37fa44e527830c39df35a7d93920cadd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

Intel MPI Library Cluster Software and Technologies Software & Solutions Group

Повестка дня Обзор Intel MPI Лабораторная работа • Возможности • Начало • Value Proposition • Архитектура • Устройства и фабрики • Поддержка Cluster Tools • • Среда Кольцо демонов Запуск приложения Debugging • Оптимизация • • Размещение процессов Выбор устройства Привязка процессов Автоматический настройщик Intel MPI Library 2 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Features MPI-2 specification conformance • • • Standardized job startup mechanism (mpiexec) Process spawning/attachment (sock device only) One-sided communication Extended collective operations File I/O Multiple communication fabrics selectable at runtime Additional thread-safe libraries at level MPI_THREAD_MULTIPLE Dynamic or static linking, plus debugging and tracing libraries Intel MPI Library 3 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Features IA-32, Itanium® 2, and Intel® 64 platforms Intel® compilers 7. 1 or later, and GNU* compilers 2. 96 or later Red Hat Linux* 7. 2 thru EL 5, SUSE Linux* 8. 0 thru SLES 10 C, C++, Fortran-77, and Fortran-90 language bindings Dynamic or static linking, plus debugging and tracing libraries Affordable SDK package Freely downloadable and royalty-free RTO package Intel MPI Library 4 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
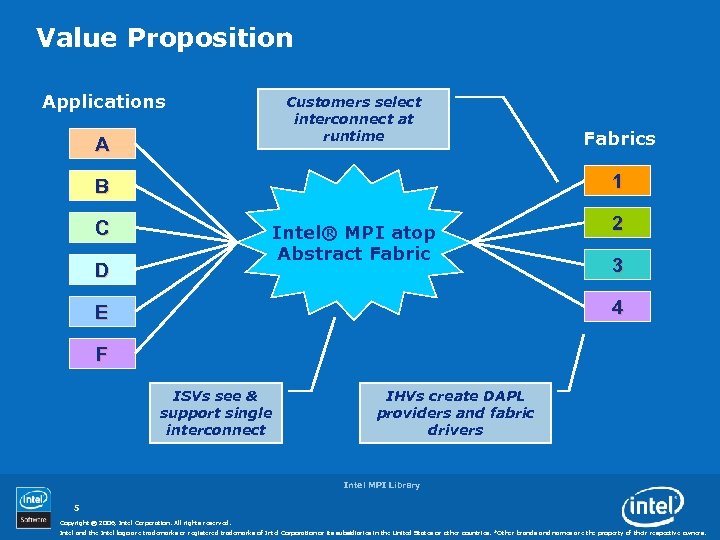
Value Proposition Applications Customers select interconnect at runtime A Fabrics 1 B C Intel® MPI atop Abstract Fabric D 2 3 4 E F ISVs see & support single interconnect IHVs create DAPL providers and fabric drivers Intel MPI Library 5 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
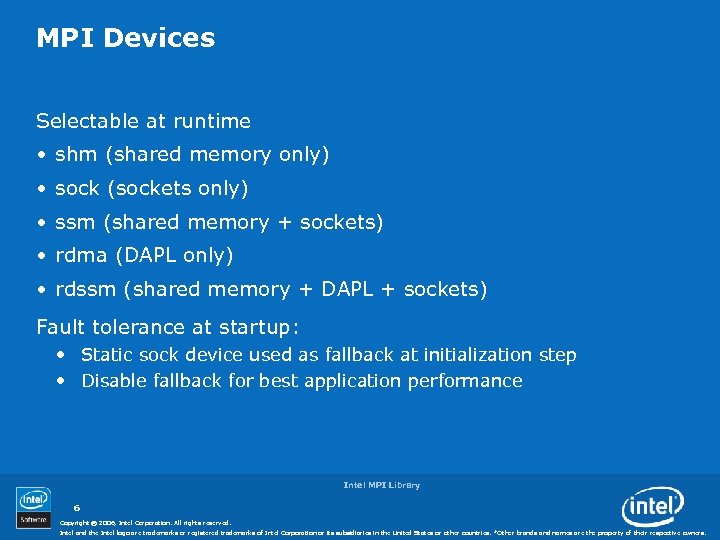
MPI Devices Selectable at runtime • shm (shared memory only) • sock (sockets only) • ssm (shared memory + sockets) • rdma (DAPL only) • rdssm (shared memory + DAPL + sockets) Fault tolerance at startup: • Static sock device used as fallback at initialization step • Disable fallback for best application performance Intel MPI Library 6 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
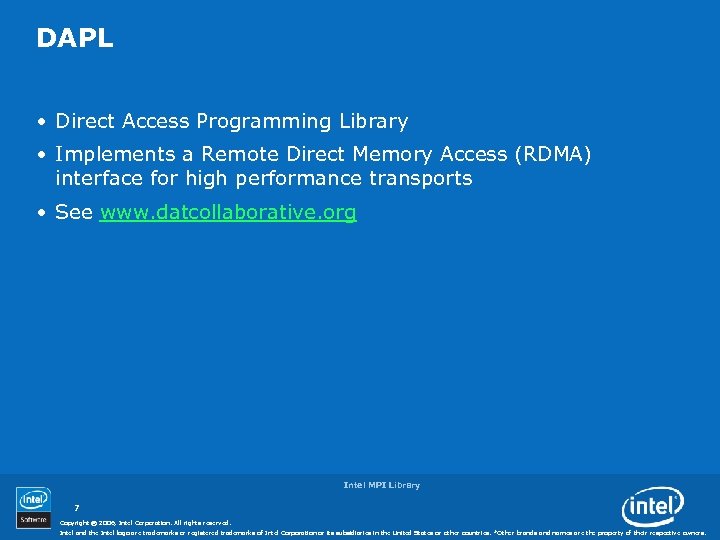
DAPL • Direct Access Programming Library • Implements a Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) interface for high performance transports • See www. datcollaborative. org Intel MPI Library 7 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Supported Fabrics Selectable at runtime • Shared memory • Infini. Band (via DAPL) • Myrinet (via DAPL) • Quadrics (via DAPL) • Ammasso RNIC (via DAPL) • Dolphin SCI (via sockets) • Ethernet (via sockets and DAPL) Additional fabrics are being investigated Intel MPI Library 8 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Intel MPI 3. 1 (shipping now) Streamlined product setup • Installation under root or ordinary user ID • mpivars. sh and mpivars. csh scripts for easy path setting Simplified process management • mpiexec -perhost and -nolocal options • mpirun script that automates MPD startup and cleanup • System-, user-, and session-specific configuration files • Transparent support for alternative IP interfaces Intel MPI Library 9 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Intel MPI 3. 1 (contd. ) Environment variables for runtime control over • Process pinning • Optimized collective operations • Device-specific protocol thresholds • Collective algorithm thresholds • Enhanced memory registration cache • Many others … Intel MPI Library 10 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Intel MPI 3. 1 (contd. ) Increased interoperability • Support for DAPL* v 1. 1 and DAPL* v 1. 2 compliant providers • Message queue browsing with Total. View* and DDT* debuggers • Internal MPI library state tracing with Intel® Trace Collector Intel MPI Library 11 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Intel MPI 3. 1 (contd. ) Enhanced support for operating systems and compilers • • • Red. Hat EL 3, EL 4, EL 5 SUSE 9. 0 – 9. 3, 10. 0, SLES 9, SLES 10 SGI Pro. Pack 4, Pro. Pack 5 Asianux 1. 0, 2. 0 (includes Red Flag DC* Server 5. 0) Turbo Linux* 10 Mandriva*/Mandrake* v 10. 1 Miracle* Linux v 4. 0 Fedora Core 1 -4 Microsoft Windows* CCS 2003 Getting Started and Reference Manual documents Intel MPI Library 12 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Supporting Cluster Tools Intel® Cluster Toolkit 3. 1 • Intel MPI Library 3. 1 • Intel Math Kernel Library 10. 0 • Intel Trace Analyzer and Collector 7. 1 • Intel MPI Benchmarks 3. 1 Integration with the job schedulers • LSF*, version 6. 1 and higher • PBS Pro*, version 7. 1 and higher • Torque*, version 1. 2. 0 and higher • Parallelnavi* NQS* for Linux V 2. 0 L 10 and higher • Parallelnavi for Linux Advanced Edition V 1. 0 L 10 A and higher More tools are coming Intel MPI Library 13 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Повестка дня Обзор Intel MPI Лабораторная работа • Возможности • Начало • Value Proposition • Архитектура • Устройства и фабрики • Поддержка Cluster Tools • • • Инсталляция Среда Компиляция приложения Запуск приложения Debugging • Оптимизация • • Размещение процессов Выбор устройства Привязка процессов Автоматический настройщик Intel MPI Library 14 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Download Intel® MPI not installed or different version required? Part of the Cluster Tools (free eval) www. intel. com/software/products/cluster Single product (free eval): www. intel. com/go/mpi From Internal License Center: select Intel® MPI Library http: //softwareproducts. intel. com Current version is 3. 1 (Build: 3. 1. 026) Intel MPI Library 15 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Installation possible as root or ordinary user! • Common step: un-zip and un-tar the library package into temporary directory • Check that you have Python* v 2. 2 or higher in your PATH Root installation follows the usual procedure • Put licenses into default location: /opt/intel/licenses • Start the. /install in the temporary directory • Follow instructions generated by the script • Default installation path: /opt/intel/impi/3. 1 User installation • Put licenses into user‘s preferred location or into temporary directory • Start the. /install in the temporary directory • Select the installation “without using RPM database” • Follow the instructions as indicated by the script: • • If required: Enter path to licenses Enter installation directory (Default: $HOME/intel/impi/3. 1) Intel MPI Library 16 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Задание № 1: настроить среду Source mpivars for your preferred shell Create default config file $HOME/. mpd. conf Create a hostfile e. g. $HOME/mpd. hosts Intel MPI Library 17 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Source mpivars in your preferred shell Important: Get the PATH and LD_LIBRARY_PATH right! (in particular on x 86_64) IA 32, Intel 64 32 -bit mode, Itanium • csh: source /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/bin/mpivars. csh • bash: source /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/bin/mpivars. sh Intel 64 64 -bit mode • csh: source /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/bin 64/mpivars. csh • bash: source /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/bin 64/mpivars. sh $ which mpicc • Intel® 64 64 -bit mode: /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/bin 64/mpicc Intel MPI Library 18 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

$HOME/. mpd. conf File $HOME/. mpd. conf needed in your home directory • Contents: secretword=<some secret word> • Access rights: read/write for the user only • Automatically created during first execution of mpdboot by the library Intel MPI Library 19 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Create mpd. hosts file Recommended: • Create a central hostfile e. g. $HOME/mpd. hosts • Contents: the list of nodes of your system Create a hostfile mpd. hosts $ cat > mpd. hosts node 1 node 2 <ctrl>-D Intel MPI Library 20 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Задание № 2: первая программа с Intel® MPI Compile and link one of test. {c, cpp, f, f 90} into executable test Start MPD daemons with mpdboot Run parallel a. out with mpiexec on the nodes Check debugging techniques Stop MPD daemons with mpdallexit Intel MPI Library 21 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Compile and Link Commands Using Intel compilers • mpiicc, mpiicpc, mpiifort, . . . Using Gnu compilers • mpicc, mpicxx, mpif 77, . . . Ease of use • Commands find Intel® MPI include files automatically • Commands link Intel MPI libraries automatically Commands use compilers from PATH (compilers not hard-wired!) Intel MPI Library 22 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Compile a Test Program Copy test directory from /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/test $ cp /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/test. *. Build one of test. {c, cpp, f, f 90} • Intel C compiler $ mpiicc –o testc test. c • Intel C++ compiler $ mpiicpc –o testcpp test. cpp • Intel Fortran compiler $ mpiifort –o testf test. f Intel MPI Library 23 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Multiple Purpose Daemons Used to start and stop Intel® MPI programs Typical use of daemons in interactive mode: • “Start once, use many times” • MPD daemons may run until next re-boot! Running Intel MPI jobs in a Batch System: • Start (and stop) one MPD ring per batch job • Overlapping MPD rings from different jobs will kill each other • Distinguish MPD ring from others? Set environment variable MPD_CON_EXT to unique value; i. e. time in seconds, etc. Intel MPI Library 24 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Multiple Purpose Daemons (contd. ) Benefit of MPD daemons: • Faster start-up of Intel® MPI programs • Ctrl-C works! All processes get the signal Experience: no zombies left on [remote] nodes • No more hung jobs! Job will be terminated according to environment variable MPIEXEC_TIMEOUT at launch Daemons start any program (multiple purpose) • Use mpiexec as a cluster “management” tool, e. g. mpiexec –l –n 4 hostname Intel MPI Library 25 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Hands-on session Start MPD Daemons on Two Nodes Start MPD daemons with mpdboot (local mpd. hosts is detected automatically) • using rsh between nodes $ mpdboot –n 2 [-f hostfile] • using ssh between nodes $ mpdboot –n 2 [-f hostfile] –r ssh Check available nodes with mpdtrace $ mpdtrace node 1 node 2 Intel MPI Library 26 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Execution Commands Model: Running an Intel® MPI program requires a multiple purpose daemon (MPD) per node for the start-up Starting the “ring” of MPD daemons • mpdboot [–d] [–v] –n #nodes –f hostfile [–r ssh] • Flags: –d = debug, –v = verbose, –r = toggle between ssh or rsh Checking the MPD daemons • mpdtrace Running an MPI program • mpiexec [– l] –n #processes executable • Flag: –l = prefix output with process id Stopping the MPD daemons • mpdallexit Intel MPI Library 27 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Execution Commands (contd. ) All-inclusive • mpirun –f hostfile –n #processes executable • Includes start and stop of an MPD ring • Convenient • May be too “slow” for interactive work • May be good for jobs in batch system “In-session” mode: mpirun inquires the list of nodes from the batch system Which i. MPI version? • mpiexec –V • cat /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/mpisupport. txt • rpm –qa | grep intel-mpi Intel MPI Library 28 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Run the Test Program Run the test program • C $ mpiexec –n 2. /testc Hello world: rank 0 of 2 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 1 of 2 running on node 2 • Fortran 77 $ mpiexec –n 2. /testf Redo the exercises, look out for node order! $ mpiexec –n 4. /testc Intel MPI Library 29 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Debugging Application run will output detailed Intel MPI information (if I_MPI_DEBUG > 0) • export I_MPI_DEBUG 3 • mpiexec -genv I_MPI_DEBUG 3. . . Support parallel debugging with Intel®, GNU*, Total. View*, and DDT* • mpiexec –idb. . . • mpiexec –gdb. . . • mpiexec –tv. . . Task #3: run Intel® MPI library debugging Check output of different debug levels $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG {1, 2, 3, 1000} –n 2. /testc Compile and link application with debug information enabled $ mpiicc -g -o testc test. c Check how Intel® MPI debug output changes at higher level: $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 1000 –n 2. /testc Start Intel MPI® allication with GDB $ mpiexec –gdb –n 2. /testc Intel MPI Library 30 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Stop MPD Daemons Stop MPD daemon with mpdallexit $ mpdallexit Check again with mpdtrace $ mpdtrace: cannot connect to local mpd (/tmp/mpd 2. console_gsslavov); possible causes: 1. no mpd is running on this host 2. an mpd is running but was started without a "console" (-n option) Re-start MPD daemons for later use $ mpdboot –n 2 [-f hostfile] [–r ssh] Intel MPI Library 31 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Перерыв 10 минут Intel MPI Library 32 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Повестка дня Обзор Intel MPI Лабораторная работа • Возможности • Начало • Value Proposition • Архитектура • Устройства и фабрики • Поддержка Cluster Tools • • • Инсталляция Среда Компиляция приложения Запуск приложения Debugging • Оптимизация • • Выбор устройства Размещение процессов Привязка процессов Автоматический настройщик Intel MPI Library 33 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Measuring Performance with IMB = Intel MPI Benchmarks (improved former PMB = Pallas MPI Benchmarks) IMB-MPI 1 measures performance of different communication patterns: Ping. Pong, Send. Recv, Allreduce, Alltoall, . . . IMB-EXT and IMB-IO measure MPI-2 features (one-sided communication: MPI_Put/Get etc. ) Download it from www. intel. com/software/products/clustertoolkit BKM: Always run full IMB before running an application. Will reveal interconnect issues! Intel MPI Library 34 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Measuring Performance with IMB (contd. ) Intel ® MPI Library supplies IMB binary for autotuning needs on each platform • /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/em 64 t/bin/IMB-MPI 1 Running full IMB-MPI 1 [or specific benchmarks] • mpiexec –n #procs IMB-MPI 1 [pingpong alltoall …] Other IMB-MPI 1 Options • –multi 1: Span several process groups (n/2 Ping. Pong pairs) • –npmin #p: Minimum group contains #p processes BKM: Read the IMB documentation Intel MPI Library 35 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Hands-on session Task #4: run IMB benchmark Run IMB-MPI 1 Ping. Pong on 1 and 2 nodes for different i. MPI devices • Compare the bandwidth (Mbytes/sec for large #bytes) e. g. for sock and rdma • Compare the latencies (time[usec] for 0 or 1 byte messages) e. g. for sock and ssm Run IMB-MPI 1 Ping. Pong on all nodes with IMB flag –multi 1 • mpiexec … IMB-MPI 1 pingpong –multi 1 Intel MPI Library 36 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning advice: Use best available communication fabric • Use default fabric selection if you can. Check the result thru I_MPI_DEBUG to 2. • If necessary, use I_MPI_DEVICE to explicitly select the desired fabric: sock shm ssm rdma[: <provider>] rdssm[: <provider>] TCP/Ethernet*/sockets Shared memory only (no sockets) TCP + shared memory Infini. Band*, Myrinet* (via specified DAPL* provider) TCP + shared memory + DAPL* with optional <provider> name as specified in /etc/dat. conf • Alternatively, use alias options: -sock -shm -ssm -rdma -rdssm TCP/Ethernet*/sockets Shared memory only (no sockets) TCP + shared memory Infini. Band*, Myrinet* (via specified DAPL* provider) TCP + shared memory + DAPL* • Select network interface for socket communications IP over IB: I_MPI_NETMASK=ib 0 I_MPI_NETMASK=192. 169. 0. 0 for IP over IB for particular subnet $ mpirun –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 2 -rdma -n <number of processes>. /your_app Intel MPI Library 37 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Task #5: run different communication devices Check selected device $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 2 –n 2 –host node 1. /testc …. . will use default device rdssm Change selected device $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 2 –genv I_MPI_DEVICE shm –n 2 –host node 1. /testc …. . will use device shm Intel MPI Library 38 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Hands-on session Task #5: run different communication devices (cont. ) Change selected device with I_MPI_DEVICE $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 2 –genv I_MPI_DEVICE ssm IMB-MPI $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_DEBUG 2 –genv I_MPI_DEVICE sock IMB-MPI Intel MPI Library 39 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning advice: Select proper process layout • Default process layout is “group round-robin” that puts consecutive MPI processes on different nodes (this may be fixed soon) • Set I_MPI_PERHOST variable to override the default process layout: • • • I_MPI_PERHOST=1 makes round-robin distribution I_MPI_PERHOST=all maps processes to all logical CPUs on a node I_MPI_PERHOST=allcores maps processes to all physical CPUs on a node • Or use an mpiexec options: -perhost <#> - "processes per host“, group round-robin distribution placing # of processes at every host -rr - "round-robin" distribution, same as ‘-perhost 1’ -grr <#> - "group round-robin", same as ‘-perhost #’ -ppn <#> - "processes per node", same as ‘-perhost #’ $ mpirun –perhost 2 -n <number of processes>. /your_app Intel MPI Library 40 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Hands-on session Task #6: Understand default process placement Observe default round robin placement $ mpiexec –n 4. /testc Hello world: rank 0 of 4 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 1 of 4 running on node 2 Hello world: rank 2 of 4 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 3 of 4 running on node 2 Intel MPI Library 41 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Hands-on session Task #7: Use group round robin placement Place 2 consecutive ranks on every node using the –perhost option $ mpiexec –perhost 2 –n 4. /testc Hello world: rank 0 of 4 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 1 of 4 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 2 of 4 running on node 2 Hello world: rank 3 of 4 running on node 2 Alternative flag names: -ppn processes per node, equivalent to -perhost -rr round robin placement (-ppn 1) -grr group round robin placement (-ppn) Intel MPI Library 42 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Hands-on session Task #8: Exact process placement (Argument Sets) Place several instances of testc exactly on the desired nodes, for example $ mpiexec –host node 1 –n 2. /testc : –host node 2 –n 1. /testc Hello world: rank 0 of 3 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 1 of 3 running on node 1 Hello world: rank 2 of 3 running on node 2 Note that you can start different executables upon different nodes Intel MPI Library 43 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning advice: Use proper process pinning • By default Intel MPI library pins sequential MPI ranks at CPU cores in the order they enumerated by OS; one process per core. • Use I_MPI_PIN_PROCESSOR_LIST to define custom map of MPI processes to CPU cores pinning. Find pinning map optimal to your application. • Reasonable strategy is to stick pair of actively exchanging process at the pair of CPU cores sharing L 2 data cache • Use the ‘cpuinfo’ utility supplied with Intel MPI Library to see the processor topology, including inter-core cache sharing information. $ mpirun –perhost 2 –genv I_MPI_PIN_PROCESSOR_LIST 0, 3 -n <number of processes>. /your_app Tuning advice: Disable pinning for threaded apps • Turn off pinning by setting I_MPI_PIN to `disable`, so that the default shell affinity mask is inherited by threads created within the process. • Apply other pinning techniques to keep performance of hybrid applications high: • • use KMP_AFFINITY for hybrid application built with Intel Open. MP use SGI Pro. Pack* “dplace” tool Intel MPI Library 44 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Task #9: try different process pining Check processor topology. Take a look at L 2 cache sharing. $ cpuinfo Place odd processes on cores sharing L 2 cache: $ mpiexec –grr 8 –genv I_MPI_PIN_PROCESSOR_LIST ? , ? , ? –n 2 IMB-MPI 1 Pingpong Place even processes on cores sharing L 2 cache: $ mpiexec –grr 8 –genv I_MPI_PIN_PROCESSOR_LIST ? , ? , ? –n 2 IMB-MPI 1 Pingpong Intel MPI Library 45 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning advice: Use Intel MPI lightweight statistics • For any Intel MPI 3. 1 application, enable gathering MPI communication statistics with the I_MPI_STATS set to a non-zero integer value. • Results will be written into a file named ‘stats. txt’ or any other file specified by the I_MPI_STATS_FILE environment variable. • Statistics includes: • • Point to point communication activity Collective operations timing Rank to rank data transfer volume Increase effectiveness of the analysis manipulating the scope of statistics with variable I_MPI_STATS_SCOPE and details of the statistics with variable I_MPI_STATS • Reasonable values to adjust collective operations algorithm are I_MPI_STATS=3 and I_MPI_STATS_SCOPE=coll Stats. txt for HPCC/Random. Access ~~~~ Process 0 of 256 on node C-21 -23 Data Transfers Src --> Dst Amount(MB) Transfers --------------------000 --> 000 0. 000000 e+00 000 --> 001 1. 548767 e-03 000 --> 002 1. 625061 e-03 000 --> 003 0. 000000 e+00 000 --> 004 1. 777649 e-03 … ===================== Totals 3. 918986 e+03 1209 0 60 60 Communication Activity Operation Volume(MB) Calls --------------------P 2 P Csend 9. 147644 e-02 1160 Send 3. 918895 e+03 49 Collectives Barrier 0. 000000 e+00 12 Bcast 3. 051758 e-05 6 Reduce 3. 433228 e-05 6 Allgather 2. 288818 e-04 30 Allreduce 4. 108429 e-03 97 $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_STATS 3 –I_MPI_STATS_SCOPE coll … Intel MPI Library 46 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning advice: Choose the best collective algorithms • There are 2 or more algorithms for each MPI collective operation. Check all to find the most suitable. • Use one of the I_MPI_ADJUST_<opname> knobs to change the algorithm, for example: • I_MPI_ADJUST_ALLREDUCE controls MPI_Allreduce algorithm, which could be (1) recursive doubling algorithm, (2) Bruck’s algorithm, (3) Reduce + Bcast or (4) Topology aware Reduce + Bcast algorithm. • Section “ 3. 5 Collective Operation Control” of Intel MPI Reference Manual defines the full set of variables and algorithm identifiers. • Recommendations: • • Focus on the most critical collective operations (see stats output). Run Intel MPI Benchmarks selecting various algorithms to find out the right protocol switchover points for hot collective operations. $ mpirun -genv I_MPI_ADJUST_REDUCE 4 -n 256. /fluent Intel MPI Library 47 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Task #10: adjust collectives Collect statistics for Alltoall test from IMB benchmark. $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_STATS –n 8 IMB-MPI 1 Alltoall Try different algorithms. Check performance impact with IMB lightweight statistics: $ mpiexec –genv I_MPI_STATS –genv I_MPI_ADJUST_? ? –n 8 IMB-MPI 1 Alltoall Intel MPI Library 48 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Tuning aqdvice: Use Intel MPI automatic tuning utility • Find optimal values for library tuning knobs on the particular cluster environment with the automated tuning utility • Run it once after installation and each time after cluster configuration change • Best configuration is recorded for each combination of communication device, number of nodes, MPI ranks and process distribution model • Per-installation tune done by cluster administrator: • Collect configuration values: $ mpitune –n 32 –f. /mpd. hosts • Check tuning results added to the package: $ ls /opt/intel/impi/3. 1/etc 64 • Reuse recorded values: $ mpiexec –tune –n 32. /your_app • Custom tune by ordinary users: • Collect configuration values: $ mpitune –n 32 –f. /mpd. hosts –o <user_dir> • Check tune results recorded to user_dir: $ ls <user_dir> • Reuse recorded values: $ export I_MPI_TUNER_DATA_DIR=<user_dir> $ mpiexec –tune –n 32. /your_app Intel MPI Library 49 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Stay tuned! • Learn more online • Intel® MPI self-help pages support. intel. com/support/performancetools/cluster/mpi/index. htm • Ask questions and share your knowledge • Intel® MPI Library support page http: //support. intel. com/support/performancetools/cluster/mpi/in dex. htm • Intel® Software Network Forums http: //softwarecommunity. intel. com/isn/Community/enus/Forums/ Intel MPI Library 50 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Backup Intel MPI Library 51 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Lab– mpiexec for Admins See how mpiexec transports the environment • Setenv (csh) or export (sh) any new variable • mpiexec –l –n 2 env | sort • Find the variable on both processes! Running scripts with mpiexec • Gather some commands in a script e. g. hostname; cat /etc/dat. conf • mpiexec –l –n 2 ascript | sort Intel MPI Library 52 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Lab– mpiexec for Admins (contd. ) Mpiexec does not transport local limits • Check limits: “limit”(csh) or “ulimit –a” (sh) • Set new stacksize limit • csh: limit stacksize 20 megabytes; csh –fc limit • sh: ulimit –s 20000; sh –c “ulimit –a” • Check remote limits • mpiexec –l –n 2 csh –fc limit | sort • mpiexec –l –n 2 sh –c “ulimit –a” | sort • Conclusion: Set limits in. cshrc or. profile or: Encapsulate in application script Intel MPI Library 53 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

Intel MPI Library 54 Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved. Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries. *Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
37fa44e527830c39df35a7d93920cadd.ppt