b0e9272f21b817bbecb507f3bbd59f3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise Organizing IHE Integration Profiles related to the Electronic Health Record Initial Thoughts Summary for the IHE International Meeting RSNA, November 2003 C. Parisot, GE
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise Organizing IHE Integration Profiles related to the Electronic Health Record Initial Thoughts Summary for the IHE International Meeting RSNA, November 2003 C. Parisot, GE
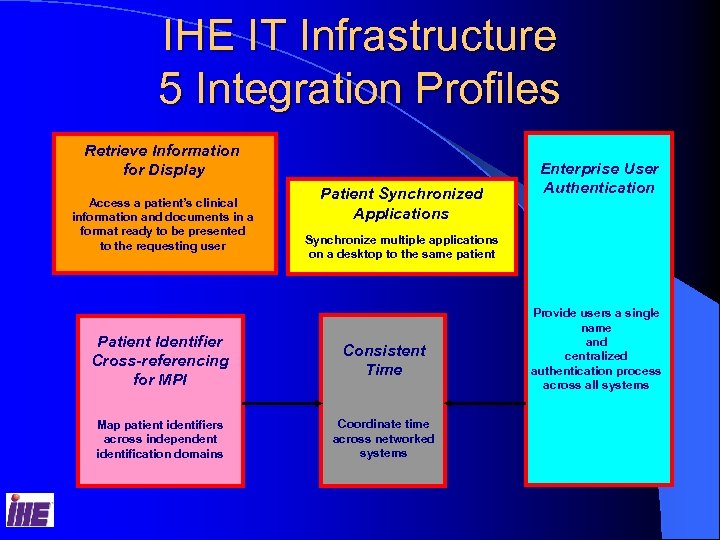 IHE IT Infrastructure 5 Integration Profiles Retrieve Information for Display Access a patient’s clinical information and documents in a format ready to be presented to the requesting user Patient Synchronized Applications Enterprise User Authentication Synchronize multiple applications on a desktop to the same patient Patient Identifier Cross-referencing for MPI Consistent Time Map patient identifiers across independent identification domains Coordinate time across networked systems Provide users a single name and centralized authentication process across all systems
IHE IT Infrastructure 5 Integration Profiles Retrieve Information for Display Access a patient’s clinical information and documents in a format ready to be presented to the requesting user Patient Synchronized Applications Enterprise User Authentication Synchronize multiple applications on a desktop to the same patient Patient Identifier Cross-referencing for MPI Consistent Time Map patient identifiers across independent identification domains Coordinate time across networked systems Provide users a single name and centralized authentication process across all systems
 New at HIMSS in 2004 l In 2002 and 2003, IHE and HL 7 have held separate demonstration – HL 7 demos were « throw away » – IHE demos were « radiology centric » IHE is now in Healthcare IT - 5 new profiles to be showcased at HIMSS 2004 l HL 7 and IHE have decided this year to combine their demos and convey a 2 tier message: l – HL 7 broad in scope but leaves choices for interoperability – IHE Profiles are narrow in scope but high interoperability
New at HIMSS in 2004 l In 2002 and 2003, IHE and HL 7 have held separate demonstration – HL 7 demos were « throw away » – IHE demos were « radiology centric » IHE is now in Healthcare IT - 5 new profiles to be showcased at HIMSS 2004 l HL 7 and IHE have decided this year to combine their demos and convey a 2 tier message: l – HL 7 broad in scope but leaves choices for interoperability – IHE Profiles are narrow in scope but high interoperability
 IHE Integration Profiles Focused on the EHR Shaping a strategy and plan for the next three years • IHE has developed close to 20 Integration Profiles focuses on Radiology, Laboratory, IT Infrastructure (MPI, Security, etc. ) and is now expanding to Cardiology. This is an intra-enterprise, bottom-up approach. • In this proposal, IHE explains how it intends to approach the longitudinal dimension of the EHR with a distributed, cross-enterprise, document centric, top-down point of view. • The strategy is to progressively bridge the two approaches as new integration profiles are developed. Feedback on this approach and expanding collaborations are sought.
IHE Integration Profiles Focused on the EHR Shaping a strategy and plan for the next three years • IHE has developed close to 20 Integration Profiles focuses on Radiology, Laboratory, IT Infrastructure (MPI, Security, etc. ) and is now expanding to Cardiology. This is an intra-enterprise, bottom-up approach. • In this proposal, IHE explains how it intends to approach the longitudinal dimension of the EHR with a distributed, cross-enterprise, document centric, top-down point of view. • The strategy is to progressively bridge the two approaches as new integration profiles are developed. Feedback on this approach and expanding collaborations are sought.
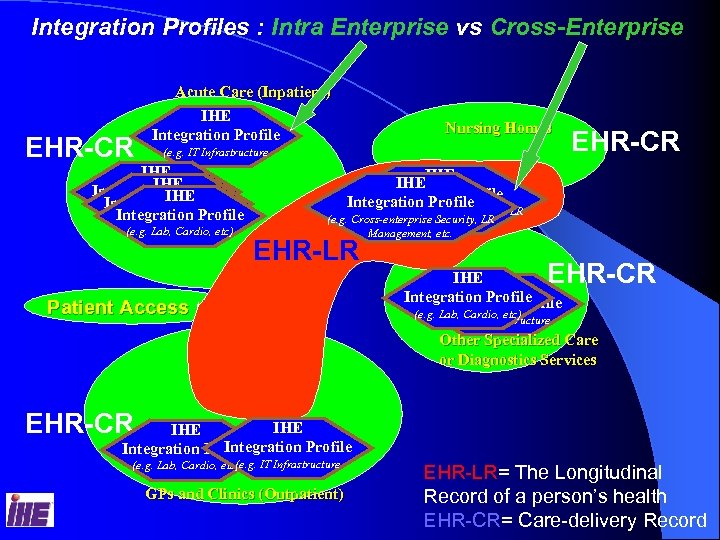 Integration Profiles : Intra Enterprise vs Cross-Enterprise EHR-CR Acute Care (Inpatient) IHE Integration Profile Nursing Homes (e. g. IT Infrastructure IHE Integration Profile (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) EHR-CR IHEIHE Integration Profile (e. g. Cross-enterprise Security, LR Management, etc. EHR-LR Patient Access EHR-CR IHE Integration Profile (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) (e. g. IT Infrastructure Other Specialized Care or Diagnostics Services EHR-CR IHE Integration Profile (e. g. IT Infrastructure (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) GPs and Clinics (Outpatient) EHR-LR= The Longitudinal Record of a person’s health EHR-CR= Care-delivery Record
Integration Profiles : Intra Enterprise vs Cross-Enterprise EHR-CR Acute Care (Inpatient) IHE Integration Profile Nursing Homes (e. g. IT Infrastructure IHE Integration Profile (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) EHR-CR IHEIHE Integration Profile (e. g. Cross-enterprise Security, LR Management, etc. EHR-LR Patient Access EHR-CR IHE Integration Profile (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) (e. g. IT Infrastructure Other Specialized Care or Diagnostics Services EHR-CR IHE Integration Profile (e. g. IT Infrastructure (e. g. Lab, Cardio, etc) GPs and Clinics (Outpatient) EHR-LR= The Longitudinal Record of a person’s health EHR-CR= Care-delivery Record
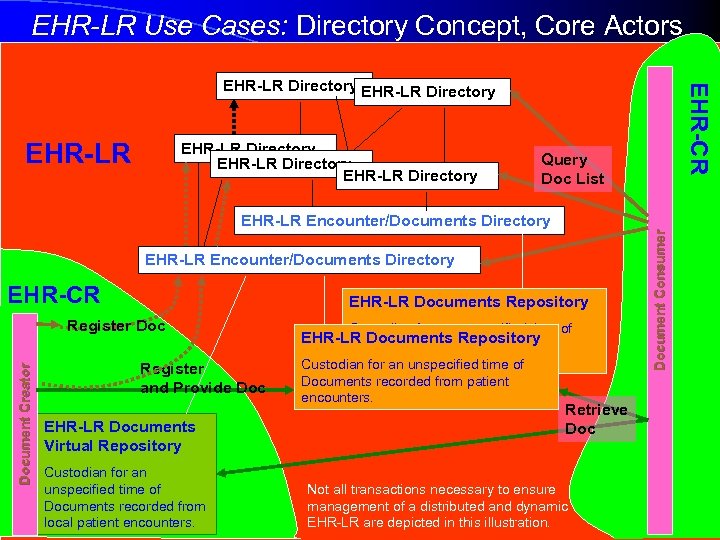 EHR-LR Use Cases: Directory Concept, Core Actors EHR-LR Directory EHR-CR EHR-LR Directory Query Doc List EHR-LR Encounter/Documents Directory EHR-CR EHR-LR Documents Repository Document Creator Register Doc Register and Provide Doc EHR-LR Documents Virtual Repository Custodian for an unspecified time of Documents recorded from local patient encounters. Custodian for an unspecified time of EHR-LR Documents Repository Documents recorded from patient encounters. Custodian for an unspecified time of Documents recorded from patient encounters. Retrieve Doc Not all transactions necessary to ensure management of a distributed and dynamic EHR-LR are depicted in this illustration. Document Consumer EHR-LR Encounter/Documents Directory
EHR-LR Use Cases: Directory Concept, Core Actors EHR-LR Directory EHR-CR EHR-LR Directory Query Doc List EHR-LR Encounter/Documents Directory EHR-CR EHR-LR Documents Repository Document Creator Register Doc Register and Provide Doc EHR-LR Documents Virtual Repository Custodian for an unspecified time of Documents recorded from local patient encounters. Custodian for an unspecified time of EHR-LR Documents Repository Documents recorded from patient encounters. Custodian for an unspecified time of Documents recorded from patient encounters. Retrieve Doc Not all transactions necessary to ensure management of a distributed and dynamic EHR-LR are depicted in this illustration. Document Consumer EHR-LR Encounter/Documents Directory
 IHE Integration Profiles Focused on the EHR • In this proposal, IHE has proposed an approach the longitudinal dimension of the EHR, with a distributed, cross-enterprise, document centric, top-down point of view. • 30 principles have been defined for the definition of EHR-LR IHE Integration Profiles. Feedback on this approach and expanding collaborations are sought. Is this a useful “brick” ? • The proposed strategy is a scoping exercise to address one of the many integration problems in the realization of the EHR vision. IHE does not claim to master and address the definition and all aspects of a complete and interoperable EHR System. • In collaboration with well established standards bodies and other EHR related initiatives world-wide (EHRCOM, CCR, HL 7, etc. ), IHE expects to contribute at a more cost-effective and rapid deployment.
IHE Integration Profiles Focused on the EHR • In this proposal, IHE has proposed an approach the longitudinal dimension of the EHR, with a distributed, cross-enterprise, document centric, top-down point of view. • 30 principles have been defined for the definition of EHR-LR IHE Integration Profiles. Feedback on this approach and expanding collaborations are sought. Is this a useful “brick” ? • The proposed strategy is a scoping exercise to address one of the many integration problems in the realization of the EHR vision. IHE does not claim to master and address the definition and all aspects of a complete and interoperable EHR System. • In collaboration with well established standards bodies and other EHR related initiatives world-wide (EHRCOM, CCR, HL 7, etc. ), IHE expects to contribute at a more cost-effective and rapid deployment.
 Draft IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap In support of the IHE Integration Profiles focused on the EHR Draft for Comments – 11/03 To be finalized January 2004.
Draft IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap In support of the IHE Integration Profiles focused on the EHR Draft for Comments – 11/03 To be finalized January 2004.
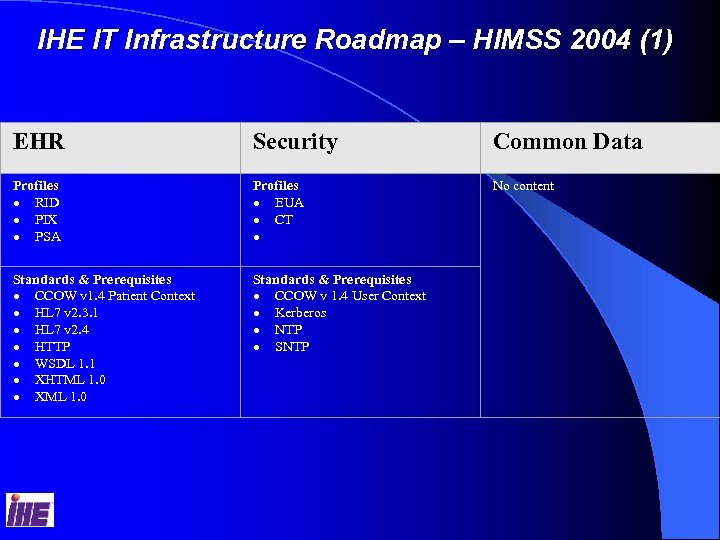 IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – HIMSS 2004 (1) EHR Security Common Data Profiles · RID · PIX · PSA Profiles · EUA · CT · No content Standards & Prerequisites · CCOW v 1. 4 Patient Context · HL 7 v 2. 3. 1 · HL 7 v 2. 4 · HTTP · WSDL 1. 1 · XHTML 1. 0 · XML 1. 0 Standards & Prerequisites · CCOW v 1. 4 User Context · Kerberos · NTP · SNTP
IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – HIMSS 2004 (1) EHR Security Common Data Profiles · RID · PIX · PSA Profiles · EUA · CT · No content Standards & Prerequisites · CCOW v 1. 4 Patient Context · HL 7 v 2. 3. 1 · HL 7 v 2. 4 · HTTP · WSDL 1. 1 · XHTML 1. 0 · XML 1. 0 Standards & Prerequisites · CCOW v 1. 4 User Context · Kerberos · NTP · SNTP
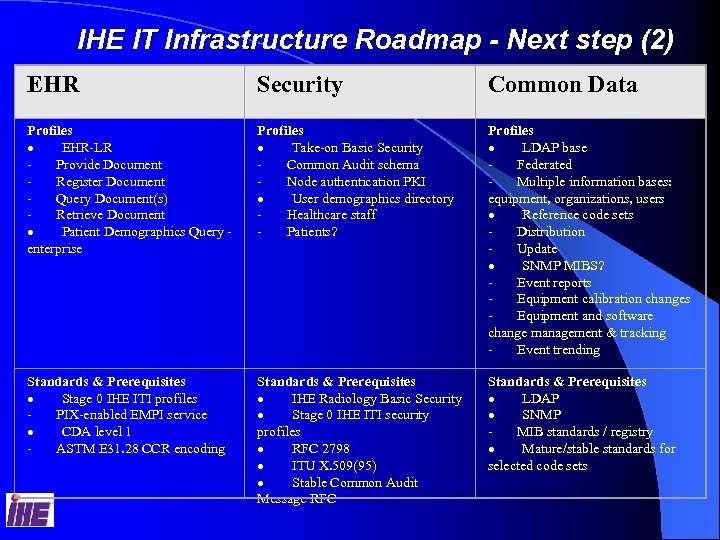 IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap - Next step (2) EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - Provide Document - Register Document - Query Document(s) - Retrieve Document · Patient Demographics Query - enterprise Profiles · Take-on Basic Security - Common Audit schema - Node authentication PKI · User demographics directory - Healthcare staff - Patients? Profiles · LDAP base - Federated - Multiple information bases: equipment, organizations, users · Reference code sets - Distribution - Update · SNMP MIBS? - Event reports - Equipment calibration changes - Equipment and software change management & tracking - Event trending Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 0 IHE ITI profiles - PIX-enabled EMPI service · CDA level 1 - ASTM E 31. 28 CCR encoding Standards & Prerequisites · IHE Radiology Basic Security · Stage 0 IHE ITI security profiles · RFC 2798 · ITU X. 509(95) · Stable Common Audit Message RFC Standards & Prerequisites · LDAP · SNMP - MIB standards / registry · Mature/stable standards for selected code sets
IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap - Next step (2) EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - Provide Document - Register Document - Query Document(s) - Retrieve Document · Patient Demographics Query - enterprise Profiles · Take-on Basic Security - Common Audit schema - Node authentication PKI · User demographics directory - Healthcare staff - Patients? Profiles · LDAP base - Federated - Multiple information bases: equipment, organizations, users · Reference code sets - Distribution - Update · SNMP MIBS? - Event reports - Equipment calibration changes - Equipment and software change management & tracking - Event trending Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 0 IHE ITI profiles - PIX-enabled EMPI service · CDA level 1 - ASTM E 31. 28 CCR encoding Standards & Prerequisites · IHE Radiology Basic Security · Stage 0 IHE ITI security profiles · RFC 2798 · ITU X. 509(95) · Stable Common Audit Message RFC Standards & Prerequisites · LDAP · SNMP - MIB standards / registry · Mature/stable standards for selected code sets
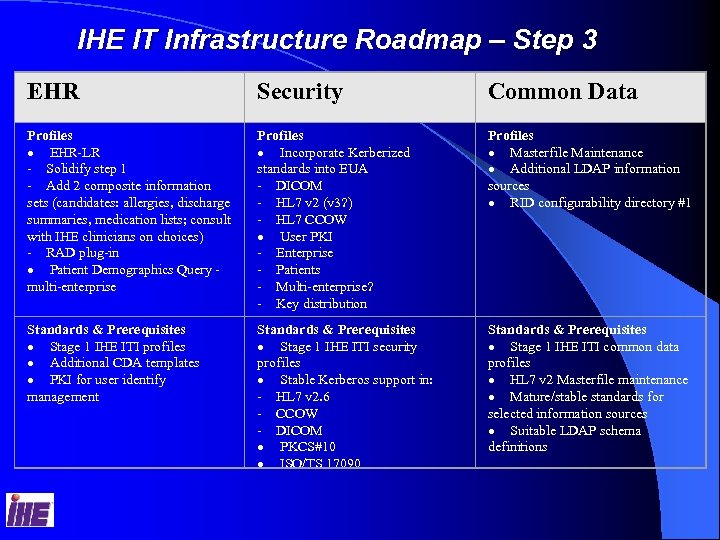 IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 3 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - Solidify step 1 - Add 2 composite information sets (candidates: allergies, discharge summaries, medication lists; consult with IHE clinicians on choices) - RAD plug-in · Patient Demographics Query - multi-enterprise Profiles · Incorporate Kerberized standards into EUA - DICOM - HL 7 v 2 (v 3? ) - HL 7 CCOW · User PKI - Enterprise - Patients - Multi-enterprise? - Key distribution Profiles · Masterfile Maintenance · Additional LDAP information sources · RID configurability directory #1 Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI profiles · Additional CDA templates · PKI for user identify management Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI security profiles · Stable Kerberos support in: - HL 7 v 2. 6 - CCOW - DICOM · PKCS#10 · ISO/TS 17090 Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI common data profiles · HL 7 v 2 Masterfile maintenance · Mature/stable standards for selected information sources · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 3 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - Solidify step 1 - Add 2 composite information sets (candidates: allergies, discharge summaries, medication lists; consult with IHE clinicians on choices) - RAD plug-in · Patient Demographics Query - multi-enterprise Profiles · Incorporate Kerberized standards into EUA - DICOM - HL 7 v 2 (v 3? ) - HL 7 CCOW · User PKI - Enterprise - Patients - Multi-enterprise? - Key distribution Profiles · Masterfile Maintenance · Additional LDAP information sources · RID configurability directory #1 Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI profiles · Additional CDA templates · PKI for user identify management Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI security profiles · Stable Kerberos support in: - HL 7 v 2. 6 - CCOW - DICOM · PKCS#10 · ISO/TS 17090 Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 1 IHE ITI common data profiles · HL 7 v 2 Masterfile maintenance · Mature/stable standards for selected information sources · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
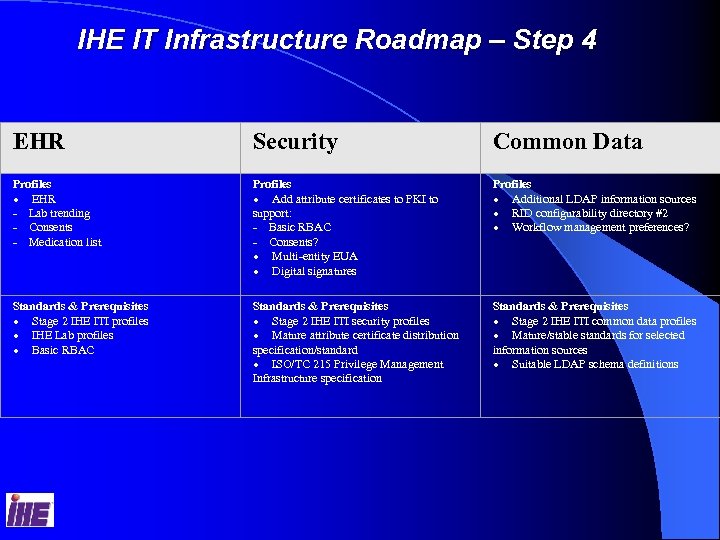 IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 4 4 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR - Lab trending - Consents - Medication list Profiles · Add attribute certificates to PKI to support: - Basic RBAC - Consents? · Multi-entity EUA · Digital signatures Profiles · Additional LDAP information sources · RID configurability directory #2 · Workflow management preferences? Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI profiles · IHE Lab profiles · Basic RBAC Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI security profiles · Mature attribute certificate distribution specification/standard · ISO/TC 215 Privilege Management Infrastructure specification Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI common data profiles · Mature/stable standards for selected information sources · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 4 4 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR - Lab trending - Consents - Medication list Profiles · Add attribute certificates to PKI to support: - Basic RBAC - Consents? · Multi-entity EUA · Digital signatures Profiles · Additional LDAP information sources · RID configurability directory #2 · Workflow management preferences? Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI profiles · IHE Lab profiles · Basic RBAC Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI security profiles · Mature attribute certificate distribution specification/standard · ISO/TC 215 Privilege Management Infrastructure specification Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 2 IHE ITI common data profiles · Mature/stable standards for selected information sources · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
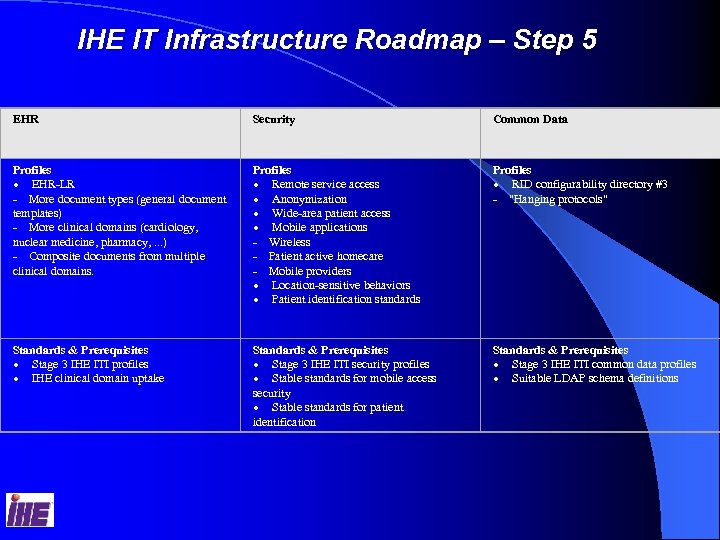 IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 5 5 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - More document types (general document templates) - More clinical domains (cardiology, nuclear medicine, pharmacy, . . . ) - Composite documents from multiple clinical domains. Profiles · Remote service access · Anonymization · Wide-area patient access · Mobile applications - Wireless - Patient active homecare - Mobile providers · Location-sensitive behaviors · Patient identification standards Profiles · RID configurability directory #3 - "Hanging protocols" Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI profiles · IHE clinical domain uptake Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI security profiles · Stable standards for mobile access security · Stable standards for patient identification Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI common data profiles · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
IHE IT Infrastructure Roadmap – Step 5 5 EHR Security Common Data Profiles · EHR-LR - More document types (general document templates) - More clinical domains (cardiology, nuclear medicine, pharmacy, . . . ) - Composite documents from multiple clinical domains. Profiles · Remote service access · Anonymization · Wide-area patient access · Mobile applications - Wireless - Patient active homecare - Mobile providers · Location-sensitive behaviors · Patient identification standards Profiles · RID configurability directory #3 - "Hanging protocols" Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI profiles · IHE clinical domain uptake Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI security profiles · Stable standards for mobile access security · Stable standards for patient identification Standards & Prerequisites · Stage 3 IHE ITI common data profiles · Suitable LDAP schema definitions
 Principles in support of the IHE Integration Profiles focused on the EHR Draft for Comments – 11/03 To be finalized January 2004.
Principles in support of the IHE Integration Profiles focused on the EHR Draft for Comments – 11/03 To be finalized January 2004.
 Key Statements : IHE Focuses on the EHR-LR 1. The EHR-LR (Longitudinal Record) federates patient encounter information managed by “EHRs within an enterprise” (EHR-CRs). EHR CRs (Care-delivery Record) may range from a large EHR of an IDN enterprise all the way down to a single practice management system. 2. EHR-LR includes repositories of encounter data that contribute to the patient’s longitudinal healthcare record. EHR-LR data will be stored in multiple repositories (depts. , sites, domains). 3. Encounter data includes some information/state/workflow info that may not end up in the EHR-LR.
Key Statements : IHE Focuses on the EHR-LR 1. The EHR-LR (Longitudinal Record) federates patient encounter information managed by “EHRs within an enterprise” (EHR-CRs). EHR CRs (Care-delivery Record) may range from a large EHR of an IDN enterprise all the way down to a single practice management system. 2. EHR-LR includes repositories of encounter data that contribute to the patient’s longitudinal healthcare record. EHR-LR data will be stored in multiple repositories (depts. , sites, domains). 3. Encounter data includes some information/state/workflow info that may not end up in the EHR-LR.
 Key Statements: What is in the EHR-LR ? 1. The EHR-LR data is made of discrete, persistent, logical documents which may be accessed by a unique identifier. 2. LR data is coded/formatted according to relevant clinical domain standards. The body of clinical domain standards is expected to evolve. 3. Conversion between EHR-CR data “formats” and EHR-LR document “formats” is the responsibility of the EHR-CR. 4. At the end of an encounter, new document(s) are added to the EHR-LR. These new EHR-LR docs could be stored (in any form) in the EHR-CR where they are created or pushed to a separate EHR-LR repository (in a standard format). 5. EHR-LR will likely be initially focused on certain pathologies (cardiology, oncology, etc) or a key information for continuity of care (CCR summaries only) and expand progressively.
Key Statements: What is in the EHR-LR ? 1. The EHR-LR data is made of discrete, persistent, logical documents which may be accessed by a unique identifier. 2. LR data is coded/formatted according to relevant clinical domain standards. The body of clinical domain standards is expected to evolve. 3. Conversion between EHR-CR data “formats” and EHR-LR document “formats” is the responsibility of the EHR-CR. 4. At the end of an encounter, new document(s) are added to the EHR-LR. These new EHR-LR docs could be stored (in any form) in the EHR-CR where they are created or pushed to a separate EHR-LR repository (in a standard format). 5. EHR-LR will likely be initially focused on certain pathologies (cardiology, oncology, etc) or a key information for continuity of care (CCR summaries only) and expand progressively.
 Key Statements : IHE Constraints 1. The domains of EHR content are primarily clinical. Other information and services are needed to provide an operational EHR-LR environment (e. g. demographics, security, consents – IHE has already addressed some). 2. Different EHR-LR and EHR-CR repositories may be using different Patient Ids. 3. The care-delivery view and form of current encounter data (EHR-CR) is out of scope of EHR-LR IHE Integration Profiles.
Key Statements : IHE Constraints 1. The domains of EHR content are primarily clinical. Other information and services are needed to provide an operational EHR-LR environment (e. g. demographics, security, consents – IHE has already addressed some). 2. Different EHR-LR and EHR-CR repositories may be using different Patient Ids. 3. The care-delivery view and form of current encounter data (EHR-CR) is out of scope of EHR-LR IHE Integration Profiles.
 Key Statements : Accessing EHR-LR 1. EHR-LR shall provide a list of available documents for a patient. Logical directories are necessary to provide such document lists. 2. The full burden of locating and filtering documents should not be placed on the EHR-LR consumer applications. The EHRLR needs to have some meta-information about the documents it tracks. 3. There is a need for the EHR-LR to provide a means to retrieve the clinical documents that have been registered with full content fidelity. 4. There is a also a need for the EHR-LR to provide clinical data to consumer applications based on processing, extracting, or combining the content multiple existing documents. 5. Documents may reference other documents including images, waveforms, etc.
Key Statements : Accessing EHR-LR 1. EHR-LR shall provide a list of available documents for a patient. Logical directories are necessary to provide such document lists. 2. The full burden of locating and filtering documents should not be placed on the EHR-LR consumer applications. The EHRLR needs to have some meta-information about the documents it tracks. 3. There is a need for the EHR-LR to provide a means to retrieve the clinical documents that have been registered with full content fidelity. 4. There is a also a need for the EHR-LR to provide clinical data to consumer applications based on processing, extracting, or combining the content multiple existing documents. 5. Documents may reference other documents including images, waveforms, etc.


