38cbbcac5759525aa7dbf0d77fa81e5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
 Interactive Game Design Final Overview Yingcai Xiao
Interactive Game Design Final Overview Yingcai Xiao
 When/Where Monday, May 4 th, 5: 15 pm – 7: 15 pm In Classroom Close Book
When/Where Monday, May 4 th, 5: 15 pm – 7: 15 pm In Classroom Close Book
 What • System/Algorithm Design • No aesthetic design • Concepts • Systems • Algorithms • Pseudo code (logic not syntax)
What • System/Algorithm Design • No aesthetic design • Concepts • Systems • Algorithms • Pseudo code (logic not syntax)
 Coverage • All lecture notes • All assignments • Thoroughly understand what you did in the assignments.
Coverage • All lecture notes • All assignments • Thoroughly understand what you did in the assignments.
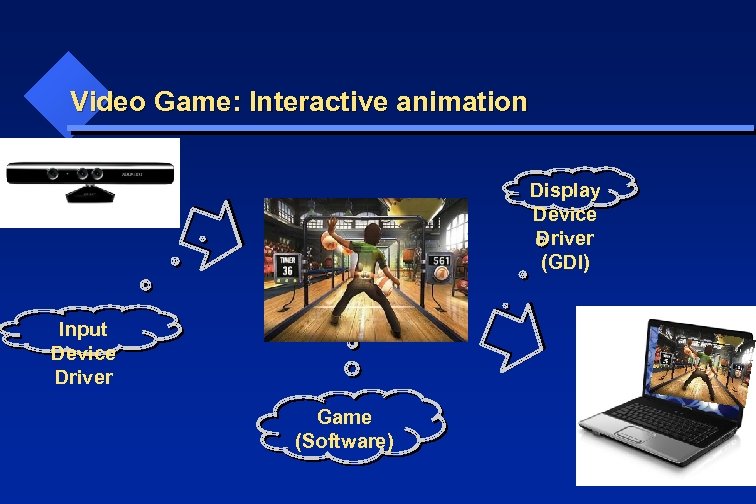 Video Game: Interactive animation Display Device Driver (GDI) Input Device Driver Game (Software)
Video Game: Interactive animation Display Device Driver (GDI) Input Device Driver Game (Software)
 Video Game: Interactive animation Similar to all other programs: data, algorithms, input, output. Data: Game Objects Algorithms: Animation Input: Interactive Events Output: Display
Video Game: Interactive animation Similar to all other programs: data, algorithms, input, output. Data: Game Objects Algorithms: Animation Input: Interactive Events Output: Display
 Game Objects (GO) GO = Geometry + Attribute
Game Objects (GO) GO = Geometry + Attribute
 Surface and Volume Representation of Game Objects Yingcai Xiao
Surface and Volume Representation of Game Objects Yingcai Xiao
 Game Objects (GO) Geometry: primitives: points, lines, triangles, polygons, spheres tetrahedrons, hexahedrons, … meshes: grids: elevation, uniform, rectlinear, structured, tin: triangular integrated network
Game Objects (GO) Geometry: primitives: points, lines, triangles, polygons, spheres tetrahedrons, hexahedrons, … meshes: grids: elevation, uniform, rectlinear, structured, tin: triangular integrated network
 Game Objects (GO) Geometry: meshes: indexed Analytical: planes, curves, surfaces, parametrical lines, curves, …
Game Objects (GO) Geometry: meshes: indexed Analytical: planes, curves, surfaces, parametrical lines, curves, …
 Parametric Form of a Line: Ø x(t) = x 0 + t * (x 1 – x 0) Ø y(t) = y 0 + t * (y 1 – y 0) Ø 0 <= t <= 1 Ø x(t) = (1 -t) * x 0 + t * x 1 Ø y(t) = (1 -t) * y 0 + t * y 1 Ø 0 <= t <= 1
Parametric Form of a Line: Ø x(t) = x 0 + t * (x 1 – x 0) Ø y(t) = y 0 + t * (y 1 – y 0) Ø 0 <= t <= 1 Ø x(t) = (1 -t) * x 0 + t * x 1 Ø y(t) = (1 -t) * y 0 + t * y 1 Ø 0 <= t <= 1
 Game Objects (GO) Geometry: Stroked: stroked primitives stroked free curves and surfaces composite: avatars, prefabs, packages, …
Game Objects (GO) Geometry: Stroked: stroked primitives stroked free curves and surfaces composite: avatars, prefabs, packages, …
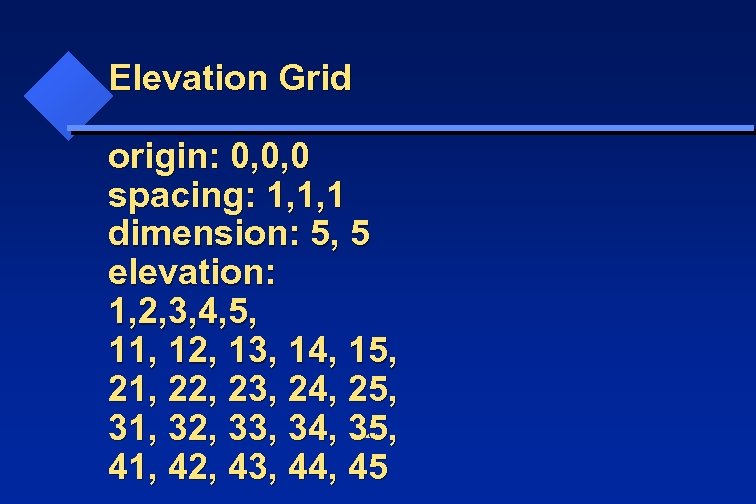 Elevation Grid origin: 0, 0, 0 spacing: 1, 1, 1 dimension: 5, 5 elevation: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45 Yingcai Xiao
Elevation Grid origin: 0, 0, 0 spacing: 1, 1, 1 dimension: 5, 5 elevation: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45 Yingcai Xiao
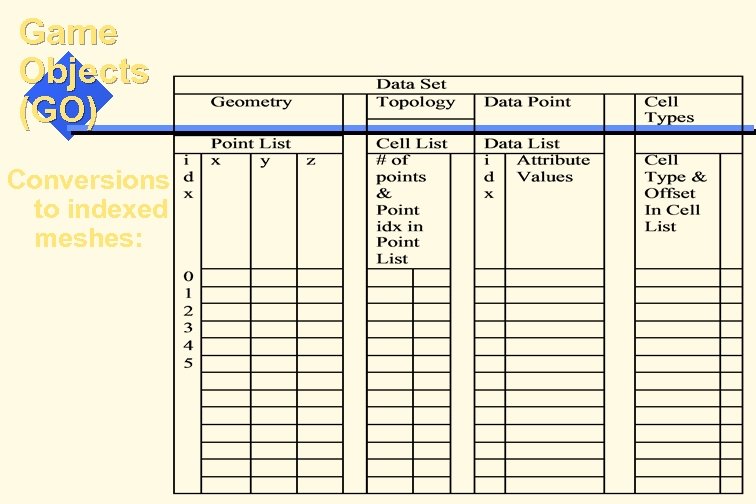 Game Objects (GO) Conversions to indexed meshes:
Game Objects (GO) Conversions to indexed meshes:
 Voxel-based Game Objects Voxelization: to partition a volume into connected voxels. Two types of voxelization: game objects game space
Voxel-based Game Objects Voxelization: to partition a volume into connected voxels. Two types of voxelization: game objects game space
 Voxelization of Game Space and GOs To partition a game space and GOs into connected voxels. Uniform Grid Rectlinear Grid Structured Grid Unstructured Grid
Voxelization of Game Space and GOs To partition a game space and GOs into connected voxels. Uniform Grid Rectlinear Grid Structured Grid Unstructured Grid
 Uniform Grid q IJK space § x = i*dx + x 0 § y = j*dy + y 0 § z = k*dz + z 0 q Data array (i, j, k), loop i first, then j, k last. q Simple, compact and speedy retrieval. q Not flexible
Uniform Grid q IJK space § x = i*dx + x 0 § y = j*dy + y 0 § z = k*dz + z 0 q Data array (i, j, k), loop i first, then j, k last. q Simple, compact and speedy retrieval. q Not flexible
 Rectlinear Grid q Dimension: nx, ny, nz q Nonuniform spacing, but straight grid lines. float x[44]={0. 0, 1. 2, 2. 8, 3. 9……. } float y[33]={1. 0, ……………} float z[22]={0. 8, ……………}
Rectlinear Grid q Dimension: nx, ny, nz q Nonuniform spacing, but straight grid lines. float x[44]={0. 0, 1. 2, 2. 8, 3. 9……. } float y[33]={1. 0, ……………} float z[22]={0. 8, ……………}
![Rectlinear Grid q IJK space. x = x[I]; y = y[J]; z = z[K]; Rectlinear Grid q IJK space. x = x[I]; y = y[J]; z = z[K];](https://present5.com/presentation/38cbbcac5759525aa7dbf0d77fa81e5f/image-19.jpg) Rectlinear Grid q IJK space. x = x[I]; y = y[J]; z = z[K]; q Data array (i, j, k), i changes first, then j, k last. q Simple q compact (takes O(nx + ny + nz) more space) q speedy retrieval q Little more flexible
Rectlinear Grid q IJK space. x = x[I]; y = y[J]; z = z[K]; q Data array (i, j, k), i changes first, then j, k last. q Simple q compact (takes O(nx + ny + nz) more space) q speedy retrieval q Little more flexible
 Structured Grid q Dimension: nx, ny, nz q Nonuniform spacing q IJK space (no formula) q Coordinates of each grid node need to be given. x(I, J, K), y(I, J, K), z(I, J, K)
Structured Grid q Dimension: nx, ny, nz q Nonuniform spacing q IJK space (no formula) q Coordinates of each grid node need to be given. x(I, J, K), y(I, J, K), z(I, J, K)
 Indexed Volume / Surface • • No dimensions parameters: nx, ny, nz No IJK space Coordinates of each node need to be given Most flexible, can represent any structures Easy to modify geometry, only need to change the point list. Not compact (need space to save xyz values and cell information) Slow retrieval
Indexed Volume / Surface • • No dimensions parameters: nx, ny, nz No IJK space Coordinates of each node need to be given Most flexible, can represent any structures Easy to modify geometry, only need to change the point list. Not compact (need space to save xyz values and cell information) Slow retrieval
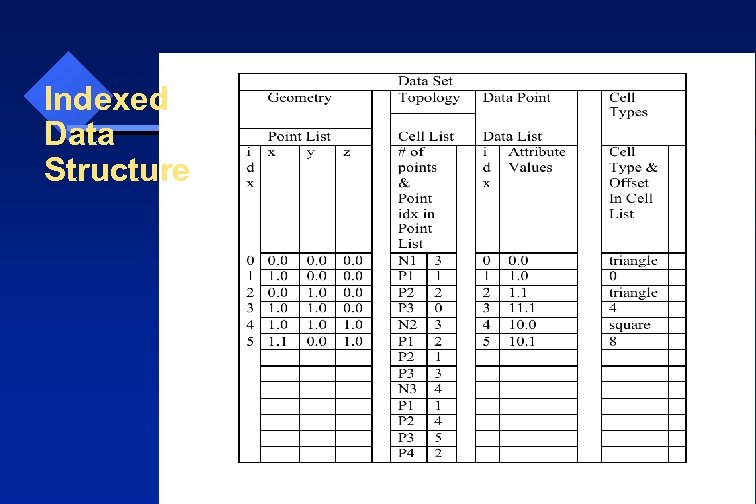 Indexed Data Structure
Indexed Data Structure
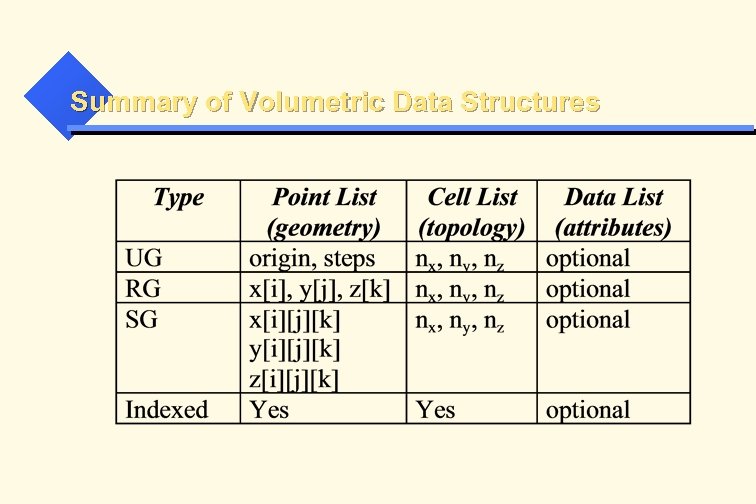 Summary of Volumetric Data Structures
Summary of Volumetric Data Structures
 Game Object Appearance
Game Object Appearance
 The Three Faces of Designing GO Appearance The Artistic Face: l l aesthetic – beautiful and ugly done by artists The Communication Face: l l show and tell (convey a message) done by communication experts The Technical Face l l the enabler (can or can’t), game engine design and development. done by computer scientists
The Three Faces of Designing GO Appearance The Artistic Face: l l aesthetic – beautiful and ugly done by artists The Communication Face: l l show and tell (convey a message) done by communication experts The Technical Face l l the enabler (can or can’t), game engine design and development. done by computer scientists
 Attributes (Appearance) 1. Color 2. Shades 3. Texture 4. Transparency
Attributes (Appearance) 1. Color 2. Shades 3. Texture 4. Transparency
 Color 1. Gamma Correction 2. Dynamic Range 3. Color Models
Color 1. Gamma Correction 2. Dynamic Range 3. Color Models
 Shading
Shading
 Shading 1. Realism 2. Speed 3. Theory 4. Implementation
Shading 1. Realism 2. Speed 3. Theory 4. Implementation
 Shading 1. Realism : Speed 2. HW tools: Frame Buffer, Z Buffer, ID Buffer, GPU 3. SW tools: LOD (Level of Details), 4. Shading Modes: Flat, Smooth, Phong
Shading 1. Realism : Speed 2. HW tools: Frame Buffer, Z Buffer, ID Buffer, GPU 3. SW tools: LOD (Level of Details), 4. Shading Modes: Flat, Smooth, Phong
 Shading Modes
Shading Modes
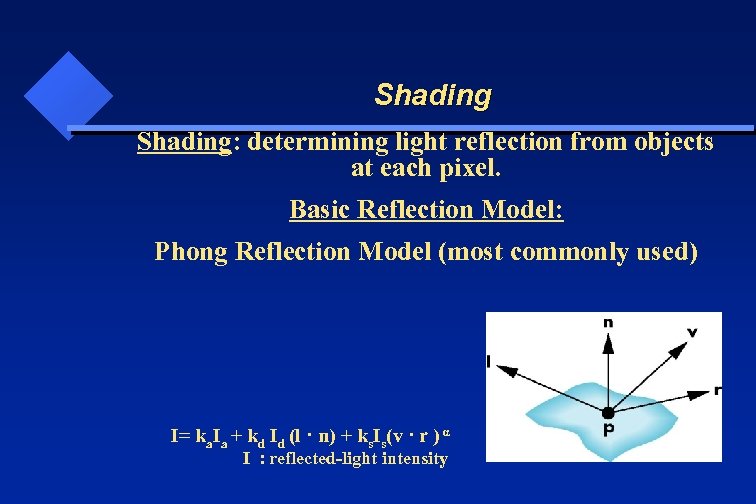 Shading: determining light reflection from objects at each pixel. Basic Reflection Model: Phong Reflection Model (most commonly used) I= ka. Ia + kd Id (l · n) + ks. Is(v · r ) α I : reflected-light intensity
Shading: determining light reflection from objects at each pixel. Basic Reflection Model: Phong Reflection Model (most commonly used) I= ka. Ia + kd Id (l · n) + ks. Is(v · r ) α I : reflected-light intensity
 Many more things consider: Shadow, Reflection, Transparency, Refraction, … http: //www. codeproject. com/KB/graphics/Ray. Tracer. Net. aspx Figure 2. Shading effects: a) Ambient, b) Diffuse, c) Highlights, d) Shadows and e) Reflection (notice the reflection on the floor also)
Many more things consider: Shadow, Reflection, Transparency, Refraction, … http: //www. codeproject. com/KB/graphics/Ray. Tracer. Net. aspx Figure 2. Shading effects: a) Ambient, b) Diffuse, c) Highlights, d) Shadows and e) Reflection (notice the reflection on the floor also)
 Phong Shading: http: //www. yourdictionary. com/phong-shading#computer for (each object) for(each triangle of the object) for(each pixel in the triangle) if(closer to the viewer than the current z buffer value) { update z buffer with the new z interpolate the pixel normal from the vertex normals compute the pixel color/relection using Phong reflection
Phong Shading: http: //www. yourdictionary. com/phong-shading#computer for (each object) for(each triangle of the object) for(each pixel in the triangle) if(closer to the viewer than the current z buffer value) { update z buffer with the new z interpolate the pixel normal from the vertex normals compute the pixel color/relection using Phong reflection
 Geometric Transformations For Game Development Yingcai Xiao
Geometric Transformations For Game Development Yingcai Xiao
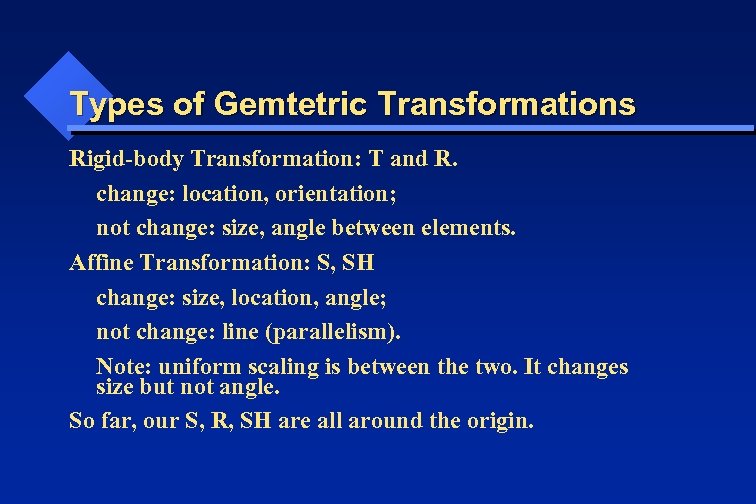 Types of Gemtetric Transformations Rigid-body Transformation: T and R. change: location, orientation; not change: size, angle between elements. Affine Transformation: S, SH change: size, location, angle; not change: line (parallelism). Note: uniform scaling is between the two. It changes size but not angle. So far, our S, R, SH are all around the origin.
Types of Gemtetric Transformations Rigid-body Transformation: T and R. change: location, orientation; not change: size, angle between elements. Affine Transformation: S, SH change: size, location, angle; not change: line (parallelism). Note: uniform scaling is between the two. It changes size but not angle. So far, our S, R, SH are all around the origin.
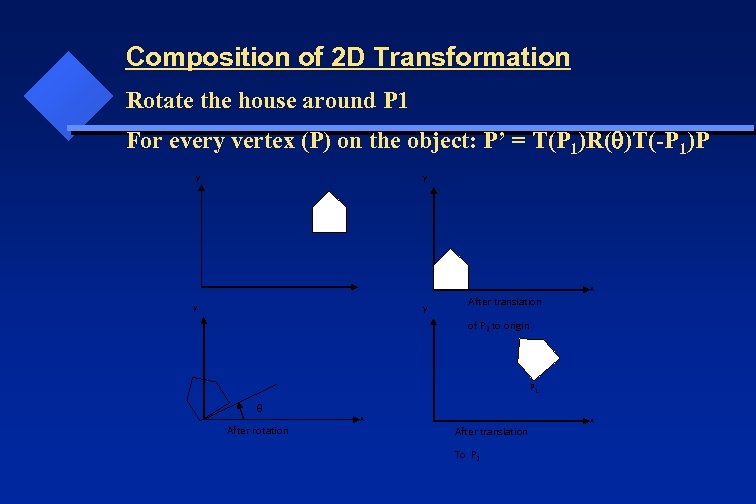 Composition of 2 D Transformation Rotate the house around P 1 For every vertex (P) on the object: P’ = T(P 1)R( )T(-P 1)P y y x y y After translation of P 1 to origin P 1 After rotation x After translation To P 1 x
Composition of 2 D Transformation Rotate the house around P 1 For every vertex (P) on the object: P’ = T(P 1)R( )T(-P 1)P y y x y y After translation of P 1 to origin P 1 After rotation x After translation To P 1 x
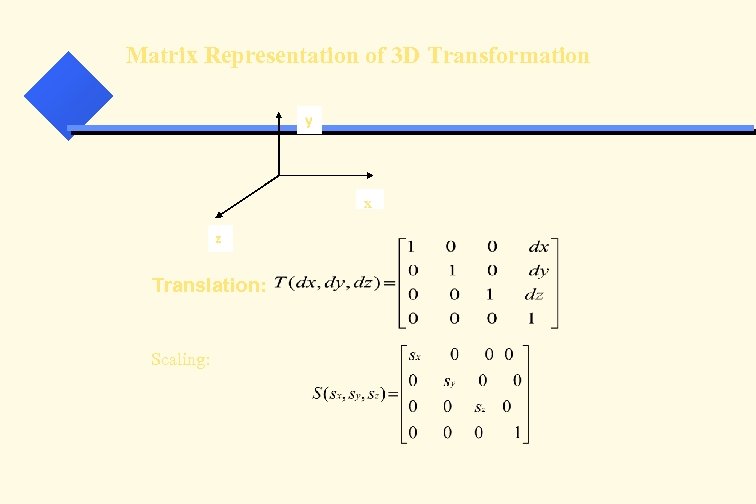 Matrix Representation of 3 D Transformation y x z Translation: Scaling:
Matrix Representation of 3 D Transformation y x z Translation: Scaling:
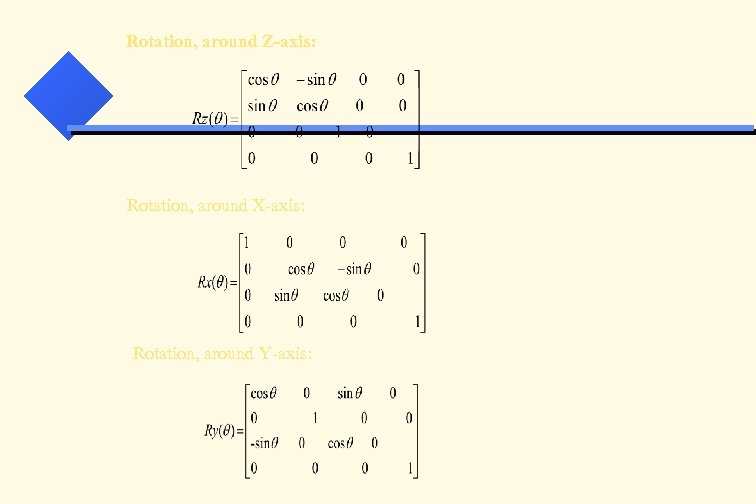 Rotation, around Z-axis: Rotation, around X-axis: Rotation, around Y-axis:
Rotation, around Z-axis: Rotation, around X-axis: Rotation, around Y-axis:
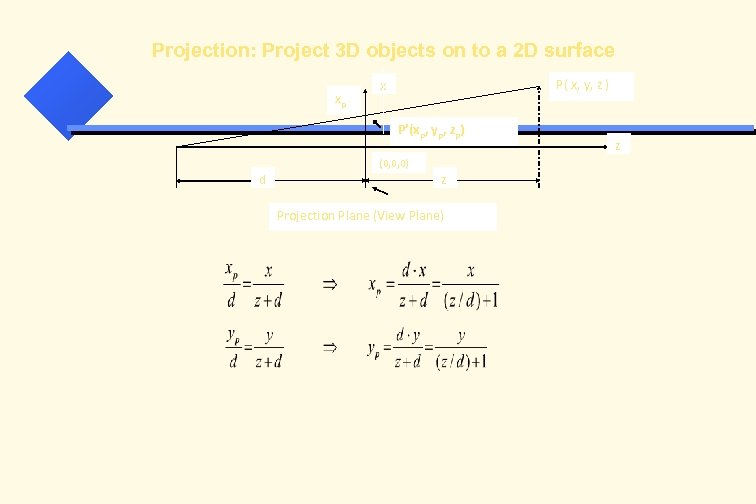 Projection: Project 3 D objects on to a 2 D surface xp P( x, y, z ) x P’(xp, yp, zp) (0, 0, 0) d z Projection Plane (View Plane) z
Projection: Project 3 D objects on to a 2 D surface xp P( x, y, z ) x P’(xp, yp, zp) (0, 0, 0) d z Projection Plane (View Plane) z
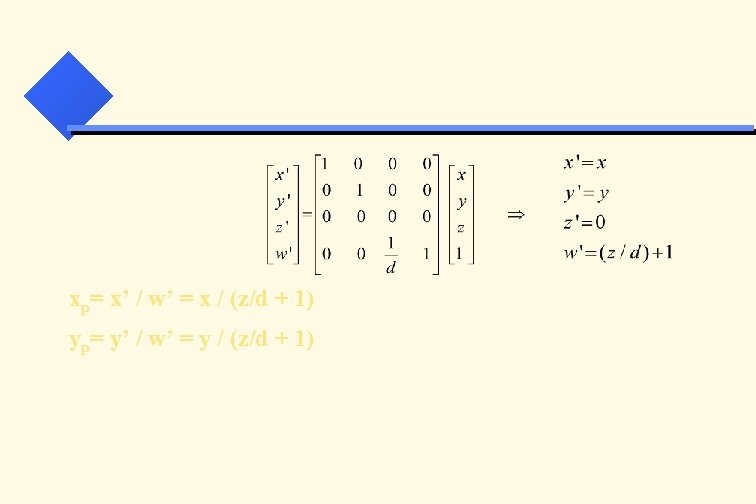 xp= x’ / w’ = x / (z/d + 1) yp= y’ / w’ = y / (z/d + 1)
xp= x’ / w’ = x / (z/d + 1) yp= y’ / w’ = y / (z/d + 1)
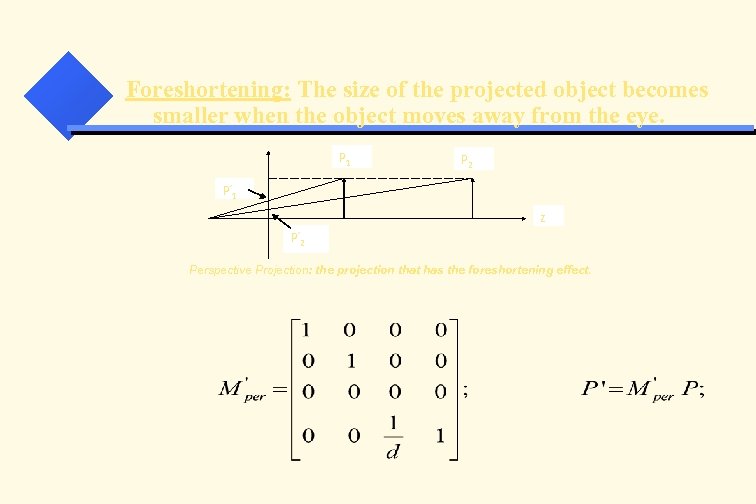 Foreshortening: The size of the projected object becomes smaller when the object moves away from the eye. P 1 P 2 P’ 1 z P’ 2 Perspective Projection: the projection that has the foreshortening effect.
Foreshortening: The size of the projected object becomes smaller when the object moves away from the eye. P 1 P 2 P’ 1 z P’ 2 Perspective Projection: the projection that has the foreshortening effect.
 Morphing and Procedural Animation
Morphing and Procedural Animation
 Procedural Morphing • Use scripts to change the geometry of game objects at run-time. • A demo in Unity 3 D to change the geometry of a plane to a wave form.
Procedural Morphing • Use scripts to change the geometry of game objects at run-time. • A demo in Unity 3 D to change the geometry of a plane to a wave form.
 Demo in Unity 3 D • • • To change the geometry of a plane to a wave form. Create a new project with Character Controller package. Add a plane (Game. Object->Create. Ohters->Plane) Scale it in the Inspector to 10 X 10 (in x and z). Uncheck the Mesh Collider (in the Inspector) Add a light (Game. Object->Create. Ohters->Directional. Light) Add a FPC (Project->Assets->Standard. Assets>Character. Controllers->First. Person. Controller, drag-and-drop it to Hierarchy. ) Move it up. (Change its y position in the Inspector to 11). Add script to morph the plane (Plane->Inspector->Add. Component ->New. Script->Java. Script) name it Wave. Add the code on the next page to the Wave. js in Mono. Build->Build All in Mono to make sure there is no compilation errors.
Demo in Unity 3 D • • • To change the geometry of a plane to a wave form. Create a new project with Character Controller package. Add a plane (Game. Object->Create. Ohters->Plane) Scale it in the Inspector to 10 X 10 (in x and z). Uncheck the Mesh Collider (in the Inspector) Add a light (Game. Object->Create. Ohters->Directional. Light) Add a FPC (Project->Assets->Standard. Assets>Character. Controllers->First. Person. Controller, drag-and-drop it to Hierarchy. ) Move it up. (Change its y position in the Inspector to 11). Add script to morph the plane (Plane->Inspector->Add. Component ->New. Script->Java. Script) name it Wave. Add the code on the next page to the Wave. js in Mono. Build->Build All in Mono to make sure there is no compilation errors.
 Demo in Unity 3 D (Wave) #pragma strict function Start () { var mesh: Mesh = this. Get. Component(Mesh. Filter). m esh; var verts: Vector 3[] = mesh. vertices; for (var v = 0; v < verts. Length; v++) { verts[v]. y = Random. Range(0, 10); } mesh. vertices = verts; mesh. Recalculate. Bounds(); mesh. Recalculate. Normals(); this. game. Object. Add. Component(Mesh. Collider); } function Update () { }
Demo in Unity 3 D (Wave) #pragma strict function Start () { var mesh: Mesh = this. Get. Component(Mesh. Filter). m esh; var verts: Vector 3[] = mesh. vertices; for (var v = 0; v < verts. Length; v++) { verts[v]. y = Random. Range(0, 10); } mesh. vertices = verts; mesh. Recalculate. Bounds(); mesh. Recalculate. Normals(); this. game. Object. Add. Component(Mesh. Collider); } function Update () { }
 Time-dependent Carpet Plots y(r, t) = A e-r-at cos(2π (r-Vt) /λ); r = sqrt ((x-x 0)*(x-x 0)+ (z-z 0)*(z-z 0)) P 0(x 0, y 0, z 0) : center of the wave A: amplitude of the wave V: velocity of the wave λ: wave length of the wave a: speed of decaying t = current time – time of impact (t )
Time-dependent Carpet Plots y(r, t) = A e-r-at cos(2π (r-Vt) /λ); r = sqrt ((x-x 0)*(x-x 0)+ (z-z 0)*(z-z 0)) P 0(x 0, y 0, z 0) : center of the wave A: amplitude of the wave V: velocity of the wave λ: wave length of the wave a: speed of decaying t = current time – time of impact (t )
 More details added from this point onward. Dr. Xiao
More details added from this point onward. Dr. Xiao
 EDP Scripting Yingcai Xiao
EDP Scripting Yingcai Xiao
 EDP EDP: Event-driven programming Application awaits in an idle state and responds to user requests by calling the corresponding even handlers.
EDP EDP: Event-driven programming Application awaits in an idle state and responds to user requests by calling the corresponding even handlers.
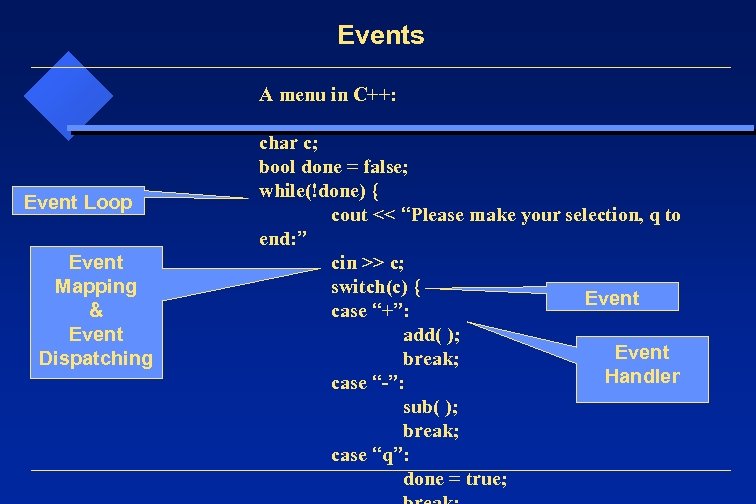 Events A menu in C++: Event Loop Event Mapping & Event Dispatching char c; bool done = false; while(!done) { cout << “Please make your selection, q to end: ” cin >> c; switch(c) { Event case “+”: add( ); Event break; Handler case “-”: sub( ); break; case “q”: done = true;
Events A menu in C++: Event Loop Event Mapping & Event Dispatching char c; bool done = false; while(!done) { cout << “Please make your selection, q to end: ” cin >> c; switch(c) { Event case “+”: add( ); Event break; Handler case “-”: sub( ); break; case “q”: done = true;
 Key Components of EDP 1. Events 2. Event loop 3. Event mapping 4. Event dispatching 5. Event handlers All, but the handlers, are taken care of by the game engine and its underplaying graphics and OS platform.
Key Components of EDP 1. Events 2. Event loop 3. Event mapping 4. Event dispatching 5. Event handlers All, but the handlers, are taken care of by the game engine and its underplaying graphics and OS platform.
 EDP in Unity 3 D • Unity game engine supports EDP. • Download the EDP-Scripting project. • Open it with Unity 3 D and select scene 1. • Object Cylinder and Terrain. • Note: animation 1 was created using Unity GUI. • IGD 5 script was created to do simulation. • Simulation is animation obeying certain rules, e. g. , trajectory of a projectile.
EDP in Unity 3 D • Unity game engine supports EDP. • Download the EDP-Scripting project. • Open it with Unity 3 D and select scene 1. • Object Cylinder and Terrain. • Note: animation 1 was created using Unity GUI. • IGD 5 script was created to do simulation. • Simulation is animation obeying certain rules, e. g. , trajectory of a projectile.
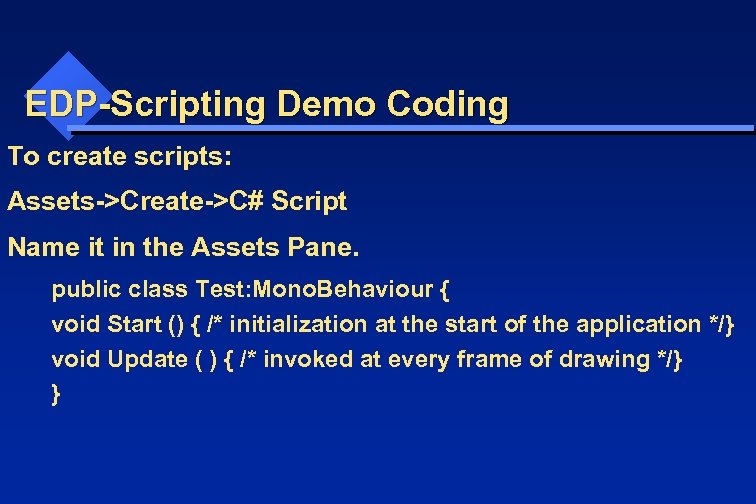 EDP-Scripting Demo Coding To create scripts: Assets->Create->C# Script Name it in the Assets Pane. public class Test: Mono. Behaviour { void Start () { /* initialization at the start of the application */} void Update ( ) { /* invoked at every frame of drawing */} }
EDP-Scripting Demo Coding To create scripts: Assets->Create->C# Script Name it in the Assets Pane. public class Test: Mono. Behaviour { void Start () { /* initialization at the start of the application */} void Update ( ) { /* invoked at every frame of drawing */} }
 C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs using Unity. Engine; using Unity. Engine. UI; using System. Collections; public class IGD 5 : Mono. Behaviour { float time = 0; float threshold = 0. 5 f; bool is. Ready = true; bool is. Simulate = false; int collision. Count = 0; public Vector 3 speed = new Vector 3(5, 5, 0); public Game. Object score; // the text object for displaying score // Use this for initialization void Start () { }
C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs using Unity. Engine; using Unity. Engine. UI; using System. Collections; public class IGD 5 : Mono. Behaviour { float time = 0; float threshold = 0. 5 f; bool is. Ready = true; bool is. Simulate = false; int collision. Count = 0; public Vector 3 speed = new Vector 3(5, 5, 0); public Game. Object score; // the text object for displaying score // Use this for initialization void Start () { }
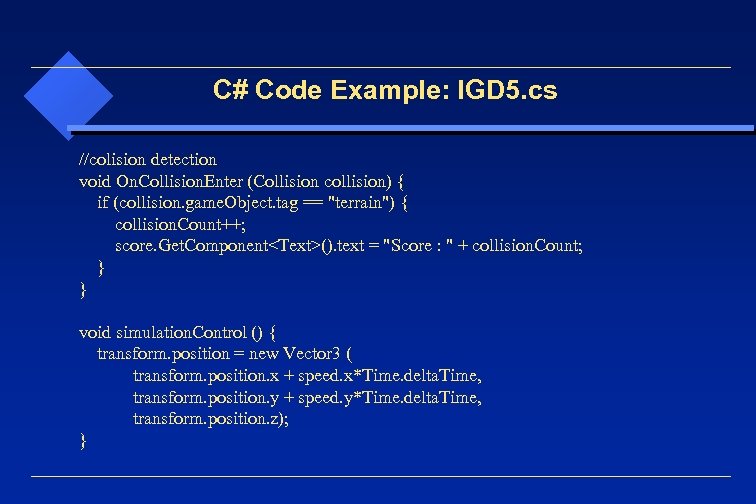 C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs //colision detection void On. Collision. Enter (Collision collision) { if (collision. game. Object. tag == "terrain") { collision. Count++; score. Get. Component
C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs //colision detection void On. Collision. Enter (Collision collision) { if (collision. game. Object. tag == "terrain") { collision. Count++; score. Get. Component
 C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs void Update () { if (!is. Ready) { if (time >= threshold) { is. Ready = true; time = 0; } else { time += Time. delta. Time; } else
C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs void Update () { if (!is. Ready) { if (time >= threshold) { is. Ready = true; time = 0; } else { time += Time. delta. Time; } else
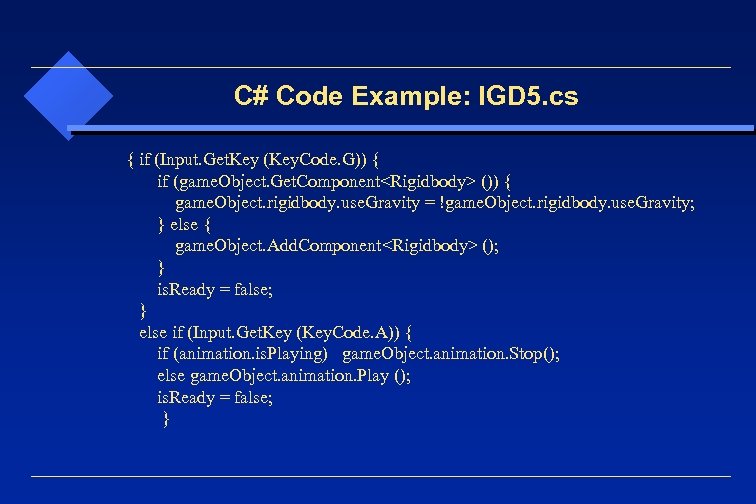 C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs { if (Input. Get. Key (Key. Code. G)) { if (game. Object. Get. Component
C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs { if (Input. Get. Key (Key. Code. G)) { if (game. Object. Get. Component
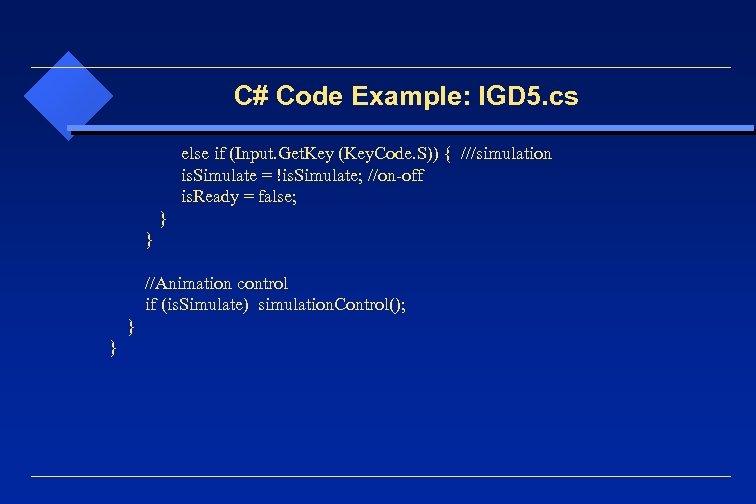 C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs else if (Input. Get. Key (Key. Code. S)) { ///simulation is. Simulate = !is. Simulate; //on-off is. Ready = false; } //Animation control if (is. Simulate) simulation. Control(); } }
C# Code Example: IGD 5. cs else if (Input. Get. Key (Key. Code. S)) { ///simulation is. Simulate = !is. Simulate; //on-off is. Ready = false; } //Animation control if (is. Simulate) simulation. Control(); } }
 Game Controller: Kinect NUI
Game Controller: Kinect NUI
 Kinect for Windows Release date : November 2010 Kinect : natural user interface that provides realtime gesture recognition. Sensors: RGB camera and 3 D depth sensor.
Kinect for Windows Release date : November 2010 Kinect : natural user interface that provides realtime gesture recognition. Sensors: RGB camera and 3 D depth sensor.
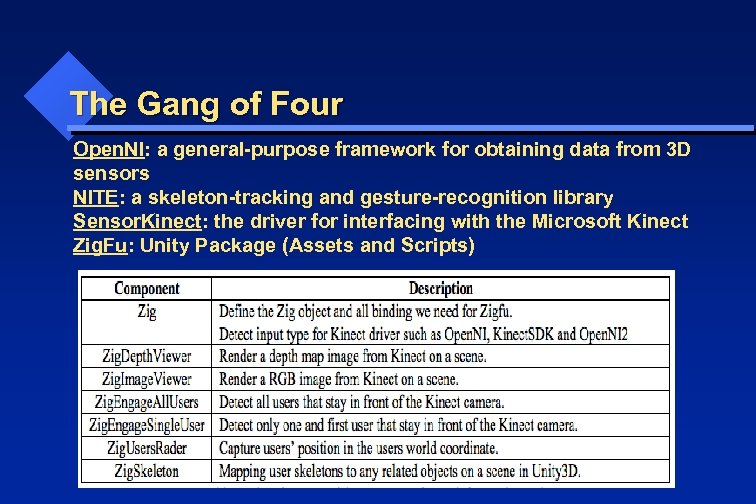 The Gang of Four Open. NI: a general-purpose framework for obtaining data from 3 D sensors NITE: a skeleton-tracking and gesture-recognition library Sensor. Kinect: the driver for interfacing with the Microsoft Kinect Zig. Fu: Unity Package (Assets and Scripts)
The Gang of Four Open. NI: a general-purpose framework for obtaining data from 3 D sensors NITE: a skeleton-tracking and gesture-recognition library Sensor. Kinect: the driver for interfacing with the Microsoft Kinect Zig. Fu: Unity Package (Assets and Scripts)
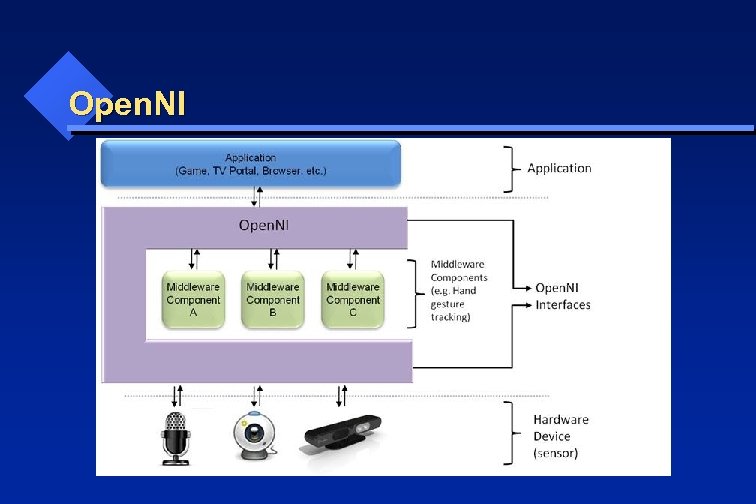 Open. NI
Open. NI
 Open. NI Production Nodes: • a set of components that have a productive role in the data creation process required for Natural Interaction based applications. • the API of the production nodes only defines the language. • The logic of data generation must be implemented by the modules that plug into Open. NI. • E. g. for a production node that represents the functionality of generating hand-point data, the logic of hand-point data generation must come from an external middleware component that is both plugged into Open. NI, and also has the knowledge of how to produce such data.
Open. NI Production Nodes: • a set of components that have a productive role in the data creation process required for Natural Interaction based applications. • the API of the production nodes only defines the language. • The logic of data generation must be implemented by the modules that plug into Open. NI. • E. g. for a production node that represents the functionality of generating hand-point data, the logic of hand-point data generation must come from an external middleware component that is both plugged into Open. NI, and also has the knowledge of how to produce such data.
 Artificial Intelligence in Game Development Yingcai Xiao
Artificial Intelligence in Game Development Yingcai Xiao
 PA 5 Coding / Flocking http: //www. cs. uakron. edu/~xiao/game/igd 5. htm Theory / Rules: cohesion - to move toward the center of the mass of the flockmates separation - to avoid flockmates alignment – to steer towards the flock direction
PA 5 Coding / Flocking http: //www. cs. uakron. edu/~xiao/game/igd 5. htm Theory / Rules: cohesion - to move toward the center of the mass of the flockmates separation - to avoid flockmates alignment – to steer towards the flock direction
 PA 5 Coding / Flocking The Example: Holistic Game Development with Unity By: Penny de Byl http: //proquest. safaribooksonline. com/book/programming/ga me-programming/9780240819334 Section 5. 6: a flock of seagulls flying against wind in small groups. http: //proquest. safaribooksonline. com/book/programming/ga me-programming/9780240819334/chapter-5 -charactermechanics/ch 5_6_006_9780240819341_web_ch 05_html
PA 5 Coding / Flocking The Example: Holistic Game Development with Unity By: Penny de Byl http: //proquest. safaribooksonline. com/book/programming/ga me-programming/9780240819334 Section 5. 6: a flock of seagulls flying against wind in small groups. http: //proquest. safaribooksonline. com/book/programming/ga me-programming/9780240819334/chapter-5 -charactermechanics/ch 5_6_006_9780240819341_web_ch 05_html
 Flocking Code Example C# code at http: //wiki. unity 3 d. com/index. php? title=Flocking (1) Create the flock at the Biod. Controller: : Start() (2) Update animation parameters in Biod. Controller: : Update () (3) Control the animation in Boid. Flocking: : Boid. Steering ()
Flocking Code Example C# code at http: //wiki. unity 3 d. com/index. php? title=Flocking (1) Create the flock at the Biod. Controller: : Start() (2) Update animation parameters in Biod. Controller: : Update () (3) Control the animation in Boid. Flocking: : Boid. Steering ()
 Professional Game Development
Professional Game Development
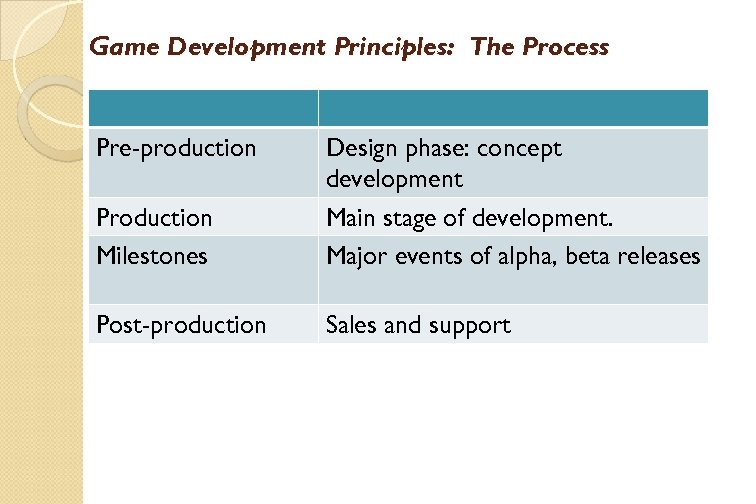 Game Development Principles: The Process Pre-production Production Milestones Design phase: concept development Main stage of development. Major events of alpha, beta releases Post-production Sales and support
Game Development Principles: The Process Pre-production Production Milestones Design phase: concept development Main stage of development. Major events of alpha, beta releases Post-production Sales and support
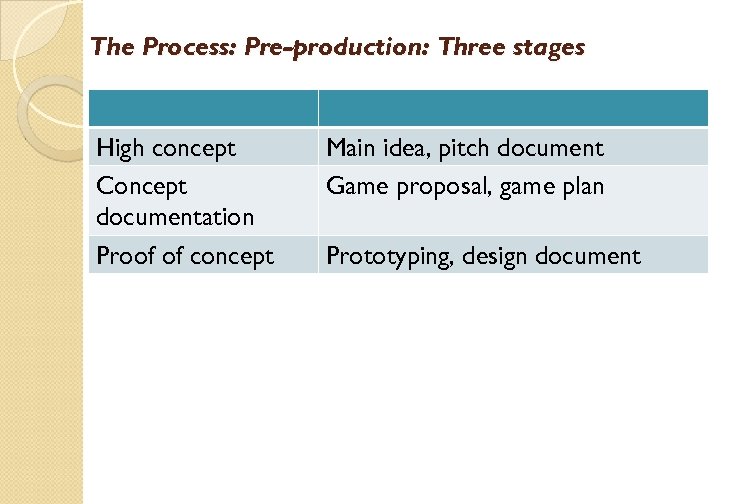 The Process: Pre-production: Three stages High concept Concept documentation Proof of concept Main idea, pitch document Game proposal, game plan Prototyping, design document
The Process: Pre-production: Three stages High concept Concept documentation Proof of concept Main idea, pitch document Game proposal, game plan Prototyping, design document
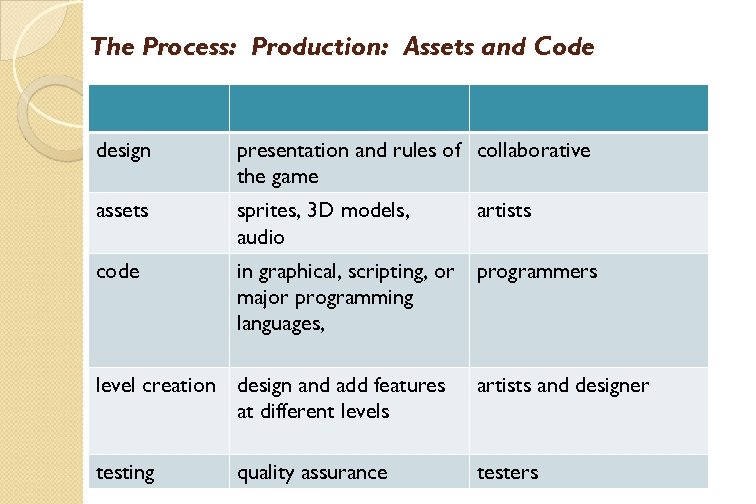 The Process: Production: Assets and Code design presentation and rules of collaborative the game assets sprites, 3 D models, audio artists code in graphical, scripting, or major programming languages, programmers level creation design and add features at different levels artists and designer testing testers quality assurance
The Process: Production: Assets and Code design presentation and rules of collaborative the game assets sprites, 3 D models, audio artists code in graphical, scripting, or major programming languages, programmers level creation design and add features at different levels artists and designer testing testers quality assurance
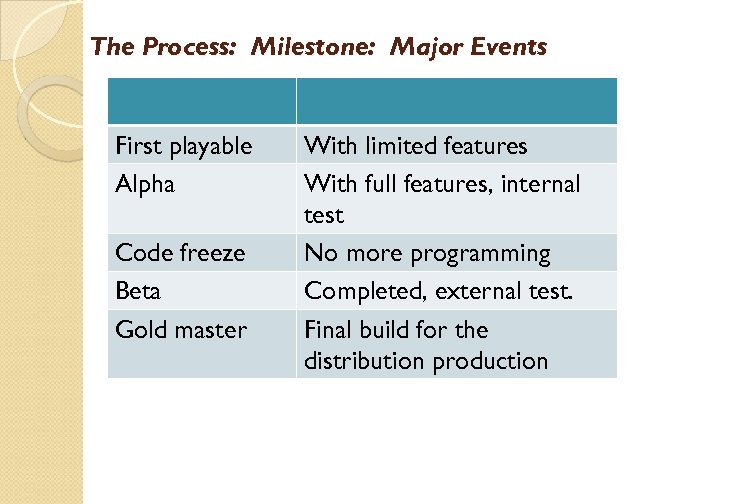 The Process: Milestone: Major Events First playable Alpha Code freeze Beta Gold master With limited features With full features, internal test No more programming Completed, external test. Final build for the distribution production
The Process: Milestone: Major Events First playable Alpha Code freeze Beta Gold master With limited features With full features, internal test No more programming Completed, external test. Final build for the distribution production
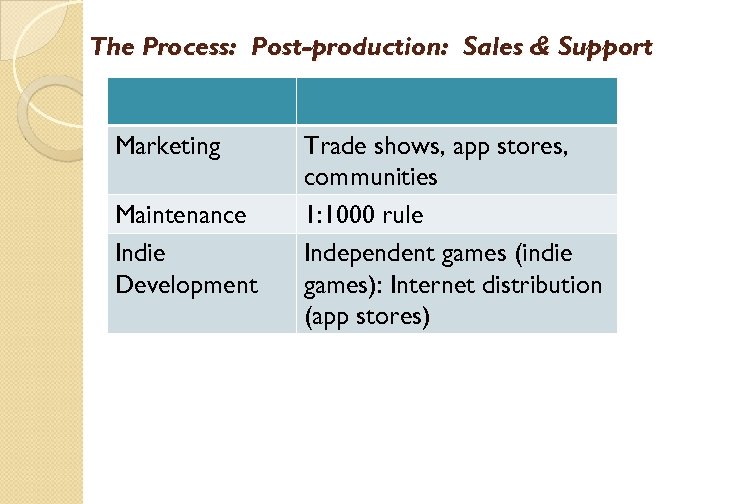 The Process: Post-production: Sales & Support Marketing Maintenance Indie Development Trade shows, app stores, communities 1: 1000 rule Independent games (indie games): Internet distribution (app stores)
The Process: Post-production: Sales & Support Marketing Maintenance Indie Development Trade shows, app stores, communities 1: 1000 rule Independent games (indie games): Internet distribution (app stores)
 Game Engine Development What do we need? What tools do we have? How can we design and implement? We will answer those questions in an agile way.
Game Engine Development What do we need? What tools do we have? How can we design and implement? We will answer those questions in an agile way.
 Video Game: Interactive animation Similar to all other programs: data, algorithms, input, output. Data: Game Objects Algorithms: Animation Input: Interactive Events Output: Display
Video Game: Interactive animation Similar to all other programs: data, algorithms, input, output. Data: Game Objects Algorithms: Animation Input: Interactive Events Output: Display
 Graphics Engine / Display Engine / Shading Engine
Graphics Engine / Display Engine / Shading Engine
 Open. GL for Gaming PA 4 Color Cube Example UA Example
Open. GL for Gaming PA 4 Color Cube Example UA Example
 An Example for Game Programming • The “Color Cube” example • Users: interactive 3 D animation • Programmers: event-driven 3 D animation of geometric transformations. • C++ • Open. GL for display • Glut (GL Utility Toolkit) for interaction • https: //www. opengl. org/resources/libraries/glut/
An Example for Game Programming • The “Color Cube” example • Users: interactive 3 D animation • Programmers: event-driven 3 D animation of geometric transformations. • C++ • Open. GL for display • Glut (GL Utility Toolkit) for interaction • https: //www. opengl. org/resources/libraries/glut/
 The “Color Cube” example • The “main” function: • • • initializes windows, display settings, and event handlers. Starts the event loop. Post the first Redisplay event.
The “Color Cube” example • The “main” function: • • • initializes windows, display settings, and event handlers. Starts the event loop. Post the first Redisplay event.
 The “Color Cube” example • The event loop: While (1) { // infinite loop event = get. Event(); // from the queue switch (event) { case Redisplay: display (); break; case Keyboard: keyboard(); break; case Window. Resize: resize(); post. Event(Redisplay); break; default: idle(); } }
The “Color Cube” example • The event loop: While (1) { // infinite loop event = get. Event(); // from the queue switch (event) { case Redisplay: display (); break; case Keyboard: keyboard(); break; case Window. Resize: resize(); post. Event(Redisplay); break; default: idle(); } }
 The “Color Cube” example • The “display” function: • • draws the game objects Open. GL is a state machine: set the active parameters before specifying vertices. Per vertex setting: color, normal, texture, … New vertices will use the current settings until they are changed.
The “Color Cube” example • The “display” function: • • draws the game objects Open. GL is a state machine: set the active parameters before specifying vertices. Per vertex setting: color, normal, texture, … New vertices will use the current settings until they are changed.
 The “Color Cube” example • The “keyboard” function: • • The event handler for keyboard events. Change display parameters to control the animation. E. g. rotation angles, parametric variable t, simulation variables such as speed. Don’t directly call the “display” function. Post the Redisplay event after everything is set. glut. Post. Redisplay();
The “Color Cube” example • The “keyboard” function: • • The event handler for keyboard events. Change display parameters to control the animation. E. g. rotation angles, parametric variable t, simulation variables such as speed. Don’t directly call the “display” function. Post the Redisplay event after everything is set. glut. Post. Redisplay();
 The “Color Cube” example • The “idle” function: • • • The event handler for the “idle” event. Invoked when no more event in the event queue. Change display parameters to control the background animation. E. g. rotation angles, parametric variable t, simulation variables such as speed. Don’t directly call the “display” function. Post the Redisplay event after everything is set. glut. Post. Redisplay();
The “Color Cube” example • The “idle” function: • • • The event handler for the “idle” event. Invoked when no more event in the event queue. Change display parameters to control the background animation. E. g. rotation angles, parametric variable t, simulation variables such as speed. Don’t directly call the “display” function. Post the Redisplay event after everything is set. glut. Post. Redisplay();
 The “Color Cube” example • The “resize/reshape” function: • • • The event handler for the “Window. Resize” event. Need to reset the viewport so that the display still fits in the viewport. Not need to post the Redisplay event. Glut does it fro you.
The “Color Cube” example • The “resize/reshape” function: • • • The event handler for the “Window. Resize” event. Need to reset the viewport so that the display still fits in the viewport. Not need to post the Redisplay event. Glut does it fro you.
 Animation
Animation
 Animation Keyframe: Most commonly used. Need to provide GUI for entering the keyframes. Procedural: For advanced physical simulation. Tracking live actor: Can be modified and saved.
Animation Keyframe: Most commonly used. Need to provide GUI for entering the keyframes. Procedural: For advanced physical simulation. Tracking live actor: Can be modified and saved.
 Animation: any change that has a visual effect. Motion Dynamics: movements (geometry change) Update Dynamics: attribute change (color, texture, …) Others: camera position, lighting, rendering techniques, …
Animation: any change that has a visual effect. Motion Dynamics: movements (geometry change) Update Dynamics: attribute change (color, texture, …) Others: camera position, lighting, rendering techniques, …
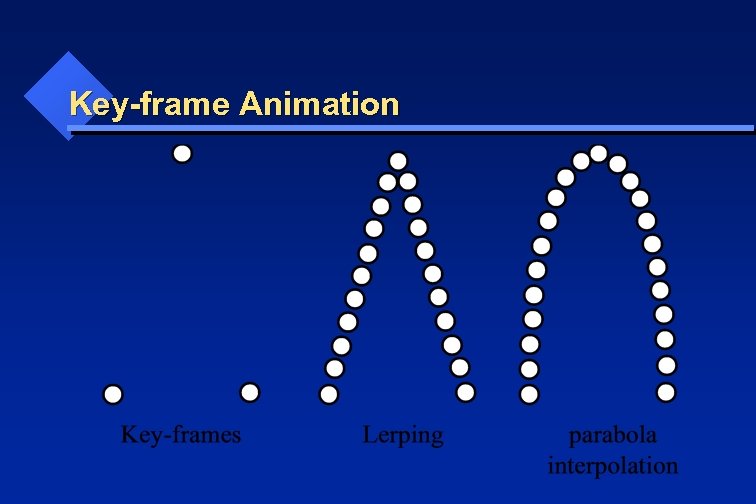
 Key-frame Animation • • Defining key-frames Inbetweening with interpolations: Lerping (linear interpolation) parabola interpolation
Key-frame Animation • • Defining key-frames Inbetweening with interpolations: Lerping (linear interpolation) parabola interpolation
 Key-frame Animation
Key-frame Animation
 Voxel Based Game Engine
Voxel Based Game Engine
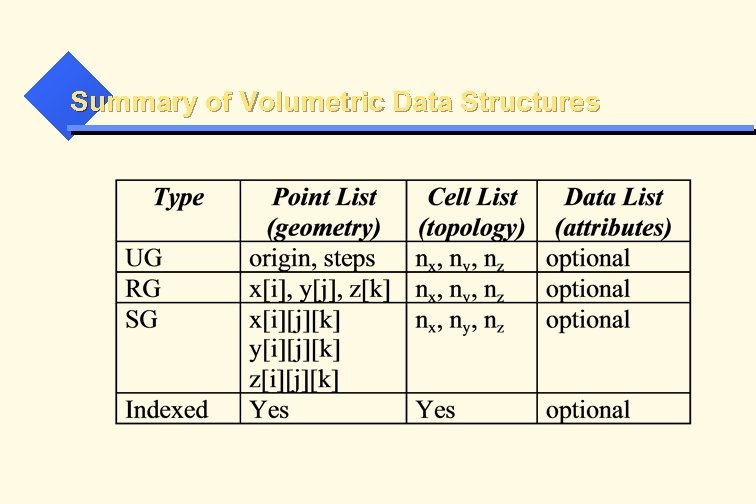 Summary of Volumetric Data Structures
Summary of Volumetric Data Structures
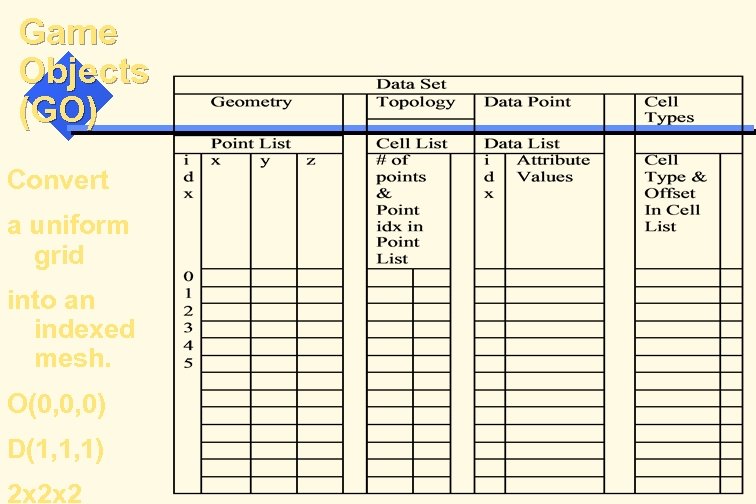 Game Objects (GO) Convert a uniform grid into an indexed mesh. O(0, 0, 0) D(1, 1, 1) 2 x 2 x 2
Game Objects (GO) Convert a uniform grid into an indexed mesh. O(0, 0, 0) D(1, 1, 1) 2 x 2 x 2
 Simple Ray Tracing for (each scan line in image ) { for (each pixel in the scan line ) { determine ray from eye through pixel; for(each object in scene) { if(object is intersected and is the closest considered thus far) record intersection point and object id. } set pixel’s color to that at closest object intersection point (using the REGULAR I formula. ) } }
Simple Ray Tracing for (each scan line in image ) { for (each pixel in the scan line ) { determine ray from eye through pixel; for(each object in scene) { if(object is intersected and is the closest considered thus far) record intersection point and object id. } set pixel’s color to that at closest object intersection point (using the REGULAR I formula. ) } }
 Tools for future voxel-based game engines: • VTK: open source voxel-based volume rendering library. http: //www. vtk. org • www. kitware. com • Take grids as input. • Output triangles to Open. GL.
Tools for future voxel-based game engines: • VTK: open source voxel-based volume rendering library. http: //www. vtk. org • www. kitware. com • Take grids as input. • Output triangles to Open. GL.


