b72ec39be2a5db68a07ccfd774c6036d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

Intelligence ABILITY: A skill you have, no additional “training” needed ACHIEVEMENT: Mastery/knowledge in a specific subject area; reflect current performance (school tests) APTITUDE: Potential ability, predict future achievement in a certain area (ACT, SAT, etc. ) INTELLIGENCE: “General Mental Ability” Ø What does this mean? Practical? Verbal? Problem-Solving?

What is Intelligence? § Intelligence § ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations

Assessing Intelligence § Aptitude Test § a test designed to predict a person’s future performance § aptitude is the capacity to learn § Achievement Test § a test designed to assess what a person has learned
Assessing Intelligence § Reliability § the extent to which a test yields consistent results § assessed by consistency of scores on: § two halves of the test § alternate forms of the test § retesting § Validity § the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
A A B B C+ C C- C- D D F F
A B C+ C CD F

Origins of Intelligence Testing 11 -1 § What is Intel? § the ability to learn from experience, think rationally, and adapt to changes in the environment § Alfred Binet § around 1900 French gov. made a law saying all children must attend school § all kids were not on the same level § Binet’s job was to fig out who needed special help § Dev test to meas mental age

Origins of Intelligence Testing § Mental Age § a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet § chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance § child who does as well as the average 8 -year-old is said to have a mental age of 8

Origins of Intelligence Testing § Stanford-Binet § the widely used American revision of Binet’s original intelligence test § revised by Terman at Stanford University

Intelligence A Little History of Intelligence Testing… Ø Goddard: Translated Binet-Simon test into English. Ø Advocated wide use of intelligence tests for social engineering Ø Coined terms moron (mental age 8 -12), imbecile, & idiot, all of whom were “unfit for society” & should be institutionalized, sterilized, segregated, or all three; work led to Army’s Alpha & Beta tests, Ellis Island testing (where most immigrants were considered “defective”); strongly supported eugenics ØTerman (1916): Felt Binet-Simon was unfair – how can we say an 8 -yearold is more intelligent than a 6 -year-old just because she got more questions correct? Worked at Stanford & adapted the test to create the Stanford-Binet test Ø First used idea of the “intelligence quotient” (I. Q. ) Ø Mental age/Chronological age x 100 = I. Q. (100 is average)
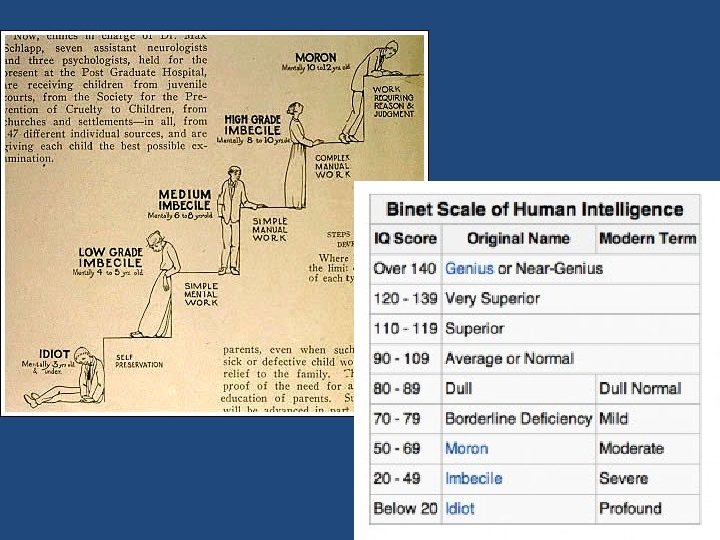

Origins of Intelligence Testing § Intelligence Quotient (IQ) § defined originally the ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100 § IQ = ma/ca x 100) § on contemporary tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned a score of 100
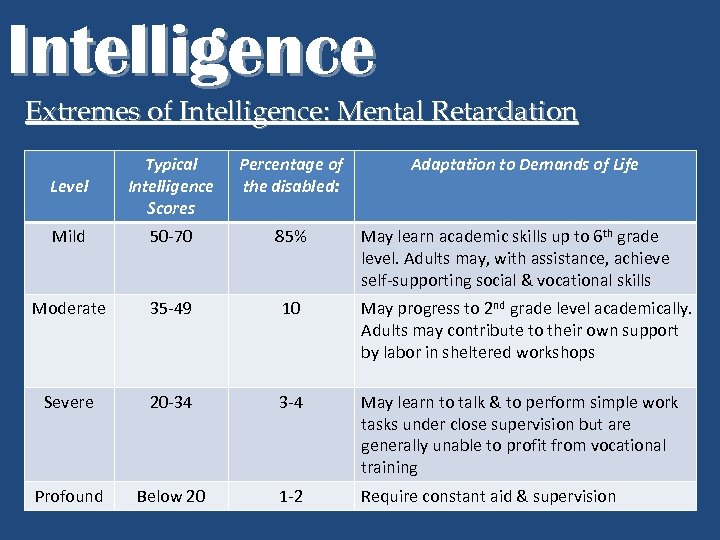
Intelligence Extremes of Intelligence: Mental Retardation Level Typical Intelligence Scores Percentage of the disabled: Adaptation to Demands of Life Mild 50 -70 85% Moderate 35 -49 10 May progress to 2 nd grade level academically. Adults may contribute to their own support by labor in sheltered workshops Severe 20 -34 3 -4 May learn to talk & to perform simple work tasks under close supervision but are generally unable to profit from vocational training Profound Below 20 1 -2 Require constant aid & supervision May learn academic skills up to 6 th grade level. Adults may, with assistance, achieve self-supporting social & vocational skills
Assessing Intelligence
Assessing Intelligence § Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) § most widely used intelligence test § subtests § verbal § performance (nonverbal)
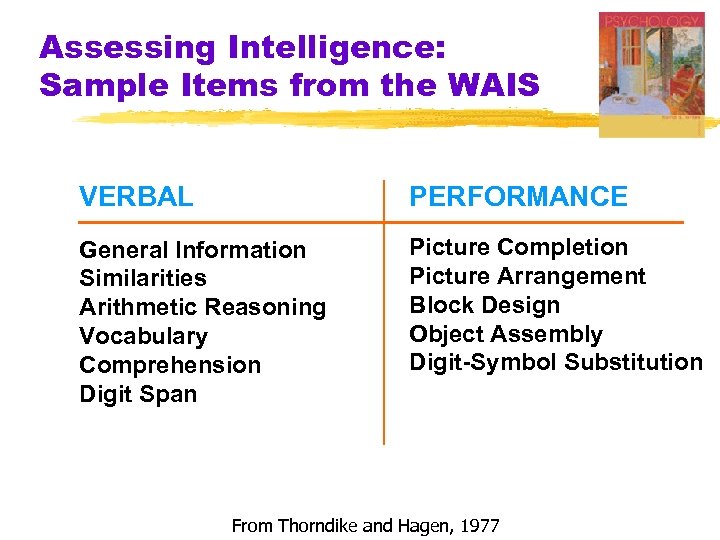
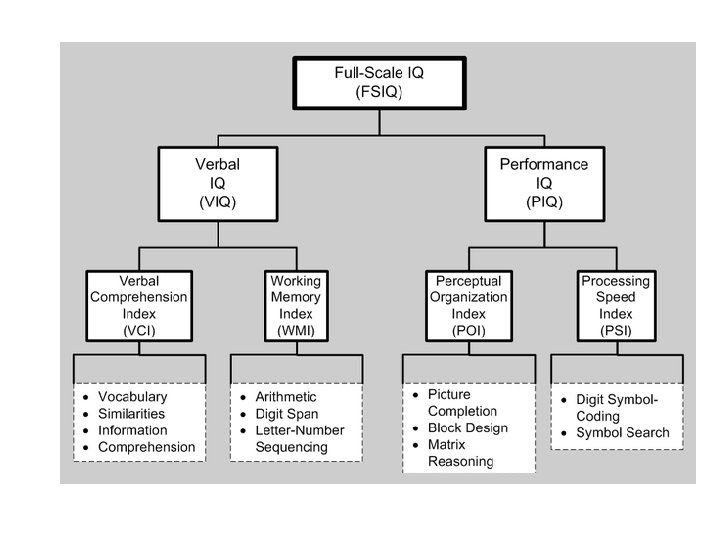
Assessing Intelligence: Sample Items from the WAIS VERBAL PERFORMANCE General Information Similarities Arithmetic Reasoning Vocabulary Comprehension Digit Span Picture Completion Picture Arrangement Block Design Object Assembly Digit-Symbol Substitution From Thorndike and Hagen, 1977
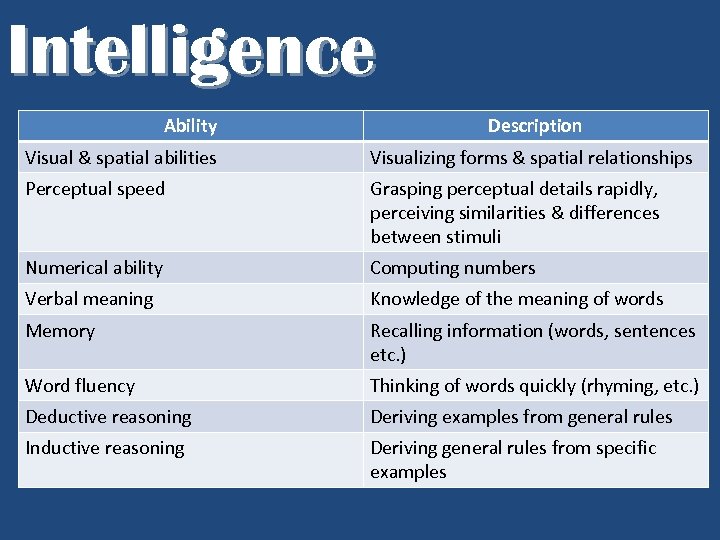
Intelligence Ability Description Visual & spatial abilities Visualizing forms & spatial relationships Perceptual speed Grasping perceptual details rapidly, perceiving similarities & differences between stimuli Numerical ability Computing numbers Verbal meaning Knowledge of the meaning of words Memory Recalling information (words, sentences etc. ) Word fluency Thinking of words quickly (rhyming, etc. ) Deductive reasoning Deriving examples from general rules Inductive reasoning Deriving general rules from specific examples

Intelligence Age Task 2 Place geometric shapes in corresponding openings; identify body parts; stack blocks; identify common objects 4 Name objects from memory; complete analogies (e. g. , fire is hot, ice is ____); identify objects of similar shape; answer simple questions (e. g. why do we have school? ) 6 Define simple words; explain differences (e. g. between a fish & a horse); identify missing body parts in a picture; count out objects 8 Answers questions about a simple story; identify absurdities (e. g. “John had to walk on crutches because he hurt his arm”); explain similarities/differences; tell how to handle certain situations (e. g. find a stray puppy)

Intelligence Age Task 10 Define more difficult words; give explanations (e. g. about why people should be quiet in a library); list as many words as possible; repeat sixdigit numbers 12 Identify more difficult verbal & pictorial absurdities; repeat five-digit numbers in reverse order; define abstract words (e. g. sorrow); fill in a missing word in a sentence 14 Solve reasoning problems; identify relationships among points of the compass; find similarities in apparently opposite concepts (e. g. high & low); predict the number of holes that will appear when a folded paper is cut & then opened Adult Supply several missing words for incomplete sentences; repeat six-digit numbers in reverse order; create a sentence using several unrelated words (e. g. forest, business-like, & dismayed); describe similarities between concepts (e. g. teaching & business)

Intelligence Verbal: Ø What day of the year is Independence Day? (Information) Ø In what way are wool and cotton alike? (Similarities) Ø If eggs cost 60 cents a dozen, what does 1 egg cost? (Arithmetic Reasoning) Ø Tell me the meaning of corrupt. (Vocabulary) Ø Why do people buy fire insurance? (Comprehension) Ø Listen carefully, & when I am through, say the numbers right after me. (Digit Span) Ø Now I am going to say some more numbers, but I want you to repeat them backward. (Digit Span)

Intelligence Performance (Picture Completion):
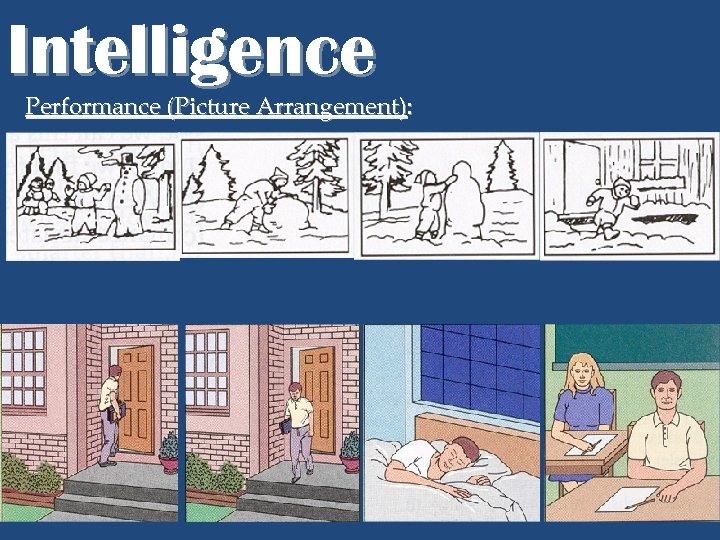
Intelligence Performance (Picture Arrangement):
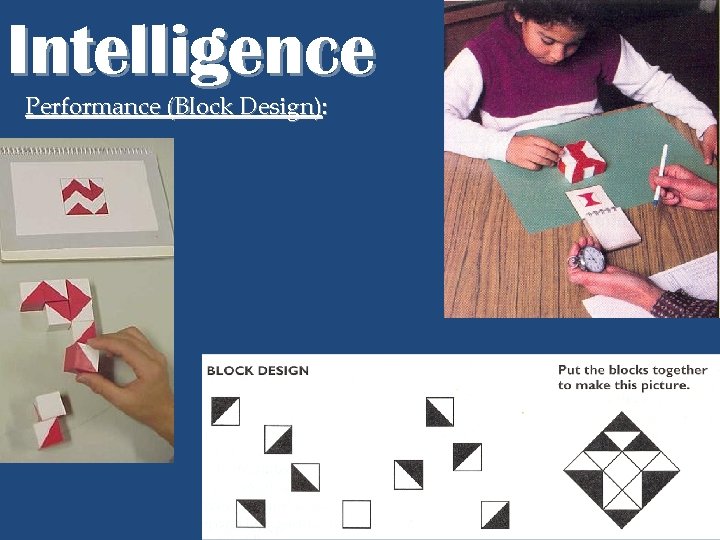
Intelligence Performance (Block Design):
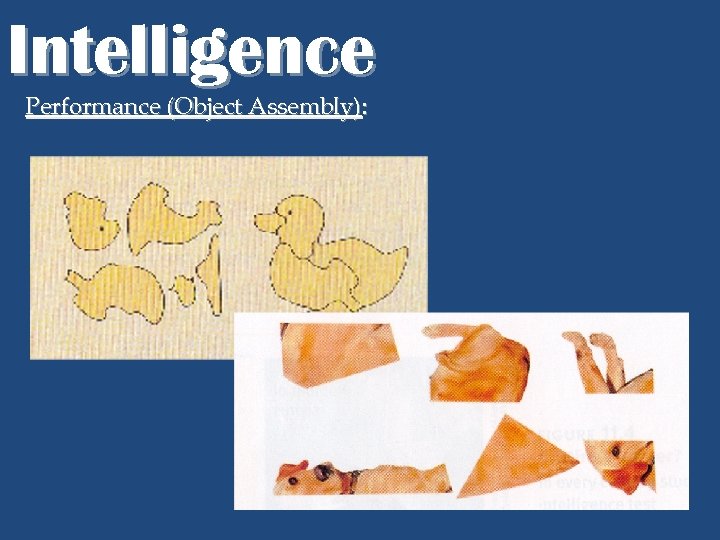
Intelligence Performance (Object Assembly):

Intelligence Performance (Letter Number Sequencing): Ø Give sequences of letters & numbers, then subject reorders them, numbers first, letters second, arranged numerically & alphabetically For example: 8 G D 6 1 S 2 2 6 8 D G S becomes: 1
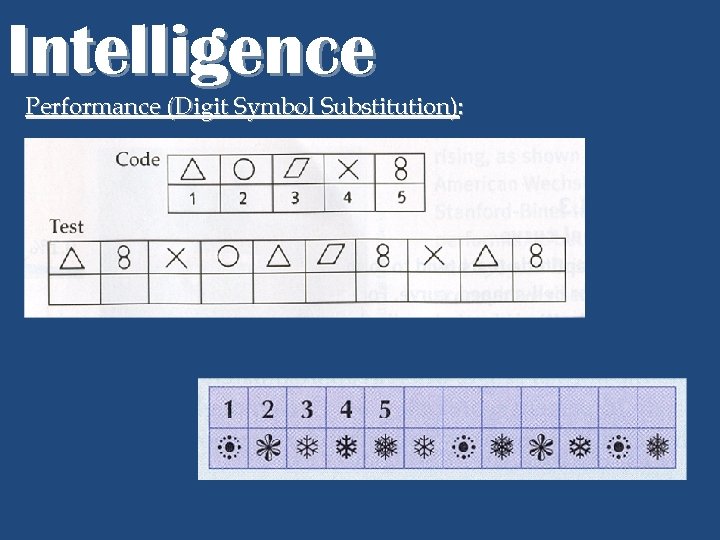
Intelligence Performance (Digit Symbol Substitution):
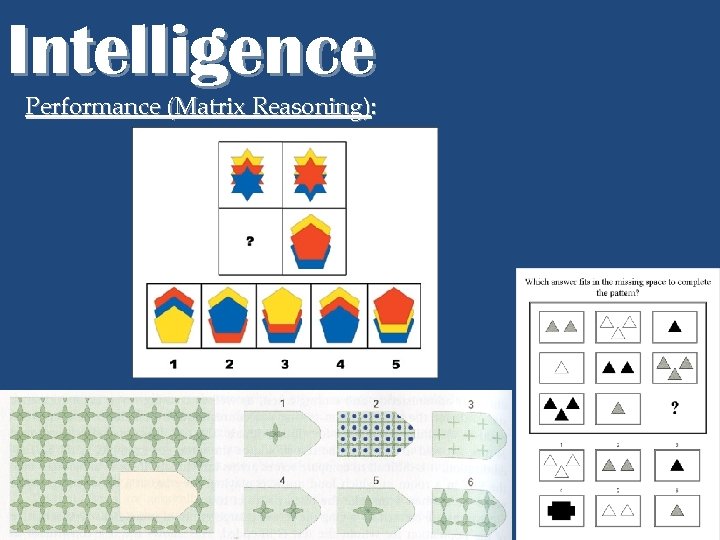
Intelligence Performance (Matrix Reasoning):

What is Intelligence? Thurstone 11 -1 § Thurstone’s Theory of Primary Mental Abilities identified 8 factors that make up intelligence § 1)visual-spatial ability § 2)perceptual speed § 3)numerical ability § 4)verbal meaning § 5)memory § 6)word fluency § 7)deductive reasoning § 8)inductive reasoning § said it is possible to be very high in one factor and low in another

What is Intelligence? – Broadened Theories: Gardner § § § § 11 -1 Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences § said there are 8 different types of intelligence 1)linguistic any famous writer 2)logical-mathematical Einstein 3)visual-spatial Picasso 4)body-kinesthetic Jordan/ Surgeon/ ballerina 5)musical-rhythmic any great composer 6)interpersonal Gandhi 7)intrapersonal Freud 8)Nature Darwin § thought each intelligence was based in different parts of the brain & each intelligence varies in intensity in every person

What is Intelligence? – Broadened Theories: Sternberg 11 -1 Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory of Intelligence -said there are 3 aspects of intelligence 1)analytical intelligence -academic problem solving skills 2)creative intelligence -being able to adapt quickly to new situations and come up with original ideas 3)practical intelligence -everyday tasks *Said Trad tests test 1 but not 2&3 which are better predictors of vocational success

11 -1 What is Intelligence? § A. Factor-Analysis § -a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test that measure a common ability § -used to find out whethere might be a general ability factor that runs throughout our specific mental abilities § Spearman’s 2 Factor Theory of theory intelligence § -Spearman helped develop factor-analysis to support g factor theory § -said intelligence was made up of 2 factors § g factor – general ability § s factor – specific ability
What is Intelligence? § Factor Analysis § statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test § used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie one’s total score § General Intelligence (g) § factor that Spearman and others believed underlies specific mental abilities § measured by every task on an intelligence test

Are There Multiple Intelligences? § g factor underlies the specific abilities § -said people who score high on one s factor usually do well on others as well § -he attributed this to the g factor 11 -1

11 -1 Biological Correlates § 2 Correlates: Brain Size, Processing Speed (Perceptual Speed & Neurological Speed) 1. Brain Size § Early 1800 s Franz Gall and his school of phrenology believed that they could tell your intelligence and other characteristics about you by the size and shape of your skull § modern studies do show a slight correlation (+. 15) b/w head size (relative to body size) and intelligence § however, there is more inside your skull than just the brain § newer studies using MRI technology to measure actual

11 -1 Biological Correlates Interesting Info: Einstein’s brain was 15% larger than average in the parietal lobes lower region (math and spatial information processing located here) -other areas of his brain were smaller than average -may indicate why he was so slow in learning to speak

11 -1 Biological Correlates 2. Processing Speed positively correlated with Intel Diff b/w Sink & Wink z ‘quick wits’ z higher verbal ability scores -PET scans have revealed that high IQ performers use less glucose when completing cog. tasks than do average people

Are There Multiple Intelligences? § Savant Syndrome § condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill § computation § drawing

Are There Multiple Intelligences? § Social Intelligence § the know-how involved in comprehending social situations and managing oneself successfully § Emotional Intelligence § ability to perceive, express, understand, and regulate emotions

What is Intelligence? – Broadened Theories: Emo Intel 11 -1 Emotional Intelligence (Daniel Goleman) § interested in finding out why very intelligent people aren’t always successful in life § listed 5 areas needed for life success § 1)self-awareness § 2)self-motivation § 3)impulse control § 4)mood management § 5)people skills

Intelligence and Creativity § the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas § expertise § imaginative thinking skills § venturesome personality § intrinsic motivation § creative environment

Assessing Intelligence § Standardization § defining meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested “standardization group” § Normal Curve § the symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes § most scores fall near the average, and fewer scores lie near the extremes
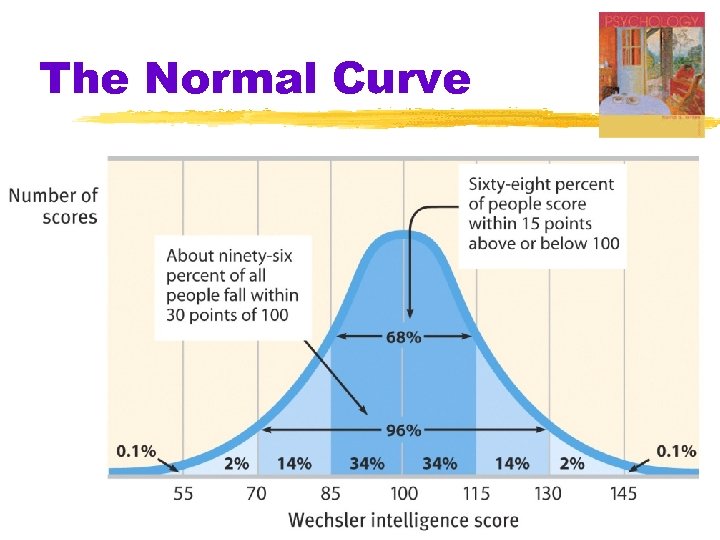
The Normal Curve
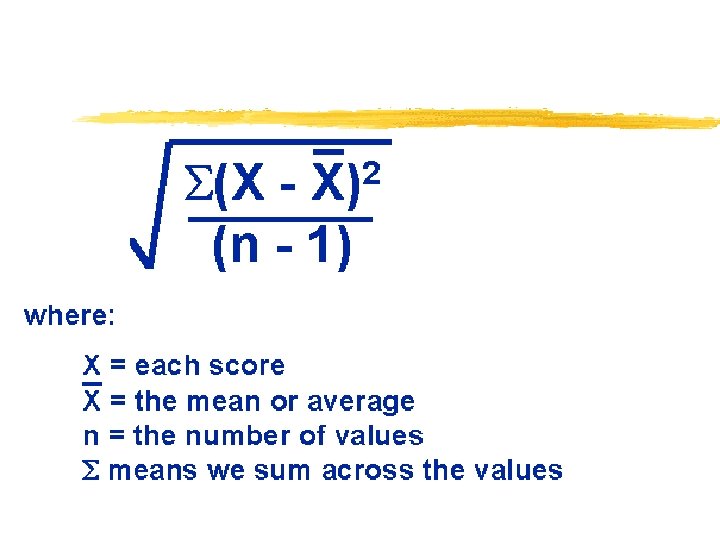
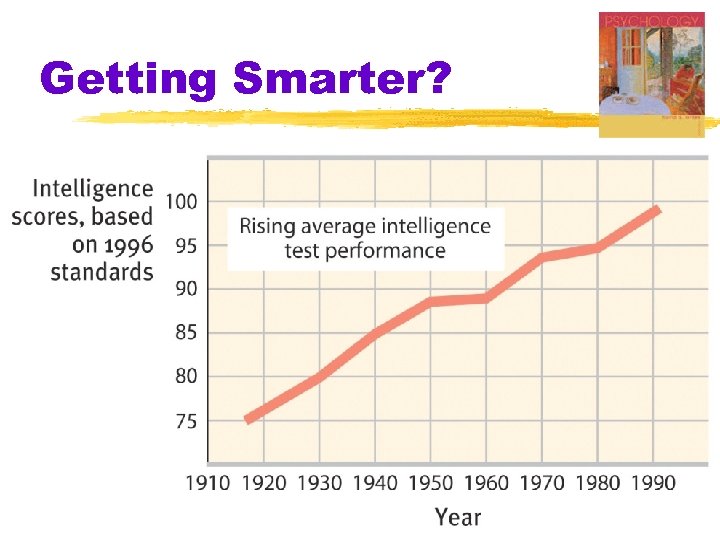
Getting Smarter?

11 -2 Assessing Intelligence § Can a test have high reliability but low validity? Yes § Can a test have low reliability but high predictive validity? No § Could have content validity if it is measuring what its supposed to § See Barron’s Manual for more in depth on Reliability & Validity if needed
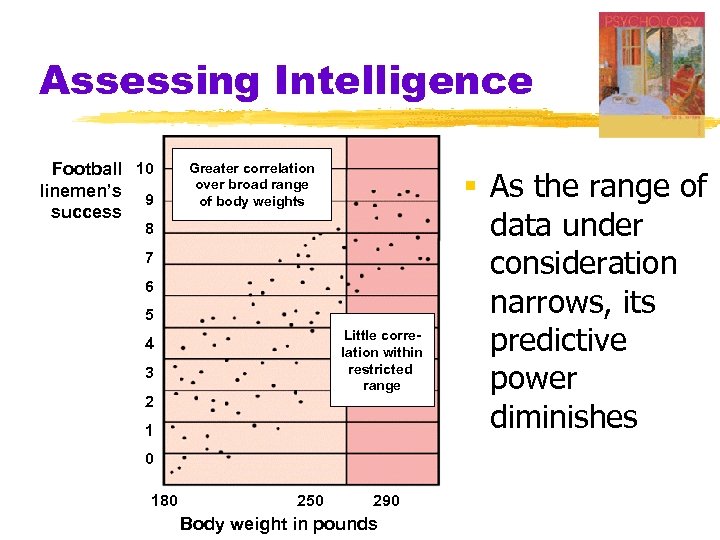
Assessing Intelligence Football 10 linemen’s 9 success Greater correlation over broad range of body weights 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Little correlation within restricted range 1 0 180 250 290 Body weight in pounds § As the range of data under consideration narrows, its predictive power diminishes

The Dynamics of Intelligence § Mental Retardation § a condition of limited mental ability § indicated by an intelligence score below 70 § produces difficulty in adapting to the demands of life § varies from mild to profound § Down Syndrome § retardation and associated physical disorders caused by an extra chromosome in one’s genetic makeup
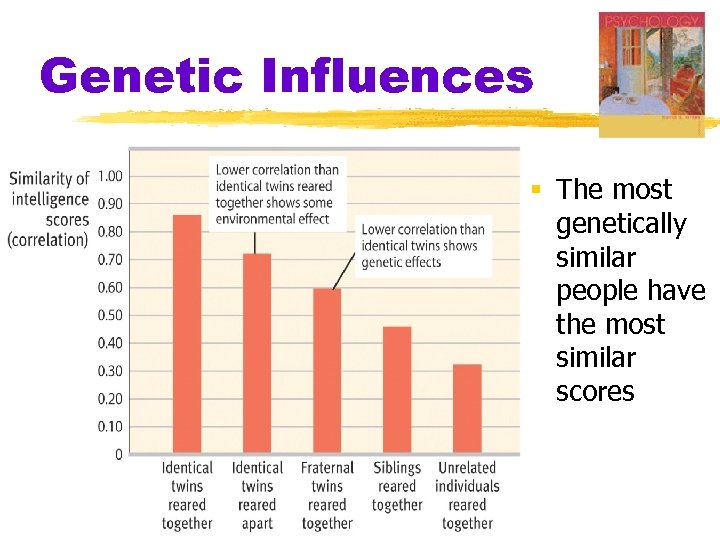
Genetic Influences § The most genetically similar people have the most similar scores

Genetic Influences § Heritability § the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes § variability depends on range of populations and environments studied
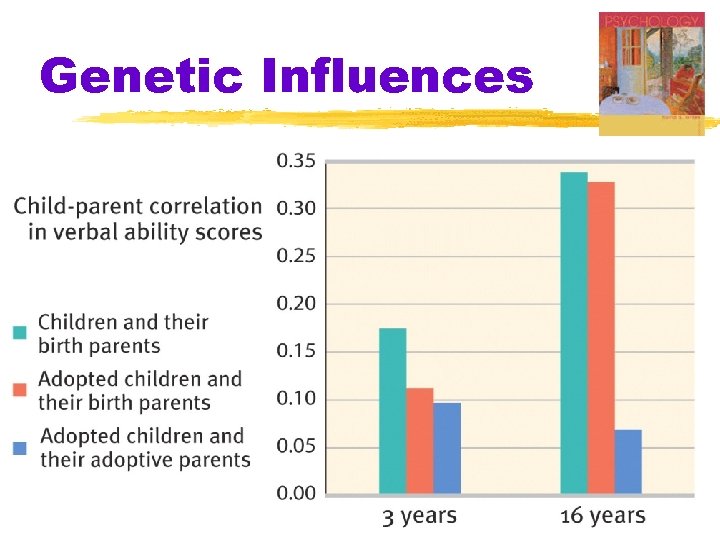
Genetic Influences
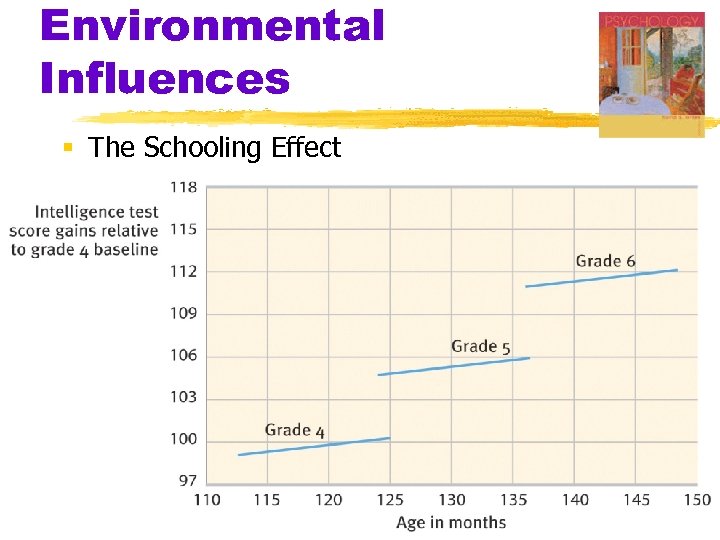
Environmental Influences § The Schooling Effect
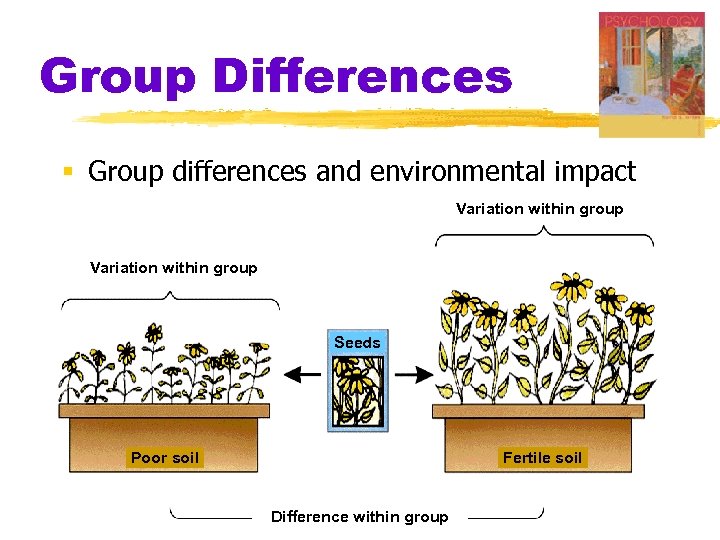
Group Differences § Group differences and environmental impact Variation within group Seeds Poor soil Fertile soil Difference within group

Gender Differences 11 -2 § Males=Females as group on math test mean scores § F higher on computation, M on prob solving (Int fact: males have a gr 8 er differentiation w/in group) § Differences can be explained in socialization differences b/w males & females § Males better on spatial tasks (evol per: hunting in 3 D space, bio per: prenatal male sex hormones) § Females better on emotion detecting (evol per: women’s ability to det emotions helped them read emo in infants & potential lovers)
b72ec39be2a5db68a07ccfd774c6036d.ppt