73a0b9d75901ea15d78525541ddc0aa0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Integrating Access Control Design into the Software Development Process G. Brose (Xtradyne AG) M. Koch, P. Löhr (FU Berlin) IDPT‘ 02, June 2002
Integrating Access Control Design into the Software Development Process G. Brose (Xtradyne AG) M. Koch, P. Löhr (FU Berlin) IDPT‘ 02, June 2002
 Overview l l l Motivation View-based Access Control Integrating Access Control in UML – – l l security analysis security design Generation of the Access Control Policy specification Conclusion
Overview l l l Motivation View-based Access Control Integrating Access Control in UML – – l l security analysis security design Generation of the Access Control Policy specification Conclusion
 Motivation l l l Security aspects are inherent in any modern software system But: Security is not a part in the development process Why ? : – – l security requirements are difficult to analyze and model system engineers are not security experts Problems: – – Unsatisfied security requirements Integration difficulties
Motivation l l l Security aspects are inherent in any modern software system But: Security is not a part in the development process Why ? : – – l security requirements are difficult to analyze and model system engineers are not security experts Problems: – – Unsatisfied security requirements Integration difficulties
 Our approach - Aims l l l Systematic support for software engineers who need to produce secure software Integration into the software development process with UML How ? – – Use of existing UML model elements Security design with UML tools No security expert knowledge neccessary UML design for the generation of security specifications
Our approach - Aims l l l Systematic support for software engineers who need to produce secure software Integration into the software development process with UML How ? – – Use of existing UML model elements Security design with UML tools No security expert knowledge neccessary UML design for the generation of security specifications
 Our approach – What we have done l l Integration of view based access control policy design into the software development process with UML Generation of the access control specification from the UML design model to configure a CORBA-based infrastructure (Raccoon)
Our approach – What we have done l l Integration of view based access control policy design into the software development process with UML Generation of the access control specification from the UML design model to configure a CORBA-based infrastructure (Raccoon)
 View-based Access Control l l Design and management of access control policies in object-oriented systems Extension of role-based access control by views View is a set of access rights Views are specified in the View Policy Language (VPL)
View-based Access Control l l Design and management of access control policies in object-oriented systems Extension of role-based access control by views View is a set of access rights Views are specified in the View Policy Language (VPL)
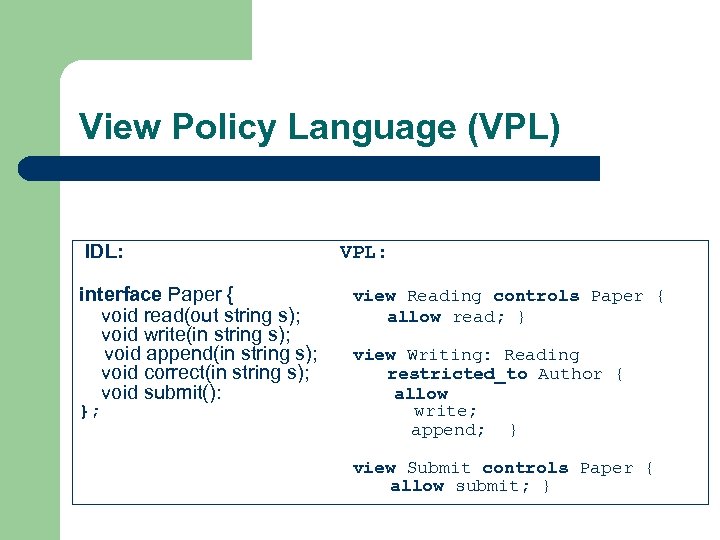 View Policy Language (VPL) IDL: interface Paper { void read(out string s); void write(in string s); void append(in string s); void correct(in string s); void submit(): }; VPL: view Reading controls Paper { allow read; } view Writing: Reading restricted_to Author { allow write; append; } view Submit controls Paper { allow submit; }
View Policy Language (VPL) IDL: interface Paper { void read(out string s); void write(in string s); void append(in string s); void correct(in string s); void submit(): }; VPL: view Reading controls Paper { allow read; } view Writing: Reading restricted_to Author { allow write; append; } view Submit controls Paper { allow submit; }
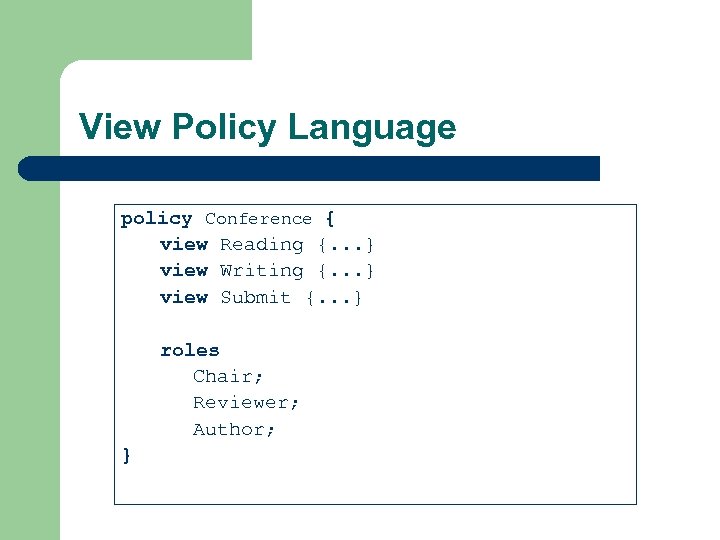 View Policy Language policy Conference { view Reading {. . . } view Writing {. . . } view Submit {. . . } roles Chair; Reviewer; Author; }
View Policy Language policy Conference { view Reading {. . . } view Writing {. . . } view Submit {. . . } roles Chair; Reviewer; Author; }
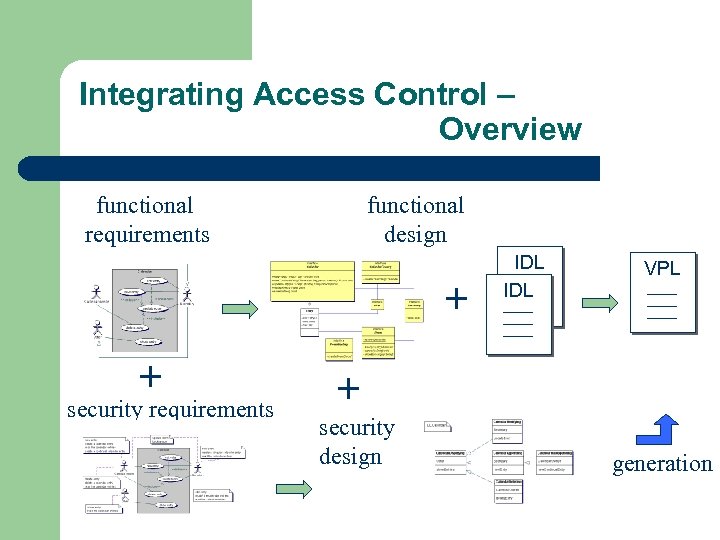 Integrating Access Control – Overview functional requirements functional design + + security requirements IDL VPL + security design generation
Integrating Access Control – Overview functional requirements functional design + + security requirements IDL VPL + security design generation
 Integrating Access Control Security Requirements
Integrating Access Control Security Requirements
 Security analysis l l l Functional requirements are expresed in use cases Security requirements are added to the use case models Access control information is inherent in functional system requirements and facilitates the integration
Security analysis l l l Functional requirements are expresed in use cases Security requirements are added to the use case models Access control information is inherent in functional system requirements and facilitates the integration
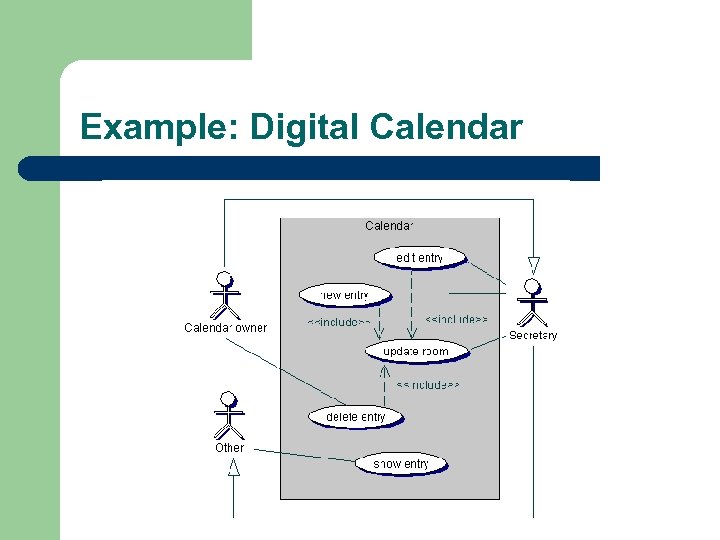 Example: Digital Calendar
Example: Digital Calendar
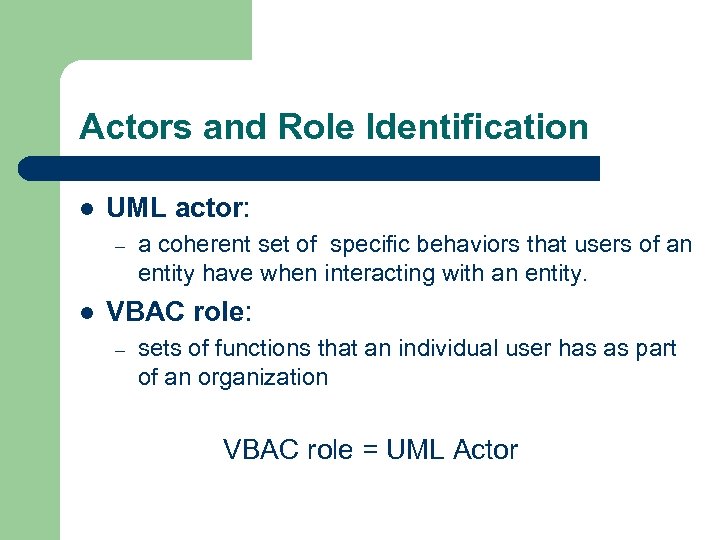 Actors and Role Identification l UML actor: – l a coherent set of specific behaviors that users of an entity have when interacting with an entity. VBAC role: – sets of functions that an individual user has as part of an organization VBAC role = UML Actor
Actors and Role Identification l UML actor: – l a coherent set of specific behaviors that users of an entity have when interacting with an entity. VBAC role: – sets of functions that an individual user has as part of an organization VBAC role = UML Actor
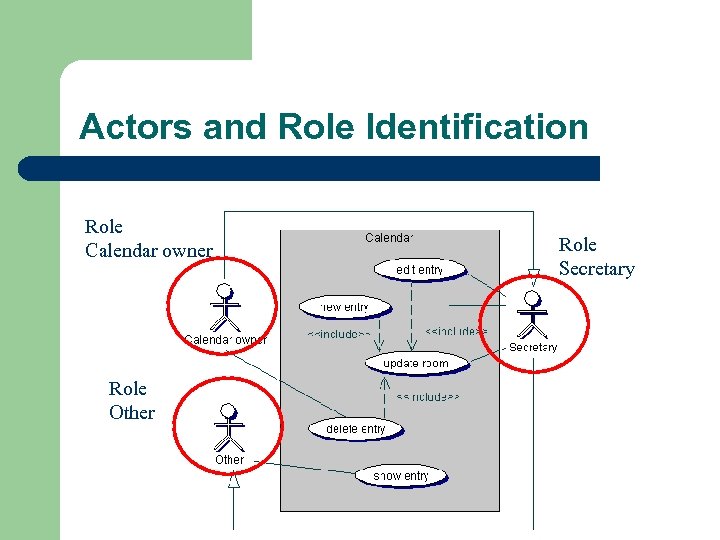 Actors and Role Identification Role Calendar owner Role Other Role Secretary
Actors and Role Identification Role Calendar owner Role Other Role Secretary
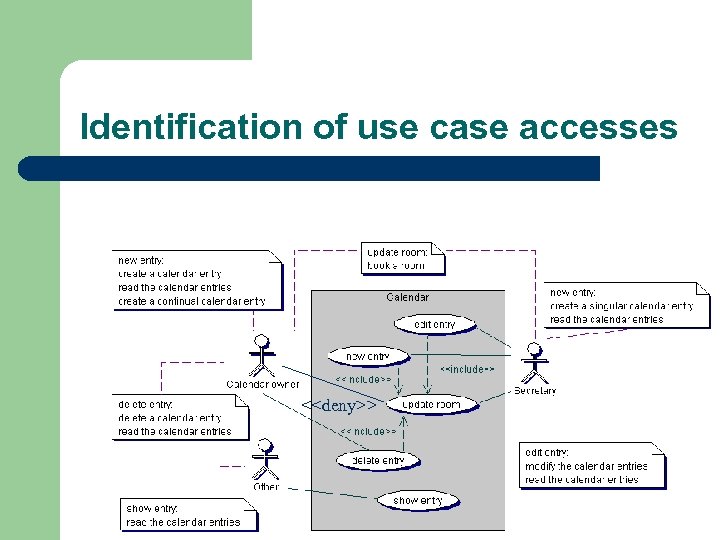
 Identification of use case accesses l l Extracting accesses from the informal use case descriptions Attaching notes to communication associations in the use case diagram – – l allowed and denied accesses high-level and informal Analyst considers and expresses security aspects already in the analysis phase
Identification of use case accesses l l Extracting accesses from the informal use case descriptions Attaching notes to communication associations in the use case diagram – – l allowed and denied accesses high-level and informal Analyst considers and expresses security aspects already in the analysis phase
 Identification of use case accesses edit entry: The calendar owner can read his/her entries and modify them. Modifications may cover the time, the day, and the room. The secretary of the calendar owner can read the calendar entries and make the calendar modifications, too. update room: A secretary books a room on behalf of the calendar owner. The calendar owner is not allowed to book a room by her-/himself.
Identification of use case accesses edit entry: The calendar owner can read his/her entries and modify them. Modifications may cover the time, the day, and the room. The secretary of the calendar owner can read the calendar entries and make the calendar modifications, too. update room: A secretary books a room on behalf of the calendar owner. The calendar owner is not allowed to book a room by her-/himself.
 Identification of use case accesses <
Identification of use case accesses <
 Security analysis - summary l l l UML Actors = VBAC Roles Modeling of denied communications in use cases Making implicit access information in natural use case description explicit in notes
Security analysis - summary l l l UML Actors = VBAC Roles Modeling of denied communications in use cases Making implicit access information in natural use case description explicit in notes
 Integrating Access Control Security Design
Integrating Access Control Security Design
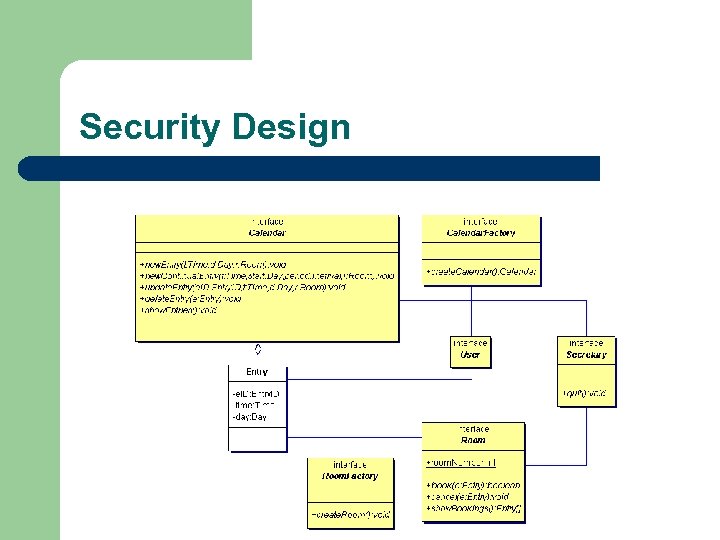
 Security Design l Starting point is the use case diagram l Class diagram (for CORBA interfaces) l View Diagram – views on CORBA interfaces
Security Design l Starting point is the use case diagram l Class diagram (for CORBA interfaces) l View Diagram – views on CORBA interfaces
 Security Design
Security Design
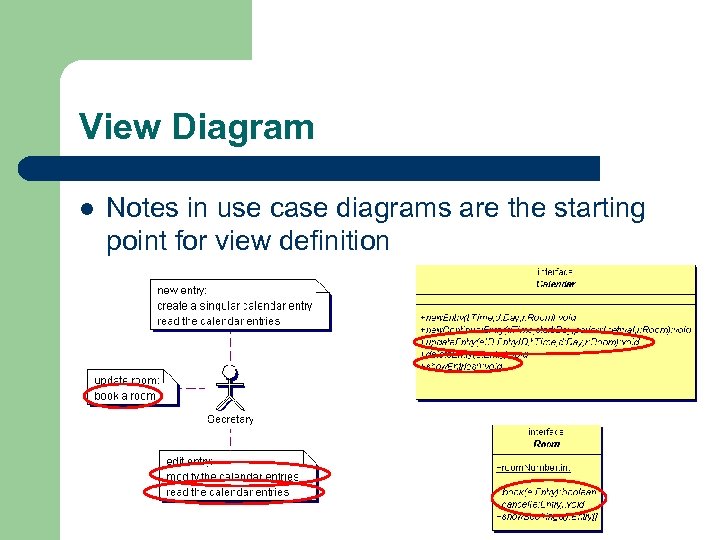 View Diagram l Notes in use case diagrams are the starting point for view definition
View Diagram l Notes in use case diagrams are the starting point for view definition
 View Diagram l For each note N: – – – l l View V(N, I) = all access rights with respect to interface I access rights are permissions to access the operation <
View Diagram l For each note N: – – – l l View V(N, I) = all access rights with respect to interface I access rights are permissions to access the operation <
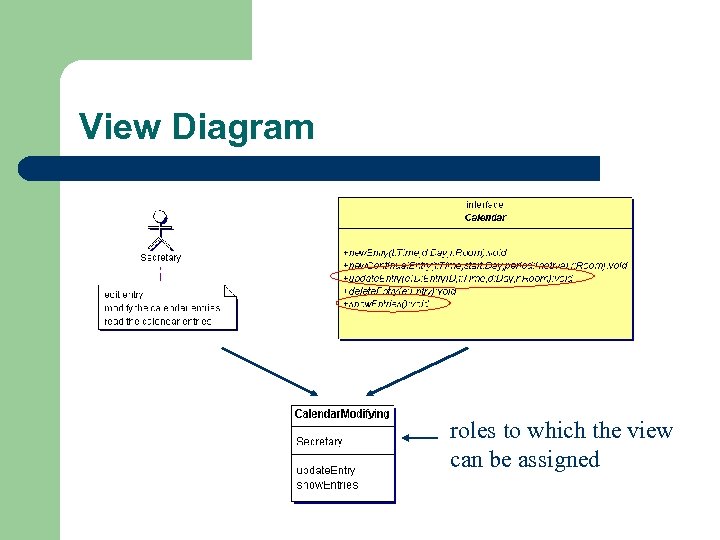 View Diagram roles to which the view can be assigned
View Diagram roles to which the view can be assigned
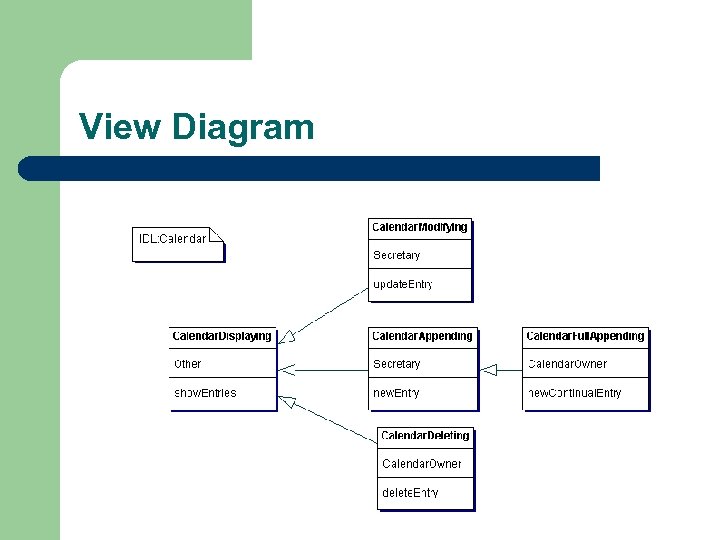 View Diagram
View Diagram
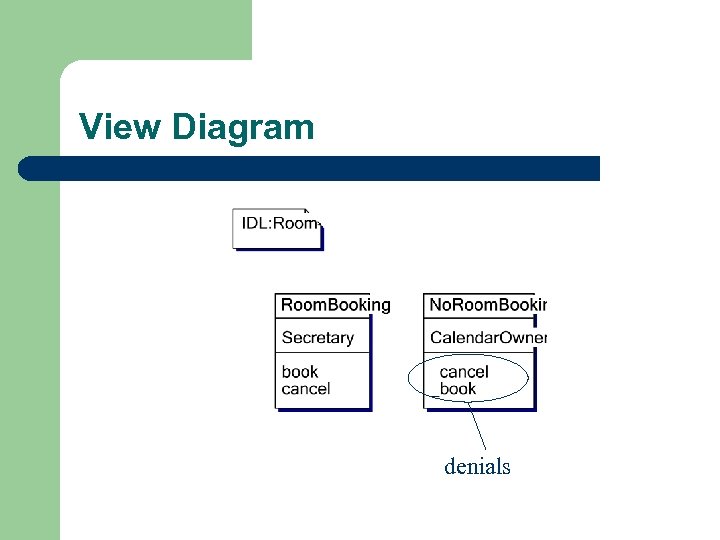 View Diagram denials
View Diagram denials
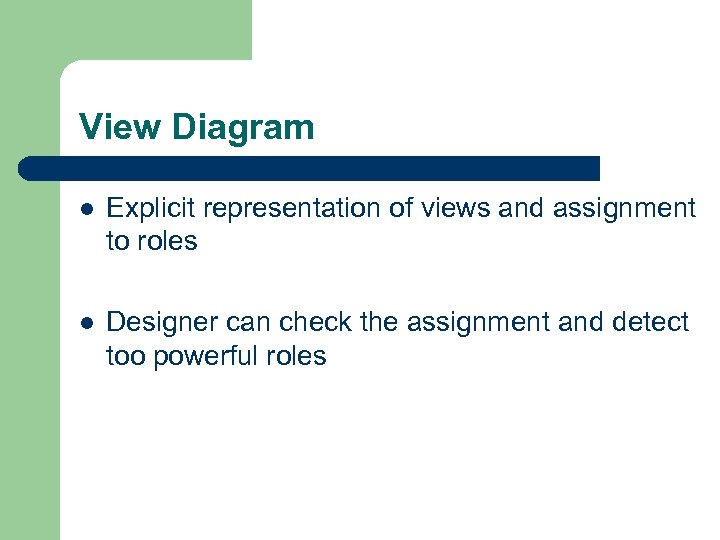 View Diagram l Explicit representation of views and assignment to roles l Designer can check the assignment and detect too powerful roles
View Diagram l Explicit representation of views and assignment to roles l Designer can check the assignment and detect too powerful roles
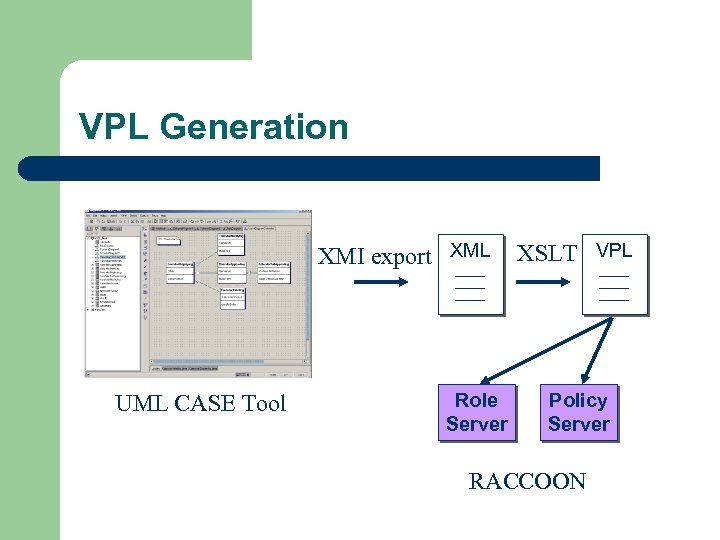 VPL Generation XMI export XML UML CASE Tool Role Server XSLT VPL Policy Server RACCOON
VPL Generation XMI export XML UML CASE Tool Role Server XSLT VPL Policy Server RACCOON
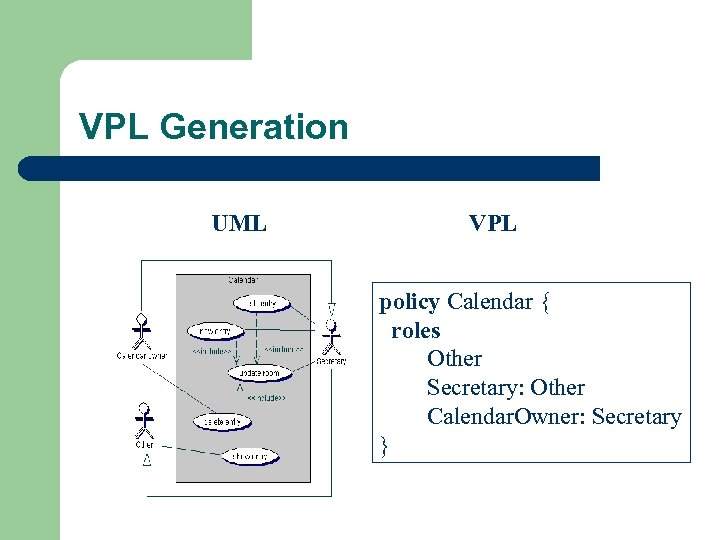 VPL Generation UML VPL policy Calendar { roles Other Secretary: Other Calendar. Owner: Secretary }
VPL Generation UML VPL policy Calendar { roles Other Secretary: Other Calendar. Owner: Secretary }
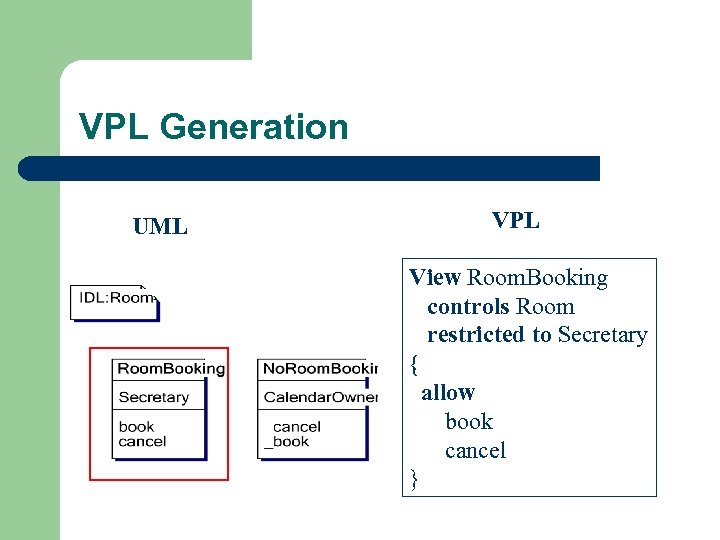 VPL Generation UML VPL View Room. Booking controls Room restricted to Secretary { allow book cancel }
VPL Generation UML VPL View Room. Booking controls Room restricted to Secretary { allow book cancel }
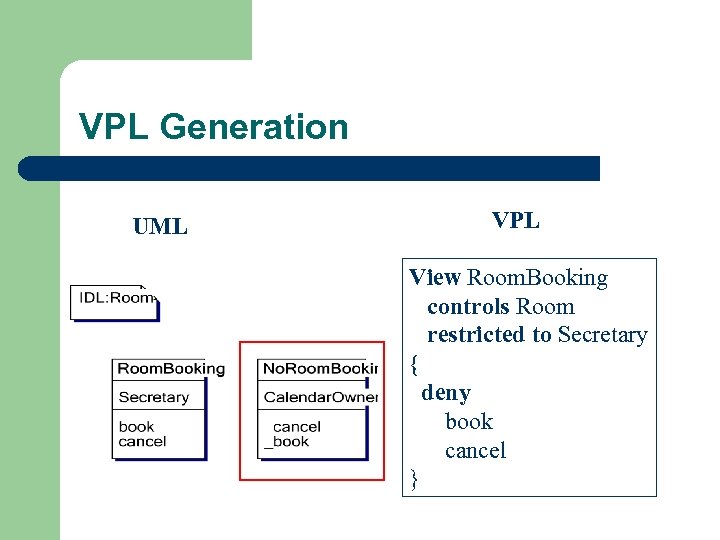 VPL Generation UML VPL View Room. Booking controls Room restricted to Secretary { deny book cancel }
VPL Generation UML VPL View Room. Booking controls Room restricted to Secretary { deny book cancel }
 Conclusion l l l Systematic approach to integrate access control policy design into the devlopment process with UML Security requirments are considered early UML model is used to genarte the VPL UML tools can be used No security expert knowledge necessary
Conclusion l l l Systematic approach to integrate access control policy design into the devlopment process with UML Security requirments are considered early UML model is used to genarte the VPL UML tools can be used No security expert knowledge necessary
 Weitere Folien
Weitere Folien
 Access Control l Preventing unauthorized access to resources Authorized accesses are specified in access control policies Security models are. . . – – – discretionary access control (e. g. , Access Contol List) mandatory access control (e. g. lattice-based access control) role-based access control view-based access control. .
Access Control l Preventing unauthorized access to resources Authorized accesses are specified in access control policies Security models are. . . – – – discretionary access control (e. g. , Access Contol List) mandatory access control (e. g. lattice-based access control) role-based access control view-based access control. .
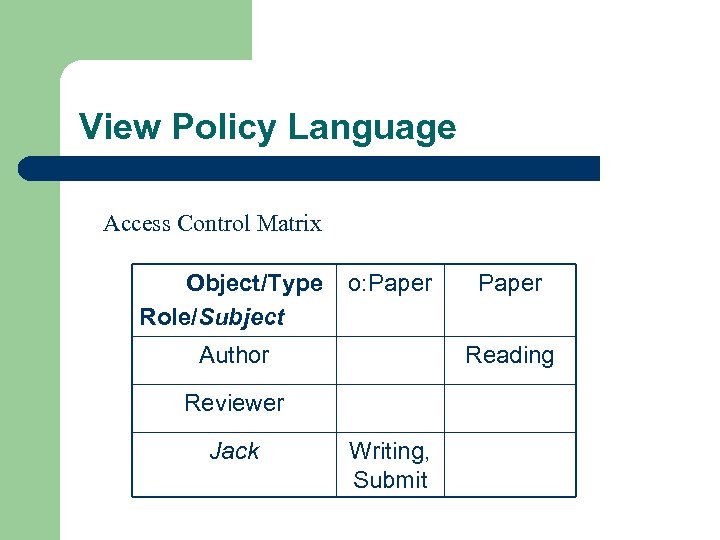 View Policy Language Access Control Matrix Object/Type Role/Subject o: Paper Author Reading Reviewer Jack Paper Writing, Submit
View Policy Language Access Control Matrix Object/Type Role/Subject o: Paper Author Reading Reviewer Jack Paper Writing, Submit
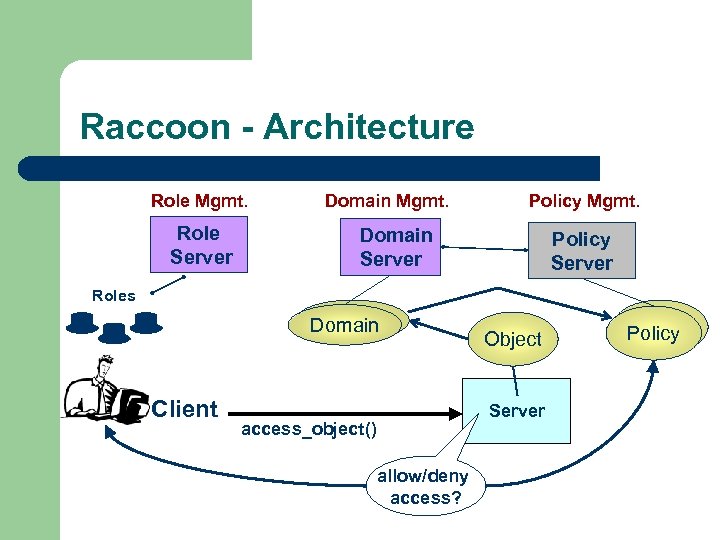 Raccoon - Architecture Role Mgmt. Role Server Domain Mgmt. Policy Mgmt. Domain Server Policy Server Roles Domain Client Object Server access_object() allow/deny access? Policy
Raccoon - Architecture Role Mgmt. Role Server Domain Mgmt. Policy Mgmt. Domain Server Policy Server Roles Domain Client Object Server access_object() allow/deny access? Policy
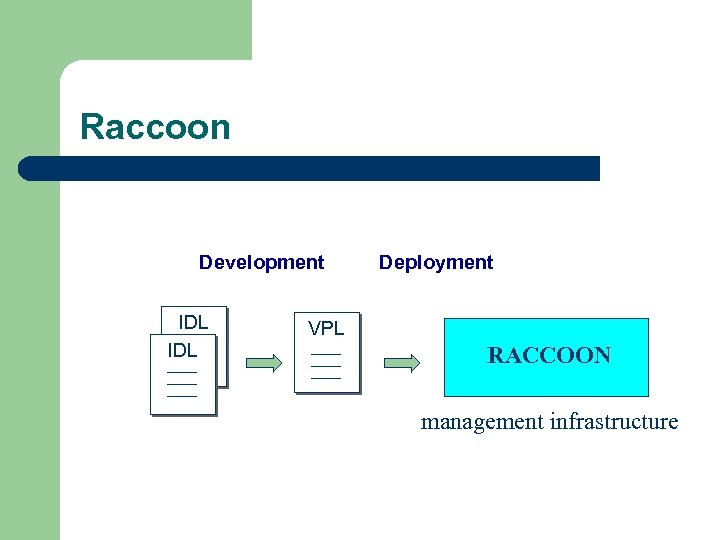 Raccoon Development IDL Deployment VPL RACCOON management infrastructure
Raccoon Development IDL Deployment VPL RACCOON management infrastructure
 Actors and Role Identification l UML role: – – l „named specific behavior of an entity participating in a particular context“ modeled by named association ends UML actor: – „a coherent set of roles that users of an entity can play when interacting with an entity. An actor has one role for each use case with which it communicates“
Actors and Role Identification l UML role: – – l „named specific behavior of an entity participating in a particular context“ modeled by named association ends UML actor: – „a coherent set of roles that users of an entity can play when interacting with an entity. An actor has one role for each use case with which it communicates“
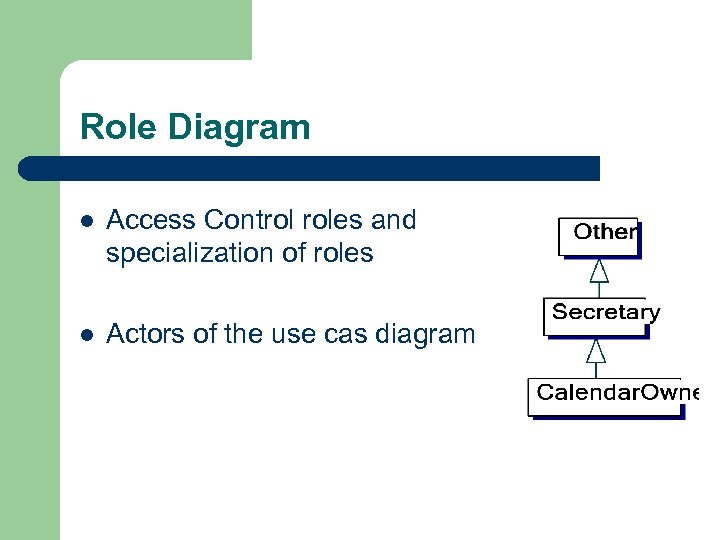 Role Diagram l Access Control roles and specialization of roles l Actors of the use cas diagram
Role Diagram l Access Control roles and specialization of roles l Actors of the use cas diagram
 Forbidden Use Cases l Specification of possible, but unallowed use case accesses l Documentation of unauthorized accesses l Stereotype <
Forbidden Use Cases l Specification of possible, but unallowed use case accesses l Documentation of unauthorized accesses l Stereotype <
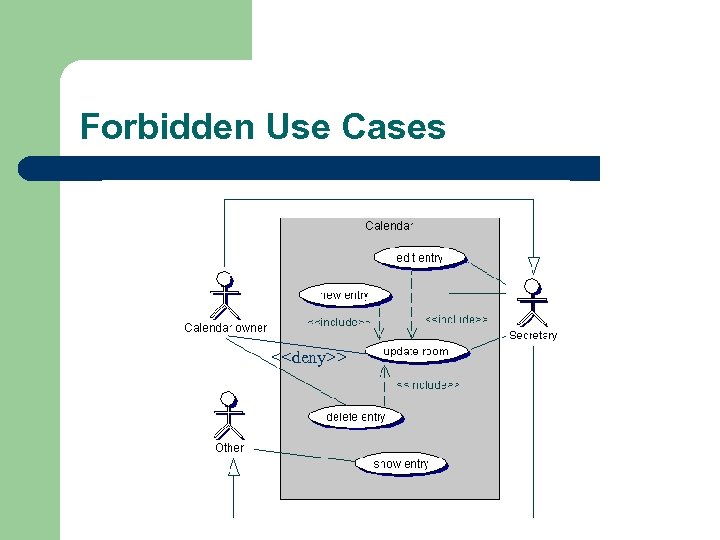 Forbidden Use Cases <
Forbidden Use Cases <
 Security design - summary l l View Diagrams are based on informal accesses in the notes of use cases Role Diagram is based on the actors in use case diagrams
Security design - summary l l View Diagrams are based on informal accesses in the notes of use cases Role Diagram is based on the actors in use case diagrams


