c990640c61ca0bf1512029f547a95784.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Integrating Canadian Accessibility Standards into your Projects David Best & Dan Shire IBM Canada April 2013 V 0. 4 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Our agenda Introduction Obligations & opportunities Accessibility & the project life cycle Resources 2 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Introduction Accessibility: 3 • Making technology usable by the greatest number of people, regardless of age or ability • Breaking down technical and organizational barriers that hinder the full participation and contribution of: – Our customers – Our employees – Our family members – Ourselves • Individuals have unique requirements and may use assistive technology to help them overcome specific barriers in order to access information and services: – Vision – Hearing – Mobility – Dexterity – Learning/cognitive © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Canadians with disabilities increase with age 0 -14 years 15 -24 years 25 -44 years 45 -64 years Population with a disability by age (2006) 3. 7% 4. 9 million Canadians 4. 7% 8% 18. 3% 65 -74 years 33% 75+years All ages 56. 3% 14. 3% Source: Statistics Canada. Participation and Activity Limitation Survey 2006: Tables. Ottawa: Statistics Canada, 2007 (Cat. No. 89 -628 -XIE - No. 003). 4 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Introducing AODA Standards Ontario’s AODA – Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act • World leadership • Public and private sector • Specific requirements – timelines and measurable • A consultative process • 5 components 5 – Customer Service – Information and Communication – Transportation – Employment – Built Environment • All public sector organizations in Ontario are under the AODA • 360, 000 private sector businesses (provincially regulated) • 20, 000 private sector businesses (>50 employees) have additional obligations under the regulations © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Obligations – legal and regulatory requirements Province of Ontario • The province requires public sector organizations (province, municipal, colleges, universities, hospitals, etc) to provide accessible customer service and accessible web sites. • The requirement for accessible information - web, content, other communication - under the AODA. Government of Canada • The federal government was sued and convicted because citizen-facing web sites were not fully accessible. Business in Canada • Larger companies in Ontario (> 50 employees) fall under more stringent Ontario regulations – external web sites and internal IT systems must meet WCAG 2. 0 accessibility requirements. • 360, 000 businesses in Ontario are affected by the provincial regulations. – US and international standards are often a factor Business in the United States • Federal contracts are obligated by S 508. • Federal, state and local by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) • Businesses are obligated by the ADA • Risk mitigation influences many companies 6 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
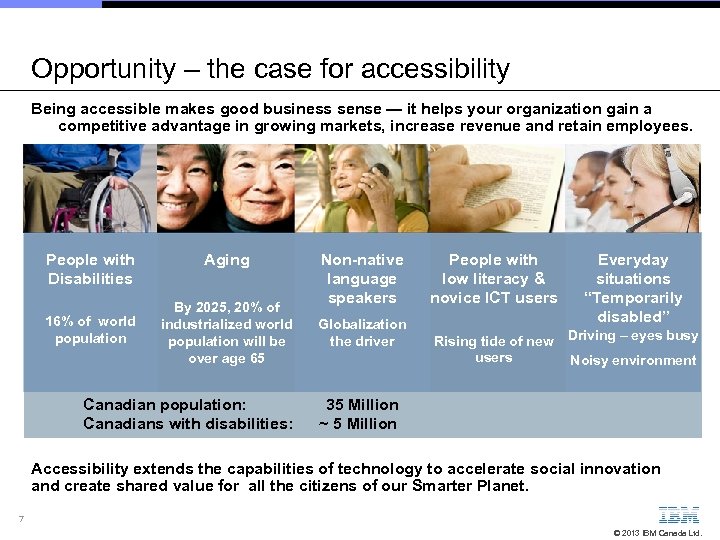
Opportunity – the case for accessibility Being accessible makes good business sense — it helps your organization gain a competitive advantage in growing markets, increase revenue and retain employees. People with Disabilities 16% of world population Aging By 2025, 20% of industrialized world population will be over age 65 Canadian population: Canadians with disabilities: Non-native language speakers Globalization the driver People with low literacy & novice ICT users Everyday situations “Temporarily disabled” Rising tide of new users Driving – eyes busy Noisy environment 35 Million ~ 5 Million Accessibility extends the capabilities of technology to accelerate social innovation and create shared value for all the citizens of our Smarter Planet. 7 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
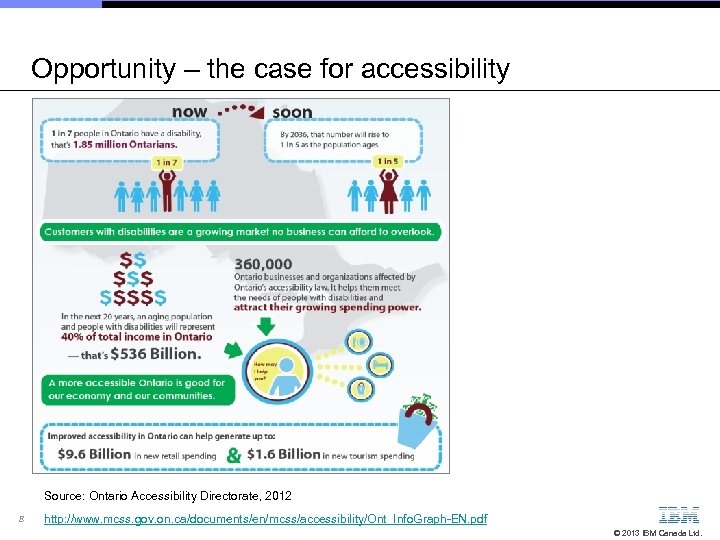
Opportunity – the case for accessibility Source: Ontario Accessibility Directorate, 2012 8 http: //www. mcss. gov. on. ca/documents/en/mcss/accessibility/Ont_Info. Graph-EN. pdf © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
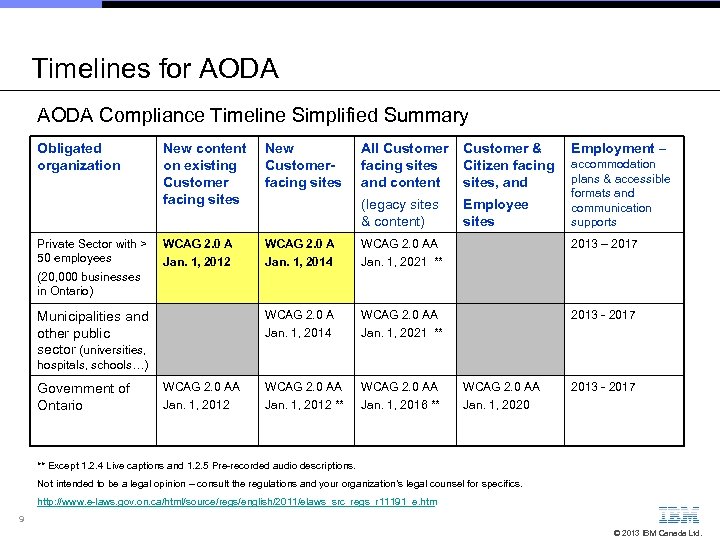
Timelines for AODA Compliance Timeline Simplified Summary Obligated organization Private Sector with > 50 employees New content on existing Customer facing sites New Customerfacing sites All Customer facing sites and content Customer & Citizen facing sites, and (legacy sites & content) Employee sites WCAG 2. 0 AA Jan. 1, 2012 Jan. 1, 2014 Jan. 1, 2021 ** WCAG 2. 0 AA WCAG 2. 0 AA Jan. 1, 2012 ** Jan. 1, 2016 ** Employment – Jan. 1, 2020 accommodation plans & accessible formats and communication supports 2013 – 2017 (20, 000 businesses in Ontario) Municipalities and other public sector (universities, 2013 - 2017 hospitals, schools…) Government of Ontario 2013 - 2017 ** Except 1. 2. 4 Live captions and 1. 2. 5 Pre-recorded audio descriptions. Not intended to be a legal opinion – consult the regulations and your organization’s legal counsel for specifics. http: //www. e-laws. gov. on. ca/html/source/regs/english/2011/elaws_src_regs_r 11191_e. htm 9 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

The consequences of not being accessible • Organizations are exposed to the threat and cost of litigation, public relations issues, and loss of government contracts. – Private companies, such as Priceline, Ramada, and Target have been sued for not having accessible Web sites and the organizations were forced to pay hefty fines and agree to re-design their sites to make them more accessible. – Designing for accessibility from the beginning is significantly less expensive than re-design after the fact, especially under courtmandated pressure. – In Canada: VIA Rail, the Government of Canada and the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) have been charged and convicted • Most government entities in the U. S. , Europe, Australia, New Zealand Japan are required to comply with some form of accessibility standards and regulations. • Procurement challenges - for private sector clients that supply services & products to the government, overlooking accessibility requirements can result in lost contracts and lost revenue, or penalties. 10 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
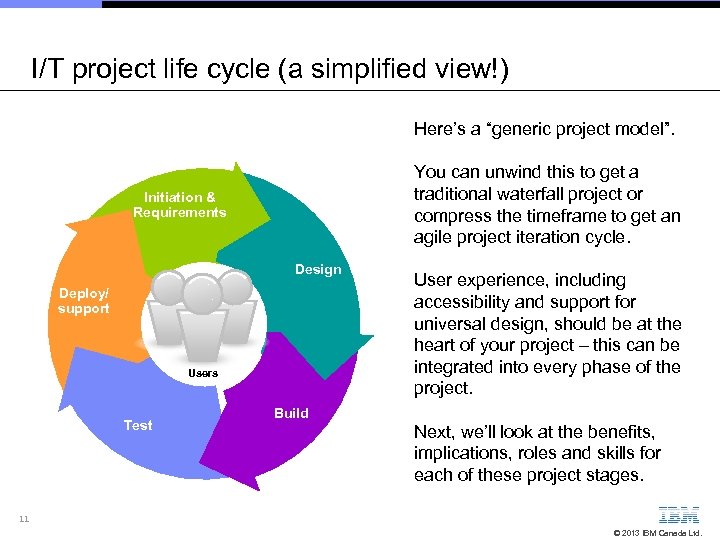
I/T project life cycle (a simplified view!) Here’s a “generic project model”. You can unwind this to get a traditional waterfall project or compress the timeframe to get an agile project iteration cycle. Initiation & Requirements Design Deploy/ support Users Test User experience, including accessibility and support for universal design, should be at the heart of your project – this can be integrated into every phase of the project. Build Next, we’ll look at the benefits, implications, roles and skills for each of these project stages. 11 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
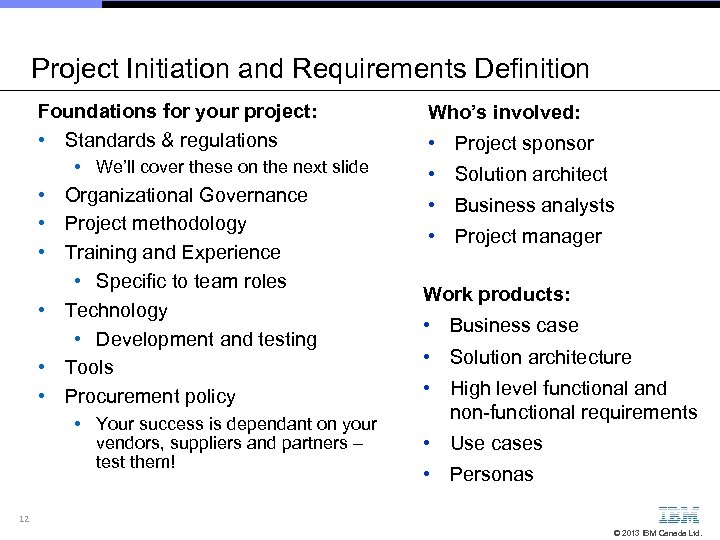
Project Initiation and Requirements Definition Foundations for your project: • Standards & regulations • We’ll cover these on the next slide • Organizational Governance • Project methodology • Training and Experience • Specific to team roles • Technology • Development and testing • Tools • Procurement policy • Your success is dependant on your vendors, suppliers and partners – test them! Who’s involved: • Project sponsor • Solution architect • Business analysts • Project manager Work products: • Business case • Solution architecture • High level functional and non-functional requirements • Use cases • Personas 12 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Standards – WCAG 2. 0 Level A & AA for the web WCAG 2. 0 Level A – 25 guidelines to meet basic accessibility WCAG 2. 0 Level AA – 13 additional guidelines provide more robust support 13 Perceivable • Provide text alternatives for non-text content. • Provide captions and alternatives for audio and video content. • Make content adaptable; and make it available to assistive technologies – images with labels. • Use sufficient contrast to make things easy to see and hear – contrast and colour. Operable • Make all functionality keyboard accessible – tabbing order. • Give users enough time to read and use content. • Do not use content that causes seizures (flashing). • Help users navigate and find content. Understandable • Make text readable and understandable – clear language • Make content appear and operate in predictable ways – headings, structure. • Help users avoid and correct mistakes. Robust • Maximize compatibility with current and future technologies. © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Design Who’s involved: • User experience specialist • Accessibility specialist • Information architect • Graphic designer • User focus groups • Developers with code design experience 14 Work products: • Creative design • The look and feel of the application, including branding. • Wire frames • Include components that describe the required user interface (mouse, keyboard, touch screen, speech, etc. ) and interaction with user agents. • This may involve user group studies to gain an understanding of adaptive technologies and user behaviour. • Responsive design – gracefully support multiple devices from traditional PC to smart phones • Web page functional components must meet user expectations. • The page landscape must be perceivable, the content understandable, the objects operable, and the overall usability must be robust. © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Build Who’s involved: • Developers • With accessibility training and tools • Accessibility Compliance Expert • Responsible for planning, coordinating and monitoring the accessibility testing throughout the development process • Requires an understanding of the compliance certification procedures, available automated testing tools, and usability testing requirements. An integrated testing strategy for accessibility is critical during development. Work products: • Functional code • Robust code which has been built and unit tested with tools that enforce (or at a minimum enable support for) the WCAG 2. 0 guidelines • Accessibility test plan/strategy • There are 3 typical elements to accessibility testing: automated testing to identify basic issues, manual testing using specialized tools (e. g. browser plug-ins), and selective testing using assistive technology such as Zoom. Text and JAWS. 15 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Test – Functional testing Who’s involved: • Development team • Accessibility Compliance Expert • Due to the dynamic construction of complex web sites it is necessary to repeat accessibility compliance testing at all levels of development (Alpha, Beta, Production). • Dynamic page rendering and operable functionality must be thoroughly tested before usability testing begins. Where native HTML 5 cannot meet accessibility requirements, then WAI-ARIA coding can be implemented. Java scripts and widgets (JQuery, Dojo) must be robust. • Test the application, and the documentation Work products: • Functional, accessible application code • Tested: automated, manual and assistive technology techniques • Test report • Accessibility issues documented & tracked • Remediation steps identified 16 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Test – Usability testing Who’s involved: • Selected end users • The more accessible the product, the fewer the remediation cycles are likely to be needed in the future. • User experience testing is performed by end-user adaptive technology users. • This may include users from the various disability groups (vision, hearing, cognitive, mobility). • If the functional compliance testing and required remediation implementation is not performed properly, the end user experience testing will be frustrating and costly. • To be effective the usability test phase must be conducted with well defined user experience test scripts – don’t “wing it”. • User experience specialist & Accessibility Compliance Expert Work products: • Usability test report • User experience and accessibility issues identified, documented & tracked • Remediation steps identified 17 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
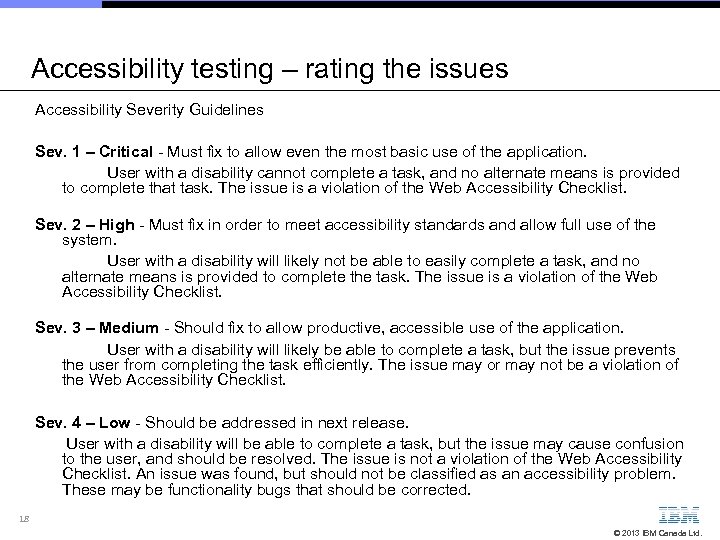
Accessibility testing – rating the issues Accessibility Severity Guidelines Sev. 1 – Critical - Must fix to allow even the most basic use of the application. User with a disability cannot complete a task, and no alternate means is provided to complete that task. The issue is a violation of the Web Accessibility Checklist. Sev. 2 – High - Must fix in order to meet accessibility standards and allow full use of the system. User with a disability will likely not be able to easily complete a task, and no alternate means is provided to complete the task. The issue is a violation of the Web Accessibility Checklist. Sev. 3 – Medium - Should fix to allow productive, accessible use of the application. User with a disability will likely be able to complete a task, but the issue prevents the user from completing the task efficiently. The issue may or may not be a violation of the Web Accessibility Checklist. Sev. 4 – Low - Should be addressed in next release. User with a disability will be able to complete a task, but the issue may cause confusion to the user, and should be resolved. The issue is not a violation of the Web Accessibility Checklist. An issue was found, but should not be classified as an accessibility problem. These may be functionality bugs that should be corrected. 18 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Deploy, support & documentation Who’s involved: • Technical writer/editor • Help desk (support team) • Accessibility consultant • User experience specialist & Accessibility Compliance Expert Work products: • Training and guidance for the help desk – supporting customers or employees who use assistive technology • When the application or product is released into production, there should be a feedback mechanism to continue evaluating the user experience. The many different browsers, user agents, and version levels, will render a wide variety of user experience results. This feedback will help improve the robustness of your product in later releases. • Support costs can be significant, there may be customer satisfaction or legal risks associated with inappropriate application support • Under the AODA, there are obligations and penalties for customer support. • Accessible documentation • Compliant with the WCAG 2. 0 standards – MS Office, PDF, captioned video, etc. 19 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Training, training and more training WCAG 2. 0 • • 38 A & AA requirements (‘success criteria’) – each with techniques www. w 3. org/WAI/WCAG 20/quickref www. ibm. com/able www. ontario. ca/Access. ON Everyone on the team needs some training • • • 20 Project stakeholders Project manager Business analysts User e. Xperience specialist (UX) & Information architects Web Designers Software developers Quality assurance experts Accessibility Compliance Expert Technical writers (application documentation) The first couple projects will cost more – there’s a training, tools and organizational learning curve. You cannot avoid this investment. The cost of remediation is much higher than the investment to design it and build it right up front. © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Technology challenges Explosive growth of mobile delivery of I/T solutions • WCAG 2. 0 does not deliver a complete picture for tablets and smart phones • Most mobile devices will not have a traditional keyboard but that doesn’t mean they cannot be accessible • Most mobile applications are hybrid applications and not simply Web • Mobile platforms are incomplete in their accessibility services support Social media • Despite rapid adoption rates, social media channels are still largely inaccessible… • Social businesses will perpetuate and widen this gap unless inclusive solutions are provided Growth of big data and analytics • I/T solutions increasingly requires the effective use of business analytics • This is an area where the accessibility technology community has done a poor job – representation of complex data and inter-relationships of the data in a way that is clear and understandable, and which is accessible with assistive technologies 21 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Important success factors Start your journey on the right foot: • Adopt proven standards • WCAG 2. 0, with ARIA extensions • On-going training for developers and testers • On-going awareness sessions for the project sponsor and other stakeholders to maintain support • Align with good user experience principles • Organizational Support: Executive Champion • Governance - Legal, procurement accessibility clause in contracts and RFP’s • Work with groups such as HR with a heightened and focused awareness of disability issues • Pick your first project carefully • Work with groups involved in highly visible customer facing applications • But, don’t overreach – don’t try to boil the ocean on the first project • Identify and get commitment on the accessibility requirements at the earliest possible stage - in the conceptual and business case process • • • Development environment • Consider a dedicated Portal for sharing and distribution of information, resources and downloadable testing tools • Integrate your accessibility testing tools with development and standard testing tools and processes Testing environment • Controlled and structured – all the testing disciplines and techniques you understand can be applied to improve your odds of success Be innovative and thought provoking Create repeatable and scalable solutions Embrace collaboration – between industry and vendors and colleagues 22 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Questions? Please contact Dan or David: Dan Shire IBM Canada danshire@ca. ibm. com David Best IBM Canada Dave. Best@ca. ibm. com 23 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

More information – check out these references § § Government of Ontario IBM accessibility checklists § § § WCAG 2. 0 guidelines www. w 3. org/WAI W 3 C – good & bad website examples www. w 3. org/WAI/demos/bad/ Worldwide Web Consortium (W 3 C) page on user testing webbism. com/2012/07/06/the-benefits-of-user-testing-with-disabledusers/www. w 3. org/wiki/Accessibility_testing#When_should_testing_be_done. 3 F WCAG sufficient techniques www. w 3. org/TR/UNDERSTANDING-WCAG 20/intro. html Involving Users in Evaluating Web Accessibility www. w 3. org/WAI/eval/users Involving Users in Web Projects for Better, Easier Accessibility www. w 3. org/WAI/users/involving. html § § § www. ontario. ca/Access. ON www. ibm. com/able Web. AIM Utah State University www. webaim. org OCAD University – Inclusive Design www. idrc. ocad. ca Government of Canada Web Experience Toolkit www. tbs-sct. gc. ca/ws-nw/wa-aw/wet-boew/index-eng. asp 24 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.

Cool tools … 1. Plug-ins for Firefox: § Fangs – screen reader simulator § WAVE – testing toolbar (from Web. AIM) 2. NVDA – free open source screen reader www. nvda-project. org 3. JAWS – screen reader – evaluation copy www. freedomscientific. com/products/fs/jaws-product-page. asp 4. IBM a. Designer – free open source accessibility simulator and test tool www. eclipse. org/actf/downloads/tools/a. Designer 25 © 2013 IBM Canada Ltd.
c990640c61ca0bf1512029f547a95784.ppt