4758a30ee0edbfec987bd4f214c84252.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Interagency Strategic Research Plan for Tropical Cyclones: The Way Ahead Dr. Naomi Surgi NOAA NCEP/EMC March 6, 2007
Interagency Strategic Research Plan for Tropical Cyclones: The Way Ahead Dr. Naomi Surgi NOAA NCEP/EMC March 6, 2007
 Overview • Key Findings and Recommendations – NWP modeling and data assimilation • Update on NCEP Hurricane Prediction System • Collaborative Ventures
Overview • Key Findings and Recommendations – NWP modeling and data assimilation • Update on NCEP Hurricane Prediction System • Collaborative Ventures
 Key Findings & Recommendations • NWP modeling and data assimilation – Increased skill in forecasting intensity and structure, sea state and storm surge, and precipitation is now on the horizon, much as improving track forecast skill was two decades or so ago – To meet operational needs, the Nation must be committed to supporting the key following areas: • Advanced observations • Advanced data assimilation technologies • Advanced NWP models • Investment in human and infrastructure resources – Complimentary efforts in developing next-generation operational hurricane forecast systems should be a National priority • NCEP Hurricane Prediction System • Navy Tropical Cyclone System
Key Findings & Recommendations • NWP modeling and data assimilation – Increased skill in forecasting intensity and structure, sea state and storm surge, and precipitation is now on the horizon, much as improving track forecast skill was two decades or so ago – To meet operational needs, the Nation must be committed to supporting the key following areas: • Advanced observations • Advanced data assimilation technologies • Advanced NWP models • Investment in human and infrastructure resources – Complimentary efforts in developing next-generation operational hurricane forecast systems should be a National priority • NCEP Hurricane Prediction System • Navy Tropical Cyclone System
 Key Findings & Recommendations • NWP modeling and data assimilation (continued) – Development efforts of next-generation hurricane forecast systems • Should form basis for projects supporting hurricane research and collaboration among experts from: -- Other Federal Agencies – Academia – International NWP centers & research community – Private sector – Sufficient human / infrastructure resources should be provided for: • Development of advanced data assimilation & NWP modeling systems • Operational NWP computing
Key Findings & Recommendations • NWP modeling and data assimilation (continued) – Development efforts of next-generation hurricane forecast systems • Should form basis for projects supporting hurricane research and collaboration among experts from: -- Other Federal Agencies – Academia – International NWP centers & research community – Private sector – Sufficient human / infrastructure resources should be provided for: • Development of advanced data assimilation & NWP modeling systems • Operational NWP computing
 NCEP’s Advanced DA and Modeling Plans • NCEP Data assimilation development strategy 2007 -2010 • NCEP Hurricane Modeling • Next-generation NCEP Production Suite – Preparing for the future – Production Suite: conceptual prototype – Implications
NCEP’s Advanced DA and Modeling Plans • NCEP Data assimilation development strategy 2007 -2010 • NCEP Hurricane Modeling • Next-generation NCEP Production Suite – Preparing for the future – Production Suite: conceptual prototype – Implications
 Data Assimilation Development Strategy • Three closely related efforts – Develop Situation-Dependent Background Errors (SDBE) and Simplified 4 D-Var (S 4 DV) – “Classical” 4 D-Var (C 4 DV) – Ensemble Data Assimilation (Ens. DA) • Partners – NCEP/EMC – NASA/GSFC/GMAO – THORPEX consortium • NOAA/ESRL • CIRES • U. Maryland • U. Washington • NCAR
Data Assimilation Development Strategy • Three closely related efforts – Develop Situation-Dependent Background Errors (SDBE) and Simplified 4 D-Var (S 4 DV) – “Classical” 4 D-Var (C 4 DV) – Ensemble Data Assimilation (Ens. DA) • Partners – NCEP/EMC – NASA/GSFC/GMAO – THORPEX consortium • NOAA/ESRL • CIRES • U. Maryland • U. Washington • NCAR
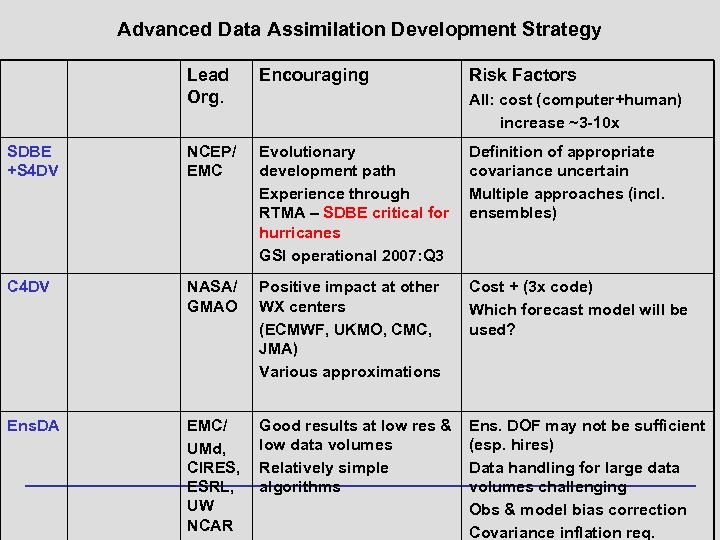 Advanced Data Assimilation Development Strategy Lead Org. Encouraging Risk Factors SDBE +S 4 DV NCEP/ EMC Evolutionary development path Experience through RTMA – SDBE critical for hurricanes GSI operational 2007: Q 3 Definition of appropriate covariance uncertain Multiple approaches (incl. ensembles) C 4 DV NASA/ GMAO Positive impact at other WX centers (ECMWF, UKMO, CMC, JMA) Various approximations Cost + (3 x code) Which forecast model will be used? Ens. DA EMC/ UMd, CIRES, ESRL, UW NCAR Good results at low res & low data volumes Relatively simple algorithms Ens. DOF may not be sufficient (esp. hires) Data handling for large data volumes challenging Obs & model bias correction Covariance inflation req. All: cost (computer+human) increase ~3 -10 x
Advanced Data Assimilation Development Strategy Lead Org. Encouraging Risk Factors SDBE +S 4 DV NCEP/ EMC Evolutionary development path Experience through RTMA – SDBE critical for hurricanes GSI operational 2007: Q 3 Definition of appropriate covariance uncertain Multiple approaches (incl. ensembles) C 4 DV NASA/ GMAO Positive impact at other WX centers (ECMWF, UKMO, CMC, JMA) Various approximations Cost + (3 x code) Which forecast model will be used? Ens. DA EMC/ UMd, CIRES, ESRL, UW NCAR Good results at low res & low data volumes Relatively simple algorithms Ens. DOF may not be sufficient (esp. hires) Data handling for large data volumes challenging Obs & model bias correction Covariance inflation req. All: cost (computer+human) increase ~3 -10 x
 NCEP DA Development Strategy • Adapt Hybrid (? ) – combine best features of advanced techniques Flexible schedule due to advanced nature of work ~yearly upgrades of SDBE/S 4 DV from NCEP/EMC Ø S 4 DV + Ens. DA – 2007 -2008 • Prototype development – 2008 • Full parallel testing • Transition decision (between 3 candidates) – 2009 -2010 • Pre-implementation testing • Operational implementation
NCEP DA Development Strategy • Adapt Hybrid (? ) – combine best features of advanced techniques Flexible schedule due to advanced nature of work ~yearly upgrades of SDBE/S 4 DV from NCEP/EMC Ø S 4 DV + Ens. DA – 2007 -2008 • Prototype development – 2008 • Full parallel testing • Transition decision (between 3 candidates) – 2009 -2010 • Pre-implementation testing • Operational implementation
 Next-generation NCEP Production Suite • Motivation • Production Suite: conceptual prototype • Implications
Next-generation NCEP Production Suite • Motivation • Production Suite: conceptual prototype • Implications
 Motivation • Support improved NWS forecast services – Greater focus on high-impact events – Additional environmental information service responsibilities – Provide more information to users and access to more info – Probabilistic and ensemble methods • Respond to external (NRC) reports – “Completing the Forecast” – “Fair Weather” • Respond to NOAA Science Advisory Board reviews – Ocean modeling (National “backbone”) – Hurricane intensity (ensemble-based system)
Motivation • Support improved NWS forecast services – Greater focus on high-impact events – Additional environmental information service responsibilities – Provide more information to users and access to more info – Probabilistic and ensemble methods • Respond to external (NRC) reports – “Completing the Forecast” – “Fair Weather” • Respond to NOAA Science Advisory Board reviews – Ocean modeling (National “backbone”) – Hurricane intensity (ensemble-based system)
 Motivation • Observations (number and availability) – Advanced Polar and Geostationary sounders (~100 X greater) – < 60 minute delivery – Next-generation Doppler radar • Advanced technologies for – Data assimilation • Discussed earlier – Ensemble processing • Bias and Ensembles (e. g. NAEFS) • Quantify value-added for multi-model ensemble system (e. g. CPC “Consolidation”) – “Reforecast” data base (CFS, Week 2 products) – Product delivery (e. g. NOMADS)
Motivation • Observations (number and availability) – Advanced Polar and Geostationary sounders (~100 X greater) – < 60 minute delivery – Next-generation Doppler radar • Advanced technologies for – Data assimilation • Discussed earlier – Ensemble processing • Bias and Ensembles (e. g. NAEFS) • Quantify value-added for multi-model ensemble system (e. g. CPC “Consolidation”) – “Reforecast” data base (CFS, Week 2 products) – Product delivery (e. g. NOMADS)
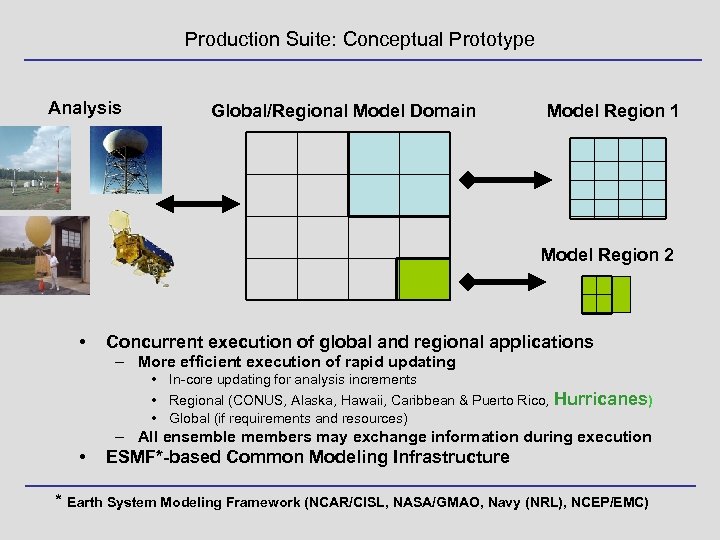 Production Suite: Conceptual Prototype Analysis Global/Regional Model Domain Model Region 1 Model Region 2 • Concurrent execution of global and regional applications – More efficient execution of rapid updating • In-core updating for analysis increments • Regional (CONUS, Alaska, Hawaii, Caribbean & Puerto Rico, Hurricanes) • Global (if requirements and resources) – All ensemble members may exchange information during execution • ESMF*-based Common Modeling Infrastructure * Earth System Modeling Framework (NCAR/CISL, NASA/GMAO, Navy (NRL), NCEP/EMC)
Production Suite: Conceptual Prototype Analysis Global/Regional Model Domain Model Region 1 Model Region 2 • Concurrent execution of global and regional applications – More efficient execution of rapid updating • In-core updating for analysis increments • Regional (CONUS, Alaska, Hawaii, Caribbean & Puerto Rico, Hurricanes) • Global (if requirements and resources) – All ensemble members may exchange information during execution • ESMF*-based Common Modeling Infrastructure * Earth System Modeling Framework (NCAR/CISL, NASA/GMAO, Navy (NRL), NCEP/EMC)
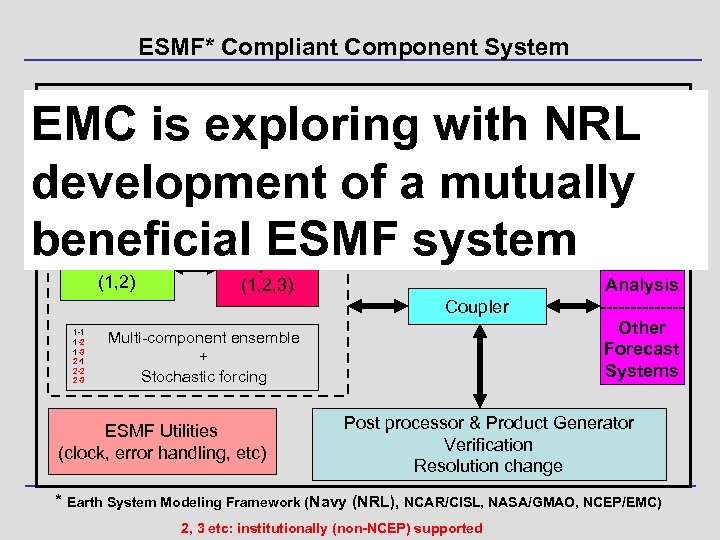 ESMF* Compliant Component System EMC is exploring with NRL development of a mutually beneficial ESMF system Application Driver ESMF Superstructure (component definitions, “mpi” communications, etc) Dynamics (1, 2) Physics (1, 2, 3) Coupler 1 -1 1 -2 1 -3 2 -1 2 -2 2 -3 Multi-component ensemble + Stochastic forcing ESMF Utilities (clock, error handling, etc) Analysis -------Other Forecast Systems Post processor & Product Generator Verification Resolution change * Earth System Modeling Framework (Navy (NRL), NCAR/CISL, NASA/GMAO, NCEP/EMC) 2, 3 etc: institutionally (non-NCEP) supported
ESMF* Compliant Component System EMC is exploring with NRL development of a mutually beneficial ESMF system Application Driver ESMF Superstructure (component definitions, “mpi” communications, etc) Dynamics (1, 2) Physics (1, 2, 3) Coupler 1 -1 1 -2 1 -3 2 -1 2 -2 2 -3 Multi-component ensemble + Stochastic forcing ESMF Utilities (clock, error handling, etc) Analysis -------Other Forecast Systems Post processor & Product Generator Verification Resolution change * Earth System Modeling Framework (Navy (NRL), NCAR/CISL, NASA/GMAO, NCEP/EMC) 2, 3 etc: institutionally (non-NCEP) supported
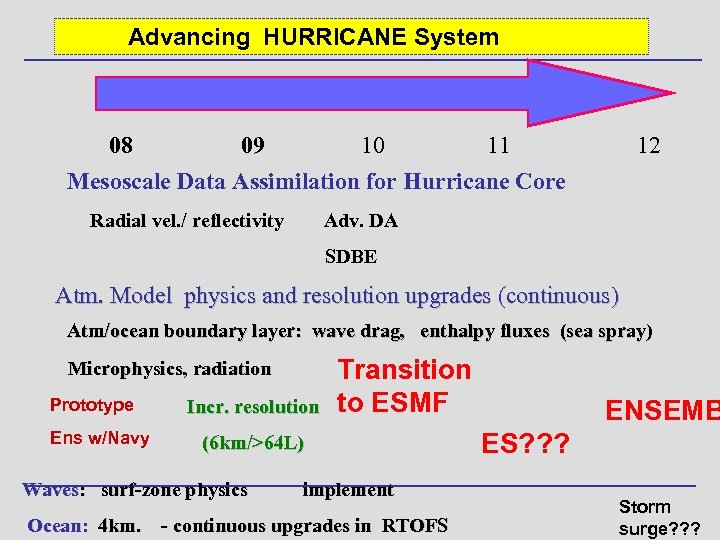 Advancing HURRICANE System 08 09 10 11 Mesoscale Data Assimilation for Hurricane Core Radial vel. / reflectivity 12 Adv. DA SDBE Atm. Model physics and resolution upgrades (continuous) Atm/ocean boundary layer: wave drag, enthalpy fluxes (sea spray) Microphysics, radiation Prototype Ens w/Navy Incr. resolution Transition to ESMF (6 km/>64 L) Waves: surf-zone physics implement Ocean: 4 km. - continuous upgrades in RTOFS ENSEMB ES? ? ? Storm surge? ? ?
Advancing HURRICANE System 08 09 10 11 Mesoscale Data Assimilation for Hurricane Core Radial vel. / reflectivity 12 Adv. DA SDBE Atm. Model physics and resolution upgrades (continuous) Atm/ocean boundary layer: wave drag, enthalpy fluxes (sea spray) Microphysics, radiation Prototype Ens w/Navy Incr. resolution Transition to ESMF (6 km/>64 L) Waves: surf-zone physics implement Ocean: 4 km. - continuous upgrades in RTOFS ENSEMB ES? ? ? Storm surge? ? ?
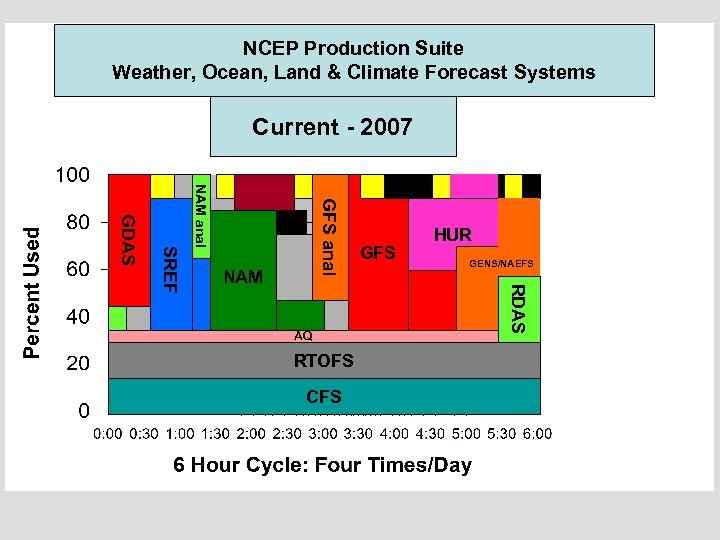 NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Current - 2007 Current (2007) GFS anal NAM anal AQ RTOFS CFS GENS/NAEFS RDAS SREF GDAS NAM GFS HUR
NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Current - 2007 Current (2007) GFS anal NAM anal AQ RTOFS CFS GENS/NAEFS RDAS SREF GDAS NAM GFS HUR
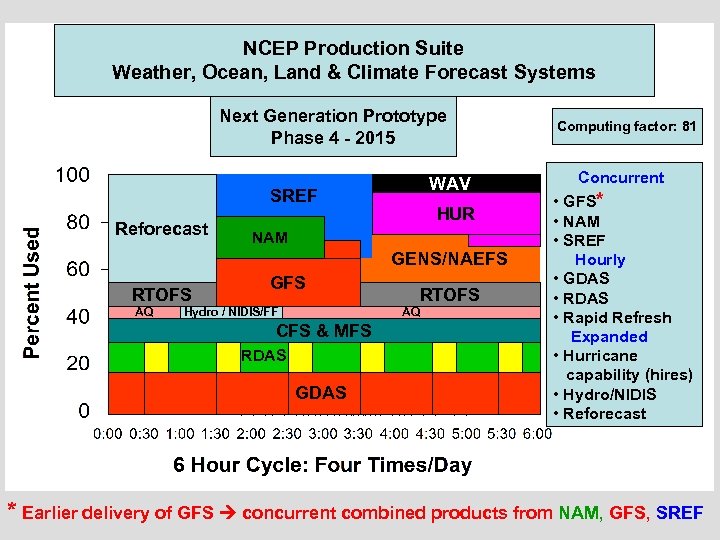 NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Next Generation Prototype Phase 4 - 2015 WAV SREF Reforecast CFS RTOFS MFS AQ HUR NAM GENS/NAEFS GFS Hydro / NIDIS/FF RTOFS AQ CFS & MFS RDAS GDAS Computing factor: 81 Rap Refresh Concurrent • GFS* • NAM • SREF Global Hourly • GDAS • Rapid Refresh Expanded Regional • Hurricane Hydro capability (hires) • Hydro/NIDIS • Reforecast * Earlier delivery of GFS concurrent combined products from NAM, GFS, SREF
NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Next Generation Prototype Phase 4 - 2015 WAV SREF Reforecast CFS RTOFS MFS AQ HUR NAM GENS/NAEFS GFS Hydro / NIDIS/FF RTOFS AQ CFS & MFS RDAS GDAS Computing factor: 81 Rap Refresh Concurrent • GFS* • NAM • SREF Global Hourly • GDAS • Rapid Refresh Expanded Regional • Hurricane Hydro capability (hires) • Hydro/NIDIS • Reforecast * Earlier delivery of GFS concurrent combined products from NAM, GFS, SREF
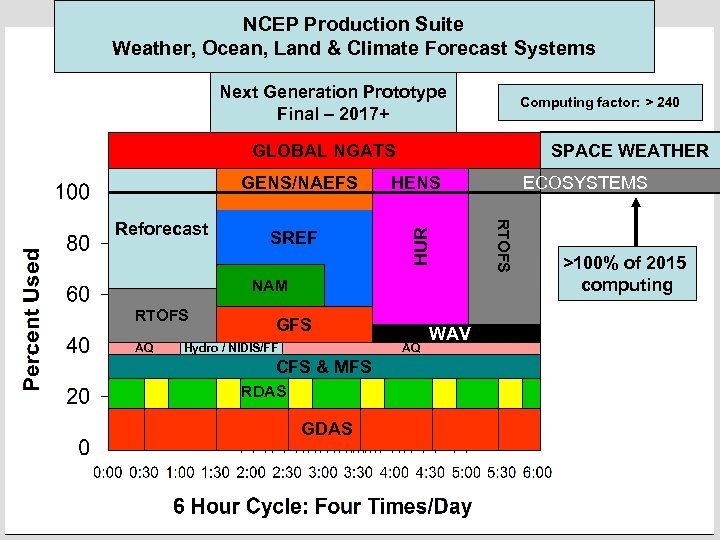 NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Next Generation Prototype Final – 2017+ Computing factor: > 240 Rap Refresh SPACE WEATHER GLOBAL NGATS CFS MFS NAM RTOFS AQ SREF GFS Hydro / NIDIS/FF CFS & MFS RDAS GDAS AQ WAV ECOSYSTEMS RTOFS Reforecast HENS HUR GENS/NAEFS Global >100% of 2015 computing Regional Hydro
NCEP Production Suite Weather, Ocean, Land & Climate Forecast Systems Next Generation Prototype Final – 2017+ Computing factor: > 240 Rap Refresh SPACE WEATHER GLOBAL NGATS CFS MFS NAM RTOFS AQ SREF GFS Hydro / NIDIS/FF CFS & MFS RDAS GDAS AQ WAV ECOSYSTEMS RTOFS Reforecast HENS HUR GENS/NAEFS Global >100% of 2015 computing Regional Hydro
 Conclusion • Principals for moving forward 1. Data assimilation advances • • • Major factor in improved forecast performance Provide return on investment in costly observing systems Require greater fraction of NCEP’s Production Suite 2. Maturing, ensemble-based, probabilistic systems offer the most potential benefits across wide spectrum of forecast services 3. Product delivery • • Time is critical (perishable product) Information availability must be maximized
Conclusion • Principals for moving forward 1. Data assimilation advances • • • Major factor in improved forecast performance Provide return on investment in costly observing systems Require greater fraction of NCEP’s Production Suite 2. Maturing, ensemble-based, probabilistic systems offer the most potential benefits across wide spectrum of forecast services 3. Product delivery • • Time is critical (perishable product) Information availability must be maximized
 Summary • Comprehensive Data Assimilation (DA) development strategy – 2007 -2010 • Phased evolution of the NCEP Production Suite – 2009 -2015 – Results in • Improved services for high impact weather • Application of advanced data assimilation techniques for improved model initial conditions • More efficient – Use of computing – Incorporation of new product lines for improved services • Earlier product delivery • More uniform and informative product stream – Advanced ensemble suite including components supported outside NCEP – Improved statistical post-processing – Reforecast and Reanalysis become operationally supported – Consistent with • ESMF • DA development strategy and interagency collaborations (current and anticipated)
Summary • Comprehensive Data Assimilation (DA) development strategy – 2007 -2010 • Phased evolution of the NCEP Production Suite – 2009 -2015 – Results in • Improved services for high impact weather • Application of advanced data assimilation techniques for improved model initial conditions • More efficient – Use of computing – Incorporation of new product lines for improved services • Earlier product delivery • More uniform and informative product stream – Advanced ensemble suite including components supported outside NCEP – Improved statistical post-processing – Reforecast and Reanalysis become operationally supported – Consistent with • ESMF • DA development strategy and interagency collaborations (current and anticipated)
 Resources • Improving intensity/structure, etc. complex problem – not only scientifically • Requires resources for science, obs, modeling systems, computing and infrastructure (in correct proportions) • Collaborations are integral to effort • Will only prove beneficial IFF collaborative efforts have sufficient resources (both $$$ and human)
Resources • Improving intensity/structure, etc. complex problem – not only scientifically • Requires resources for science, obs, modeling systems, computing and infrastructure (in correct proportions) • Collaborations are integral to effort • Will only prove beneficial IFF collaborative efforts have sufficient resources (both $$$ and human)


