f85359dfb52fe5d8b60e8b0cd424ec44.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 INTELLIGENT VISION SYSTEMS ENT 496 Lecture 1. Ms. HEMA C. R. IVS and its Components Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1
INTELLIGENT VISION SYSTEMS ENT 496 Lecture 1. Ms. HEMA C. R. IVS and its Components Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1
 • What is Intelligent Vision Road Map • Image and Vision • Intelligent Vision Systems • Components of an Intelligent Vision System [IVS] • Applications of vision systems • Advantages of IVS • Vision Optics • Frame Grabbers • Lighting and Illumination Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 2
• What is Intelligent Vision Road Map • Image and Vision • Intelligent Vision Systems • Components of an Intelligent Vision System [IVS] • Applications of vision systems • Advantages of IVS • Vision Optics • Frame Grabbers • Lighting and Illumination Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 2
 Intelligent Vision Why do Machine/ Robots need vision? – Vision is provided to enhance the component of Intelligence Why is Vision important? – About 70% of our intelligence is from derived from vision. – The remaining 30% from sound. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 3
Intelligent Vision Why do Machine/ Robots need vision? – Vision is provided to enhance the component of Intelligence Why is Vision important? – About 70% of our intelligence is from derived from vision. – The remaining 30% from sound. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 3
 Intelligent Vision • Intelligent Vision is the application of computer vision to industry. • It is a subfield of engineering that encompasses – – Computer science, Optics Mechanical engineering and Industrial automation. • One of the most common applications of IVS is the inspection of manufactured goods such as semiconductor chips, automobiles, food and pharmaceuticals. • Bio-mementics is changing all this and vision applications are now being designed to serve Hema –ENT 496– 4 the community Lecture 1
Intelligent Vision • Intelligent Vision is the application of computer vision to industry. • It is a subfield of engineering that encompasses – – Computer science, Optics Mechanical engineering and Industrial automation. • One of the most common applications of IVS is the inspection of manufactured goods such as semiconductor chips, automobiles, food and pharmaceuticals. • Bio-mementics is changing all this and vision applications are now being designed to serve Hema –ENT 496– 4 the community Lecture 1
 Image and Vision • Image – Images are two-dimensional projections of the three-dimensional world • Vision – Vision is the most Complex of human senses, about a fourth of the brain’s volume is devoted to it. • Image Processing – Processing images to give new images • Computer Vision – Deals with what the images mean – aims to interpret images • Intelligent Vision – Apply vision and image processing • Vision System – A Vision System recovers useful information about a scene from its two dimensional projections Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 5
Image and Vision • Image – Images are two-dimensional projections of the three-dimensional world • Vision – Vision is the most Complex of human senses, about a fourth of the brain’s volume is devoted to it. • Image Processing – Processing images to give new images • Computer Vision – Deals with what the images mean – aims to interpret images • Intelligent Vision – Apply vision and image processing • Vision System – A Vision System recovers useful information about a scene from its two dimensional projections Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 5
 Intelligent Vision Systems • Characteristics – Ability to extract pertinent information from a background of irrelevant details – The capacity to learn from examples and apply to new situations – Ability to infer facts from incomplete information – Capability to generate self motivated goals and formulate plans for meeting these goals. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 6
Intelligent Vision Systems • Characteristics – Ability to extract pertinent information from a background of irrelevant details – The capacity to learn from examples and apply to new situations – Ability to infer facts from incomplete information – Capability to generate self motivated goals and formulate plans for meeting these goals. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 6
 Components of a Intelligent Vision System – Input source • objects, scene, prints etc – Optics • sensors, digital cameras – Lighting • illumination levels – A part sensor [optional] • to indicate presence of objects – A frame grabber • stores images & interface – PC platform [optional] – Inspection software • Image processing algorithms Digital I/O Hema –ENT 496– – Lecture 1 • Display, Print, Interface 7
Components of a Intelligent Vision System – Input source • objects, scene, prints etc – Optics • sensors, digital cameras – Lighting • illumination levels – A part sensor [optional] • to indicate presence of objects – A frame grabber • stores images & interface – PC platform [optional] – Inspection software • Image processing algorithms Digital I/O Hema –ENT 496– – Lecture 1 • Display, Print, Interface 7
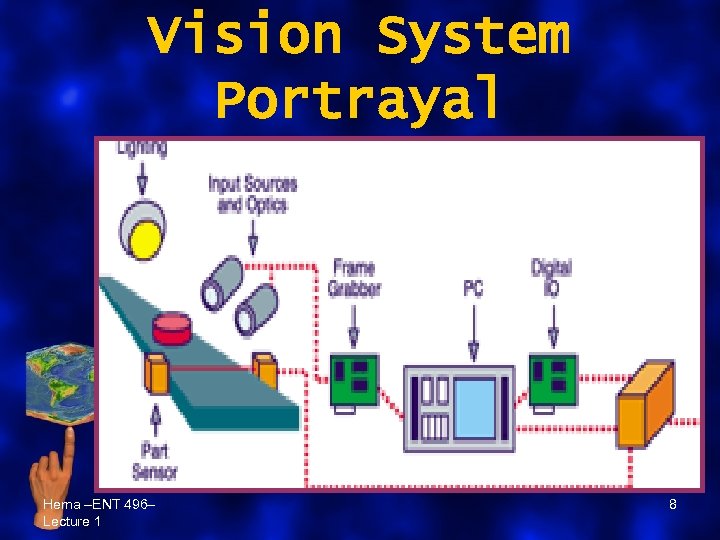 Vision System Portrayal Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 8
Vision System Portrayal Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 8
 Operations to be performed by IVS • Describe images, objects and physical world – Mathematical models of image and objects and knowledge representation • Image Processing – Improves image for human and computer consumption, highlight / extract relevant feature The Ultimate Aim of a Vision System is to recognize objects • Segmentation within edge, regions, surfaces etc. – Extract features such aa image • Pattern Recognition – Classify the images • Measurement Analysis – Measure features on the object • Image Understanding – Locate objects in the image, classify them and build 3 D Hema –ENT 496– models 9 Lecture 1
Operations to be performed by IVS • Describe images, objects and physical world – Mathematical models of image and objects and knowledge representation • Image Processing – Improves image for human and computer consumption, highlight / extract relevant feature The Ultimate Aim of a Vision System is to recognize objects • Segmentation within edge, regions, surfaces etc. – Extract features such aa image • Pattern Recognition – Classify the images • Measurement Analysis – Measure features on the object • Image Understanding – Locate objects in the image, classify them and build 3 D Hema –ENT 496– models 9 Lecture 1
 Applications of Intelligent Vision Systems • • Large-scale industrial manufacture Safety systems in industrial environments Inspection of pre-manufactured objects Visual stock control and management systems (counting, barcode reading, store interfaces for digital systems) • Control of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) • Automated monitoring of sites for security and safety Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 10
Applications of Intelligent Vision Systems • • Large-scale industrial manufacture Safety systems in industrial environments Inspection of pre-manufactured objects Visual stock control and management systems (counting, barcode reading, store interfaces for digital systems) • Control of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) • Automated monitoring of sites for security and safety Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 10
 Applications of an Intelligent Vision System • Monitoring of agricultural production • Quality control and refinement of food products • Retail automation • Consumer equipment control • Medical imaging processes (e. g. Interventional Radiology) • Medical remote examination and procedures Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 11
Applications of an Intelligent Vision System • Monitoring of agricultural production • Quality control and refinement of food products • Retail automation • Consumer equipment control • Medical imaging processes (e. g. Interventional Radiology) • Medical remote examination and procedures Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 11
 Autonomous Vehicles Transport Safety Aerial Navigation Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 12
Autonomous Vehicles Transport Safety Aerial Navigation Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 12
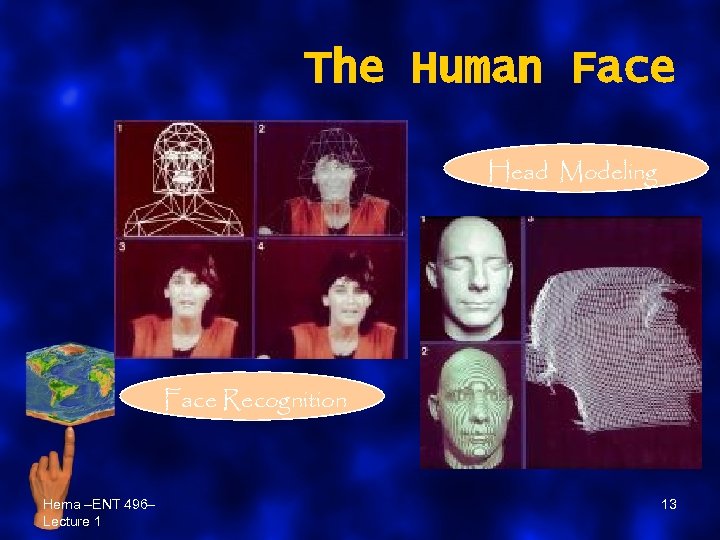 The Human Face Head Modeling Face Recognition Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 13
The Human Face Head Modeling Face Recognition Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 13
 Industrial Inspection Detecting Objects Intelligent parts Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 14
Industrial Inspection Detecting Objects Intelligent parts Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 14
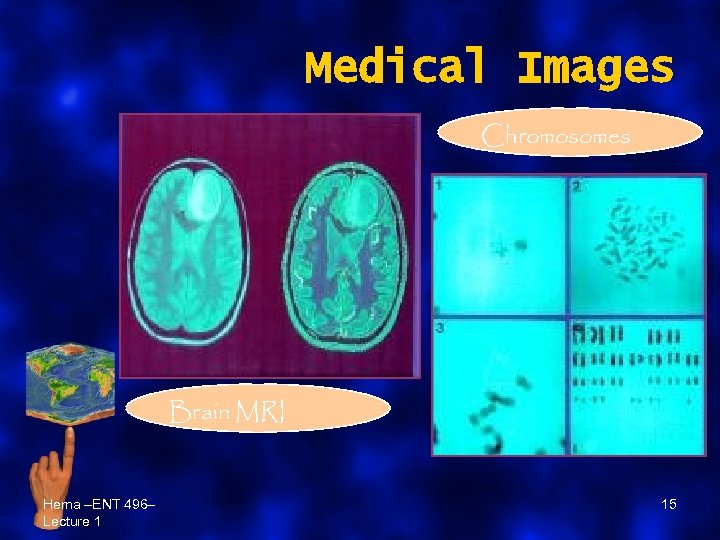 Medical Images Chromosomes Brain MRI Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 15
Medical Images Chromosomes Brain MRI Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 15
 Remote Sensing Land Management Crop Classification Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 16
Remote Sensing Land Management Crop Classification Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 16
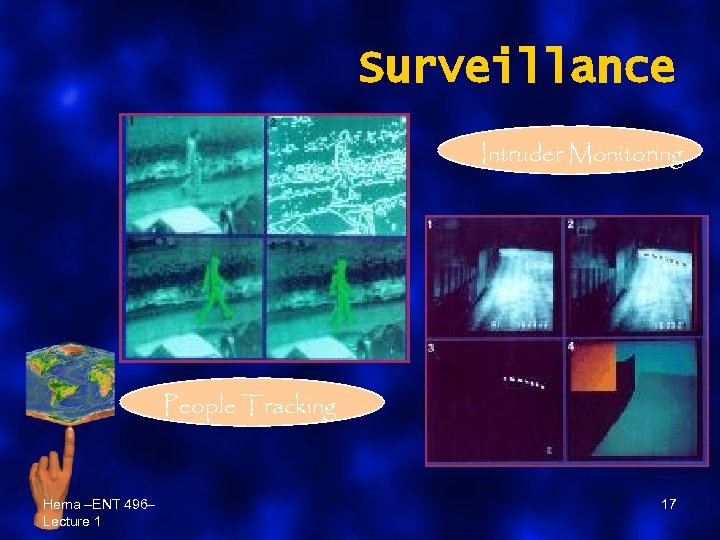 Surveillance Intruder Monitoring People Tracking Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 17
Surveillance Intruder Monitoring People Tracking Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 17
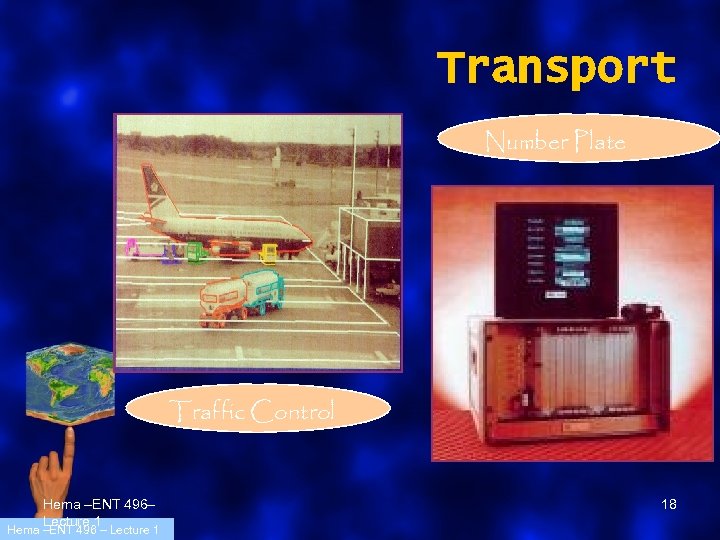 Transport Number Plate Traffic Control Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Hema –ENT 496 – Lecture 1 18
Transport Number Plate Traffic Control Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Hema –ENT 496 – Lecture 1 18
 Advantages of IVS in Industries • Cutting out defective goods • Making better use of raw materials • Cutting the cost of quality control • Enabling real-time process monitoring • Improving employment conditions Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 19
Advantages of IVS in Industries • Cutting out defective goods • Making better use of raw materials • Cutting the cost of quality control • Enabling real-time process monitoring • Improving employment conditions Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 19
 Vision Optics • A Cognex In-Sight Vision Sensor • • • Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Vision Systems – Stand alone – PC based Smart Camera – Self contained [no pc req. ] • CCD image sensors Neural Network-Based • CMOS image sensors Zi. CAMs from JAI Pulnix Vision Sensors – Integrated devices Compact Vision System – No programming required from National Instruments – Between smart cams and vision systems Digital Cameras – CCD image – CMOS image – Flash memory – Memory stick – Smart. Media cards 20 – Removable [microdrives, CD, DVD]
Vision Optics • A Cognex In-Sight Vision Sensor • • • Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Vision Systems – Stand alone – PC based Smart Camera – Self contained [no pc req. ] • CCD image sensors Neural Network-Based • CMOS image sensors Zi. CAMs from JAI Pulnix Vision Sensors – Integrated devices Compact Vision System – No programming required from National Instruments – Between smart cams and vision systems Digital Cameras – CCD image – CMOS image – Flash memory – Memory stick – Smart. Media cards 20 – Removable [microdrives, CD, DVD]
 Imaging Sensors • Image sensors convert light into electric charge and process it into electronic signals • Image Sensors – Charge Coupled Device CCD • All pixels are devoted to light capture • Output is uniform • High image quality • Used in cell phone cameras – Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS • Pixels devoted to light capture are limited • Output is not uniform • High Image quality • Used in professional and industrial cameras Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 21
Imaging Sensors • Image sensors convert light into electric charge and process it into electronic signals • Image Sensors – Charge Coupled Device CCD • All pixels are devoted to light capture • Output is uniform • High image quality • Used in cell phone cameras – Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS • Pixels devoted to light capture are limited • Output is not uniform • High Image quality • Used in professional and industrial cameras Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 21
![Frame Grabbers • A frame grabber is a device to acquire [grab] and convert Frame Grabbers • A frame grabber is a device to acquire [grab] and convert](https://present5.com/presentation/f85359dfb52fe5d8b60e8b0cd424ec44/image-22.jpg) Frame Grabbers • A frame grabber is a device to acquire [grab] and convert analog to digital images. Modern FG have many additional features like more storage, multiple camera links etc. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 22
Frame Grabbers • A frame grabber is a device to acquire [grab] and convert analog to digital images. Modern FG have many additional features like more storage, multiple camera links etc. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 22
 Frame Grabbers • A typical frame grabber consists of – a circuit to recover the horizontal and vertical synchronization pulses from the input signal; – An analog to digital converter – a colour decoder circuit, a function that can also be implemented in software – some memory for storing the acquired image (frame buffer) – a bus interface through which the main processor can control the acquisition and access the data. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 23
Frame Grabbers • A typical frame grabber consists of – a circuit to recover the horizontal and vertical synchronization pulses from the input signal; – An analog to digital converter – a colour decoder circuit, a function that can also be implemented in software – some memory for storing the acquired image (frame buffer) – a bus interface through which the main processor can control the acquisition and access the data. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 23
 Lighting • Correct lighting is the single most important design parameter in a vision system • Selection of a light source for a vision application is governed by three factors: – The type of features that must be captured by the vision system – The need for the part to be either moving or stationary when the image is captured. – The degree of visibility of the environment in which the image is captured. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 24
Lighting • Correct lighting is the single most important design parameter in a vision system • Selection of a light source for a vision application is governed by three factors: – The type of features that must be captured by the vision system – The need for the part to be either moving or stationary when the image is captured. – The degree of visibility of the environment in which the image is captured. Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 24
 Lighting Techniques • The three lighting techniques used in vision applications are: – Front lighting, – Back lighting – Structured lighting Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 25
Lighting Techniques • The three lighting techniques used in vision applications are: – Front lighting, – Back lighting – Structured lighting Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 25
 Front Lighting Sources Ring Shape Lighting to detect loose caps Spot Lighting to check chip orientation in embossed tape Tube Lighting to detect stains on sheets Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Area type lighting to detect hole position in lead frames 26
Front Lighting Sources Ring Shape Lighting to detect loose caps Spot Lighting to check chip orientation in embossed tape Tube Lighting to detect stains on sheets Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 Area type lighting to detect hole position in lead frames 26
 Interesting Links Visit http: //www. Intelligentvisiononline. org http: //www. eeng. dcu. e/~whelanp/proverbs. pdf to understand vision systems better References: http: //www. bmva. ac. uk/apps/ http: //en. wikipedia. org www. Intelligentvisiononline. org http: //homepages. inf. ed. ac. uk/rbf/CVonline Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 27
Interesting Links Visit http: //www. Intelligentvisiononline. org http: //www. eeng. dcu. e/~whelanp/proverbs. pdf to understand vision systems better References: http: //www. bmva. ac. uk/apps/ http: //en. wikipedia. org www. Intelligentvisiononline. org http: //homepages. inf. ed. ac. uk/rbf/CVonline Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1 27
 IVS and its Components End of Lecture 1 Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1
IVS and its Components End of Lecture 1 Hema –ENT 496– Lecture 1


