6bc8e65dea23877b9e8515dbd875da7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 Integrating Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Training into the Medical Home Kara Cadwallader, MD Family Medicine Residency of Idaho Honor Mac. Naughton, MD Rebecca Simons, MD, MPH Beth Israel Residency in Urban Family Practice, New York
Integrating Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Training into the Medical Home Kara Cadwallader, MD Family Medicine Residency of Idaho Honor Mac. Naughton, MD Rebecca Simons, MD, MPH Beth Israel Residency in Urban Family Practice, New York
 Objectives 1) List indications for and benefits of use of early pregnancy ultrasound in the family medicine setting 2) Describe techniques for teaching and evaluating competency of early pregnancy ultrasound skills 3) Discuss barriers and potential solutions to integrating early pregnancy ultrasound training into a family medicine residency
Objectives 1) List indications for and benefits of use of early pregnancy ultrasound in the family medicine setting 2) Describe techniques for teaching and evaluating competency of early pregnancy ultrasound skills 3) Discuss barriers and potential solutions to integrating early pregnancy ultrasound training into a family medicine residency
 Background Pregnancy ultrasound is common need in family medicine office, yet few family physicians offer officebased ultrasound Benefits include cost, continuity, access Several studies support accuracy of prenatal ultrasounds provided by family physicians
Background Pregnancy ultrasound is common need in family medicine office, yet few family physicians offer officebased ultrasound Benefits include cost, continuity, access Several studies support accuracy of prenatal ultrasounds provided by family physicians
 Indications for Ultrasound Establishing gestational age Evaluation of first trimester bleeding or pain Ectopic pregnancy Threatened abortion / early pregnancy failure IUD localization Determining completion of abortion (spontaneous and induced) Evaluation of abortion complications (hemorrhage, pain, fever)
Indications for Ultrasound Establishing gestational age Evaluation of first trimester bleeding or pain Ectopic pregnancy Threatened abortion / early pregnancy failure IUD localization Determining completion of abortion (spontaneous and induced) Evaluation of abortion complications (hemorrhage, pain, fever)
 “Limited” Ultrasound What does this mean? Coding and reimbursement Liability When to refer for complete ultrasound
“Limited” Ultrasound What does this mean? Coding and reimbursement Liability When to refer for complete ultrasound
 Teaching Techniques Didactics Lectures On-line teaching sites CD-ROMs Reading Workshops with paid models Supervised scanning Hand-on-hand
Teaching Techniques Didactics Lectures On-line teaching sites CD-ROMs Reading Workshops with paid models Supervised scanning Hand-on-hand
 Teaching Logistics What service will be offered / taught? Limited vs complete ultrasound, anatomic survey, BPP, placental location, fetal presentation? Where / when in residency curriculum? Taught by whom? Taught to all residents?
Teaching Logistics What service will be offered / taught? Limited vs complete ultrasound, anatomic survey, BPP, placental location, fetal presentation? Where / when in residency curriculum? Taught by whom? Taught to all residents?
 Evaluating Competency Documented supervised scans How many? Competency checklists Written exams Compare to FM attending, radiology or OB/GYN scans Clinical outcomes: compare to delivery date or Dubowitz scores
Evaluating Competency Documented supervised scans How many? Competency checklists Written exams Compare to FM attending, radiology or OB/GYN scans Clinical outcomes: compare to delivery date or Dubowitz scores
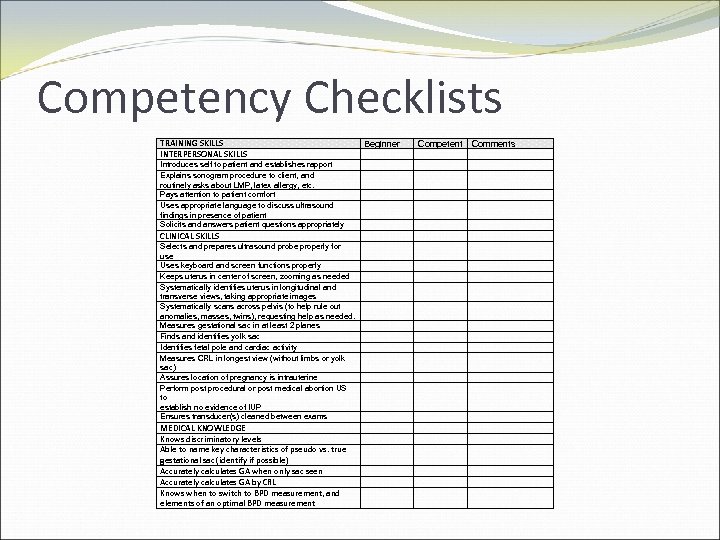 Competency Checklists TRAINING SKILLS INTERPERSONAL SKILLS Introduces self to patient and establishes rapport Explains sonogram procedure to client, and routinely asks about LMP, latex allergy, etc. Pays attention to patient comfort Uses appropriate language to discuss ultrasound findings in presence of patient Solicits and answers patient questions appropriately CLINICAL SKILLS Selects and prepares ultrasound probe properly for use Uses keyboard and screen functions properly Keeps uterus in center of screen, zooming as needed Systematically identifies uterus in longitudinal and transverse views, taking appropriate images Systematically scans across pelvis (to help rule out anomalies, masses, twins), requesting help as needed. Measures gestational sac in at least 2 planes Finds and identifies yolk sac Identifies fetal pole and cardiac activity Measures CRL in longest view (without limbs or yolk sac) Assures location of pregnancy is intrauterine Perform post procedural or post medical abortion US to establish no evidence of IUP Ensures transducer(s) cleaned between exams MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE Knows discriminatory levels Able to name key characteristics of pseudo vs. true gestational sac (identify if possible) Accurately calculates GA when only sac seen Accurately calculates GA by CRL Knows when to switch to BPD measurement, and elements of an optimal BPD measurement Beginner Competent Comments
Competency Checklists TRAINING SKILLS INTERPERSONAL SKILLS Introduces self to patient and establishes rapport Explains sonogram procedure to client, and routinely asks about LMP, latex allergy, etc. Pays attention to patient comfort Uses appropriate language to discuss ultrasound findings in presence of patient Solicits and answers patient questions appropriately CLINICAL SKILLS Selects and prepares ultrasound probe properly for use Uses keyboard and screen functions properly Keeps uterus in center of screen, zooming as needed Systematically identifies uterus in longitudinal and transverse views, taking appropriate images Systematically scans across pelvis (to help rule out anomalies, masses, twins), requesting help as needed. Measures gestational sac in at least 2 planes Finds and identifies yolk sac Identifies fetal pole and cardiac activity Measures CRL in longest view (without limbs or yolk sac) Assures location of pregnancy is intrauterine Perform post procedural or post medical abortion US to establish no evidence of IUP Ensures transducer(s) cleaned between exams MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE Knows discriminatory levels Able to name key characteristics of pseudo vs. true gestational sac (identify if possible) Accurately calculates GA when only sac seen Accurately calculates GA by CRL Knows when to switch to BPD measurement, and elements of an optimal BPD measurement Beginner Competent Comments
 Teaching Areas Proper set-up (patient and machine) Consent, communication, patient education Physics and orientation of images Systematic scanning Location of pregnancy Measuring gestational age Determining viability Determining completed abortion
Teaching Areas Proper set-up (patient and machine) Consent, communication, patient education Physics and orientation of images Systematic scanning Location of pregnancy Measuring gestational age Determining viability Determining completed abortion
 Proper Set-Up Selects and prepares ultrasound probe for use Ensures probe is cleaned before use Uses keyboard and screen functions properly Labels images with name, MRN, date, location
Proper Set-Up Selects and prepares ultrasound probe for use Ensures probe is cleaned before use Uses keyboard and screen functions properly Labels images with name, MRN, date, location
 Communication Introduces self, establishes rapport Explains procedure to client, asks about LMP, latex allergy, etc. Pays attention to patient comfort, allows for selfinsertion of probe Uses appropriate language to discuss findings with patient
Communication Introduces self, establishes rapport Explains procedure to client, asks about LMP, latex allergy, etc. Pays attention to patient comfort, allows for selfinsertion of probe Uses appropriate language to discuss findings with patient
 Physics and Orientation How do you teach trainees orientation? CD-ROM Didactic sessions Real time or patient models
Physics and Orientation How do you teach trainees orientation? CD-ROM Didactic sessions Real time or patient models
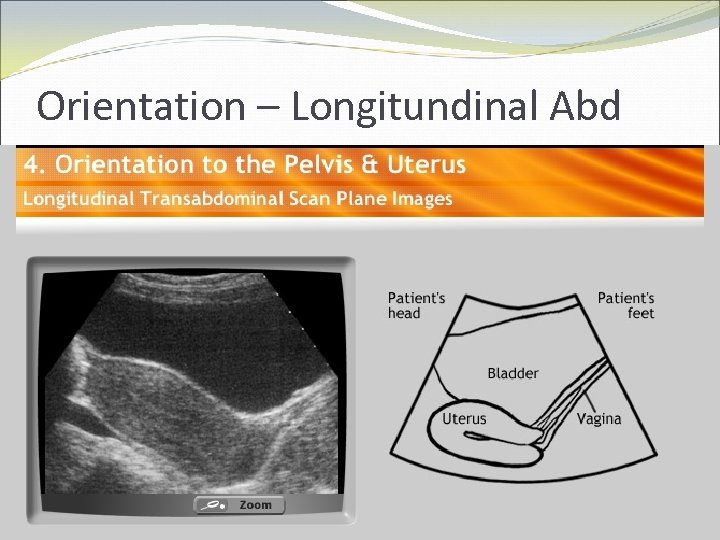 Orientation – Longitundinal Abd
Orientation – Longitundinal Abd
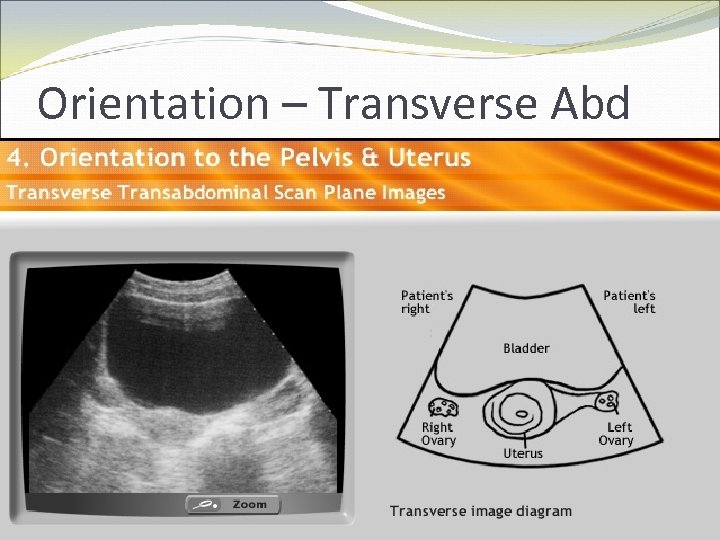 Orientation – Transverse Abd
Orientation – Transverse Abd
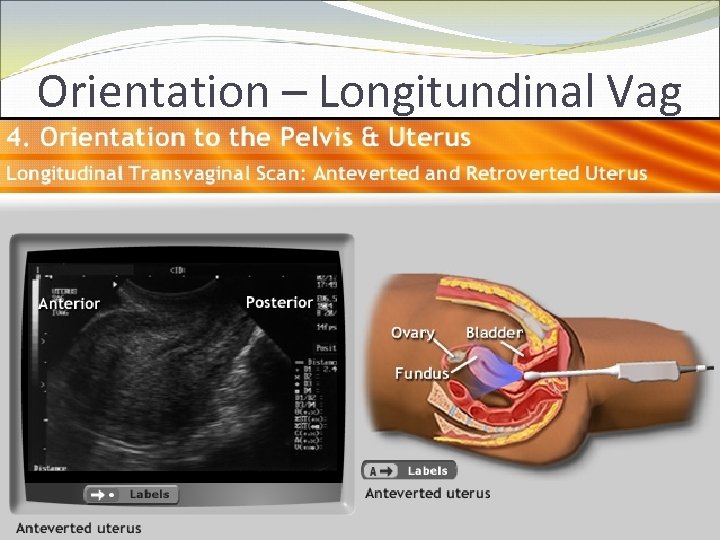 Orientation – Longitundinal Vag
Orientation – Longitundinal Vag
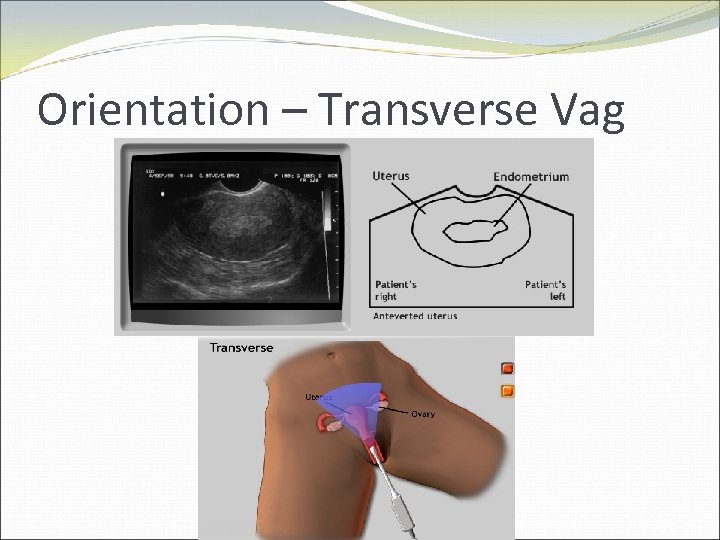 Orientation – Transverse Vag
Orientation – Transverse Vag
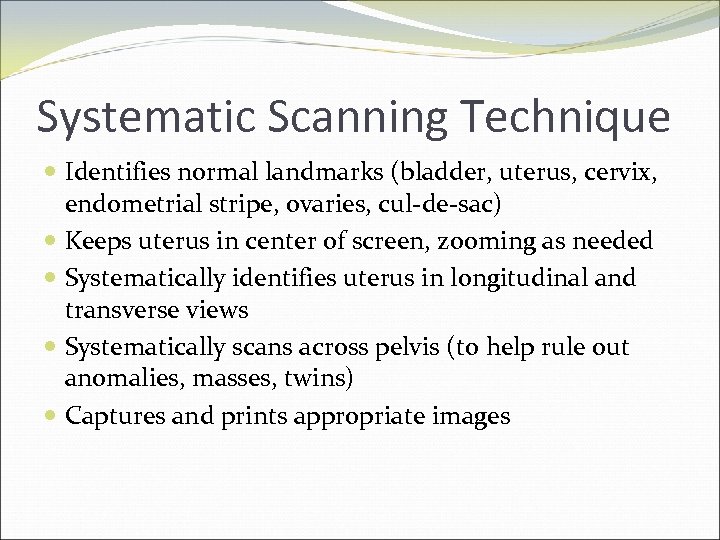 Systematic Scanning Technique Identifies normal landmarks (bladder, uterus, cervix, endometrial stripe, ovaries, cul-de-sac) Keeps uterus in center of screen, zooming as needed Systematically identifies uterus in longitudinal and transverse views Systematically scans across pelvis (to help rule out anomalies, masses, twins) Captures and prints appropriate images
Systematic Scanning Technique Identifies normal landmarks (bladder, uterus, cervix, endometrial stripe, ovaries, cul-de-sac) Keeps uterus in center of screen, zooming as needed Systematically identifies uterus in longitudinal and transverse views Systematically scans across pelvis (to help rule out anomalies, masses, twins) Captures and prints appropriate images
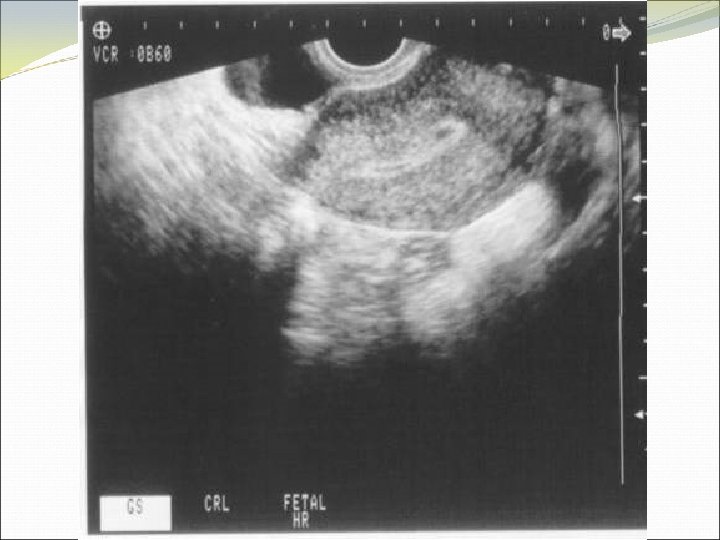
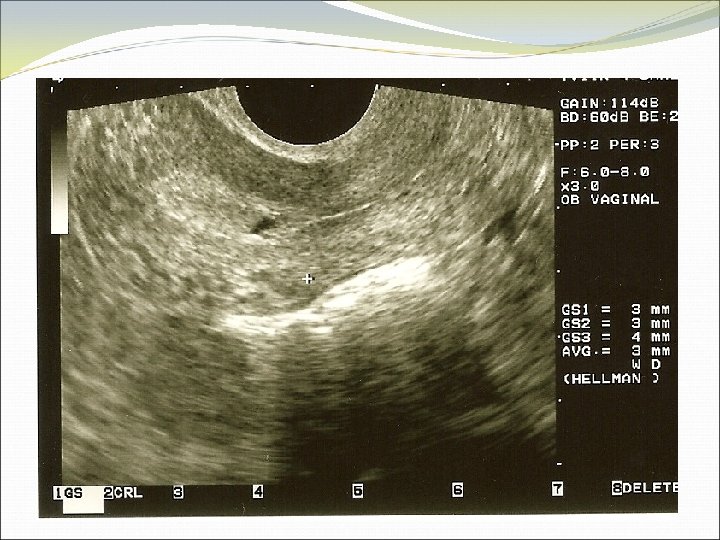
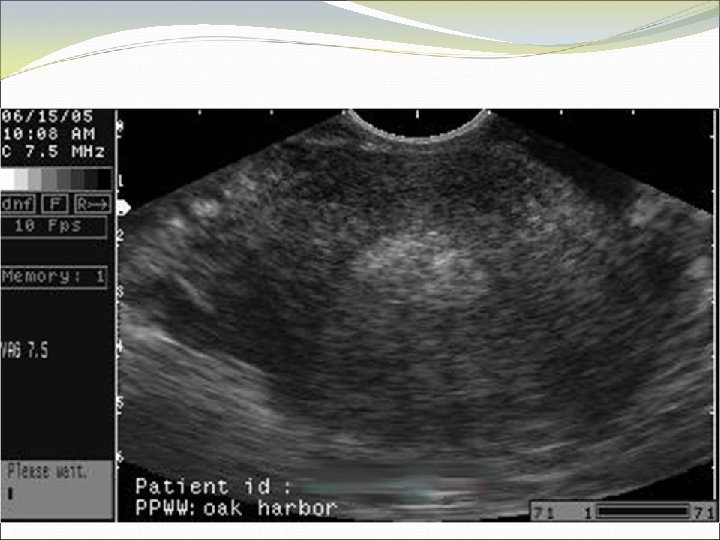
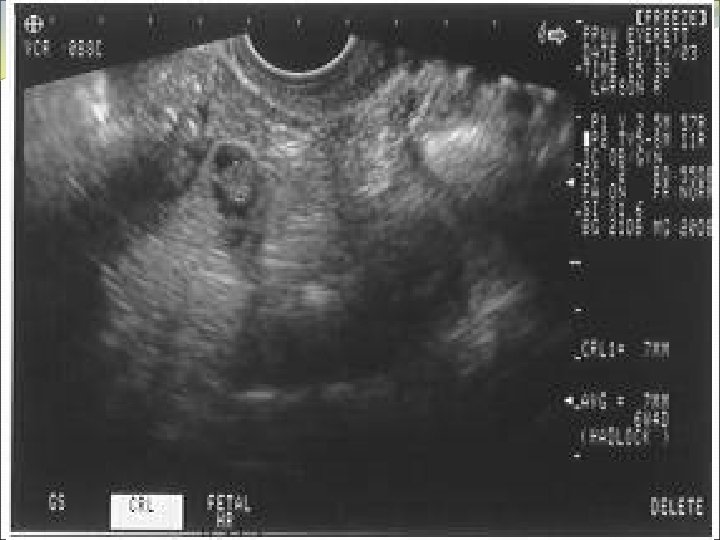
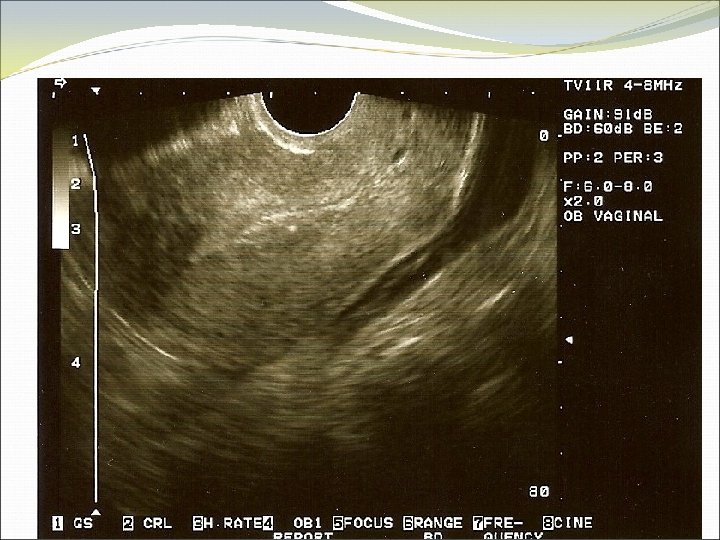
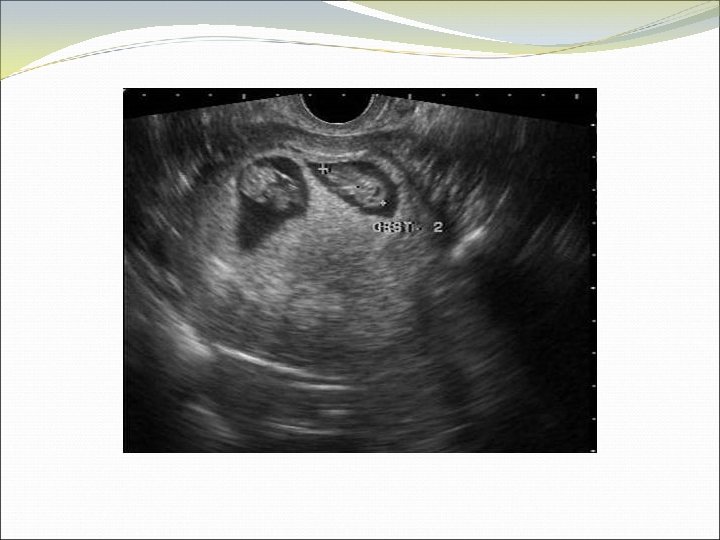
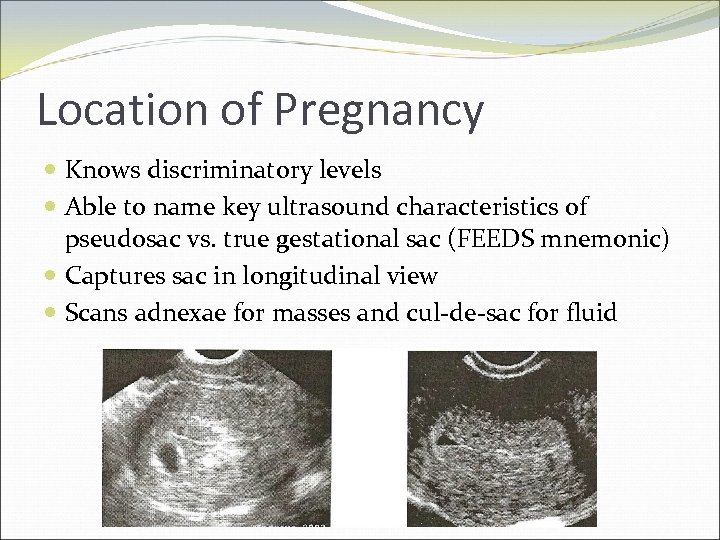 Location of Pregnancy Knows discriminatory levels Able to name key ultrasound characteristics of pseudosac vs. true gestational sac (FEEDS mnemonic) Captures sac in longitudinal view Scans adnexae for masses and cul-de-sac for fluid
Location of Pregnancy Knows discriminatory levels Able to name key ultrasound characteristics of pseudosac vs. true gestational sac (FEEDS mnemonic) Captures sac in longitudinal view Scans adnexae for masses and cul-de-sac for fluid
 FEEDS mnemonic Normal gestational sac is: Fundal Elliptical in 2 planes Eccentric to endometrial stripe Double ring sign - Decidual reaction Size >4 mm or grows 1 mm/day Significance of yolk sac
FEEDS mnemonic Normal gestational sac is: Fundal Elliptical in 2 planes Eccentric to endometrial stripe Double ring sign - Decidual reaction Size >4 mm or grows 1 mm/day Significance of yolk sac
 Case 1 WS is a 32 yo G 1 P 0 who presents with a positive UCG from home. She has no idea when her last period was, maybe 3 -5 weeks ago. She isn’t sure what she plans to do. She wants to know how far along she is before discussing options.
Case 1 WS is a 32 yo G 1 P 0 who presents with a positive UCG from home. She has no idea when her last period was, maybe 3 -5 weeks ago. She isn’t sure what she plans to do. She wants to know how far along she is before discussing options.
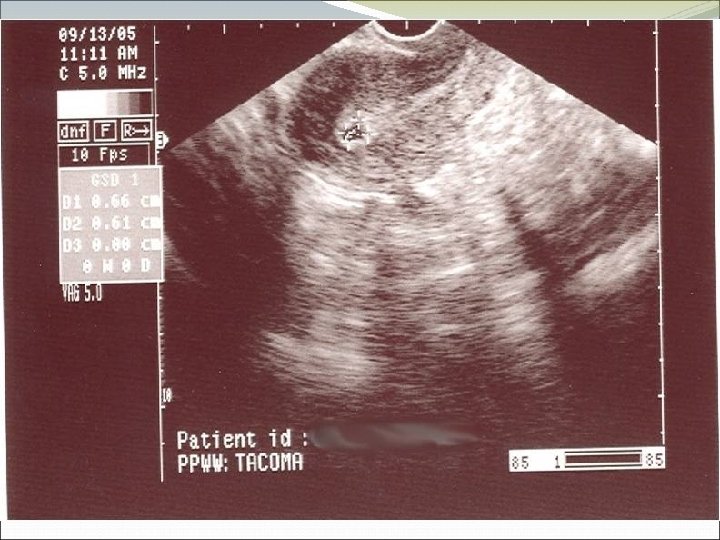
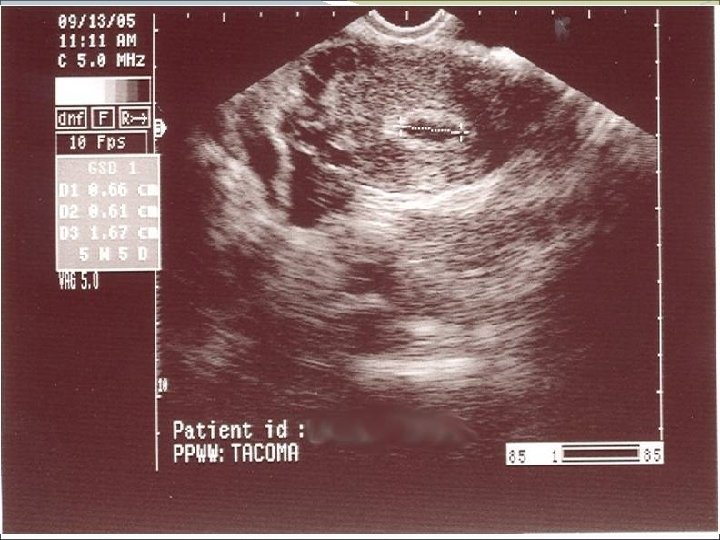
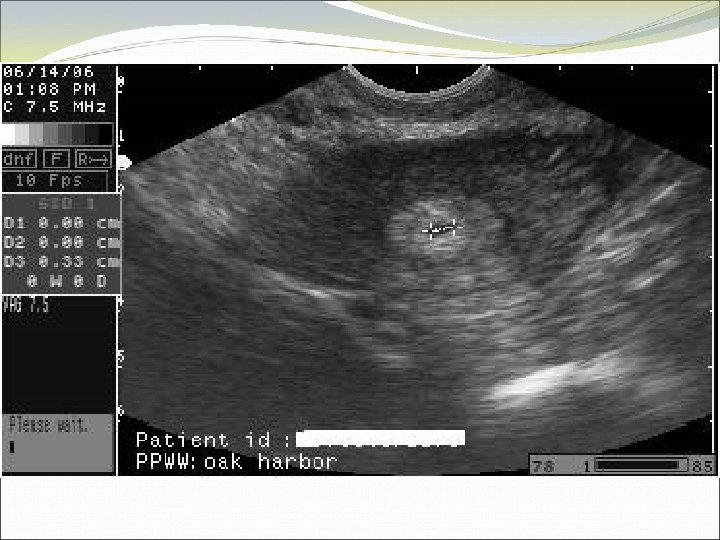
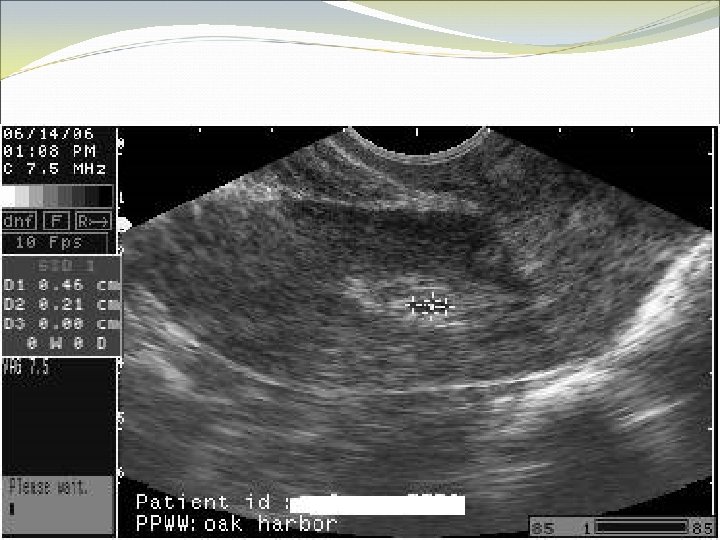
 Case 2 FY is a 37 year old woman who presents to the office with lower abdominal pain, worsening over several days. Her pregnancy test is positive, and she explains that she has missed some birth control pills in the last couple of packs. The pain is fairly severe when you examine her, more on the right than left. She has no fever, no vaginal discharge, no urinary symptoms.
Case 2 FY is a 37 year old woman who presents to the office with lower abdominal pain, worsening over several days. Her pregnancy test is positive, and she explains that she has missed some birth control pills in the last couple of packs. The pain is fairly severe when you examine her, more on the right than left. She has no fever, no vaginal discharge, no urinary symptoms.
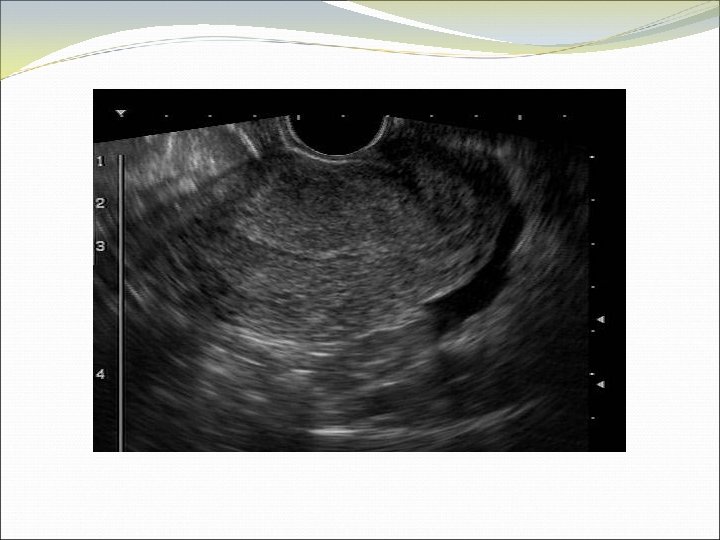
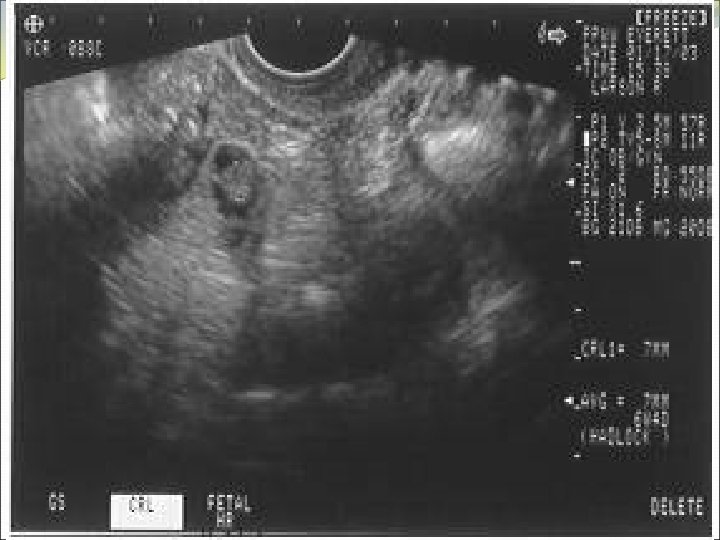
 Determining Gestational Age Measures mean sac diameter in 3 planes Finds and identifies yolk sac Accurately calculates GA when only gestational sac (+/- yolk sac) seen Identifies fetal pole and cardiac activity Measures CRL in longest view (without limbs or yolk sac) Accurately calculates GA by CRL Knows when to switch to BPD measurement, and elements of an optimal BPD measurement
Determining Gestational Age Measures mean sac diameter in 3 planes Finds and identifies yolk sac Accurately calculates GA when only gestational sac (+/- yolk sac) seen Identifies fetal pole and cardiac activity Measures CRL in longest view (without limbs or yolk sac) Accurately calculates GA by CRL Knows when to switch to BPD measurement, and elements of an optimal BPD measurement
 Case 3 PM is a 20 yo G 6 P 2 who presents to the office with an LMP of about 5 -6 weeks. She would like to know her due date.
Case 3 PM is a 20 yo G 6 P 2 who presents to the office with an LMP of about 5 -6 weeks. She would like to know her due date.
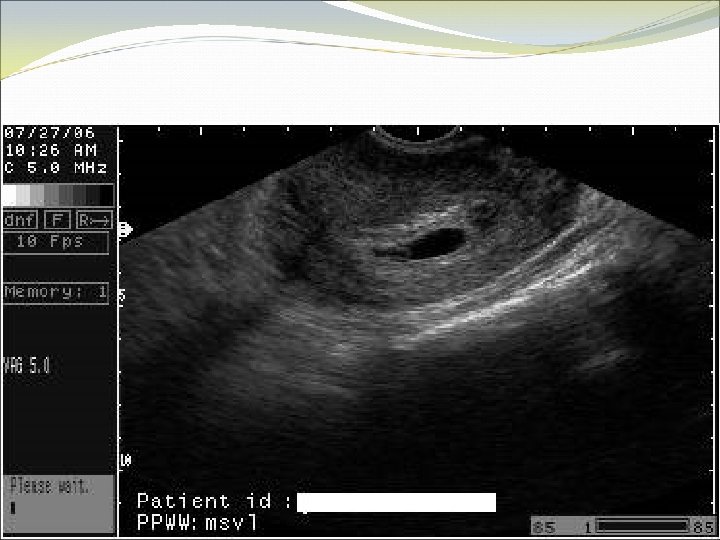
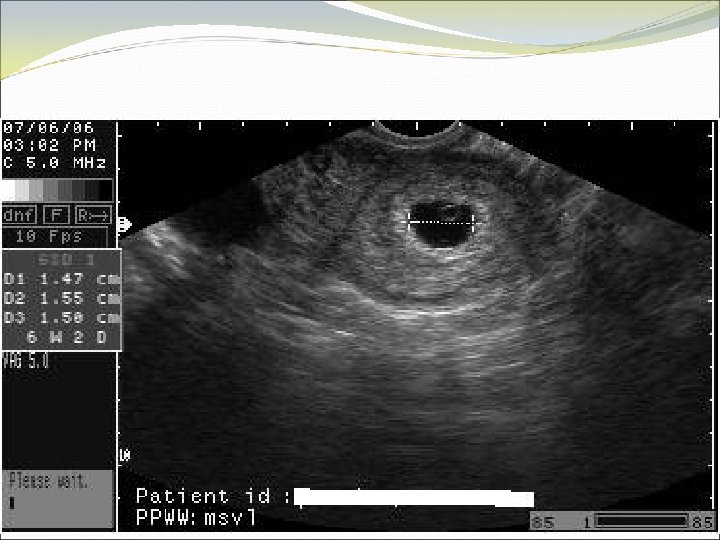
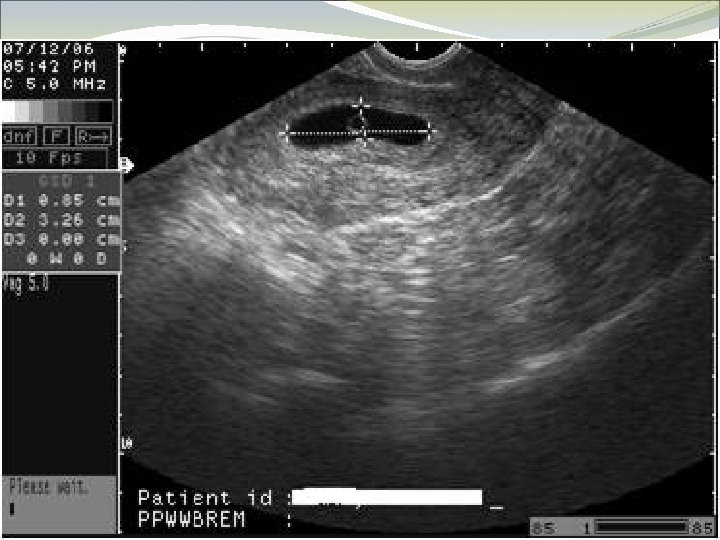
 Case 4 KO is a 41 yo G 3 P 2. She thinks she has missed 2 periods. She is wants to know she can have a medication abortion.
Case 4 KO is a 41 yo G 3 P 2. She thinks she has missed 2 periods. She is wants to know she can have a medication abortion.
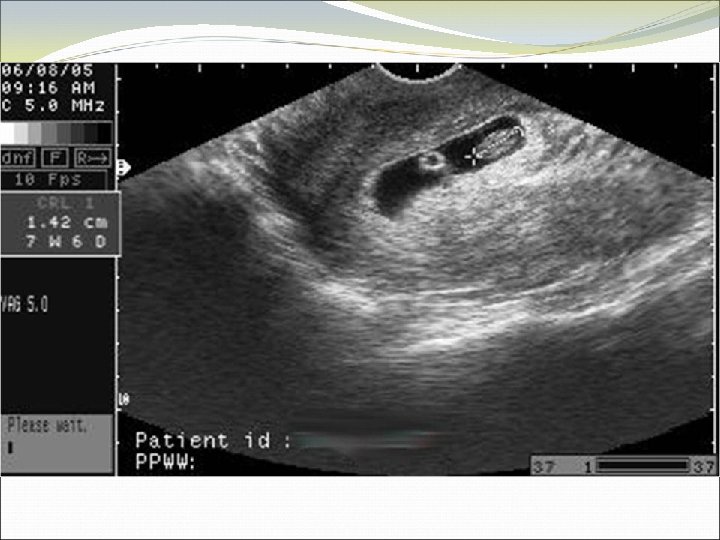
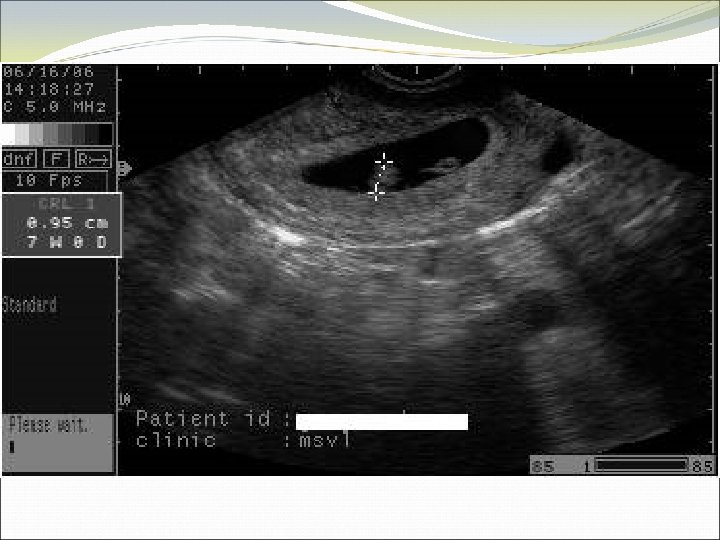
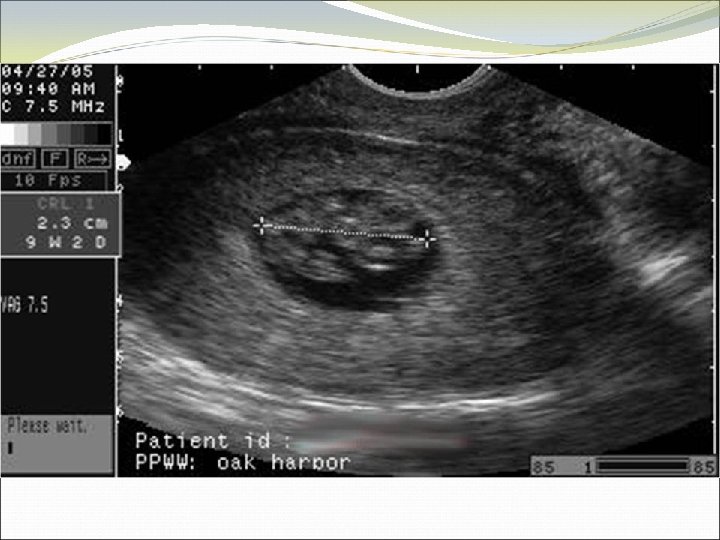
 Case 5 SR is a 17 year old who has irregular periods, with an LMP ~3 months ago. She has had some spotting and nausea.
Case 5 SR is a 17 year old who has irregular periods, with an LMP ~3 months ago. She has had some spotting and nausea.
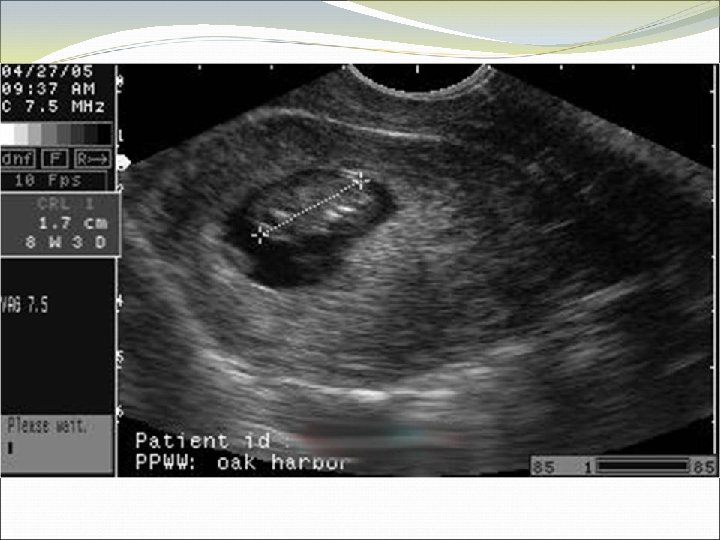
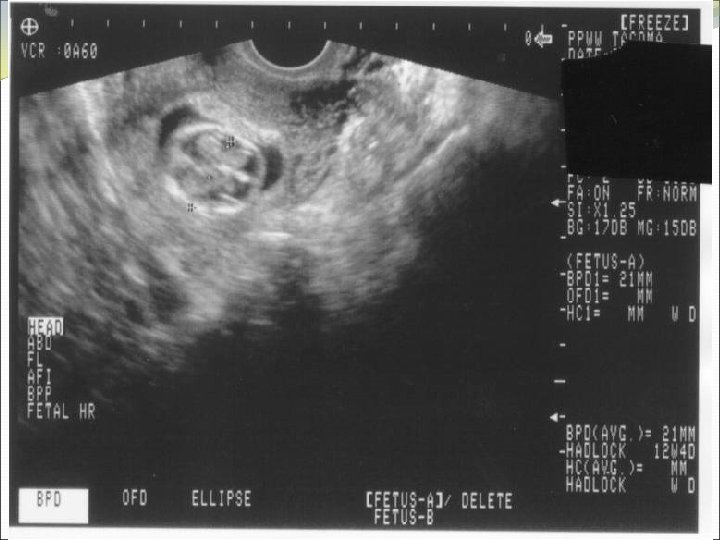
 Determining Viability Knows red flags for early pregnancy failure No yolk sac by 13 mm gestational sac (43 days) No cardiac activity by 5 mm CRL (47 days) No embryonic pole by 49 days No change in ultrasound over 1 -2 weeks Identifies fetal cardiac activity
Determining Viability Knows red flags for early pregnancy failure No yolk sac by 13 mm gestational sac (43 days) No cardiac activity by 5 mm CRL (47 days) No embryonic pole by 49 days No change in ultrasound over 1 -2 weeks Identifies fetal cardiac activity
 Case 6 TR is a 29 yo G 4 P 1 with an LMP of about 6 weeks. She has had a bit of spotting over the last several days, no significant cramping.
Case 6 TR is a 29 yo G 4 P 1 with an LMP of about 6 weeks. She has had a bit of spotting over the last several days, no significant cramping.
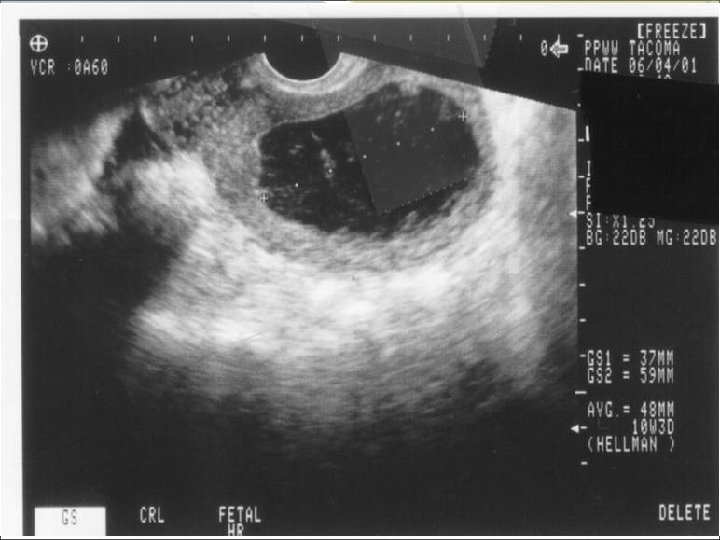
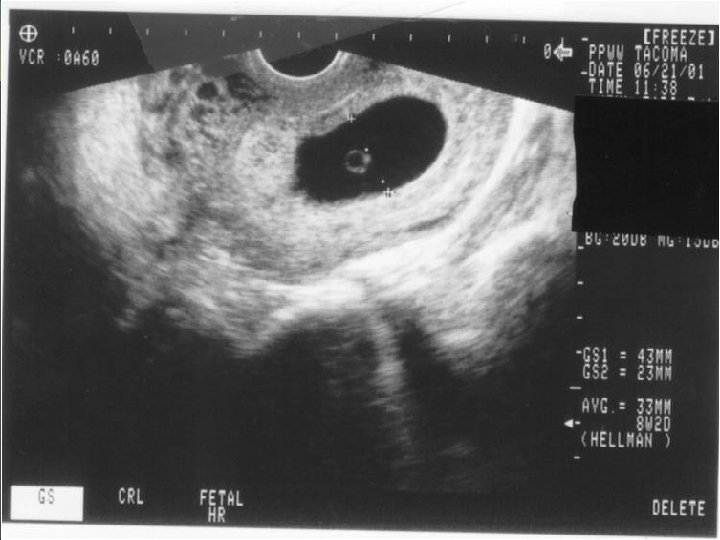
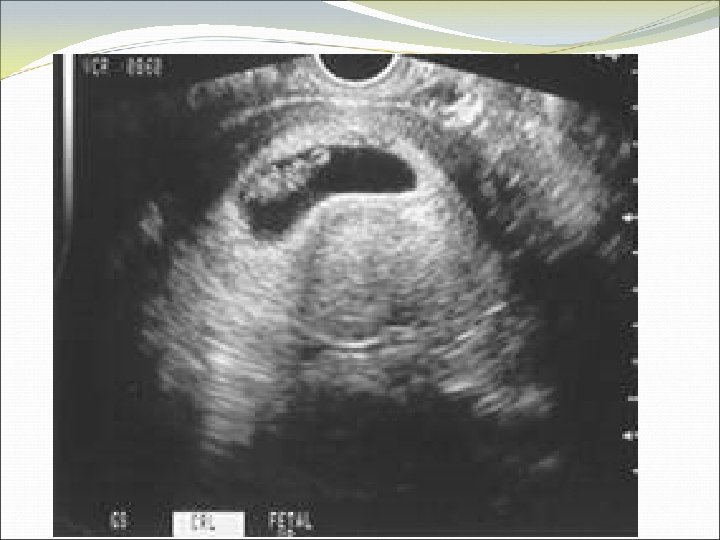
 Documenting Completed Abortion Establishes that there is no evidence of pregnancy following induced or spontaneous abortion Describes expected sonographic findings associated with post-abortion complications
Documenting Completed Abortion Establishes that there is no evidence of pregnancy following induced or spontaneous abortion Describes expected sonographic findings associated with post-abortion complications
 Case 7 KS is a 30 yo woman one week s/p medication abortion with mifepristone and misoprostol at 8 weeks 4 days gestation. She had heavy bleeding and cramping for several hours after using the misoprostol and is now using two pads /day. She reports resolution of pregnancy symptoms, is having minimal cramping and no fever.
Case 7 KS is a 30 yo woman one week s/p medication abortion with mifepristone and misoprostol at 8 weeks 4 days gestation. She had heavy bleeding and cramping for several hours after using the misoprostol and is now using two pads /day. She reports resolution of pregnancy symptoms, is having minimal cramping and no fever.
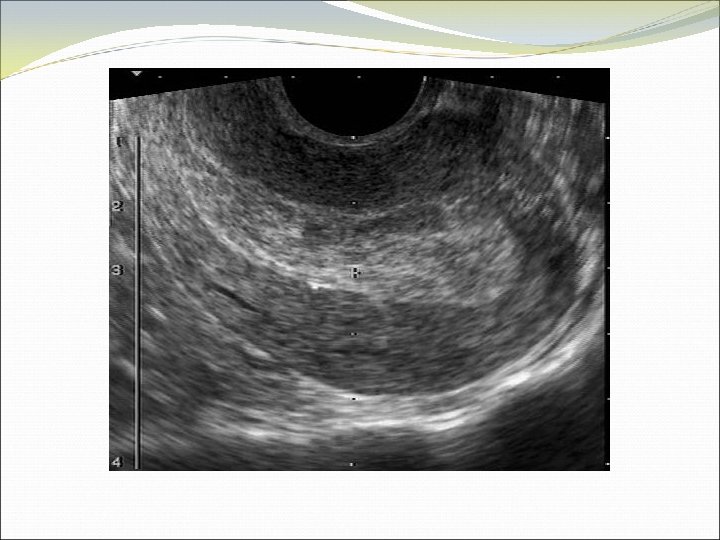
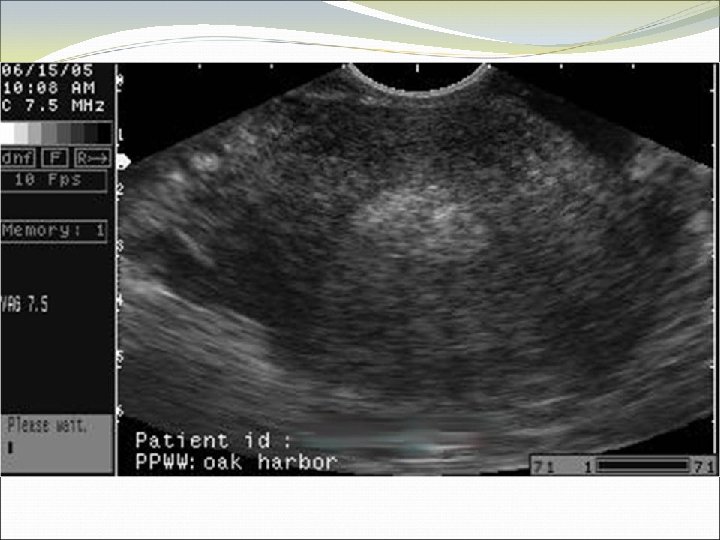
 Case 8 JL is a 40 year old healthy woman who presents to the office because she cannot feel her Paragard IUD strings. No IUD strings are visible on speculum exam.
Case 8 JL is a 40 year old healthy woman who presents to the office because she cannot feel her Paragard IUD strings. No IUD strings are visible on speculum exam.
 Barriers to Implementation?
Barriers to Implementation?
 Resources Competency Checklists Ultrasound Written Quiz Online Teaching Tools Documentation of Ultrasound Form Policy and Procedure for Cleaning Ultrasound Probe Cleaning Vaginal Probe Poster
Resources Competency Checklists Ultrasound Written Quiz Online Teaching Tools Documentation of Ultrasound Form Policy and Procedure for Cleaning Ultrasound Probe Cleaning Vaginal Probe Poster
 Wrap Up Questions? Feeback? Thank You!
Wrap Up Questions? Feeback? Thank You!


