e99e1a1c040e64a0f1bec846f7ffe454.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Intelligent Information Processing (IIP-2002) Montreal, 29 August 2002 Personalized Web Interaction Wolfgang Wahlster German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence DFKI Gmb. H Stuhlsatzenhausweg 3 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany phone: (+49 681) 302 -5252/4162 fax: (+49 681) 302 -5341 e-mail: wahlster@dfki. de WWW: http: //www. dfki. de/~wahlster
Intelligent Information Processing (IIP-2002) Montreal, 29 August 2002 Personalized Web Interaction Wolfgang Wahlster German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence DFKI Gmb. H Stuhlsatzenhausweg 3 66123 Saarbruecken, Germany phone: (+49 681) 302 -5252/4162 fax: (+49 681) 302 -5341 e-mail: wahlster@dfki. de WWW: http: //www. dfki. de/~wahlster
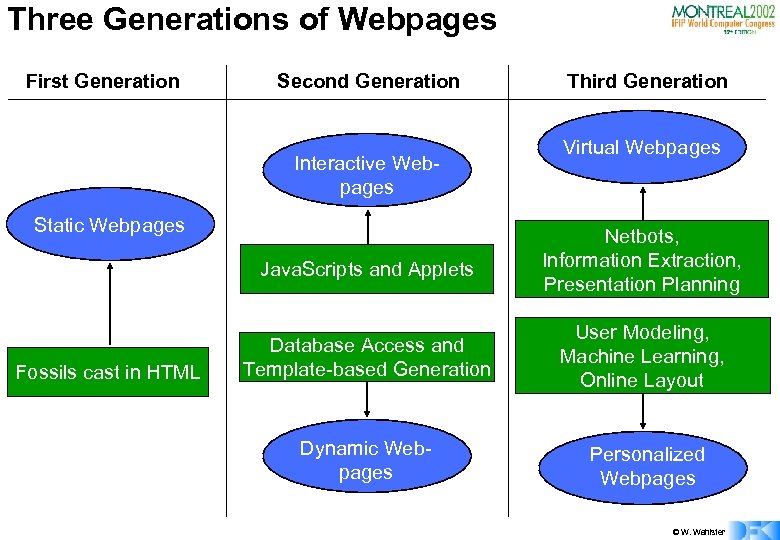 Three Generations of Webpages First Generation Second Generation Interactive Webpages Static Webpages Third Generation Virtual Webpages Java. Scripts and Applets Fossils cast in HTML Netbots, Information Extraction, Presentation Planning Database Access and Template-based Generation User Modeling, Machine Learning, Online Layout Dynamic Webpages Personalized Webpages © W. Wahlster
Three Generations of Webpages First Generation Second Generation Interactive Webpages Static Webpages Third Generation Virtual Webpages Java. Scripts and Applets Fossils cast in HTML Netbots, Information Extraction, Presentation Planning Database Access and Template-based Generation User Modeling, Machine Learning, Online Layout Dynamic Webpages Personalized Webpages © W. Wahlster
 Outline of the Talk 1. 3 rd Generation Websites: Adaptive and Virtual Webpages 2. The Need for Personalization 3. Component Technologies for Personalized Web Interaction 4. - Constraint-based Layout 5. - Plan-based Presentation Generation 6. 4. Multimodal Interaction with Personalized Presentation Agents 7. 5. Affective Personalization 8. 6. Conclusions © W. Wahlster
Outline of the Talk 1. 3 rd Generation Websites: Adaptive and Virtual Webpages 2. The Need for Personalization 3. Component Technologies for Personalized Web Interaction 4. - Constraint-based Layout 5. - Plan-based Presentation Generation 6. 4. Multimodal Interaction with Personalized Presentation Agents 7. 5. Affective Personalization 8. 6. Conclusions © W. Wahlster
 What is a Virtual Webpage? Virtual Memory, Virtual Relation, Virtual Reality. . . A Virtual Webpage l is generated on the fly as a combination of various media objects from multiple websites or as a transformation of a real webpage. l looks like a real webpage, but is not persistently stored. l integrates generated and retrieved material in a coordinated way. l can be tailored to a particular user profile and adapted to a particular interaction context. l has an underlying representation of the presentation context so that an Interface Agent can comment, point to and explain its components. © W. Wahlster
What is a Virtual Webpage? Virtual Memory, Virtual Relation, Virtual Reality. . . A Virtual Webpage l is generated on the fly as a combination of various media objects from multiple websites or as a transformation of a real webpage. l looks like a real webpage, but is not persistently stored. l integrates generated and retrieved material in a coordinated way. l can be tailored to a particular user profile and adapted to a particular interaction context. l has an underlying representation of the presentation context so that an Interface Agent can comment, point to and explain its components. © W. Wahlster
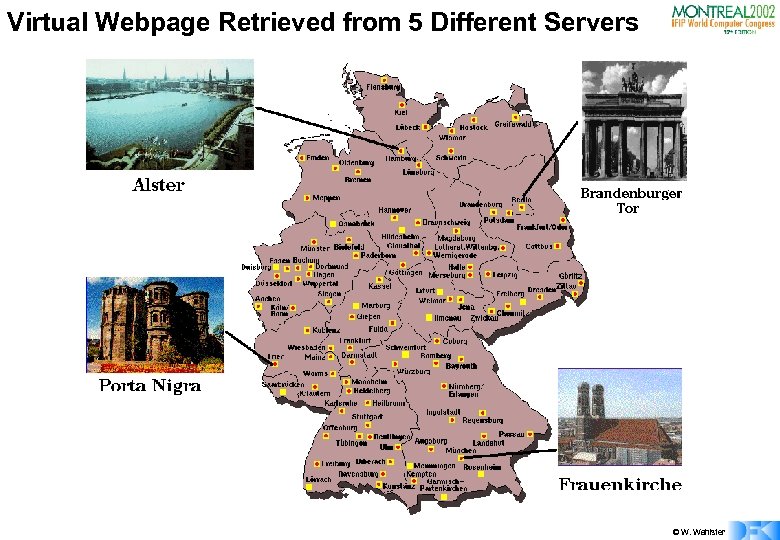 Virtual Webpage Retrieved from 5 Different Servers © W. Wahlster
Virtual Webpage Retrieved from 5 Different Servers © W. Wahlster
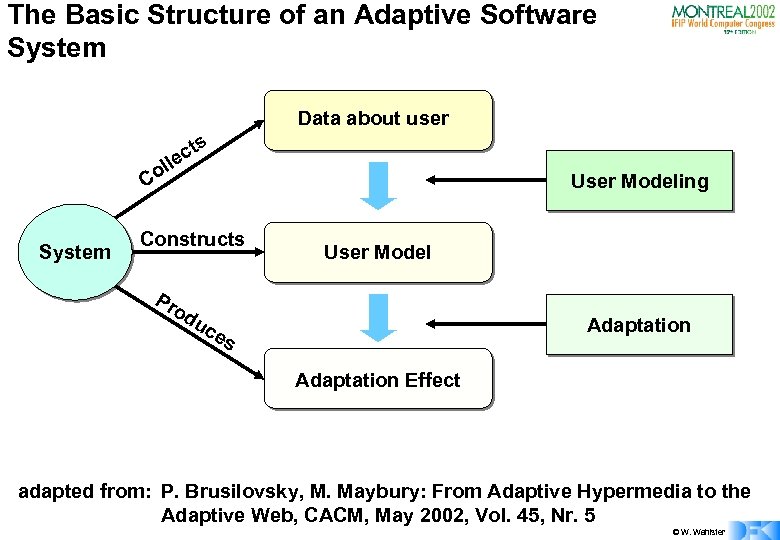 The Basic Structure of an Adaptive Software System Data about user cts le l Co System User Modeling Constructs Pr o du ce User Model Adaptation s Adaptation Effect adapted from: P. Brusilovsky, M. Maybury: From Adaptive Hypermedia to the Adaptive Web, CACM, May 2002, Vol. 45, Nr. 5 © W. Wahlster
The Basic Structure of an Adaptive Software System Data about user cts le l Co System User Modeling Constructs Pr o du ce User Model Adaptation s Adaptation Effect adapted from: P. Brusilovsky, M. Maybury: From Adaptive Hypermedia to the Adaptive Web, CACM, May 2002, Vol. 45, Nr. 5 © W. Wahlster
 Two Meanings of Personalization = Adaptation of a Webpage to a Particular User Personalization = Presentation of a Webpage by a Life-Like Character © W. Wahlster
Two Meanings of Personalization = Adaptation of a Webpage to a Particular User Personalization = Presentation of a Webpage by a Life-Like Character © W. Wahlster
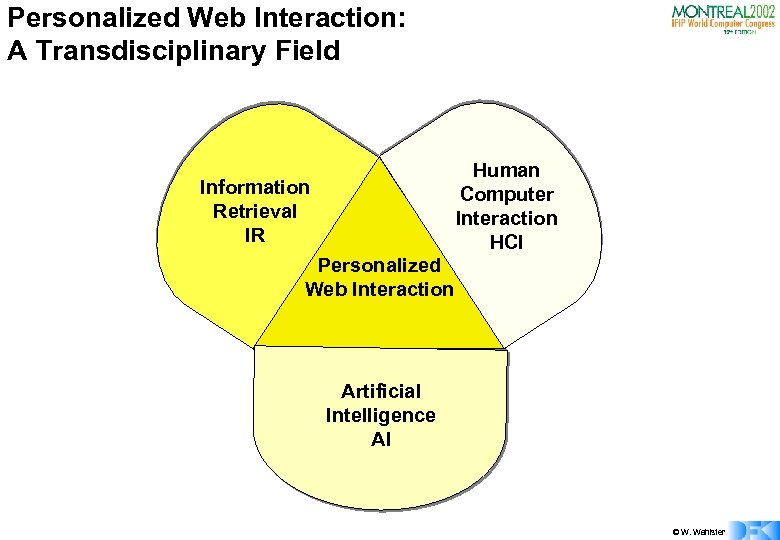 Personalized Web Interaction: A Transdisciplinary Field Human Computer Interaction HCI Information Retrieval IR Personalized Web Interaction Artificial Intelligence AI © W. Wahlster
Personalized Web Interaction: A Transdisciplinary Field Human Computer Interaction HCI Information Retrieval IR Personalized Web Interaction Artificial Intelligence AI © W. Wahlster
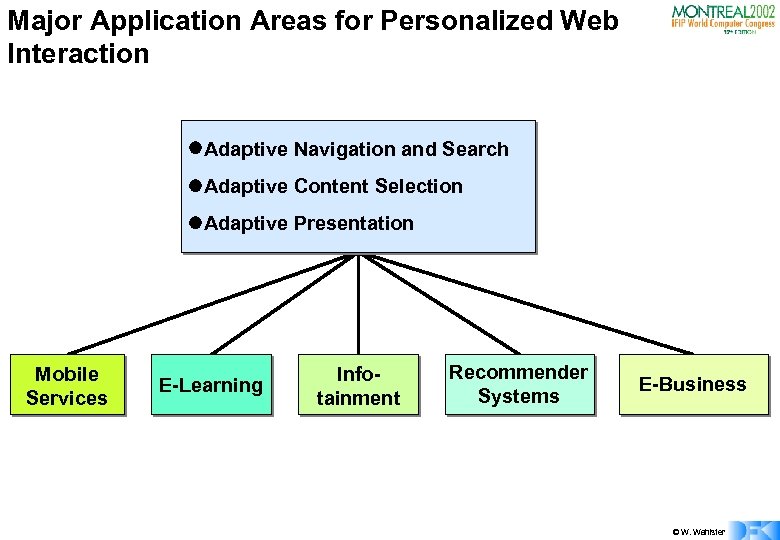 Major Application Areas for Personalized Web Interaction l. Adaptive Navigation and Search l. Adaptive Content Selection l. Adaptive Presentation Mobile Services E-Learning Infotainment Recommender Systems E-Business © W. Wahlster
Major Application Areas for Personalized Web Interaction l. Adaptive Navigation and Search l. Adaptive Content Selection l. Adaptive Presentation Mobile Services E-Learning Infotainment Recommender Systems E-Business © W. Wahlster
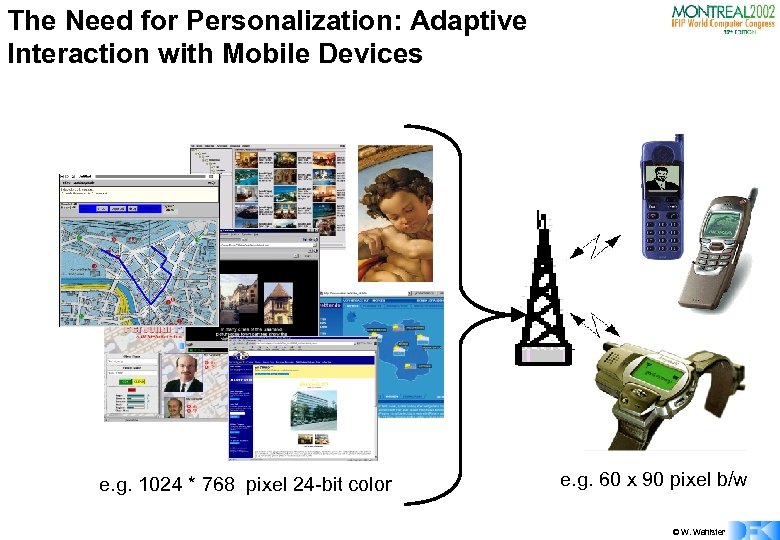 The Need for Personalization: Adaptive Interaction with Mobile Devices ? e. g. 1024 * 768 pixel 24 -bit color e. g. 60 x 90 pixel b/w © W. Wahlster
The Need for Personalization: Adaptive Interaction with Mobile Devices ? e. g. 1024 * 768 pixel 24 -bit color e. g. 60 x 90 pixel b/w © W. Wahlster
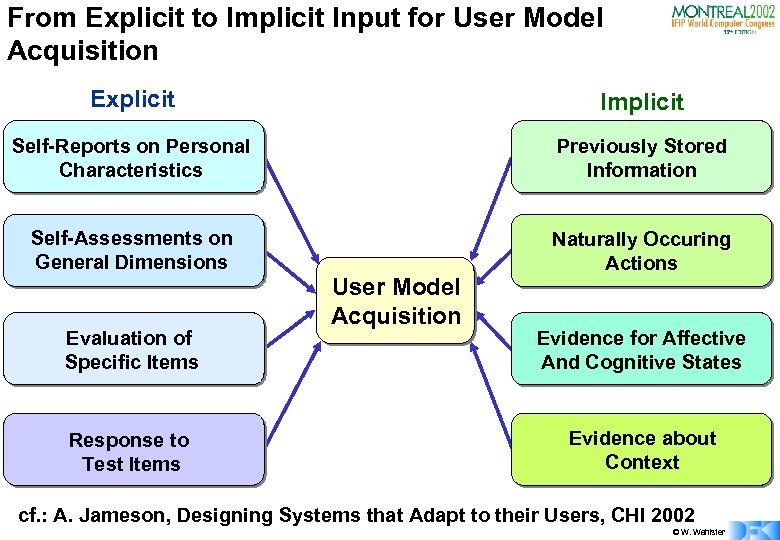 From Explicit to Implicit Input for User Model Acquisition Explicit Implicit Self-Reports on Personal Characteristics Previously Stored Information Self-Assessments on General Dimensions Naturally Occuring Actions Evaluation of Specific Items Response to Test Items User Model Acquisition Evidence for Affective And Cognitive States Evidence about Context cf. : A. Jameson, Designing Systems that Adapt to their Users, CHI 2002 © W. Wahlster
From Explicit to Implicit Input for User Model Acquisition Explicit Implicit Self-Reports on Personal Characteristics Previously Stored Information Self-Assessments on General Dimensions Naturally Occuring Actions Evaluation of Specific Items Response to Test Items User Model Acquisition Evidence for Affective And Cognitive States Evidence about Context cf. : A. Jameson, Designing Systems that Adapt to their Users, CHI 2002 © W. Wahlster
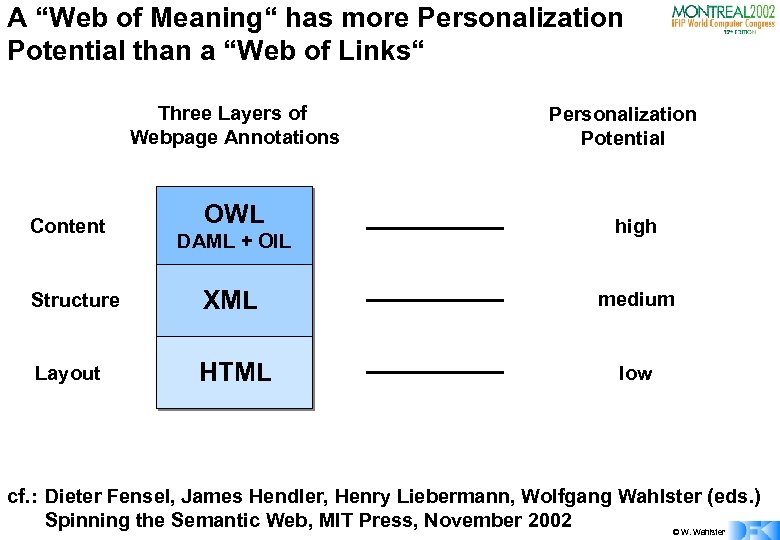 A “Web of Meaning“ has more Personalization Potential than a “Web of Links“ Three Layers of Webpage Annotations Content OWL DAML + OIL Personalization Potential high Structure XML medium Layout HTML low cf. : Dieter Fensel, James Hendler, Henry Liebermann, Wolfgang Wahlster (eds. ) Spinning the Semantic Web, MIT Press, November 2002 © W. Wahlster
A “Web of Meaning“ has more Personalization Potential than a “Web of Links“ Three Layers of Webpage Annotations Content OWL DAML + OIL Personalization Potential high Structure XML medium Layout HTML low cf. : Dieter Fensel, James Hendler, Henry Liebermann, Wolfgang Wahlster (eds. ) Spinning the Semantic Web, MIT Press, November 2002 © W. Wahlster
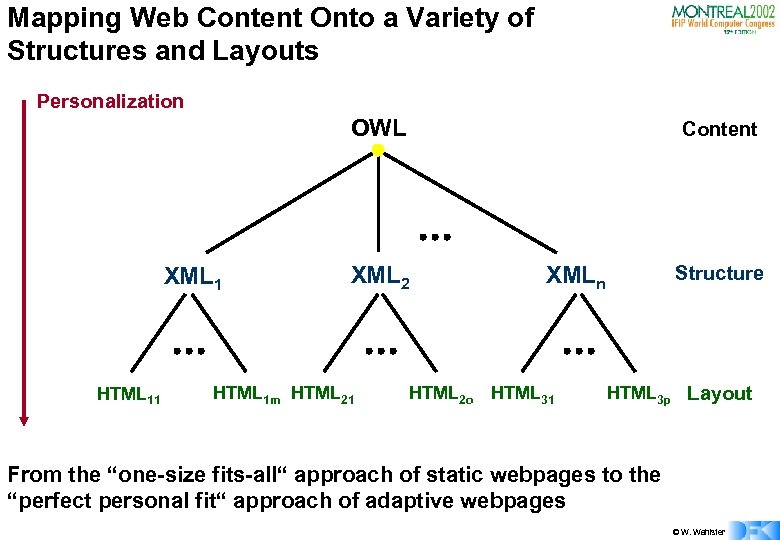 Mapping Web Content Onto a Variety of Structures and Layouts Personalization OWL XML 1 HTML 11 Content XML 2 HTML 1 m HTML 21 XMLn HTML 2 o HTML 31 Structure HTML 3 p Layout From the “one-size fits-all“ approach of static webpages to the “perfect personal fit“ approach of adaptive webpages © W. Wahlster
Mapping Web Content Onto a Variety of Structures and Layouts Personalization OWL XML 1 HTML 11 Content XML 2 HTML 1 m HTML 21 XMLn HTML 2 o HTML 31 Structure HTML 3 p Layout From the “one-size fits-all“ approach of static webpages to the “perfect personal fit“ approach of adaptive webpages © W. Wahlster
![The Architecture of WIP (cf. [Wahlster et al. 91]): The First System for the The Architecture of WIP (cf. [Wahlster et al. 91]): The First System for the](https://present5.com/presentation/e99e1a1c040e64a0f1bec846f7ffe454/image-14.jpg) The Architecture of WIP (cf. [Wahlster et al. 91]): The First System for the Plan-based Personalization of Presentations Presentation Goal Presentation Planner Layout Manager Text Design Generation Parameters Text Realization Graphics Design Document Design Plan Graphics Realization Illustrated Document Application Knowledge coded in RAT Mower Espresso Machine Modem Basic Ontology User Model RAT Presentation Strategies . . . TAG Graphics Design Strategies © W. Wahlster
The Architecture of WIP (cf. [Wahlster et al. 91]): The First System for the Plan-based Personalization of Presentations Presentation Goal Presentation Planner Layout Manager Text Design Generation Parameters Text Realization Graphics Design Document Design Plan Graphics Realization Illustrated Document Application Knowledge coded in RAT Mower Espresso Machine Modem Basic Ontology User Model RAT Presentation Strategies . . . TAG Graphics Design Strategies © W. Wahlster
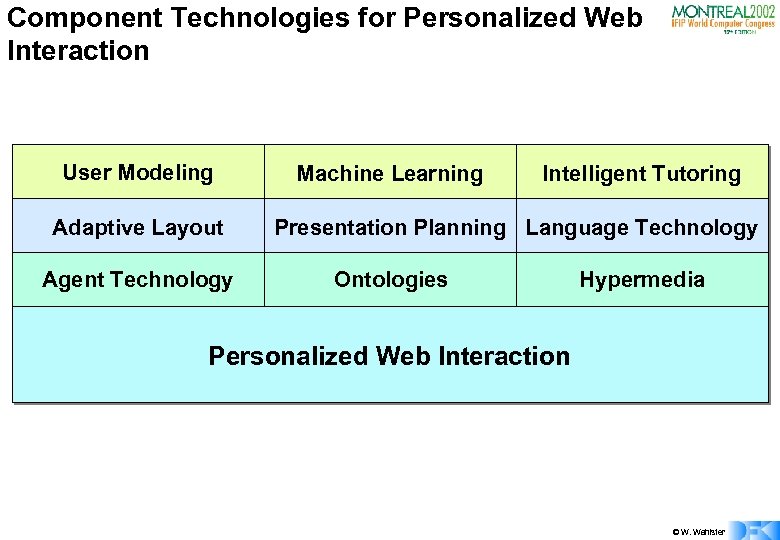 Component Technologies for Personalized Web Interaction User Modeling Adaptive Layout Agent Technology Machine Learning Intelligent Tutoring Presentation Planning Language Technology Ontologies Hypermedia Personalized Web Interaction © W. Wahlster
Component Technologies for Personalized Web Interaction User Modeling Adaptive Layout Agent Technology Machine Learning Intelligent Tutoring Presentation Planning Language Technology Ontologies Hypermedia Personalized Web Interaction © W. Wahlster
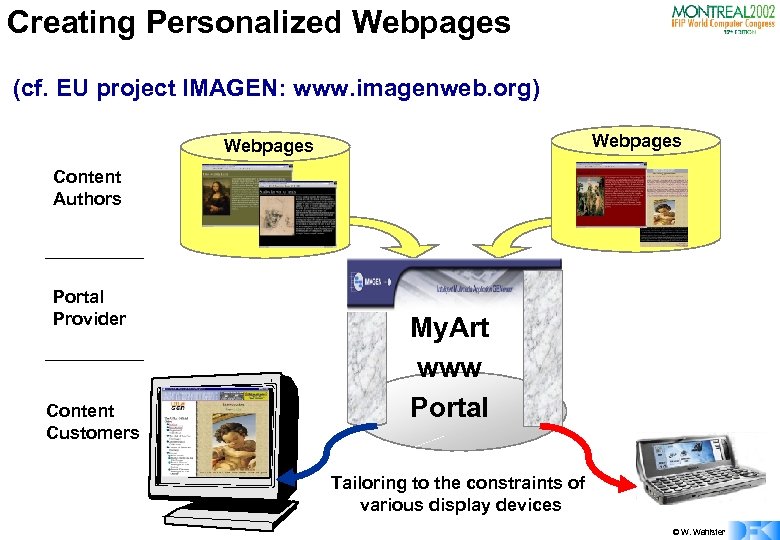 Creating Personalized Webpages (cf. EU project IMAGEN: www. imagenweb. org) Webpages Content Authors Portal Provider Content Customers My. Art www Portal Tailoring to the constraints of various display devices © W. Wahlster
Creating Personalized Webpages (cf. EU project IMAGEN: www. imagenweb. org) Webpages Content Authors Portal Provider Content Customers My. Art www Portal Tailoring to the constraints of various display devices © W. Wahlster
 Creating a New Webpage from Available Media Objects 1. Content Selection 2. Content Packaging 3. Layout Revision © W. Wahlster
Creating a New Webpage from Available Media Objects 1. Content Selection 2. Content Packaging 3. Layout Revision © W. Wahlster
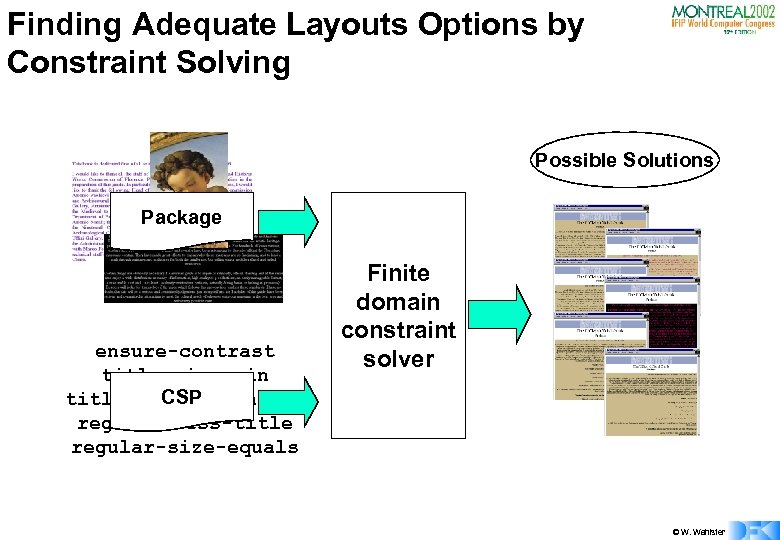 Finding Adequate Layouts Options by Constraint Solving Possible Solutions Package ensure-contrast title-size-min CSP title-size-hierarchy regular-less-title regular-size-equals Finite domain constraint solver © W. Wahlster
Finding Adequate Layouts Options by Constraint Solving Possible Solutions Package ensure-contrast title-size-min CSP title-size-hierarchy regular-less-title regular-size-equals Finite domain constraint solver © W. Wahlster
 Example of a Layout Constraint (Kröner 2002) Purpose – use a title font that is larger than all fonts of subtitles Approach – Add a binary constraint between the related font sizes Constraint Formulation
Example of a Layout Constraint (Kröner 2002) Purpose – use a title font that is larger than all fonts of subtitles Approach – Add a binary constraint between the related font sizes Constraint Formulation
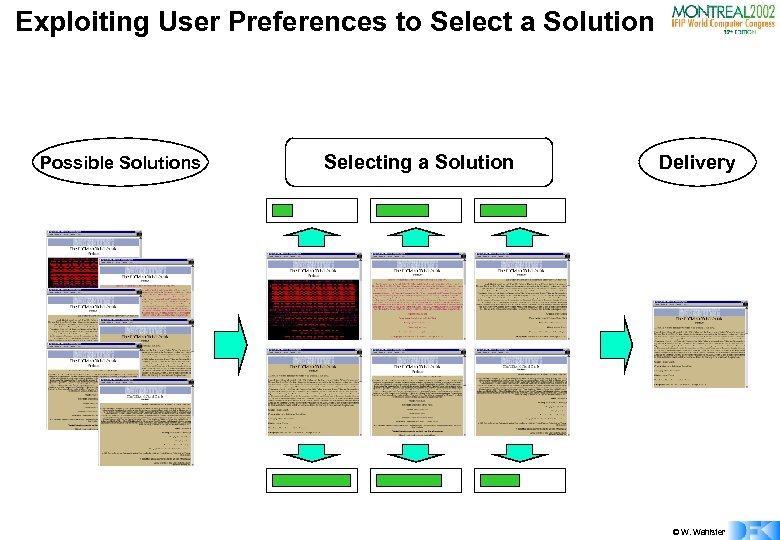 Exploiting User Preferences to Select a Solution Possible Solutions Selecting a Solution Delivery © W. Wahlster
Exploiting User Preferences to Select a Solution Possible Solutions Selecting a Solution Delivery © W. Wahlster
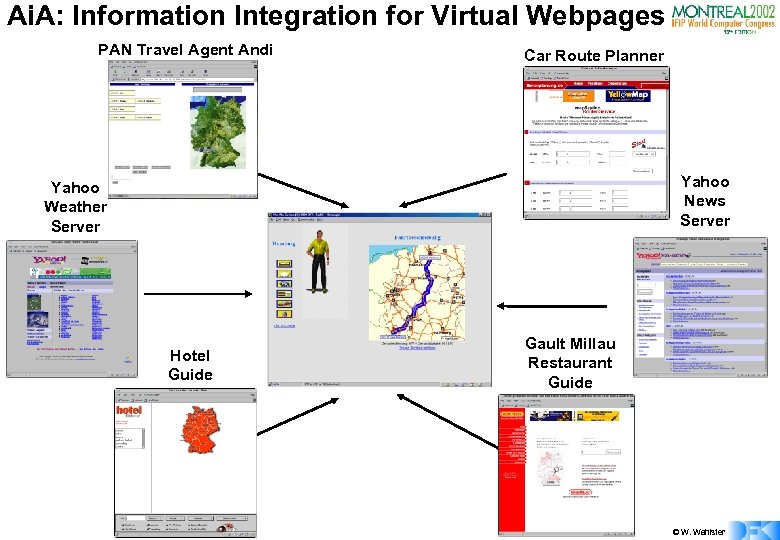 Ai. A: Information Integration for Virtual Webpages PAN Travel Agent Andi Car Route Planner Yahoo News Server Yahoo Weather Server Hotel Guide Gault Millau Restaurant Guide © W. Wahlster
Ai. A: Information Integration for Virtual Webpages PAN Travel Agent Andi Car Route Planner Yahoo News Server Yahoo Weather Server Hotel Guide Gault Millau Restaurant Guide © W. Wahlster
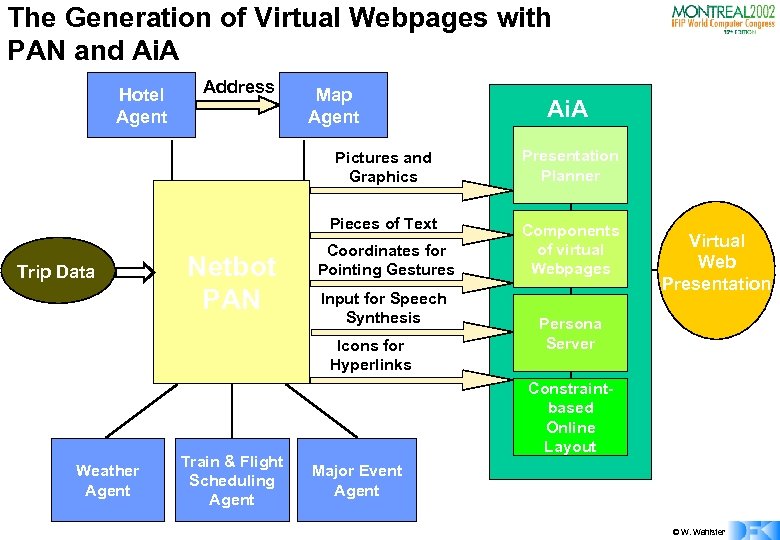 The Generation of Virtual Webpages with PAN and Ai. A Hotel Agent Address Map Agent Ai. A Pictures and Graphics Pieces of Text Trip Data Netbot PAN Presentation Planner Components of virtual Webpages Coordinates for Pointing Gestures Input for Speech Synthesis Icons for Hyperlinks Weather Agent Train & Flight Scheduling Agent Virtual Web Presentation Persona Server Constraintbased Online Layout Major Event Agent © W. Wahlster
The Generation of Virtual Webpages with PAN and Ai. A Hotel Agent Address Map Agent Ai. A Pictures and Graphics Pieces of Text Trip Data Netbot PAN Presentation Planner Components of virtual Webpages Coordinates for Pointing Gestures Input for Speech Synthesis Icons for Hyperlinks Weather Agent Train & Flight Scheduling Agent Virtual Web Presentation Persona Server Constraintbased Online Layout Major Event Agent © W. Wahlster
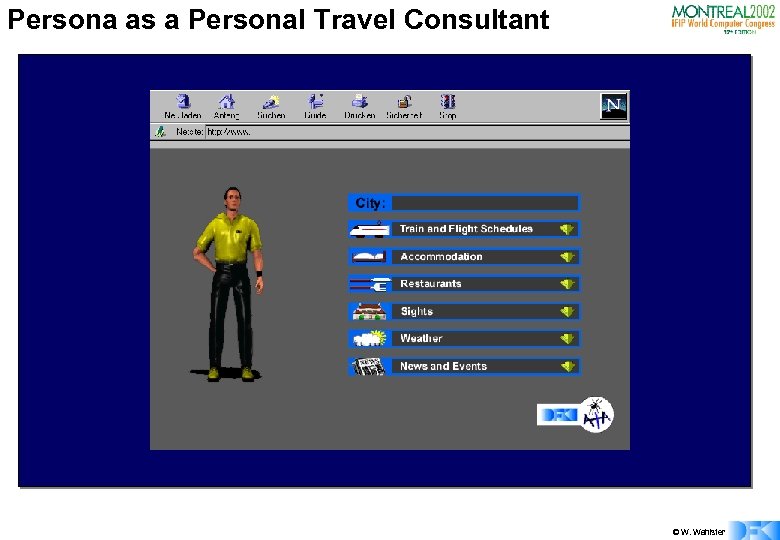 Persona as a Personal Travel Consultant © W. Wahlster
Persona as a Personal Travel Consultant © W. Wahlster
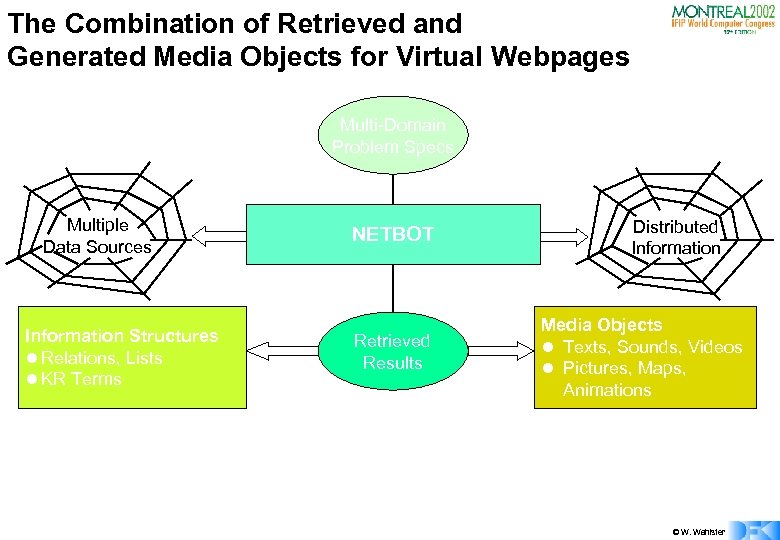 The Combination of Retrieved and Generated Media Objects for Virtual Webpages Multi-Domain Problem Specs Multiple Data Sources Information Structures l Relations, Lists l KR Terms NETBOT Retrieved Results Distributed Information Media Objects l Texts, Sounds, Videos l Pictures, Maps, Animations © W. Wahlster
The Combination of Retrieved and Generated Media Objects for Virtual Webpages Multi-Domain Problem Specs Multiple Data Sources Information Structures l Relations, Lists l KR Terms NETBOT Retrieved Results Distributed Information Media Objects l Texts, Sounds, Videos l Pictures, Maps, Animations © W. Wahlster
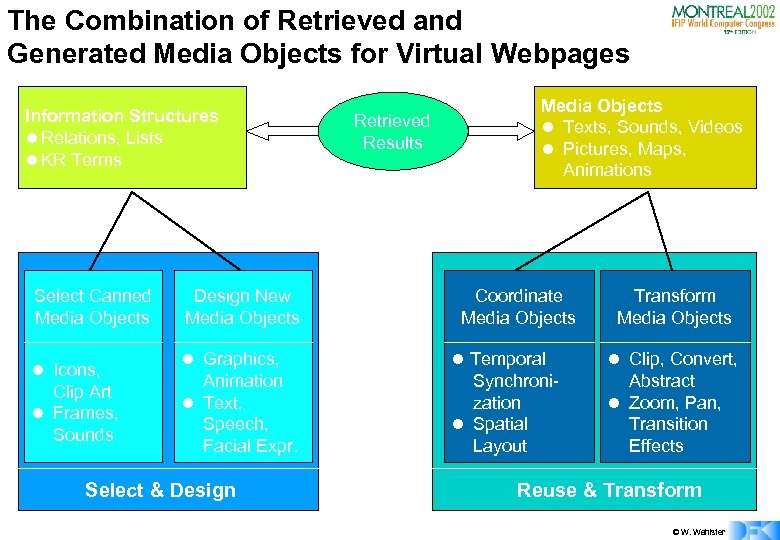 The Combination of Retrieved and Generated Media Objects for Virtual Webpages Information Structures l Relations, Lists l KR Terms Select Canned Media Objects Design New Media Objects l Icons, Clip Art l Frames, Sounds l Graphics, Animation l Text, Speech, Facial Expr. Select & Design Retrieved Results Media Objects l Texts, Sounds, Videos l Pictures, Maps, Animations Coordinate Media Objects l Temporal Synchronization l Spatial Layout Transform Media Objects l Clip, Convert, Abstract l Zoom, Pan, Transition Effects Reuse & Transform © W. Wahlster
The Combination of Retrieved and Generated Media Objects for Virtual Webpages Information Structures l Relations, Lists l KR Terms Select Canned Media Objects Design New Media Objects l Icons, Clip Art l Frames, Sounds l Graphics, Animation l Text, Speech, Facial Expr. Select & Design Retrieved Results Media Objects l Texts, Sounds, Videos l Pictures, Maps, Animations Coordinate Media Objects l Temporal Synchronization l Spatial Layout Transform Media Objects l Clip, Convert, Abstract l Zoom, Pan, Transition Effects Reuse & Transform © W. Wahlster
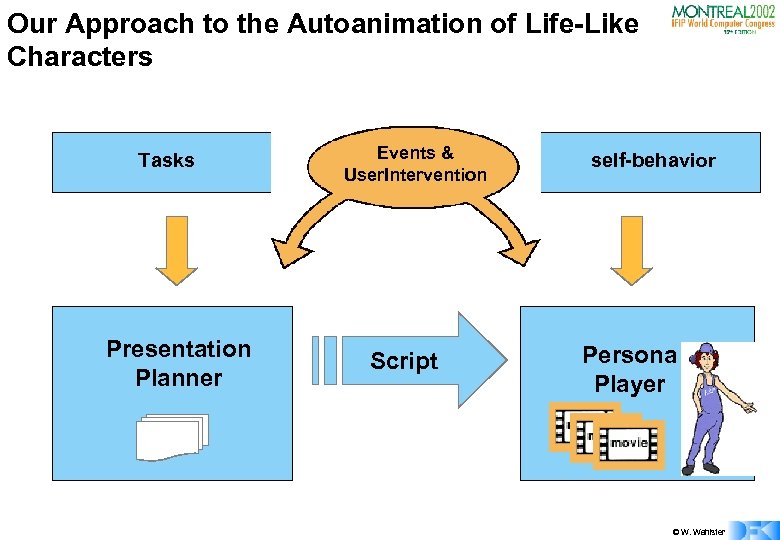 Our Approach to the Autoanimation of Life-Like Characters Tasks Presentation Planner Events & User. Intervention Script self-behavior Persona Player © W. Wahlster
Our Approach to the Autoanimation of Life-Like Characters Tasks Presentation Planner Events & User. Intervention Script self-behavior Persona Player © W. Wahlster
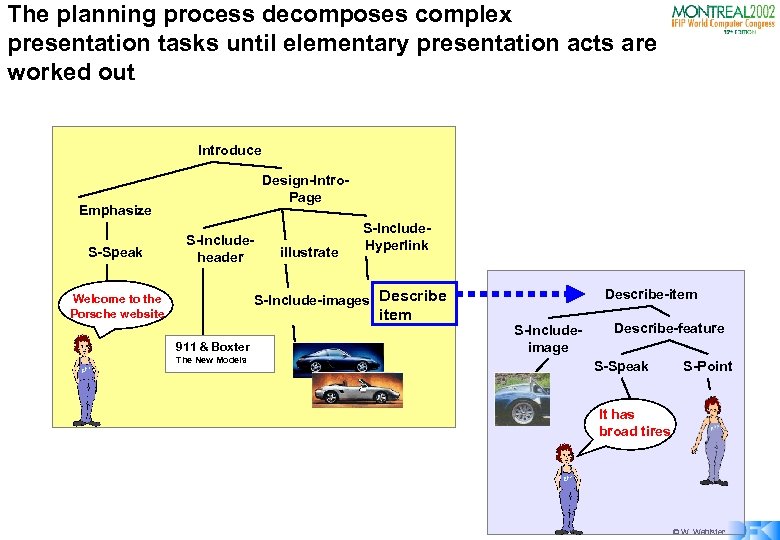 The planning process decomposes complex presentation tasks until elementary presentation acts are worked out Introduce Design-Intro. Page Emphasize S-Speak S-Includeheader illustrate S-Include. Hyperlink Describe-item S-Include-images Describe Welcome to the Porsche website item 911 & Boxter The New Models S-Includeimage Describe-feature S-Speak S-Point It has broad tires © W. Wahlster
The planning process decomposes complex presentation tasks until elementary presentation acts are worked out Introduce Design-Intro. Page Emphasize S-Speak S-Includeheader illustrate S-Include. Hyperlink Describe-item S-Include-images Describe Welcome to the Porsche website item 911 & Boxter The New Models S-Includeimage Describe-feature S-Speak S-Point It has broad tires © W. Wahlster
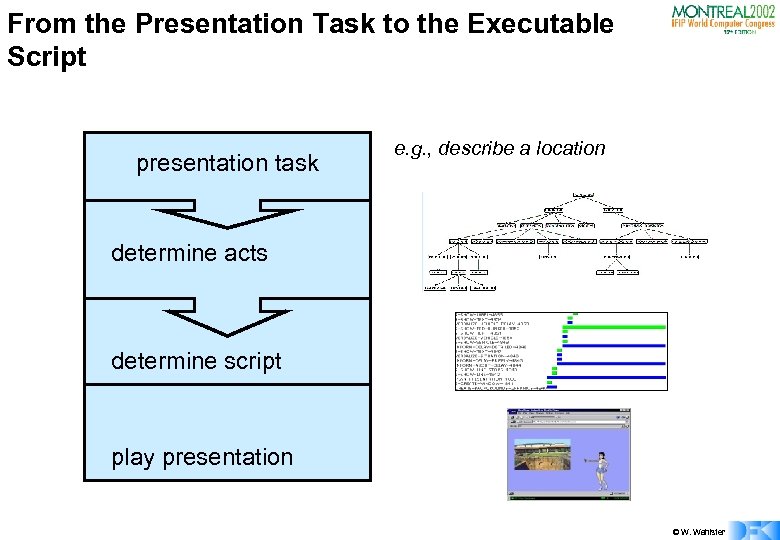 From the Presentation Task to the Executable Script presentation task e. g. , describe a location determine acts determine script play presentation © W. Wahlster
From the Presentation Task to the Executable Script presentation task e. g. , describe a location determine acts determine script play presentation © W. Wahlster
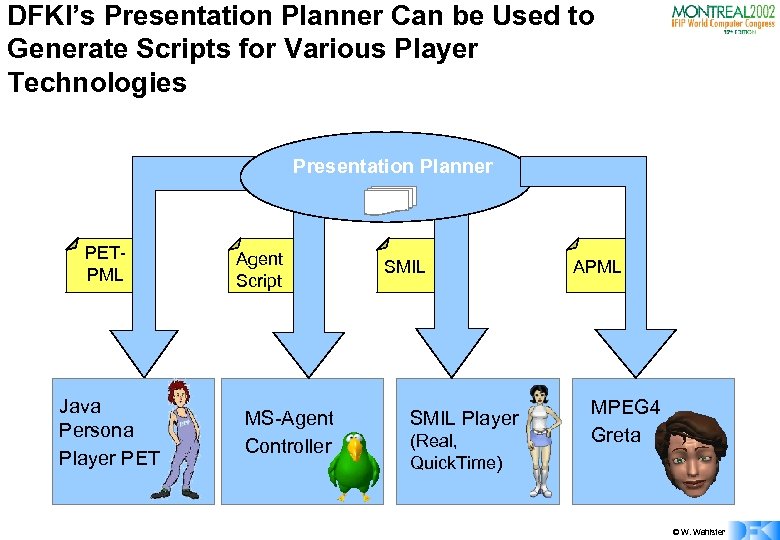 DFKI’s Presentation Planner Can be Used to Generate Scripts for Various Player Technologies Presentation Planner PETPML Java Persona Player PET Agent Script MS-Agent Controller SMIL Player (Real, Quick. Time) APML MPEG 4 Greta © W. Wahlster
DFKI’s Presentation Planner Can be Used to Generate Scripts for Various Player Technologies Presentation Planner PETPML Java Persona Player PET Agent Script MS-Agent Controller SMIL Player (Real, Quick. Time) APML MPEG 4 Greta © W. Wahlster
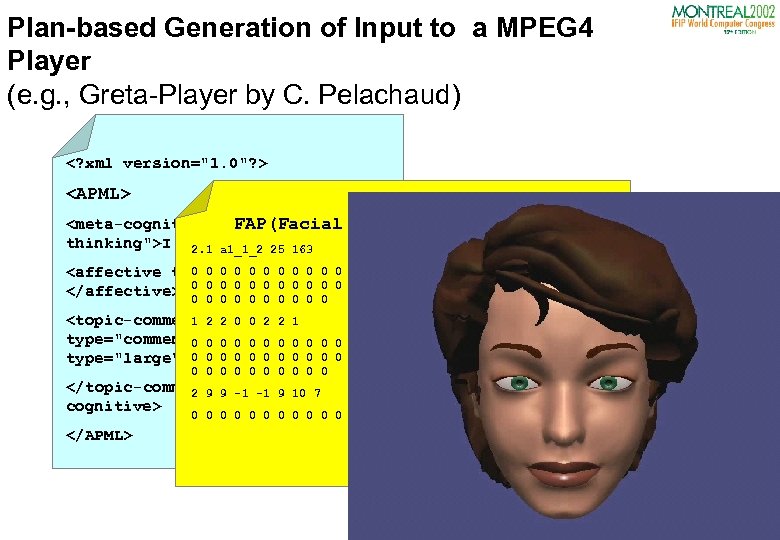 Plan-based Generation of Input to a MPEG 4 Player (e. g. , Greta-Player by C. Pelachaud)
Plan-based Generation of Input to a MPEG 4 Player (e. g. , Greta-Player by C. Pelachaud)
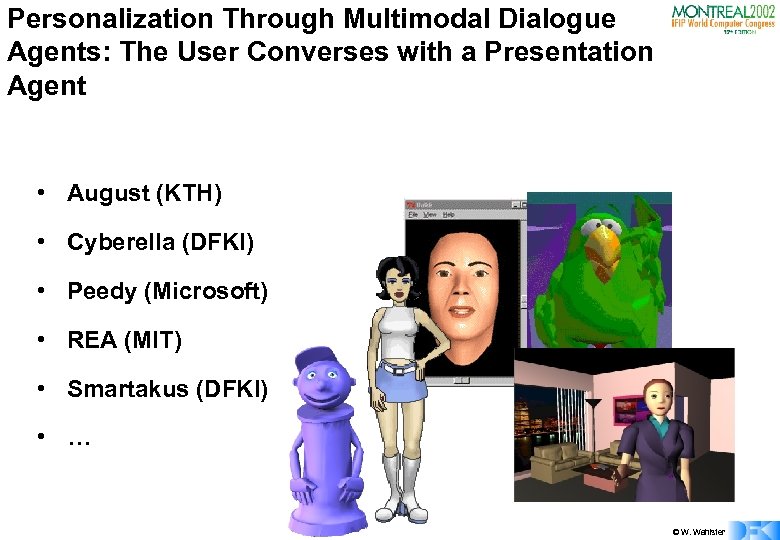 Personalization Through Multimodal Dialogue Agents: The User Converses with a Presentation Agent • August (KTH) • Cyberella (DFKI) • Peedy (Microsoft) • REA (MIT) • Smartakus (DFKI) • … © W. Wahlster
Personalization Through Multimodal Dialogue Agents: The User Converses with a Presentation Agent • August (KTH) • Cyberella (DFKI) • Peedy (Microsoft) • REA (MIT) • Smartakus (DFKI) • … © W. Wahlster
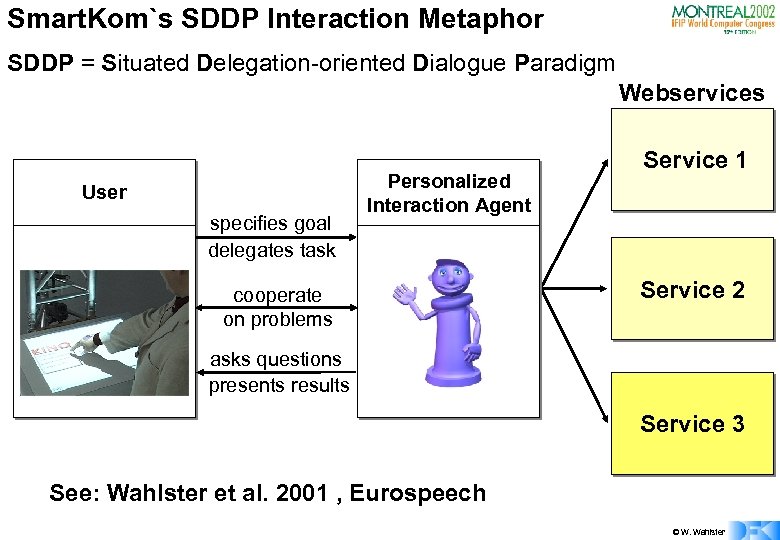 Smart. Kom`s SDDP Interaction Metaphor SDDP = Situated Delegation-oriented Dialogue Paradigm Webservices User specifies goal delegates task Personalized Interaction Agent cooperate on problems Service 1 Service 2 asks questions presents results Service 3 See: Wahlster et al. 2001 , Eurospeech © W. Wahlster
Smart. Kom`s SDDP Interaction Metaphor SDDP = Situated Delegation-oriented Dialogue Paradigm Webservices User specifies goal delegates task Personalized Interaction Agent cooperate on problems Service 1 Service 2 asks questions presents results Service 3 See: Wahlster et al. 2001 , Eurospeech © W. Wahlster
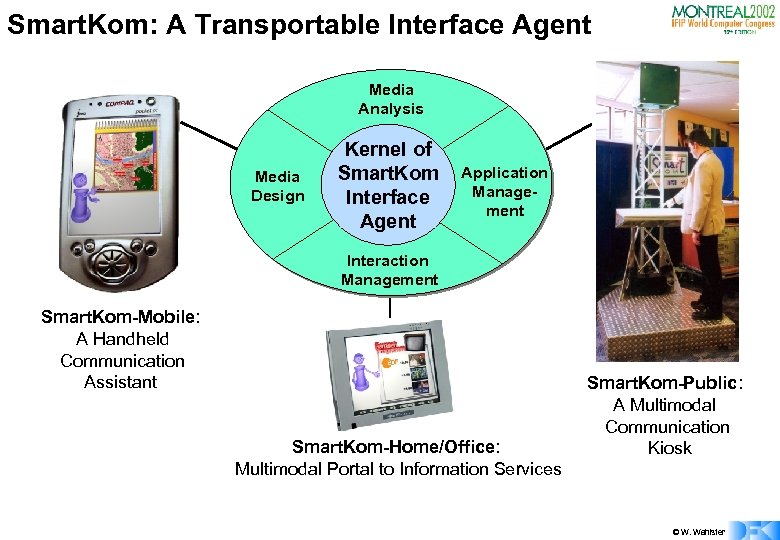 Smart. Kom: A Transportable Interface Agent Media Analysis Media Design Kernel of Smart. Kom Interface Agent Application Management Interaction Management Smart. Kom-Mobile: A Handheld Communication Assistant Smart. Kom-Home/Office: Multimodal Portal to Information Services Smart. Kom-Public: A Multimodal Communication Kiosk © W. Wahlster
Smart. Kom: A Transportable Interface Agent Media Analysis Media Design Kernel of Smart. Kom Interface Agent Application Management Interaction Management Smart. Kom-Mobile: A Handheld Communication Assistant Smart. Kom-Home/Office: Multimodal Portal to Information Services Smart. Kom-Public: A Multimodal Communication Kiosk © W. Wahlster
 Personalized Interaction with Web. TVs via Smart. Kom (DFKI with Sony, Philips, Siemens) Example: Multimodal Access to Electronic Program Guides for TV User: Switch on the TV. Smartakus: Okay, the TV is on. User: Which channels are presenting the latest news right now? Smartakus: CNN and NTV are presenting news. User: Please record this news channel on a videotape. Smartakus: Okay, the VCR is now recording the selected program. © W. Wahlster
Personalized Interaction with Web. TVs via Smart. Kom (DFKI with Sony, Philips, Siemens) Example: Multimodal Access to Electronic Program Guides for TV User: Switch on the TV. Smartakus: Okay, the TV is on. User: Which channels are presenting the latest news right now? Smartakus: CNN and NTV are presenting news. User: Please record this news channel on a videotape. Smartakus: Okay, the VCR is now recording the selected program. © W. Wahlster
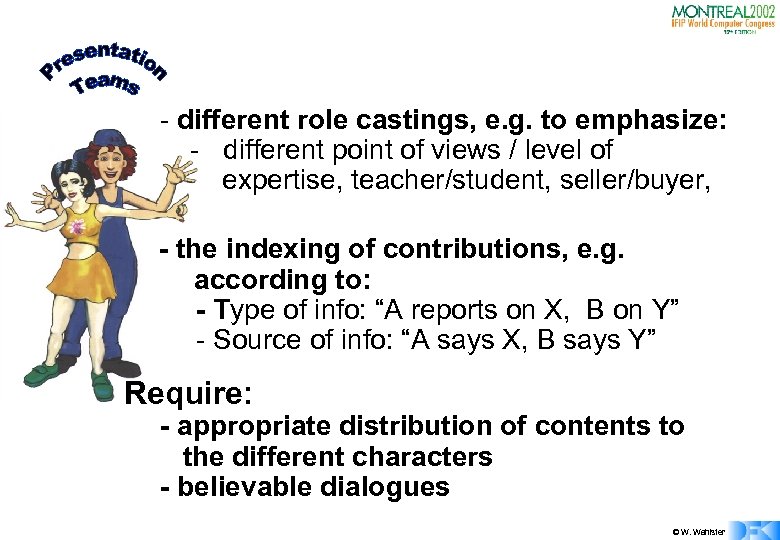 Presentation Teams - different role castings, e. g. to emphasize: - different point of views / level of expertise, teacher/student, seller/buyer, - the indexing of contributions, e. g. according to: - Type of info: “A reports on X, B on Y” - Source of info: “A says X, B says Y” Require: - appropriate distribution of contents to the different characters - believable dialogues © W. Wahlster
Presentation Teams - different role castings, e. g. to emphasize: - different point of views / level of expertise, teacher/student, seller/buyer, - the indexing of contributions, e. g. according to: - Type of info: “A reports on X, B on Y” - Source of info: “A says X, B says Y” Require: - appropriate distribution of contents to the different characters - believable dialogues © W. Wahlster
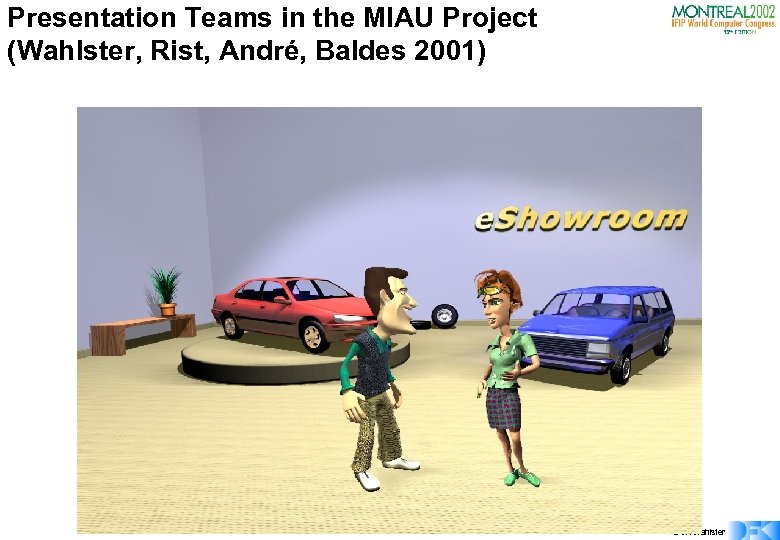 Presentation Teams in the MIAU Project (Wahlster, Rist, André, Baldes 2001) © W. Wahlster
Presentation Teams in the MIAU Project (Wahlster, Rist, André, Baldes 2001) © W. Wahlster
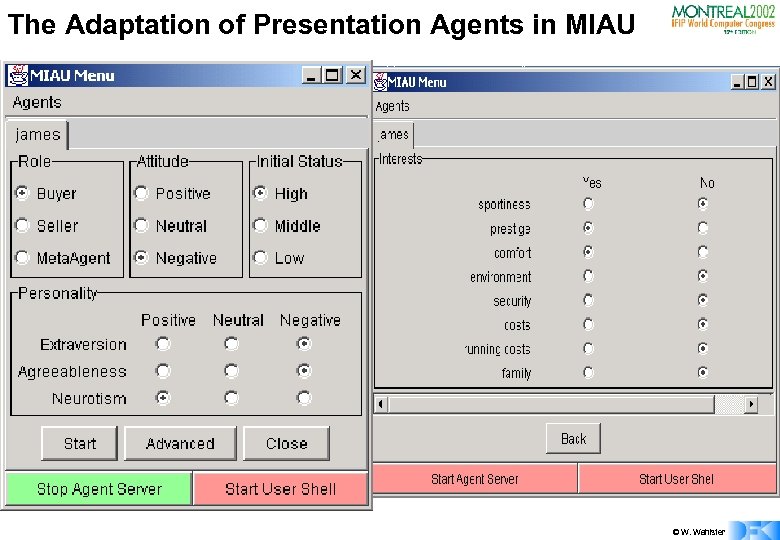 The Adaptation of Presentation Agents in MIAU • Character-Centered Approach – Story is not defined by a script, but by the character‘s role, personality, status, attitude etc. © W. Wahlster
The Adaptation of Presentation Agents in MIAU • Character-Centered Approach – Story is not defined by a script, but by the character‘s role, personality, status, attitude etc. © W. Wahlster
 Interactive Presentation Teams in MIAU (DFKI) Hello, I am Peter. © W. Wahlster
Interactive Presentation Teams in MIAU (DFKI) Hello, I am Peter. © W. Wahlster
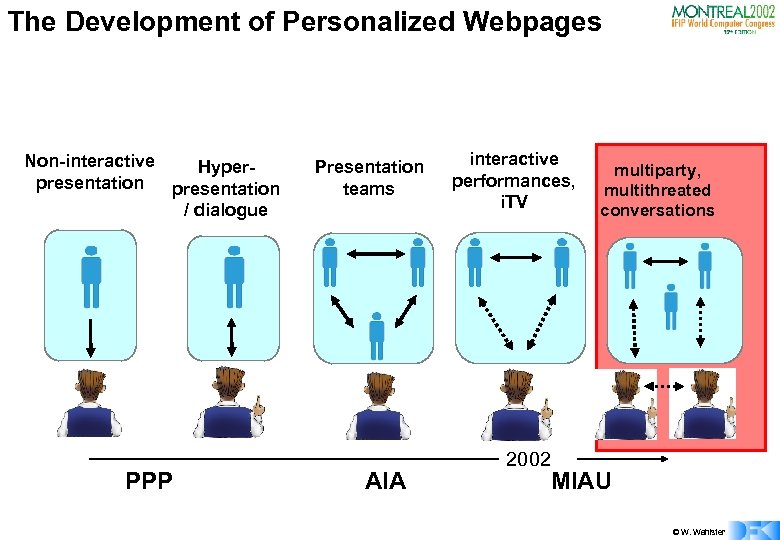 The Development of Personalized Webpages Non-interactive Hyperpresentation / dialogue PPP Presentation teams AIA interactive performances, i. TV 2002 multiparty, multithreated conversations MIAU © W. Wahlster
The Development of Personalized Webpages Non-interactive Hyperpresentation / dialogue PPP Presentation teams AIA interactive performances, i. TV 2002 multiparty, multithreated conversations MIAU © W. Wahlster
 Personalized Multiparty Interaction with Multiple Interface Agents © W. Wahlster
Personalized Multiparty Interaction with Multiple Interface Agents © W. Wahlster
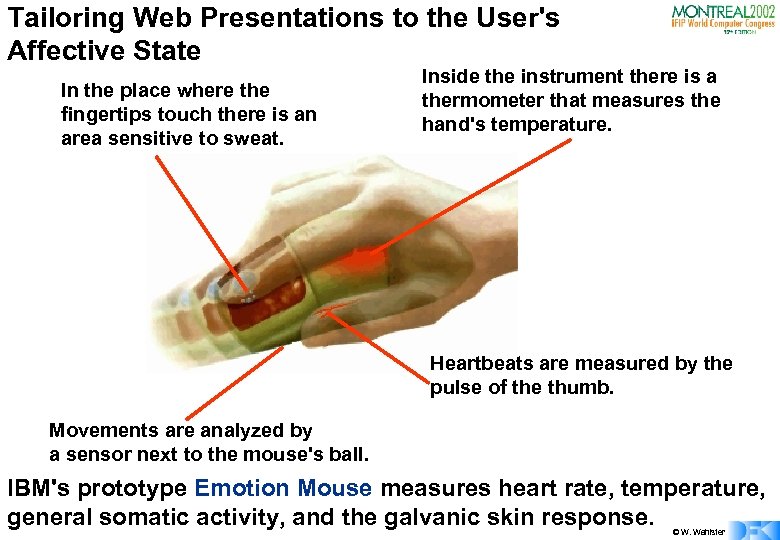 Tailoring Web Presentations to the User's Affective State In the place where the fingertips touch there is an area sensitive to sweat. Inside the instrument there is a thermometer that measures the hand's temperature. Heartbeats are measured by the pulse of the thumb. Movements are analyzed by a sensor next to the mouse's ball. IBM's prototype Emotion Mouse measures heart rate, temperature, general somatic activity, and the galvanic skin response. © W. Wahlster
Tailoring Web Presentations to the User's Affective State In the place where the fingertips touch there is an area sensitive to sweat. Inside the instrument there is a thermometer that measures the hand's temperature. Heartbeats are measured by the pulse of the thumb. Movements are analyzed by a sensor next to the mouse's ball. IBM's prototype Emotion Mouse measures heart rate, temperature, general somatic activity, and the galvanic skin response. © W. Wahlster
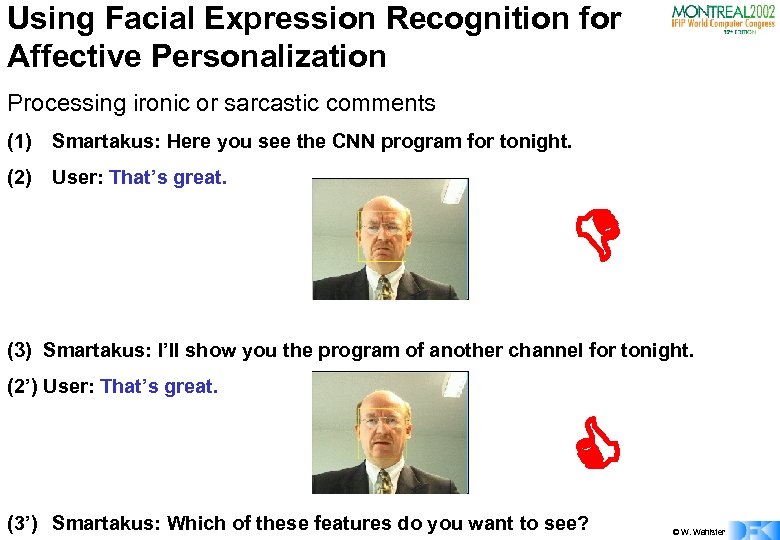 Using Facial Expression Recognition for Affective Personalization Processing ironic or sarcastic comments (1) Smartakus: Here you see the CNN program for tonight. (2) User: That’s great. (3) Smartakus: I’ll show you the program of another channel for tonight. (2’) User: That’s great. (3’) Smartakus: Which of these features do you want to see? © W. Wahlster
Using Facial Expression Recognition for Affective Personalization Processing ironic or sarcastic comments (1) Smartakus: Here you see the CNN program for tonight. (2) User: That’s great. (3) Smartakus: I’ll show you the program of another channel for tonight. (2’) User: That’s great. (3’) Smartakus: Which of these features do you want to see? © W. Wahlster
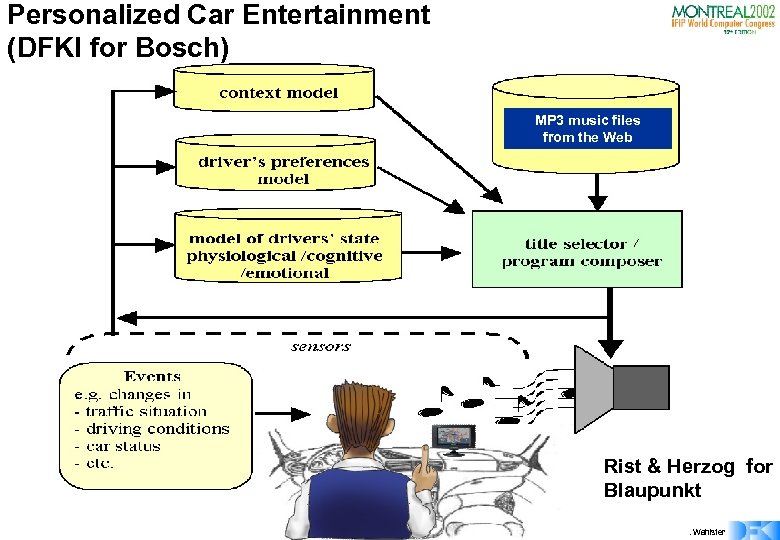 Personalized Car Entertainment (DFKI for Bosch) MP 3 music files from the Web Rist & Herzog for Blaupunkt © W. Wahlster
Personalized Car Entertainment (DFKI for Bosch) MP 3 music files from the Web Rist & Herzog for Blaupunkt © W. Wahlster
 Recent Overviews about Personalized Web Interaction l. Peter Brusilovsky, Oliviero Stock, Carlo Strapparava (eds. ) Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-based Systems, First International Conference, AH 2000, Trento, August 2000, LNCS 1892 l. Peter Brusilovsky, Mark Maybury (eds) The Adaptive Web. CACM, Vol. 45, Issue 5, May 2002 l. Peter Brusilovsky, Carlo Tasso (eds. ): Special Issue on User Modeling for Web and Hypermedia Information Retrieval, In: User Modeling and User. Adapted Interaction: The Journal of Personalization Research, Kluwer, 2002 l. Jameson, Anthony: Designing Systems that Adapt to Their Users. Tutorial presented at CHI 2002, Minneapolis, May 2002, ACM, Tutorial Notes 13 l Paul de Bra, Peter Brusilovsky, Ricardo Conejo (eds): Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-based Systems, Second International Conference, AH 2002, Malaga, May 2002, LNCS 2347 © W. Wahlster
Recent Overviews about Personalized Web Interaction l. Peter Brusilovsky, Oliviero Stock, Carlo Strapparava (eds. ) Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-based Systems, First International Conference, AH 2000, Trento, August 2000, LNCS 1892 l. Peter Brusilovsky, Mark Maybury (eds) The Adaptive Web. CACM, Vol. 45, Issue 5, May 2002 l. Peter Brusilovsky, Carlo Tasso (eds. ): Special Issue on User Modeling for Web and Hypermedia Information Retrieval, In: User Modeling and User. Adapted Interaction: The Journal of Personalization Research, Kluwer, 2002 l. Jameson, Anthony: Designing Systems that Adapt to Their Users. Tutorial presented at CHI 2002, Minneapolis, May 2002, ACM, Tutorial Notes 13 l Paul de Bra, Peter Brusilovsky, Ricardo Conejo (eds): Adaptive Hypermedia and Adaptive Web-based Systems, Second International Conference, AH 2002, Malaga, May 2002, LNCS 2347 © W. Wahlster
 Conclusions • The goal of adaptive personalization is to increase the usage and acceptance of ubiquitous webservices. • The intelligent adaptation to cognitive and technical resource limitations of the user is an important prerequisite of user-friendly web interaction. • Plan-based and constraint-based methods are now available for the advanced personalization of adaptive and virtual webpages. • The Semantic Web is increasing the potential for the effective personalization of webpages. © W. Wahlster
Conclusions • The goal of adaptive personalization is to increase the usage and acceptance of ubiquitous webservices. • The intelligent adaptation to cognitive and technical resource limitations of the user is an important prerequisite of user-friendly web interaction. • Plan-based and constraint-based methods are now available for the advanced personalization of adaptive and virtual webpages. • The Semantic Web is increasing the potential for the effective personalization of webpages. © W. Wahlster


