221b99d9a7f1645b3d7a32619029c8ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Integrating Test Data with other Clinical Information • Three Important Principles – Avoid the Fallacy of Affirming the Consequent • because B often follows A, occurrence of B proves that A has occurred – Be Open Minded • generate as many reasonable explanations for what you see – Apply Occam’s Razor • “the most likely explanation for a pattern is the one that requires the least number of unlikely events to account for it “
Integrating Test Data with other Clinical Information • Three Important Principles – Avoid the Fallacy of Affirming the Consequent • because B often follows A, occurrence of B proves that A has occurred – Be Open Minded • generate as many reasonable explanations for what you see – Apply Occam’s Razor • “the most likely explanation for a pattern is the one that requires the least number of unlikely events to account for it “
 Errors in Formulation Affirming the Consequent • Complains of memory change after MVA • Testing - diffuse pattern (moderate-severe deficits in attention, executive function, processing speed c/w traumatic brain injury) • MRI – subtle, diffuse changes in deep white matter
Errors in Formulation Affirming the Consequent • Complains of memory change after MVA • Testing - diffuse pattern (moderate-severe deficits in attention, executive function, processing speed c/w traumatic brain injury) • MRI – subtle, diffuse changes in deep white matter
 Additional History • No loss of consciousness in MVA • History of functional declines, sensory and motor changes in year prior to MVA • Testing 1 year later shows further declines • Neurologic examination shows abnormal nerve conduction consistent with multiple sclerosis
Additional History • No loss of consciousness in MVA • History of functional declines, sensory and motor changes in year prior to MVA • Testing 1 year later shows further declines • Neurologic examination shows abnormal nerve conduction consistent with multiple sclerosis
 Errors in Formulation Keeping an Open Mind • • Acute onset word-finding deficits – no recent events History of worsening depression Neurologic exam normal Neuropsychological testing is normal except for severe impairment in confrontation naming with paraphasias • Imaging shows multiple lesions, one in right temporal lobe with fresh blood
Errors in Formulation Keeping an Open Mind • • Acute onset word-finding deficits – no recent events History of worsening depression Neurologic exam normal Neuropsychological testing is normal except for severe impairment in confrontation naming with paraphasias • Imaging shows multiple lesions, one in right temporal lobe with fresh blood
 Additional History • Left-handed • Strong family history of – left-handedness – early strokes • Findings consistent with hemorrhage of genetically-based, cavernous angioma (small tumor of vessel wall) in right, language dominant hemisphere • Depression is irrelevant in this context
Additional History • Left-handed • Strong family history of – left-handedness – early strokes • Findings consistent with hemorrhage of genetically-based, cavernous angioma (small tumor of vessel wall) in right, language dominant hemisphere • Depression is irrelevant in this context
 Errors in Formulation ‘Occam’s Razor’ • • 54 yo. M with recent memory complaints Neurologic exam normal Normal neuroimaging Family is concerned about ‘early Alzheimer’s’
Errors in Formulation ‘Occam’s Razor’ • • 54 yo. M with recent memory complaints Neurologic exam normal Normal neuroimaging Family is concerned about ‘early Alzheimer’s’
 Additional History • Long-standing history of major depressive disorder • No family history of dementia • Trouble caring for home and finances after partner died 4 years ago • Recently ‘got lost’ standing in front of his house, recovered quickly • Continues to perform at high level at cognitively demanding job
Additional History • Long-standing history of major depressive disorder • No family history of dementia • Trouble caring for home and finances after partner died 4 years ago • Recently ‘got lost’ standing in front of his house, recovered quickly • Continues to perform at high level at cognitively demanding job
 Behavioral Geography of the Brain
Behavioral Geography of the Brain
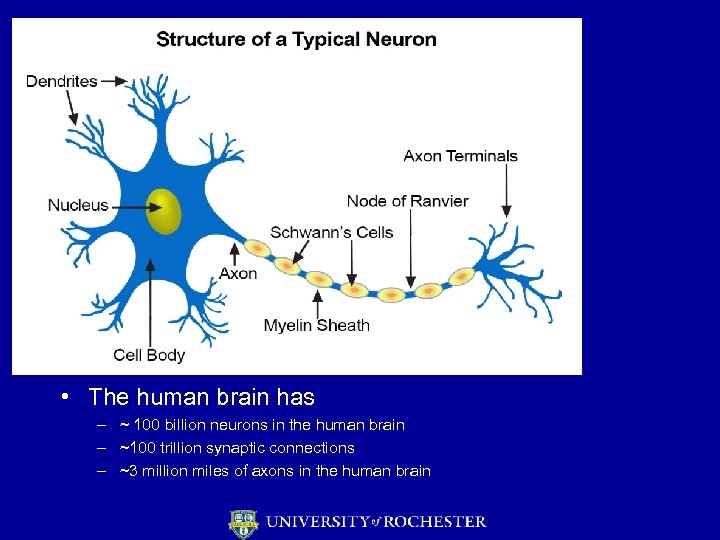 • The human brain has – ~ 100 billion neurons in the human brain – ~100 trillion synaptic connections – ~3 million miles of axons in the human brain
• The human brain has – ~ 100 billion neurons in the human brain – ~100 trillion synaptic connections – ~3 million miles of axons in the human brain
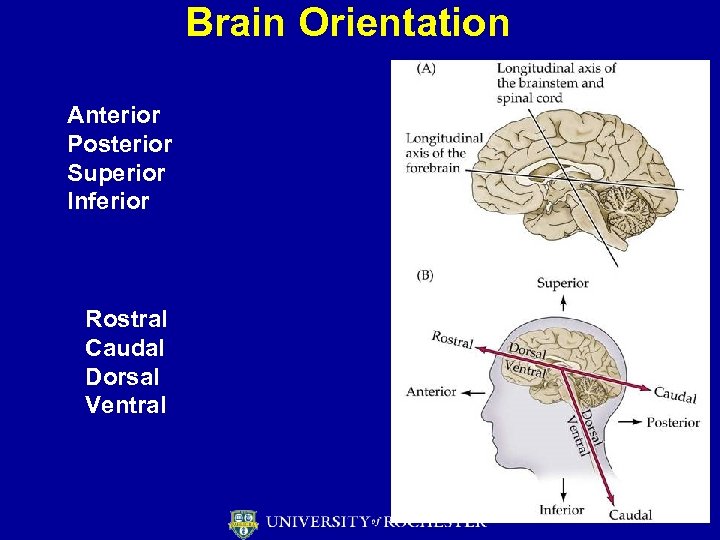 Brain Orientation Anterior Posterior Superior Inferior Rostral Caudal Dorsal Ventral
Brain Orientation Anterior Posterior Superior Inferior Rostral Caudal Dorsal Ventral
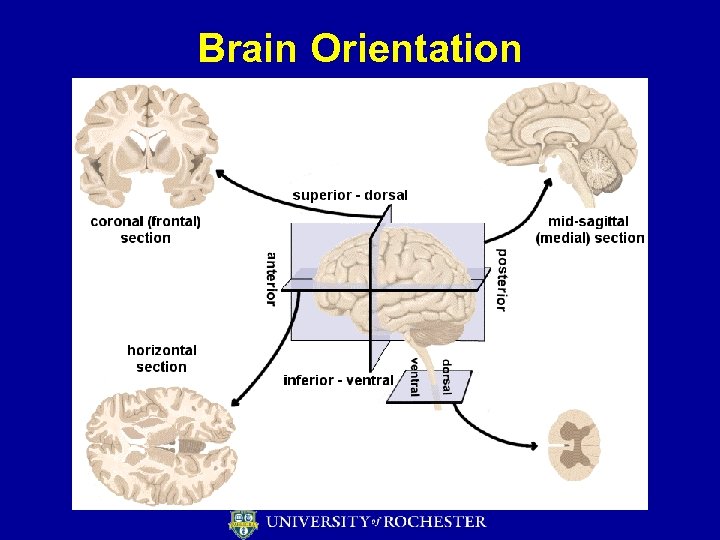 Brain Orientation
Brain Orientation
 Other definitions • • Lateral – to the side Medial (mesial) – toward the middle Proximal – areas of brain near to one another Distal – areas of the brain far from one another • Ipsilateral – structures on same side of the body • Contralateral – structures on opposite sides of body
Other definitions • • Lateral – to the side Medial (mesial) – toward the middle Proximal – areas of brain near to one another Distal – areas of the brain far from one another • Ipsilateral – structures on same side of the body • Contralateral – structures on opposite sides of body
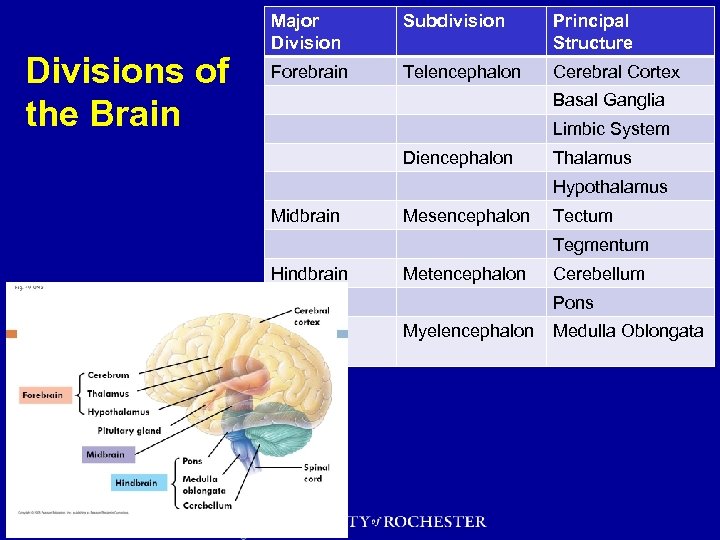 Divisions of the Brain Major Division Subdivision Principal Structure Forebrain Telencephalon Cerebral Cortex Basal Ganglia Limbic System Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Mesencephalon Tectum Tegmentum Hindbrain Metencephalon Cerebellum Pons Myelencephalon Medulla Oblongata
Divisions of the Brain Major Division Subdivision Principal Structure Forebrain Telencephalon Cerebral Cortex Basal Ganglia Limbic System Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus Midbrain Mesencephalon Tectum Tegmentum Hindbrain Metencephalon Cerebellum Pons Myelencephalon Medulla Oblongata
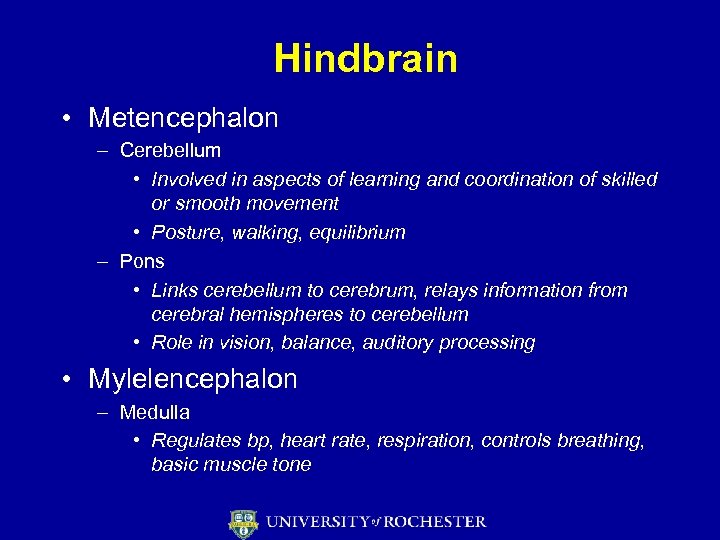 Hindbrain • Metencephalon – Cerebellum • Involved in aspects of learning and coordination of skilled or smooth movement • Posture, walking, equilibrium – Pons • Links cerebellum to cerebrum, relays information from cerebral hemispheres to cerebellum • Role in vision, balance, auditory processing • Mylelencephalon – Medulla • Regulates bp, heart rate, respiration, controls breathing, basic muscle tone
Hindbrain • Metencephalon – Cerebellum • Involved in aspects of learning and coordination of skilled or smooth movement • Posture, walking, equilibrium – Pons • Links cerebellum to cerebrum, relays information from cerebral hemispheres to cerebellum • Role in vision, balance, auditory processing • Mylelencephalon – Medulla • Regulates bp, heart rate, respiration, controls breathing, basic muscle tone
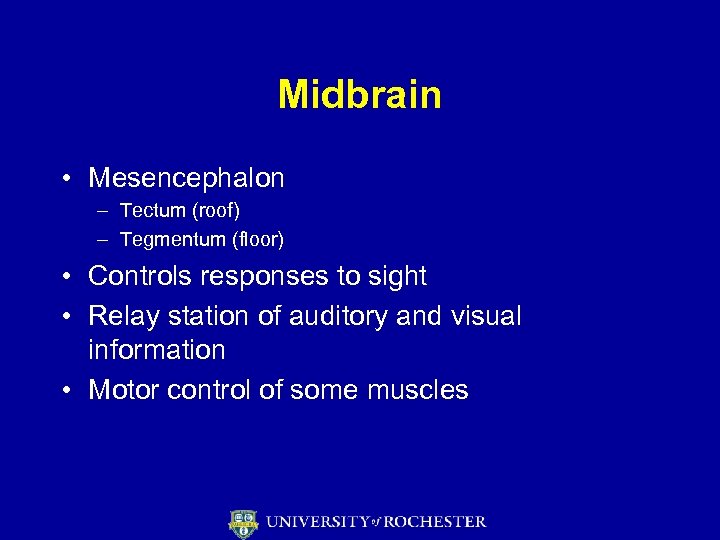 Midbrain • Mesencephalon – Tectum (roof) – Tegmentum (floor) • Controls responses to sight • Relay station of auditory and visual information • Motor control of some muscles
Midbrain • Mesencephalon – Tectum (roof) – Tegmentum (floor) • Controls responses to sight • Relay station of auditory and visual information • Motor control of some muscles
 Forebrain • Diencephalon – Thalamus – hypothalamus • Telencephalon – Limbic System – Basal Ganglia – Cerebral Cortex
Forebrain • Diencephalon – Thalamus – hypothalamus • Telencephalon – Limbic System – Basal Ganglia – Cerebral Cortex
 Diencephalon • Hypothalamus – Controls aspects of motivated (pleasure and pain) and regulatory bx • bodily functions, body temp, thirst, hunger • circadian rhythms • “master gland” – regulation and secretion of hormones • Thalamus – Gateway to cortex – Relay center for sensory information – Links nervous and endocrine system
Diencephalon • Hypothalamus – Controls aspects of motivated (pleasure and pain) and regulatory bx • bodily functions, body temp, thirst, hunger • circadian rhythms • “master gland” – regulation and secretion of hormones • Thalamus – Gateway to cortex – Relay center for sensory information – Links nervous and endocrine system
 Limbic system • Groups of structures in center of brain above brainstem – – – – amygdala hippocampus parahippocampal gyrus cingulate gyrus fornix septum olfactory bulbs • Maintains homeostasis • Emotional reactions needed for survival
Limbic system • Groups of structures in center of brain above brainstem – – – – amygdala hippocampus parahippocampal gyrus cingulate gyrus fornix septum olfactory bulbs • Maintains homeostasis • Emotional reactions needed for survival
 Basal Ganglia • Collection of subcortical nuclei in forebrain – Caudate nucleus – Putamen – Globus pallidus • Structures involved in voluntary control of movement • Motor planning and programming for speech • Attention and alerting before a motor response
Basal Ganglia • Collection of subcortical nuclei in forebrain – Caudate nucleus – Putamen – Globus pallidus • Structures involved in voluntary control of movement • Motor planning and programming for speech • Attention and alerting before a motor response
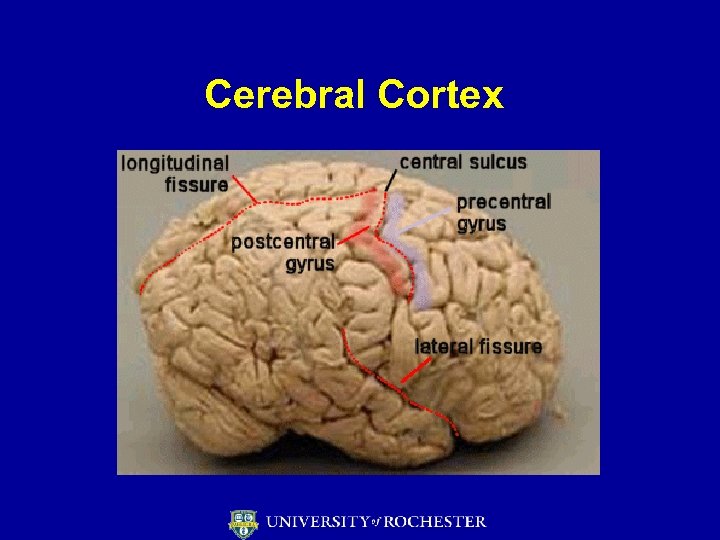 Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex
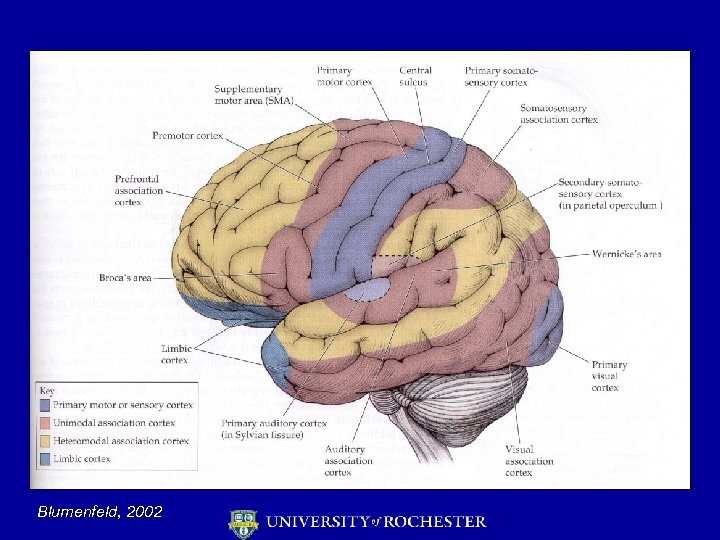 Blumenfeld, 2002
Blumenfeld, 2002
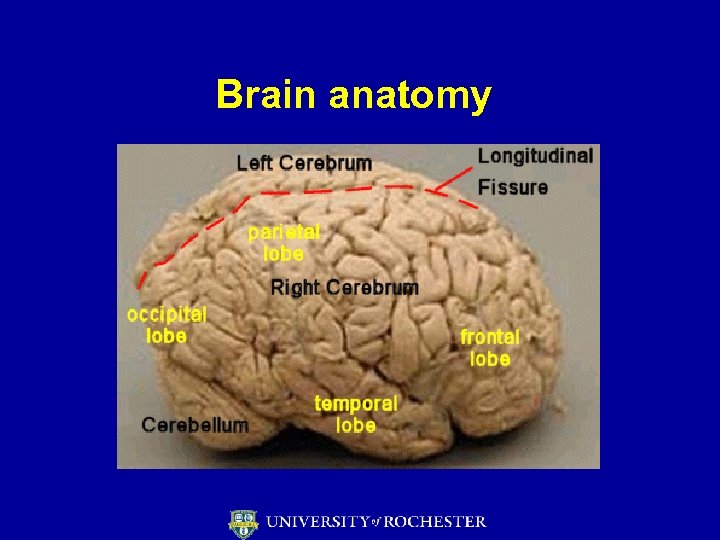 Brain anatomy
Brain anatomy
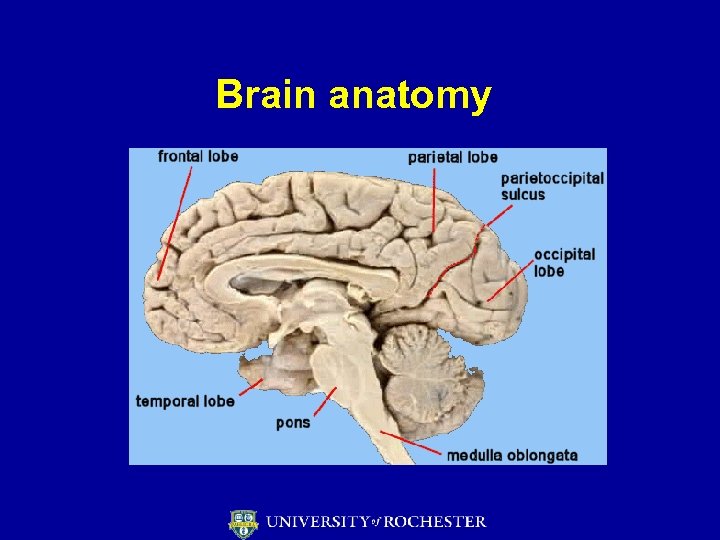 Brain anatomy
Brain anatomy