992b6fbeb1f7a8712122723759234826.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Integrating Genomic Databases Chris Stoeckert, Ph. D. Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory

Talk Outline • • Challenge of integrating biological data Federations vs warehouses GUS/RAD - warehouse approach K 2 - connecting to other systems
Challenge of Integrating Biological Data • Many sources of different types – Different types of data • • Biological sequence (DNA, RNA, protein) Gene expression Structure Etc… – Different representations of data • • Flat file Relational Object-oriented Etc… • Imposing semantics of biology – Genes and RNAs and Proteins are related • But may have different names – Biology is context dependent
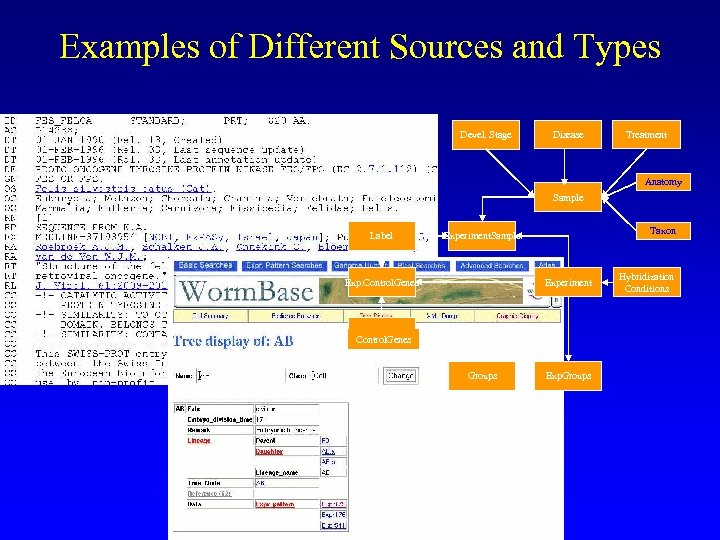
Examples of Different Sources and Types Devel. Stage Disease Treatment Anatomy Sample Label Taxon Experiment. Sample Exp. Control. Genes Experiment Control. Genes Groups Exp. Groups Hybridization Conditions
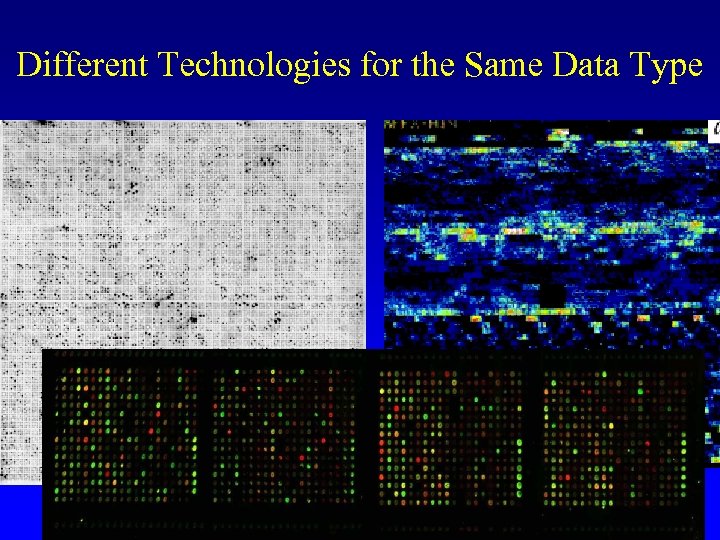
Different Technologies for the Same Data Type
Why Bother to Integrate? Remember the fable of the blind men and the elephant! http: //www. noogenesis. com/pineapple/blind_men_elephant. html

Federations vs Warehouses • Federations v. Link to everybody v. Always current – Generally stuck with data as is • Warehouses v. Bring everything in house v. Can cleanse and add value to integrated data – Staying up to date Davidson et al. IBM Systems Journal 2001
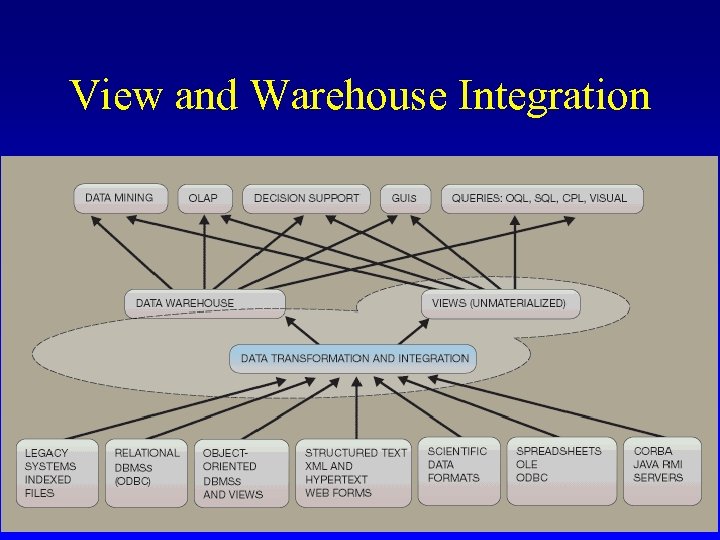
View and Warehouse Integration

GUS/RAD - Warehouse Approach • Gene Discovery – EST analysis – Genomic sequence analysis • Gene Regulation – Microarray analysis – Promoter/ regulatory region analysis • Biological data representation – Data integration – Ontology

Computational Biology and Informatics Laboratory October, 2001
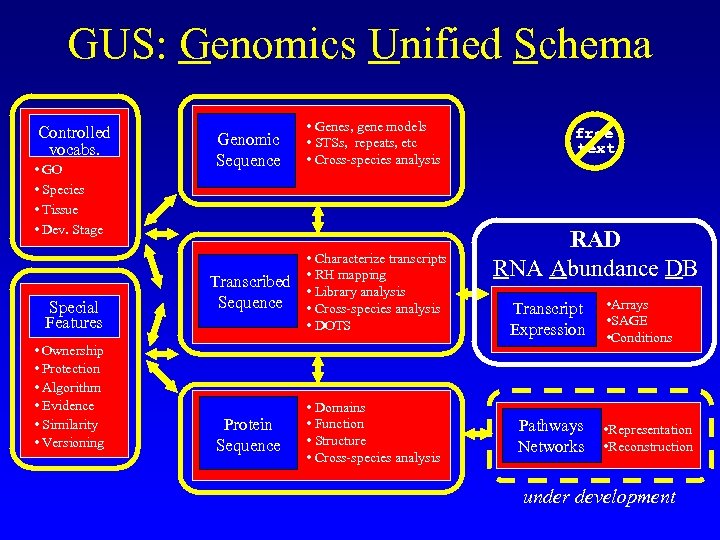
GUS: Genomics Unified Schema Controlled vocabs. • GO • Species • Tissue • Dev. Stage Special Features • Ownership • Protection • Algorithm • Evidence • Similarity • Versioning Genomic Sequence • Genes, gene models • STSs, repeats, etc • Cross-species analysis Transcribed Sequence • Characterize transcripts • RH mapping • Library analysis • Cross-species analysis • DOTS Protein Sequence • Domains • Function • Structure • Cross-species analysis free text RAD RNA Abundance DB Transcript Expression Pathways Networks • Arrays • SAGE • Conditions • Representation • Reconstruction under development
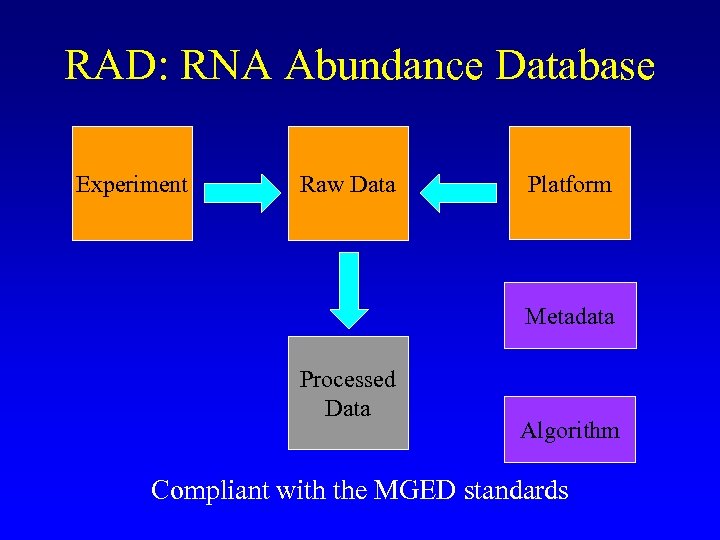
RAD: RNA Abundance Database Experiment Raw Data Platform Metadata Processed Data Algorithm Compliant with the MGED standards
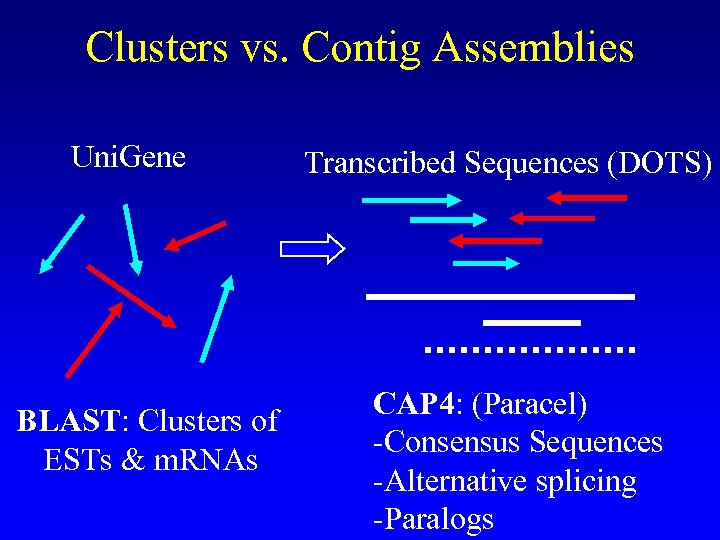
Clusters vs. Contig Assemblies Uni. Gene BLAST: Clusters of ESTs & m. RNAs Transcribed Sequences (DOTS) CAP 4: (Paracel) -Consensus Sequences -Alternative splicing -Paralogs
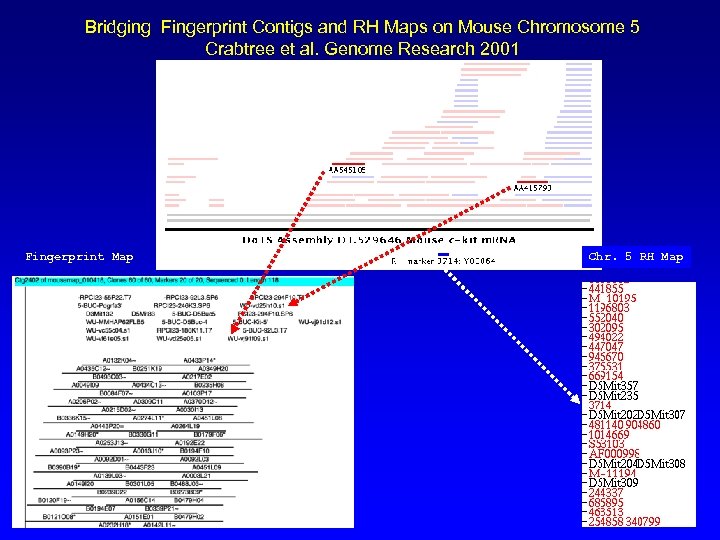
Bridging Fingerprint Contigs and RH Maps on Mouse Chromosome 5 Crabtree et al. Genome Research 2001 Fingerprint Map Chr. 5 RH Map
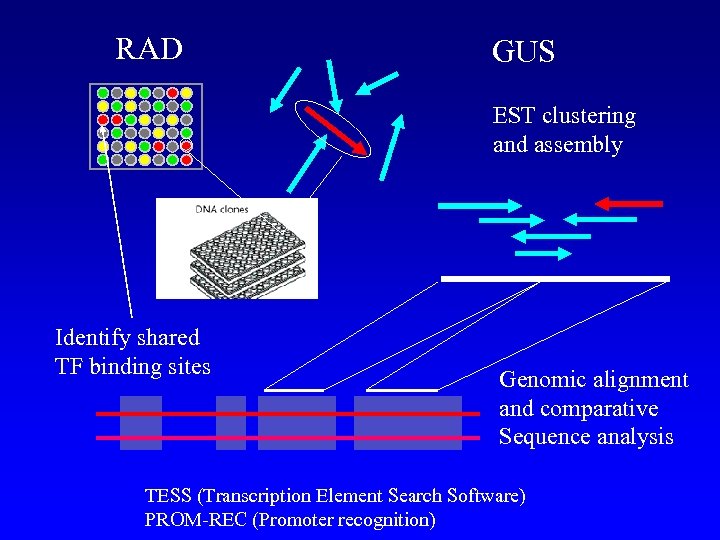
RAD GUS EST clustering and assembly Identify shared TF binding sites Genomic alignment and comparative Sequence analysis TESS (Transcription Element Search Software) PROM-REC (Promoter recognition)
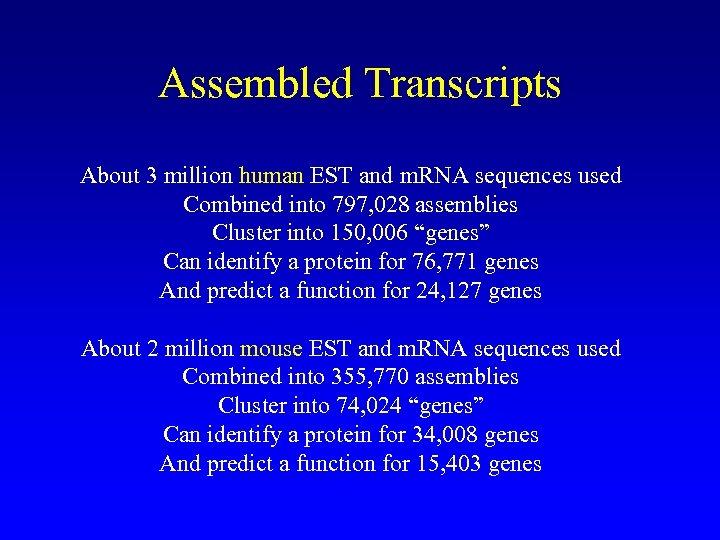
Assembled Transcripts About 3 million human EST and m. RNA sequences used Combined into 797, 028 assemblies Cluster into 150, 006 “genes” Can identify a protein for 76, 771 genes And predict a function for 24, 127 genes About 2 million mouse EST and m. RNA sequences used Combined into 355, 770 assemblies Cluster into 74, 024 “genes” Can identify a protein for 34, 008 genes And predict a function for 15, 403 genes
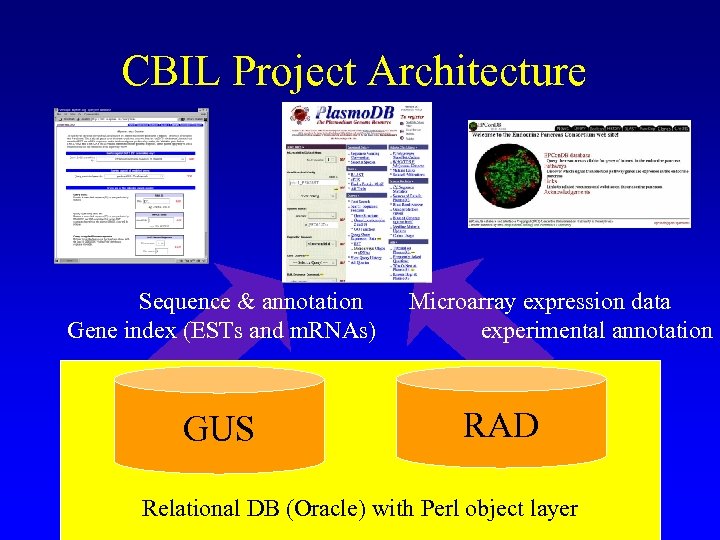
CBIL Project Architecture Sequence & annotation Gene index (ESTs and m. RNAs) GUS Microarray expression data experimental annotation RAD Relational DB (Oracle) with Perl object layer
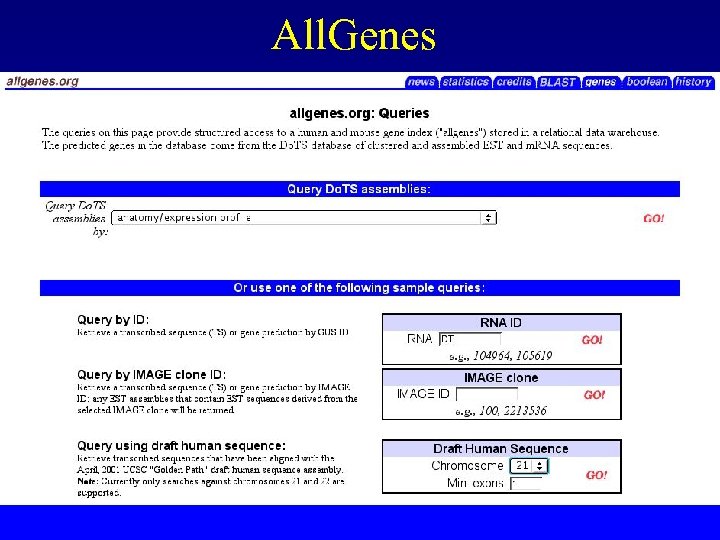
All. Genes
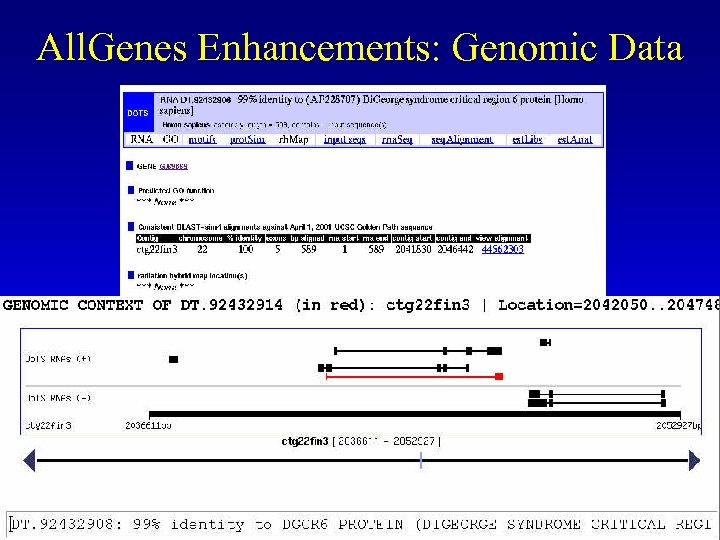
All. Genes Enhancements: Genomic Data

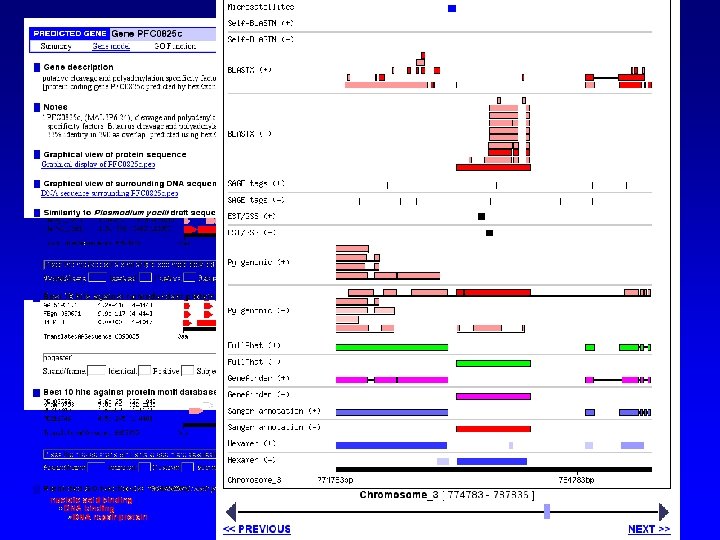
http: //plasmodb. org
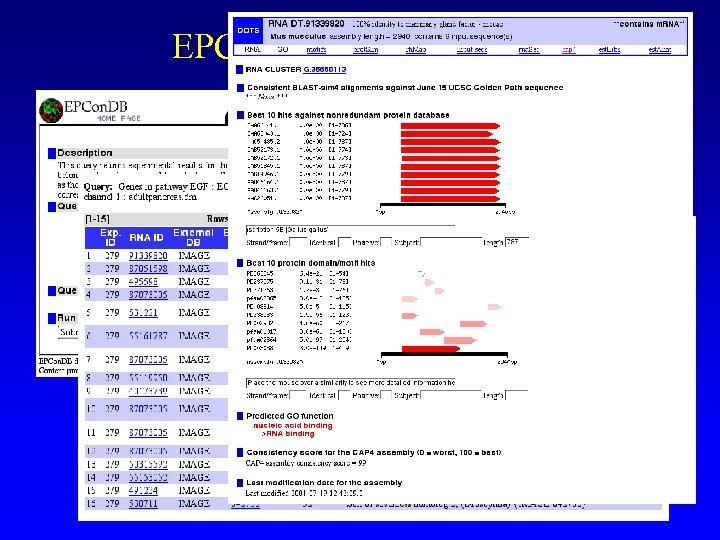
EPCon. DB Pathway query
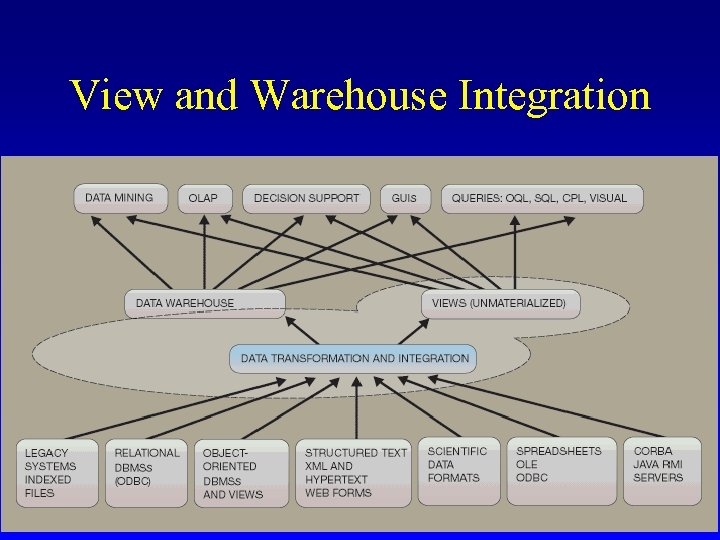
View and Warehouse Integration
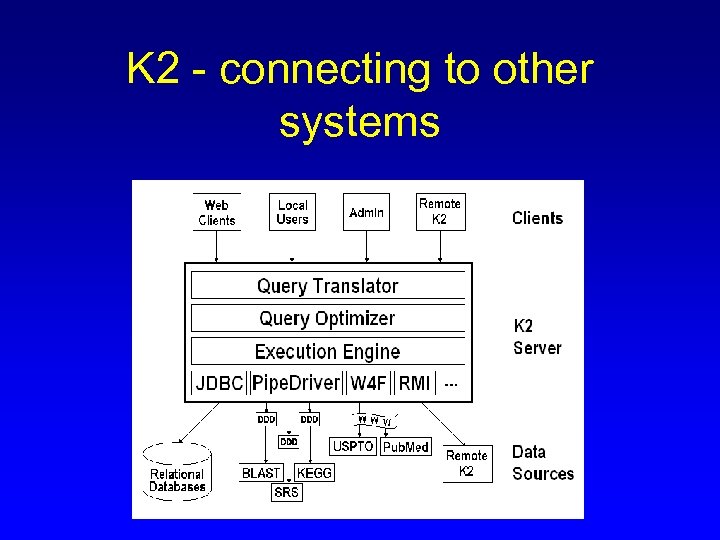
K 2 - connecting to other systems
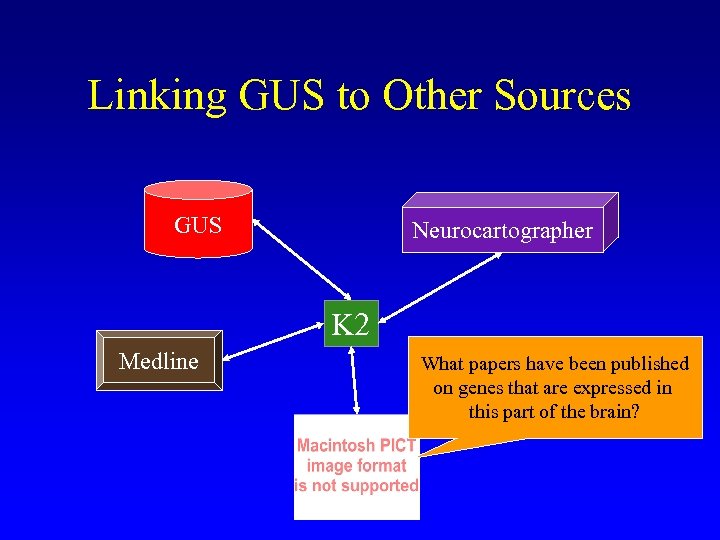
Linking GUS to Other Sources GUS Neurocartographer K 2 Medline What papers have been published on genes that are expressed in this part of the brain?

Acknowledgements CBIL: Chris Stoeckert Vladimir Babenko Brian Brunk Jonathan Crabtree Sharon Diskin Greg Grant Yuri Kondrakhin Georgi Kostov Phil Le Li Li Junmin Liu Elisabetta Manduchi Joan Mazzarelli Shannon Mc. Weeney Debbie Pinney Angel Pizarro Jonathan Schug http: //www. cbil. upenn. edu Plasmo. DB collaborators: David Roos Martin Fraunholz Jesse Kissinger Jules Milgram Ross Koppel, Monash U. Malarial Genome Sequencing Consortium (Sanger Centre, Stanford U. , TIGR/NMRC) EPCon. DB collaborators: Klaus Kaestner Marie Scearce Doug Melton, Harvard Alan Permutt, Wash. U Comparative Sequence Analysis Collaborators: Maja Bucan Shaying Zhao Whitehead/MIT Center for Genome Research K 2/DARPA: Sue Davidson Scott Harker Jonathan Nissanov Carl Gustafson
992b6fbeb1f7a8712122723759234826.ppt