02 Integration.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 11

Integration 02

Today’s objectives • To use integration by substitution to integrate some products and some quotients.

The general idea of substitution • Integration by substitution is similar to differentiating by the chain rule. • It lets you integrate products and quotients involving functions of functions by simplifying the integral. • We write part of the integral in terms of u, where u is a function of x, and then rewrite the whole integral in terms of u and du.
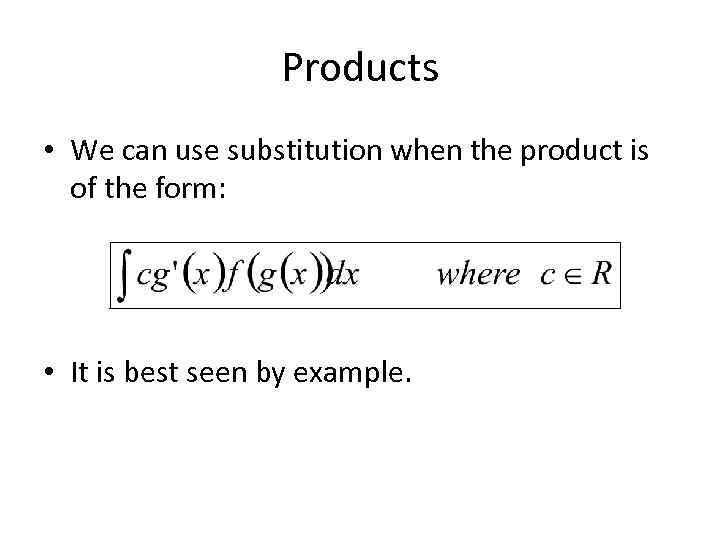
Products • We can use substitution when the product is of the form: • It is best seen by example.

Product examples Integrate the following w. r. t. x: 1. 2 xex^2 2. 2 x(x 2 + 3)7 3. x 2√(x 3 + 5) 4. x 3 cos(x 4 + 2) 5. sin 5 xcosx 6. sec 2 xtan 5 x 7. x 2√(x + 1) (Note: #7 is a special case since x 2 is not the derivative of x + 1 but substitution can still be used because it makes the integral simpler. )
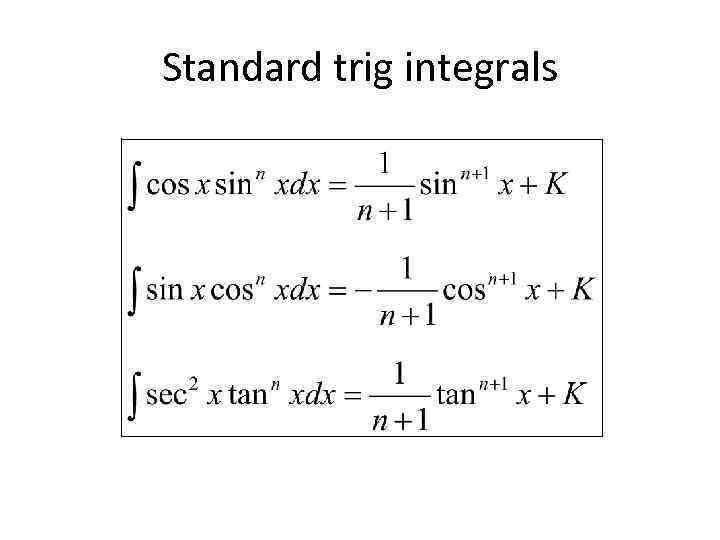
Standard trig integrals
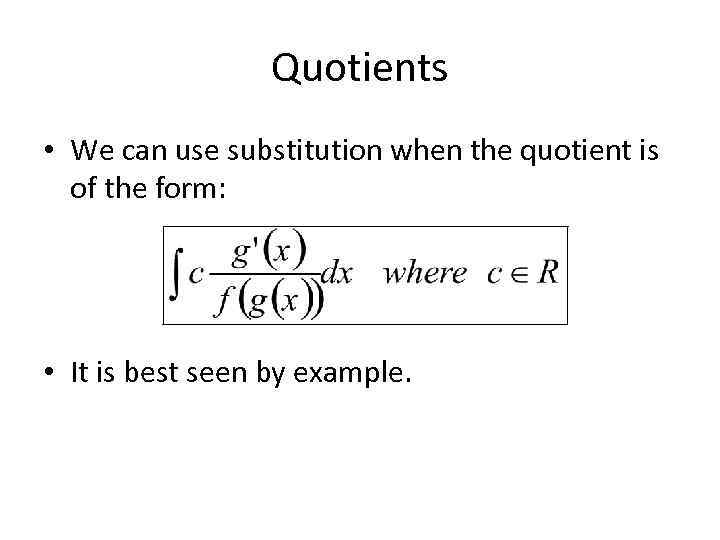
Quotients • We can use substitution when the quotient is of the form: • It is best seen by example.

Quotient examples Integrate the following w. r. t. x: 1. 2 x/ √(x 2 +1) 2. cosx/sin 4 x 3. 1/xlnx (special case) 4. x/ √(1 – 4 x 2) 5. 1/ √(1 – 4 x 2) (inverse trig) 6. π/(49 + 9 x 2) (inverse trig) 7. (3 x + 4)/ √(x + 1) 8. e 2 x/ √(ex + 1) (special case) (Note: #7&8 are special cases since their numerators are not the derivative of the denominator but substitution can still be used. )
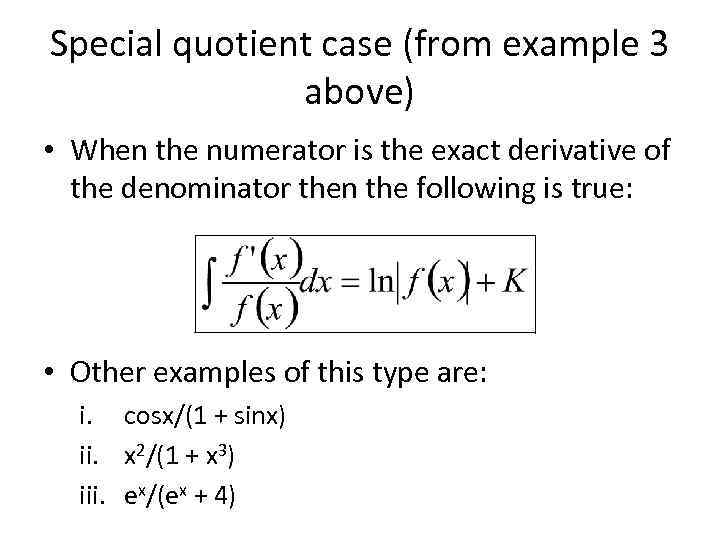
Special quotient case (from example 3 above) • When the numerator is the exact derivative of the denominator then the following is true: • Other examples of this type are: i. cosx/(1 + sinx) ii. x 2/(1 + x 3) iii. ex/(ex + 4)
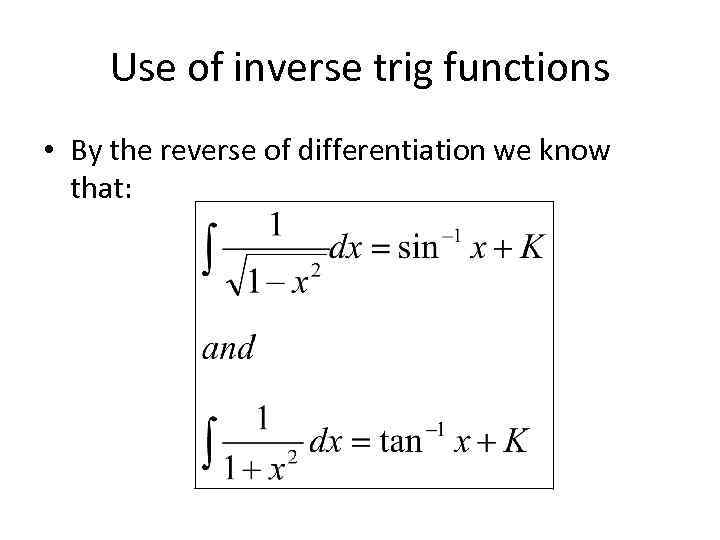
Use of inverse trig functions • By the reverse of differentiation we know that:
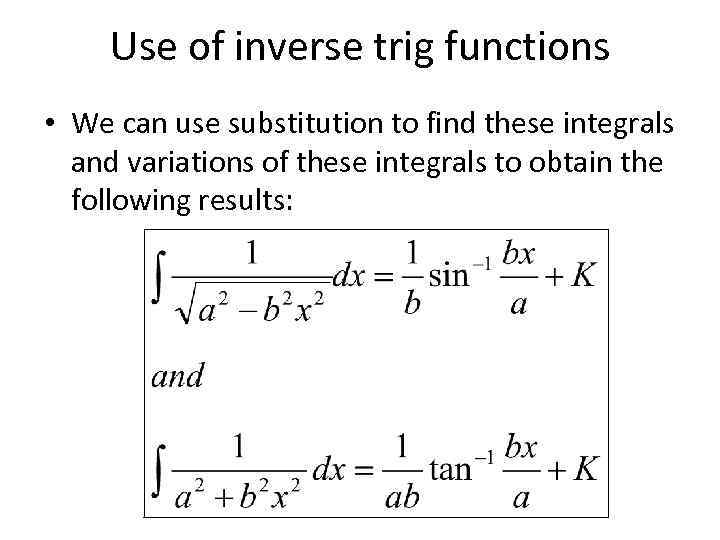
Use of inverse trig functions • We can use substitution to find these integrals and variations of these integrals to obtain the following results:
02 Integration.pptx