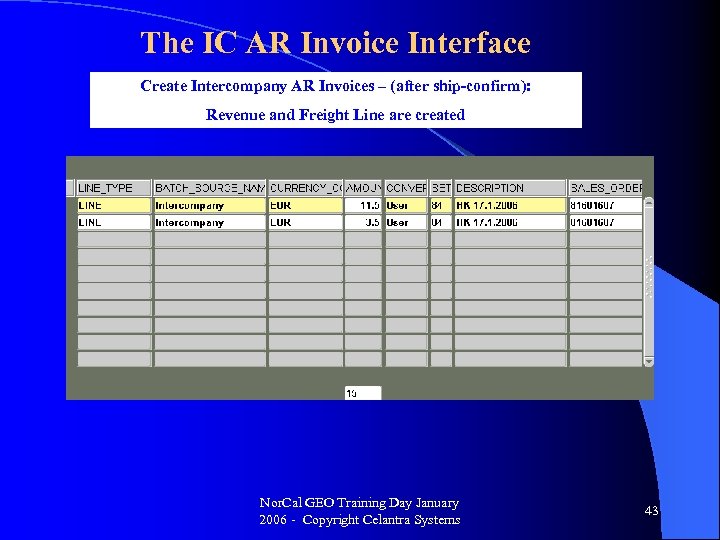 The IC AR Invoice Interface Create Intercompany AR Invoices – (after ship-confirm): Revenue and Freight Line are created Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 43
The IC AR Invoice Interface Create Intercompany AR Invoices – (after ship-confirm): Revenue and Freight Line are created Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 43
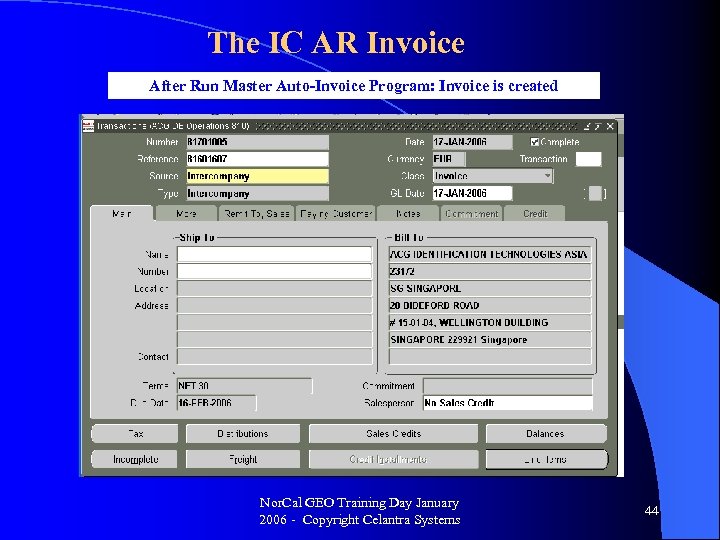 The IC AR Invoice After Run Master Auto-Invoice Program: Invoice is created Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 44
The IC AR Invoice After Run Master Auto-Invoice Program: Invoice is created Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 44
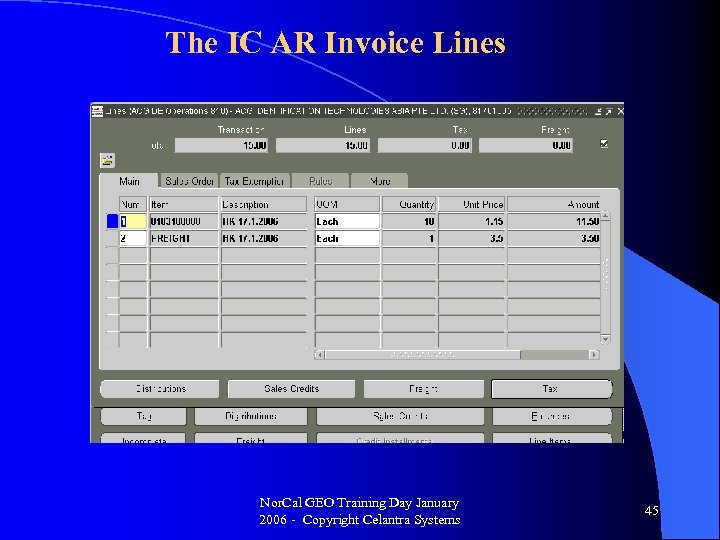 The IC AR Invoice Lines Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 45
The IC AR Invoice Lines Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 45
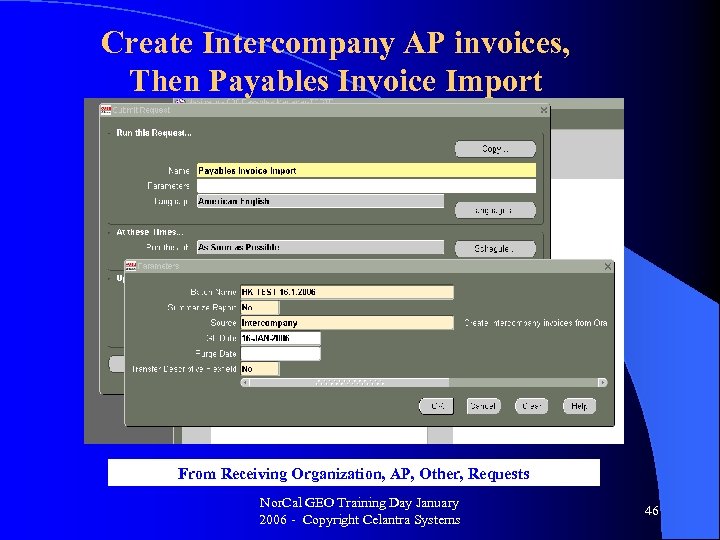 Create Intercompany AP invoices, Then Payables Invoice Import From Receiving Organization, AP, Other, Requests Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 46
Create Intercompany AP invoices, Then Payables Invoice Import From Receiving Organization, AP, Other, Requests Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 46
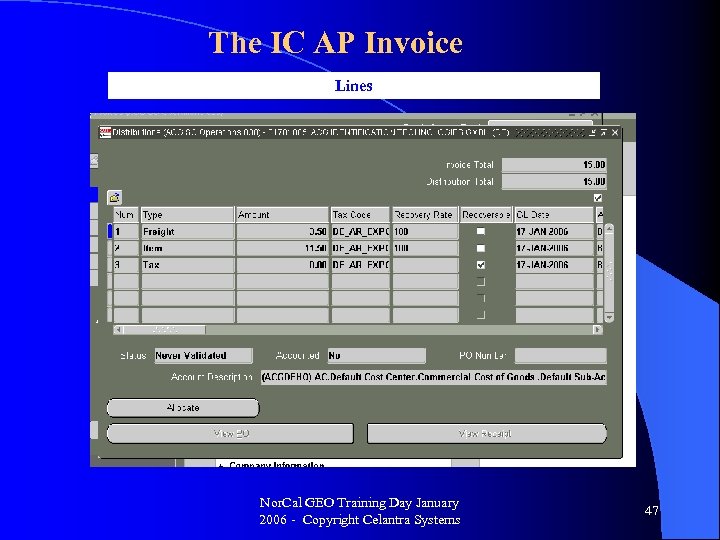 The IC AP Invoice Lines Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 47
The IC AP Invoice Lines Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 47
 Break – Discussion Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 48
Break – Discussion Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 48
 Setup Elements - Profile Options and New Accounting Options Intercompany Relationships Customers and Vendors, Addresses Organizations and Locations Price List Sources and Transaction Types Item Setup Currency Setups Accounting Setups Security Rules Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 49
Setup Elements - Profile Options and New Accounting Options Intercompany Relationships Customers and Vendors, Addresses Organizations and Locations Price List Sources and Transaction Types Item Setup Currency Setups Accounting Setups Security Rules Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 49
 Internal Order Intercompany – Detail Setup Check List Profile Options: CST: Transfer Price Option - Site Level – Incoming Price, No/Yes Intercompany Invoicing for internal orders YES Advanced Pricing for internal orders? ? Shipping Network Define Profit in inventory account, AP accrual account Intercompany Relationships: Check Customer/Vendor Header and Site Check Customer Locations Inventory Organization and Location: Check Location record is “internal” AR Setup: AR Intercompany Transaction Type IC Customer and Vendor Setup Check header and site, accounting setups on Bill-to Site Check Customer locations, Check Price List (OM Tab) on ship to and Bill to Setup bill-to and ship-to customer site for Receiving Entity within Receiving OU Price List: check item is on list, Check pricing precedence is not duplicated Item Setup: Check item parameters for internal requisitions and orders Responsibility Access: Costing Processor needs have rights across both organizations and balancing segments. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 50
Internal Order Intercompany – Detail Setup Check List Profile Options: CST: Transfer Price Option - Site Level – Incoming Price, No/Yes Intercompany Invoicing for internal orders YES Advanced Pricing for internal orders? ? Shipping Network Define Profit in inventory account, AP accrual account Intercompany Relationships: Check Customer/Vendor Header and Site Check Customer Locations Inventory Organization and Location: Check Location record is “internal” AR Setup: AR Intercompany Transaction Type IC Customer and Vendor Setup Check header and site, accounting setups on Bill-to Site Check Customer locations, Check Price List (OM Tab) on ship to and Bill to Setup bill-to and ship-to customer site for Receiving Entity within Receiving OU Price List: check item is on list, Check pricing precedence is not duplicated Item Setup: Check item parameters for internal requisitions and orders Responsibility Access: Costing Processor needs have rights across both organizations and balancing segments. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 50
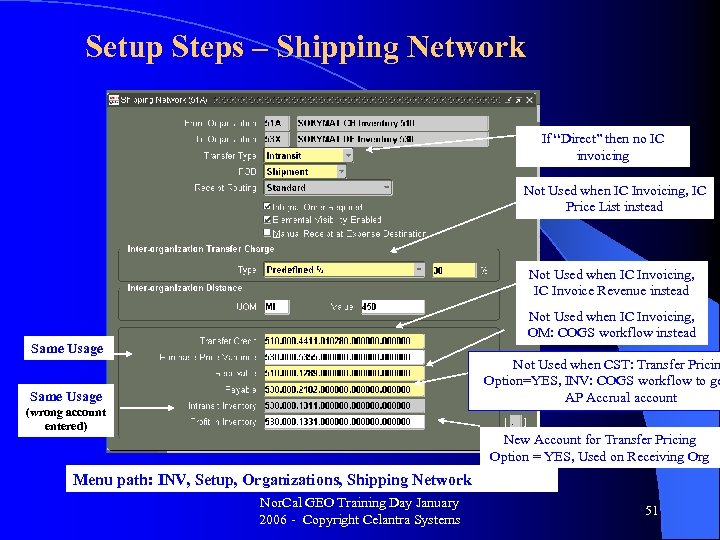 Setup Steps – Shipping Network If “Direct” then no IC invoicing Not Used when IC Invoicing, IC Price List instead Not Used when IC Invoicing, IC Invoice Revenue instead Not Used when IC Invoicing, OM: COGS workflow instead Same Usage Not Used when CST: Transfer Pricin Option=YES, INV: COGS workflow to ge AP Accrual account Same Usage (wrong account entered) New Account for Transfer Pricing Option = YES, Used on Receiving Org Menu path: INV, Setup, Organizations, Shipping Network Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 51
Setup Steps – Shipping Network If “Direct” then no IC invoicing Not Used when IC Invoicing, IC Price List instead Not Used when IC Invoicing, IC Invoice Revenue instead Not Used when IC Invoicing, OM: COGS workflow instead Same Usage Not Used when CST: Transfer Pricin Option=YES, INV: COGS workflow to ge AP Accrual account Same Usage (wrong account entered) New Account for Transfer Pricing Option = YES, Used on Receiving Org Menu path: INV, Setup, Organizations, Shipping Network Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 51
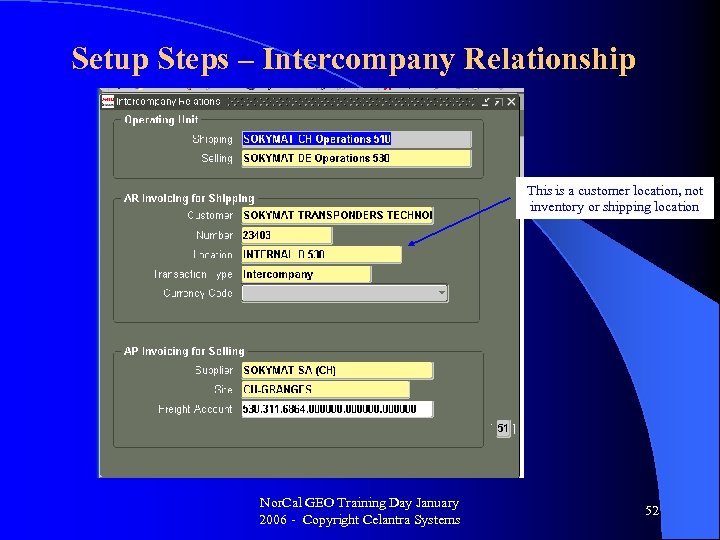 Setup Steps – Intercompany Relationship This is a customer location, not inventory or shipping location Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 52
Setup Steps – Intercompany Relationship This is a customer location, not inventory or shipping location Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 52
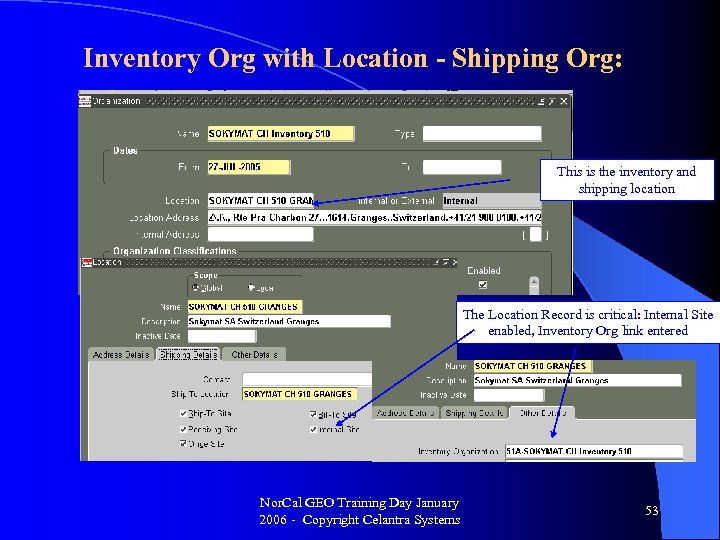 Inventory Org with Location - Shipping Org: This is the inventory and shipping location The Location Record is critical: Internal Site enabled, Inventory Org link entered Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 53
Inventory Org with Location - Shipping Org: This is the inventory and shipping location The Location Record is critical: Internal Site enabled, Inventory Org link entered Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 53
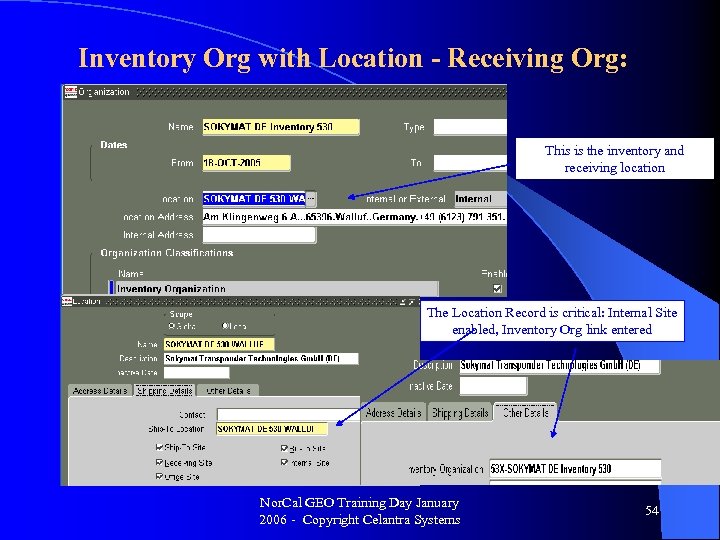 Inventory Org with Location - Receiving Org: This is the inventory and receiving location The Location Record is critical: Internal Site enabled, Inventory Org link entered Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 54
Inventory Org with Location - Receiving Org: This is the inventory and receiving location The Location Record is critical: Internal Site enabled, Inventory Org link entered Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 54
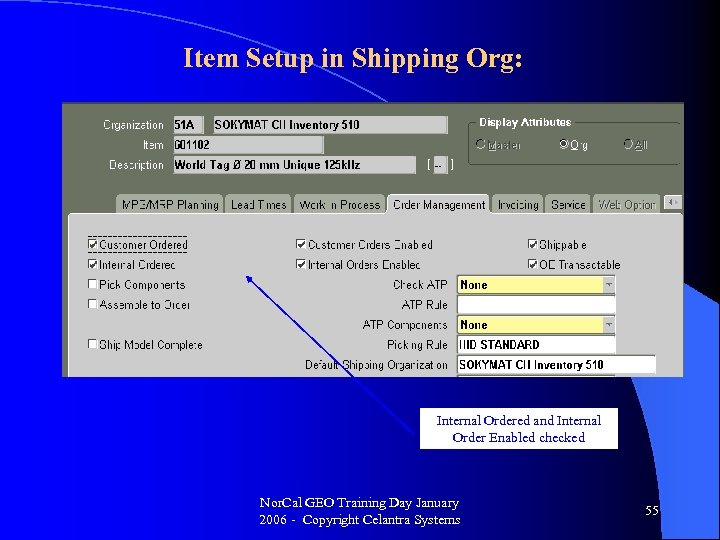 Item Setup in Shipping Org: Internal Ordered and Internal Order Enabled checked Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 55
Item Setup in Shipping Org: Internal Ordered and Internal Order Enabled checked Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 55
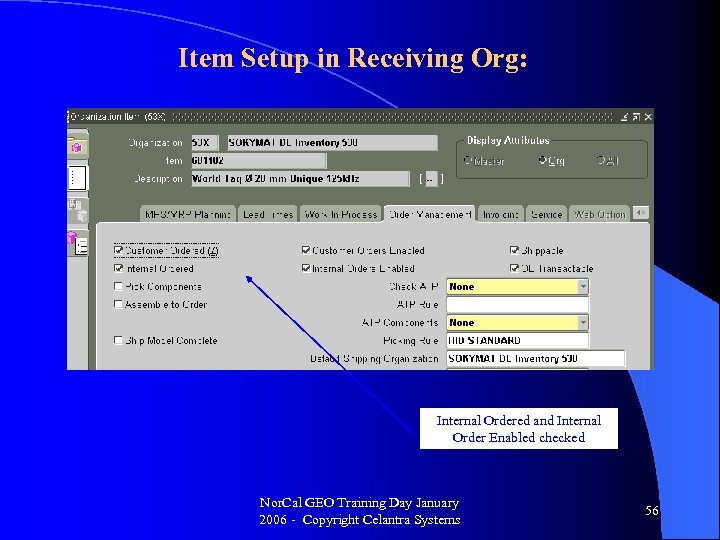 Item Setup in Receiving Org: Internal Ordered and Internal Order Enabled checked Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 56
Item Setup in Receiving Org: Internal Ordered and Internal Order Enabled checked Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 56
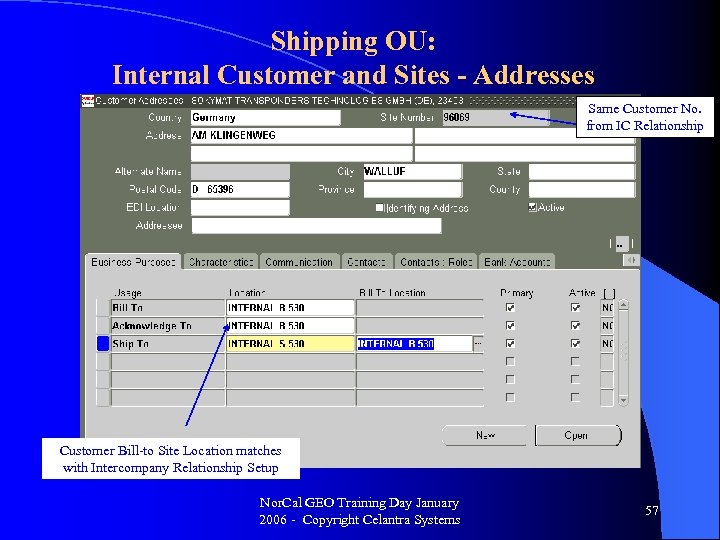 Shipping OU: Internal Customer and Sites - Addresses Same Customer No. from IC Relationship Customer Bill-to Site Location matches with Intercompany Relationship Setup Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 57
Shipping OU: Internal Customer and Sites - Addresses Same Customer No. from IC Relationship Customer Bill-to Site Location matches with Intercompany Relationship Setup Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 57
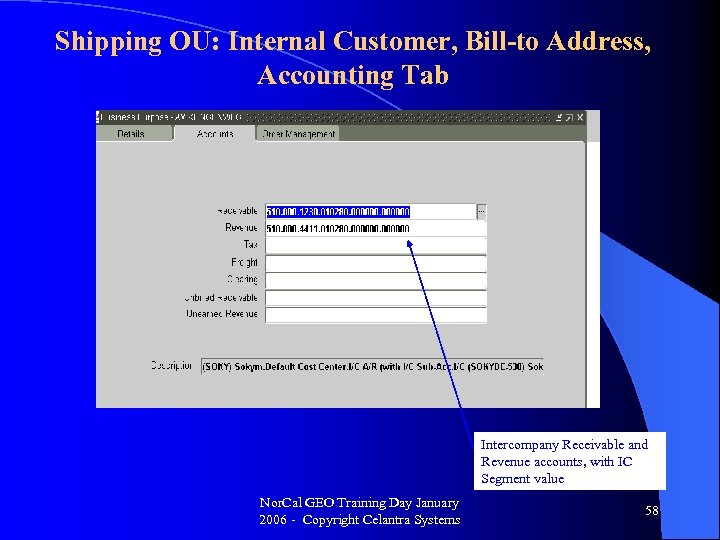 Shipping OU: Internal Customer, Bill-to Address, Accounting Tab Intercompany Receivable and Revenue accounts, with IC Segment value Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 58
Shipping OU: Internal Customer, Bill-to Address, Accounting Tab Intercompany Receivable and Revenue accounts, with IC Segment value Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 58
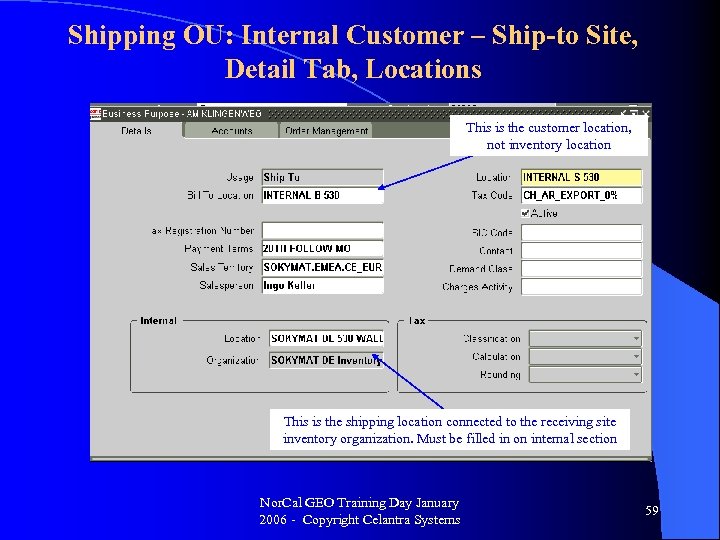 Shipping OU: Internal Customer – Ship-to Site, Detail Tab, Locations This is the customer location, not inventory location This is the shipping location connected to the receiving site inventory organization. Must be filled in on internal section Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 59
Shipping OU: Internal Customer – Ship-to Site, Detail Tab, Locations This is the customer location, not inventory location This is the shipping location connected to the receiving site inventory organization. Must be filled in on internal section Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 59
 Shipping OU: Internal Customer – Ship-to Site, Order Management Tab, Price List This Price List is used for IC Invoicing Warehouse is default ship-from warehouse in shipping organization Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 60
Shipping OU: Internal Customer – Ship-to Site, Order Management Tab, Price List This Price List is used for IC Invoicing Warehouse is default ship-from warehouse in shipping organization Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 60
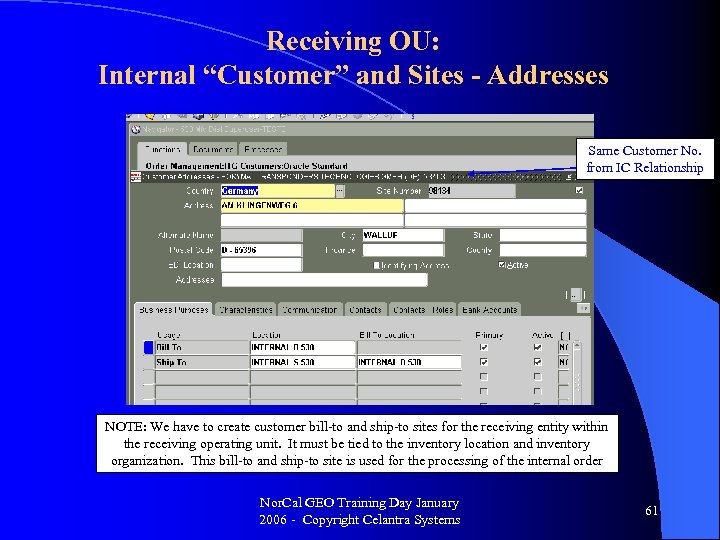 Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” and Sites - Addresses Same Customer No. from IC Relationship NOTE: We have to create customer bill-to and ship-to sites for the receiving entity within the receiving operating unit. It must be tied to the inventory location and inventory organization. This bill-to and ship-to site is used for the processing of the internal order Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 61
Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” and Sites - Addresses Same Customer No. from IC Relationship NOTE: We have to create customer bill-to and ship-to sites for the receiving entity within the receiving operating unit. It must be tied to the inventory location and inventory organization. This bill-to and ship-to site is used for the processing of the internal order Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 61
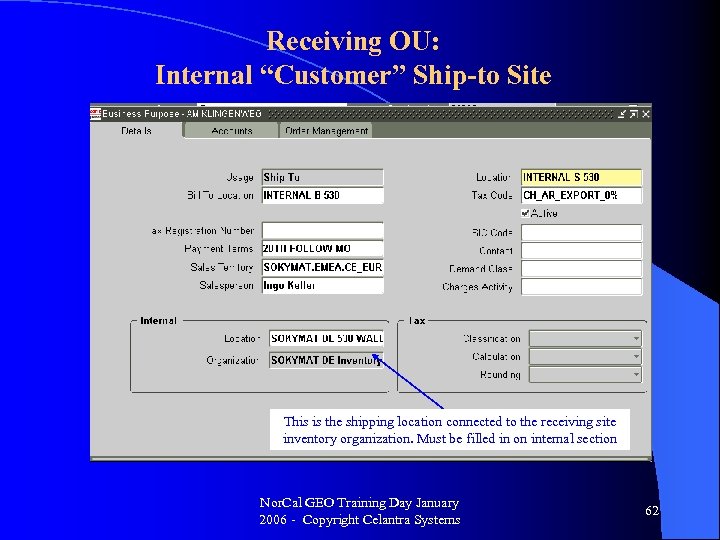 Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” Ship-to Site This is the shipping location connected to the receiving site inventory organization. Must be filled in on internal section Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 62
Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” Ship-to Site This is the shipping location connected to the receiving site inventory organization. Must be filled in on internal section Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 62
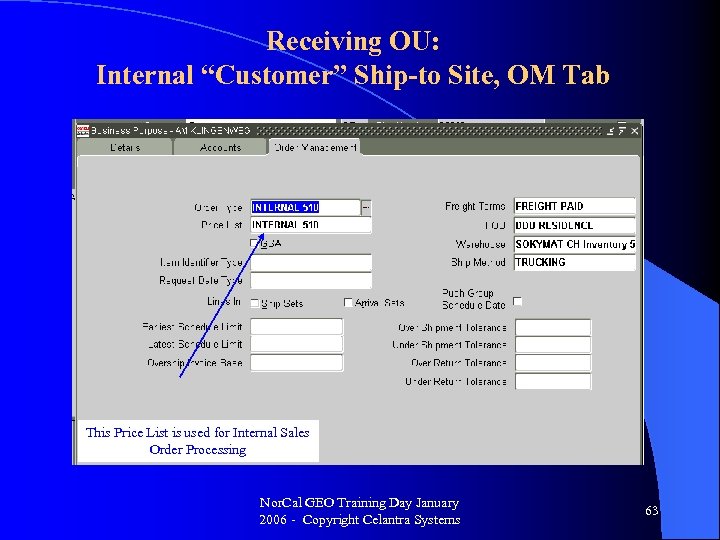 Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” Ship-to Site, OM Tab This Price List is used for Internal Sales Order Processing Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 63
Receiving OU: Internal “Customer” Ship-to Site, OM Tab This Price List is used for Internal Sales Order Processing Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 63
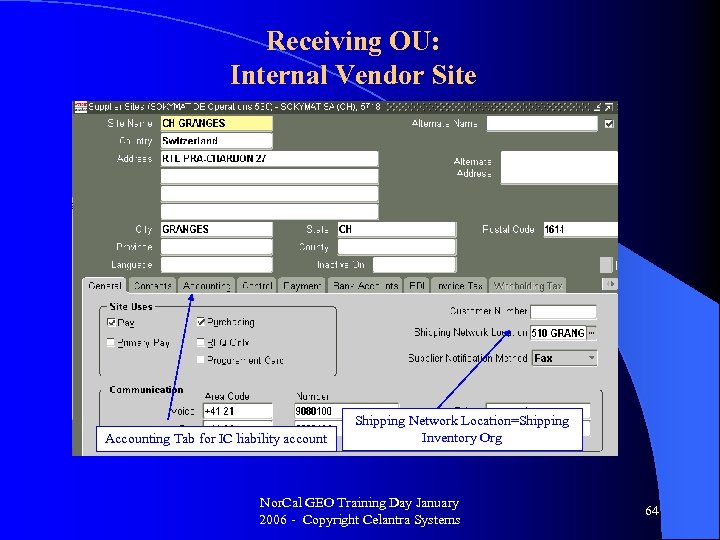 Receiving OU: Internal Vendor Site Accounting Tab for IC liability account Shipping Network Location=Shipping Inventory Org Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 64
Receiving OU: Internal Vendor Site Accounting Tab for IC liability account Shipping Network Location=Shipping Inventory Org Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 64
 Issues and Action Items - Internal Order Intercompany - - Profile Option CST: Transfer Price should be set for entity to entity pair. If different intercompany policies current setting is impractical Sales Order Price is not IC Price: needs customization of external documents, Ship-to Address is not printed on invoice: needs customization of external documents, Duplicate IC Invoices for old internal shipments – resolved (needs patch) Tax functionality: only based on Bill-to account; no ship-to account available. Needs review. May be sufficient. Accounting Definition: Profit-In-Inventory – account needed, IC COGS accounts (changes in workflow? ); (client extension). Freight on IC Invoices: Tar outstanding with development – Resolved. User needs to manually “unfreeze pricing” on each internal sales order and set to “partial calculate”. Accounting IC AP Invoice: Accrual debit cannot be configured to specific IC Relationship (should use shipping network detail (IC Relationship). Implementation: only big bang with site wide profile option. Can we continue halfmanual internal sales order invoicing? IC invoicing for internal sales orders needs to be switched globally. However, the invoices are selectively generated by shipping organization. Therefore specific shipping organizations do not need to participate. However the shipment accounting will change for all organization across the Oracle instance. Client extensions can be made to Costing workflows: Appendix C in Costing Manual R 11. 5. 10; h Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 65 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems
Issues and Action Items - Internal Order Intercompany - - Profile Option CST: Transfer Price should be set for entity to entity pair. If different intercompany policies current setting is impractical Sales Order Price is not IC Price: needs customization of external documents, Ship-to Address is not printed on invoice: needs customization of external documents, Duplicate IC Invoices for old internal shipments – resolved (needs patch) Tax functionality: only based on Bill-to account; no ship-to account available. Needs review. May be sufficient. Accounting Definition: Profit-In-Inventory – account needed, IC COGS accounts (changes in workflow? ); (client extension). Freight on IC Invoices: Tar outstanding with development – Resolved. User needs to manually “unfreeze pricing” on each internal sales order and set to “partial calculate”. Accounting IC AP Invoice: Accrual debit cannot be configured to specific IC Relationship (should use shipping network detail (IC Relationship). Implementation: only big bang with site wide profile option. Can we continue halfmanual internal sales order invoicing? IC invoicing for internal sales orders needs to be switched globally. However, the invoices are selectively generated by shipping organization. Therefore specific shipping organizations do not need to participate. However the shipment accounting will change for all organization across the Oracle instance. Client extensions can be made to Costing workflows: Appendix C in Costing Manual R 11. 5. 10; h Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 65 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems
 Alternative Step-by-Step Implementation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. CST: Transfer Price Option, No: will leave old accounting with balancing sheet accrual entries. Set at Site Level, i. e. for all entities. INV Intercompany invoicing for internal orders = YES at User Level. Automatic IC Invoicing from Price List can be activated where needed. Manual invoices can continue where desired. Additional restriction is possible by leaving IC relationship blank. Then no IC invoices are generated. Automatic IC AR and AP invoice works with accounting from Shipping Network – mapping IC AR account and Transfer Credit account to COGS. Incoming markup can be booked either to PPV account or matched up with Material overhead account on receiving side. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 66
Alternative Step-by-Step Implementation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. CST: Transfer Price Option, No: will leave old accounting with balancing sheet accrual entries. Set at Site Level, i. e. for all entities. INV Intercompany invoicing for internal orders = YES at User Level. Automatic IC Invoicing from Price List can be activated where needed. Manual invoices can continue where desired. Additional restriction is possible by leaving IC relationship blank. Then no IC invoices are generated. Automatic IC AR and AP invoice works with accounting from Shipping Network – mapping IC AR account and Transfer Credit account to COGS. Incoming markup can be booked either to PPV account or matched up with Material overhead account on receiving side. Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 66
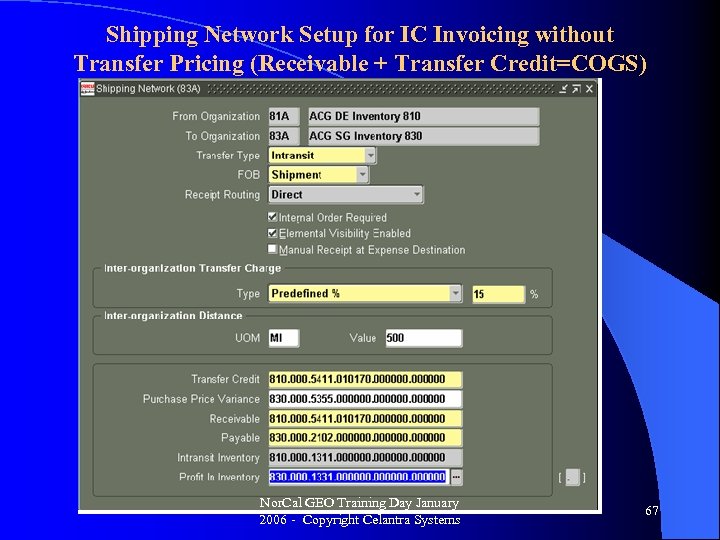 Shipping Network Setup for IC Invoicing without Transfer Pricing (Receivable + Transfer Credit=COGS) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 67
Shipping Network Setup for IC Invoicing without Transfer Pricing (Receivable + Transfer Credit=COGS) Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 67
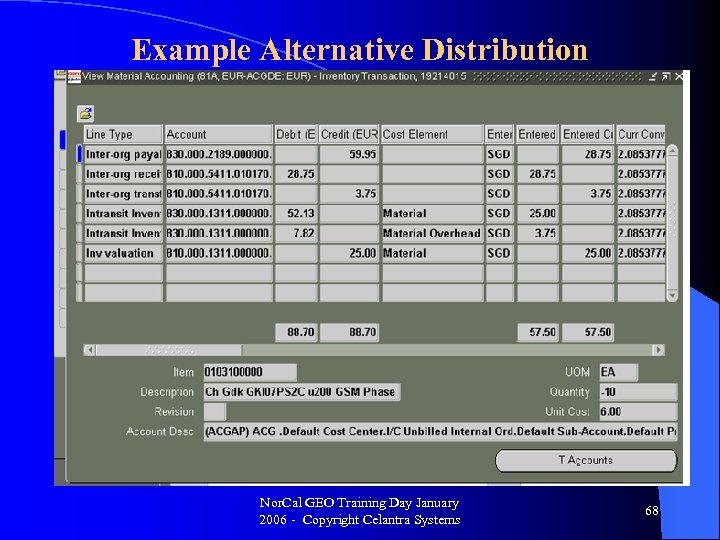 Example Alternative Distribution Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 68
Example Alternative Distribution Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 68
 Thank you ! Hans Kolbe, Celantra Systems hanskolbe@celantrasystem. com + 1 (415) 730 - 1131 Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 69
Thank you ! Hans Kolbe, Celantra Systems hanskolbe@celantrasystem. com + 1 (415) 730 - 1131 Nor. Cal GEO Training Day January 2006 - Copyright Celantra Systems 69


