4570037f815a2e4cc47576b9963e9e0a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

INTELLIGENCE & NEED by Cristy Oakes Dr. Helms/Independent Study

1) Intelligence Testing- refers to individual differences in mental ability 2) Aptitude Testing- measures innate or hereditary talents 3) Achievement Tests- Level of knowledge accomplished in a certain area of endeavor (most common)

• First written test in Cambridge (1702) • Not used in US until 1845 • First objective test was handwriting • Common features of Mental Ability Tests • Standardization -Same guidelines, same scoring • Reliability - Consistency of a test

• Validity - Ability of a test to measure what it is suppose to measure • Three (3) types of validity a) Content Validity- Does test cover material it is suppose to? b) Criterion Validity- Compare test scores with outside measure of success c) Construct Validity- Extent to which test measures abstract quality

• Http: //www. cwrl. utexas. edu/~tonya/309 m/class/ paper 4/browser/sfg. htm • Thought intelligence related to sensory ability • Founder of Eugenics: - Galton thought Govt. Should give $ to intelligent people to have children together

• Put Galton’s work to the real test to measure intelligence • Studied students at the University of Pa. • Found college success unrelated to sensory keeness (around 1886) • http: //www. indiana. edu/ ~intell/jcattell. html


• Http: //www. infoplease. com/ce 5/CE 006052. html • Http: //userwww. sfsu. edu/~rsauzier/Binet. /html • Http: //encarta. msn. com/find/Concise. asp? ti=000 D 6000 • Http: //www. optonline. com/comptons/ce/ 00541_A. html


• • • Turned Eugenics around Worked at Vineland Training School Administered IQ. Tests Coined the term “moron” Wanted retarded people sterilized • Http: //www. indiana. edu/~intell/goddard. html


• Terman believed Heredity was responsible for intelligence • Revised the Simon - Binet scale • Made average score 100 • Began one of the longest running studies on gifted and talented children • Studied Intelligence in the Army • Http: //www. stats. org/newsletters/9811/lame. htm

• • • 40 % of recruits could not read (oral exam) Only. 005% failed (Army let them serve) 1/2 while soldiers had a mental age of 13 Black soldiers did a little worse Test was biased according to where soldiers were from • Black soldiers from Ohio, Illinois and Indiana did better than white soldiers from 7 southern states • Geography, environment appeared to be factors
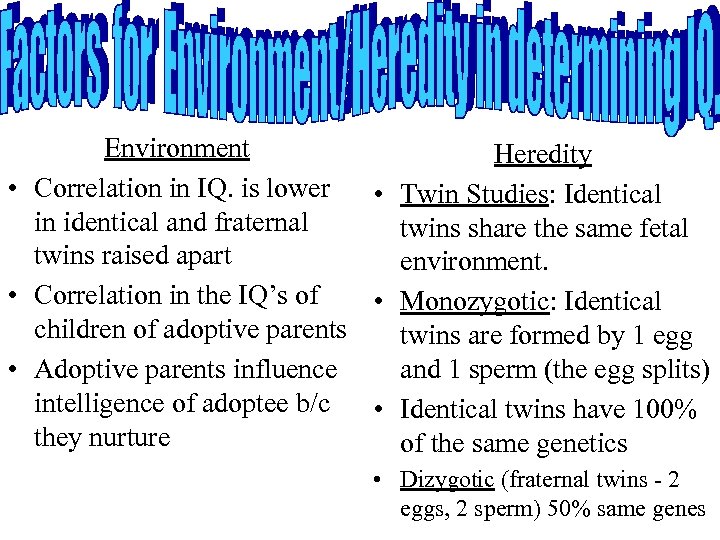
Environment Heredity • Correlation in IQ. is lower • Twin Studies: Identical in identical and fraternal twins share the same fetal twins raised apart environment. • Correlation in the IQ’s of • Monozygotic: Identical children of adoptive parents twins are formed by 1 egg and 1 sperm (the egg splits) • Adoptive parents influence intelligence of adoptee b/c • Identical twins have 100% they nurture of the same genetics • Dizygotic (fraternal twins - 2 eggs, 2 sperm) 50% same genes
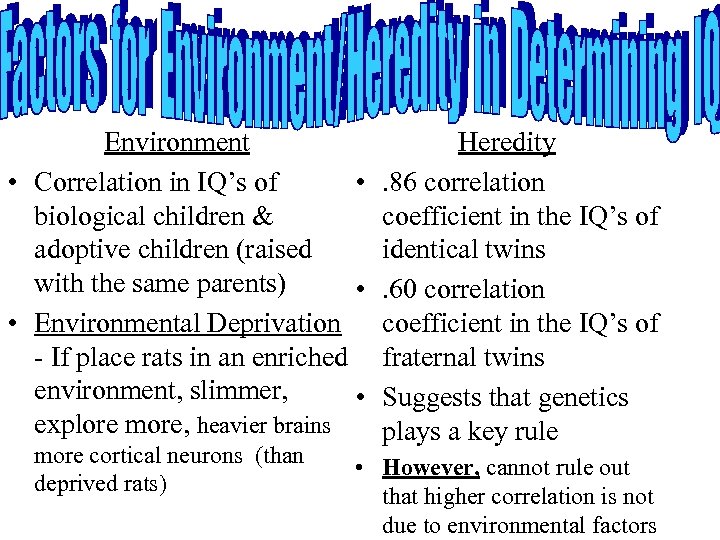
Environment • Correlation in IQ’s of • biological children & adoptive children (raised with the same parents) • • Environmental Deprivation - If place rats in an enriched environment, slimmer, • explore more, heavier brains more cortical neurons (than deprived rats) Heredity. 86 correlation coefficient in the IQ’s of identical twins. 60 correlation coefficient in the IQ’s of fraternal twins Suggests that genetics plays a key rule • However, cannot rule out that higher correlation is not due to environmental factors

• Robert J. Sternberg believed in 3 levels of intelligence 1) Contextual - Culturally defined 2) Experiential- Relationship between experience & intelligence to deal with novelty & handle familiar tasks automatically

3) Componential Intelligence- (3 parts) a) Metacomponents - Executive processes that make us decide what to do b) Performance Components - What allow us to undertake a task c) Knowledge/Acquisition Components Involved in learning and memory; Allow us to encode, combine and compare information • http: //www. uwsp. edu/acad/educ/lwilson/learning/STERNB

• • • 1) Logical - Mathematical 2) Linguistic - Sensitive to language, word meanings 3) Musical - Good at music 4) Spatial - Hand-eye coordination, map reading 5) Bodily Kinesthetic - Body coordination 6) Interpersonal - Can read & respond to moods, and nonverbal language • 7) Intrapersonal - Knowledge of self-reflection

A. Motivation : Mechanism that initiates, sustains and directs behavior B. Drive Theory : All of our behavior has a purpose 1) Drive : An internal state of tension produced by a physiological need 2) Need is physiological 3) Drive is Psychological 4) Drive Reduction : We do whatever is necessary to bring us back to homeostasis (equilibrium, stability)

Three types of Motives: 1) Biological Motives: Based on our innate survival needs – air, hunger, etc. 2) Social Motives: Come from innate need for stimulation -exploration, dominance, nurture, exhibition 3) Learned/Secondary Motives: Greatest diversity in human activity - environment, society, culture, experienced, cognitive, conditional factors

• Thought Freud taking human nature away from humans • Developed Humanistic Psychology, a main branch of Psychology • Ranked order of motivations • He called this “Hierarchy of needs”

Functionally absent = already fulfilled or hasn’t emerged yet P = Physiological S=Safety L=Belongingness/Love E=Esteem SA=Self-Actualization Red= Deficiency Needs Green=Growth Needs

1) Physiological needs - (basic needs) 2) Safety and Security - long term survival, stability 3) Love and belonging - alienation, acceptance 4) Esteem-Self Esteem- Recognition 5) Growth Needs 1) Cognitive Needs - Learning, understanding 2) Aesthetic Needs - Buy art, change world around you

• • Http: www. cfil. com/docs/maslow. html Http: encarta. msn. com/find/Concise. asp? ti=0613 F 000 Http: www. connect. net/georgen/maslow. htm Http: //www. wynja. com/personality/maslow. htm Http: //www. maslow. com/articles 2. html Http: //www. inst-mgt. org. uk/bookshop/- manthk/thk-9. htm Http: //academics. smcvt. edu/klewis/third_force_in_psyc

4570037f815a2e4cc47576b9963e9e0a.ppt