bafd2d565abf35ff9034bd47ba641c9a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Integrated Public Financial Management Systems (PFMS) Cem Dener ECSPE u u u June 2006 Definitions Evolution of Treasury Systems Design and Implementation Information & Communication Technology PFMS Projects in ECA Recommendations PFMS 1

Definitions Public Financial Management System (PFMS) is designed to u support all financial operations, u collect accurate, timely, complete, reliable and consistent information on all public financial events, u provide adequate management reporting, u support government-wide and agency policy decisions, u produce auditable financial statements. June 2006 PFMS 2
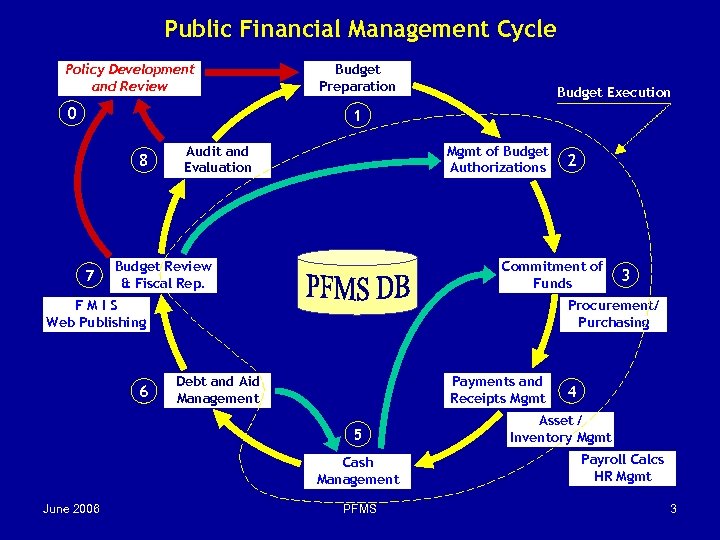
Public Financial Management Cycle Policy Development and Review 0 Budget Preparation Budget Execution 1 8 7 Audit and Evaluation Mgmt of Budget Authorizations Budget Review & Fiscal Rep. Commitment of Funds FMIS Web Publishing 6 3 Procurement/ Purchasing Debt and Aid Management Payments and Receipts Mgmt 5 Cash Management June 2006 2 PFMS 4 Asset / Inventory Mgmt Payroll Calcs HR Mgmt 3

Components Core Treasury System includes the following components: 2 u 4 u 5 u 7 u 8 u 4 u Budget Execution and Monitoring Accounting (general ledger, management of payments and receipts) Cash Management Financial Reporting Purchasing / Commitment Asset / Inventory Management u Operational support for Spending Units Other Public Financial Management System components: 1 u 6 u 4 u 8 u 7 u Macro Economic Forecasting Budget Preparation and Approval Debt and Aid Management HR Management /Payroll Calculations Support for Financial Control and Auditing Web publishing 7 u Financial Management Information System The combination of above components is referred to as integrated PFMS June 2006 PFMS 4

Evolution of Treasury Systems Treasury development process: (Treasury Reference Model) 1. Establishment of legal and institutional frameworks 2. Definition of coverage 3. Definition of system functionality 4. Design and implementation of Information Systems June 2006 PFMS 5

Evolution of Treasury Systems 1. Establishment of legal and institutional frameworks u Legal : Approval and implementation of the organic budget law u Organization : Establishment of a countrywide Mo. F / Treasury organization u Personnel : Allocation of adequate qualified staff for Mo. F / Treasury management and operations June 2006 PFMS 6

Evolution of Treasury Systems 2. Definition of coverage u Treasury control over government financial resources (Treasury Single Account) u Coverage of central budget (all government transactions are routed through treasury) u Coverage of extra budgetary funds and off-budget funds u Coverage of local (sub-national) governments June 2006 PFMS 7
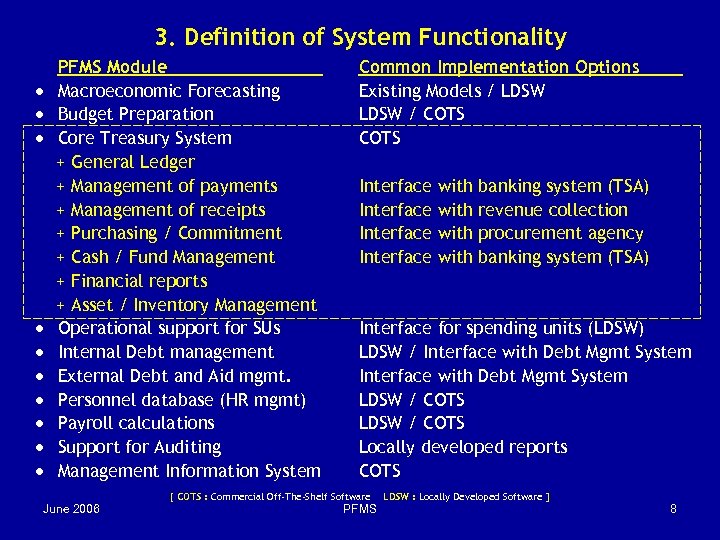
3. Definition of System Functionality · · · · · PFMS Module Macroeconomic Forecasting Budget Preparation Core Treasury System + General Ledger + Management of payments + Management of receipts + Purchasing / Commitment + Cash / Fund Management + Financial reports + Asset / Inventory Management Operational support for SUs Internal Debt management External Debt and Aid mgmt. Personnel database (HR mgmt) Payroll calculations Support for Auditing Management Information System Common Implementation Options Existing Models / LDSW / COTS Interface banking system (TSA) revenue collection procurement agency banking system (TSA) Interface for spending units (LDSW) LDSW / Interface with Debt Mgmt System LDSW / COTS Locally developed reports COTS [ COTS : Commercial Off-The-Shelf Software June 2006 with PFMS LDSW : Locally Developed Software ] 8

Evolution of Treasury Systems 4. Design and implementation of information systems u Secure countrywide network infrastructure u Development of web-based application software u Central servers and data storage/backup units u Standard field hardware u System and network management tools u Technical maintenance and support systems u System safety / security and business continuity solutions u Web publishing (web portal) June 2006 PFMS 9

Design and Implementation Treasury System Project Lifecycle A. Design phase (9 -18 months) u High Level Functional Design: Legal and institutional framework u Detailed Functional Design: Coverage, functionality, scope, budget execution, budget classification, chart of accounts, reporting u Technical System Design: Technical architecture, software, hardware and networking requirements, implementation plan u Component sizing and preparation of procurement specifications B. Procurement phase (9 -18 months) u International Competitive Bidding (ICB) for the development of application software (usually two-stage) u ICB for the installation of hardware and network equipment C. System integration and implementation (18 -36 months) June 2006 PFMS 10

Design and Implementation C. System integration and implementation (18 -36 months) u u u u Application Software (SW) design to meet functional requirements SW customization and parameterization + locally developed SW Communication infrastructure Network (NW) equipment, and cabling Hardware (HW) installations – central and field offices Security solutions (incl. support for digital signature) Pilot implementation Training Countrywide implementation (replication) Data entry and migration Backup and recovery solutions Business continuity solution Technical support and maintenance Call Center / Help Desk operations Documentation and manuals + web publishing June 2006 PFMS 11

Design and Implementation (contd. ) Technical Assistance (TA) requirements vary depending on the existing institutional capacity u Development of the legal, regulatory and operational framework u Review/revision of existing budget classification and chart of accounts u Development of GFS / IPSAS compliant financial reports u Development of PFMS functional requirements u Design of technological architecture u Preparation of the technical specifications and bidding documents u Technical support during the implementation of Treasury/PFM system u Data conversion and interfaces with other systems u Training u Project management June 2006 PFMS 12
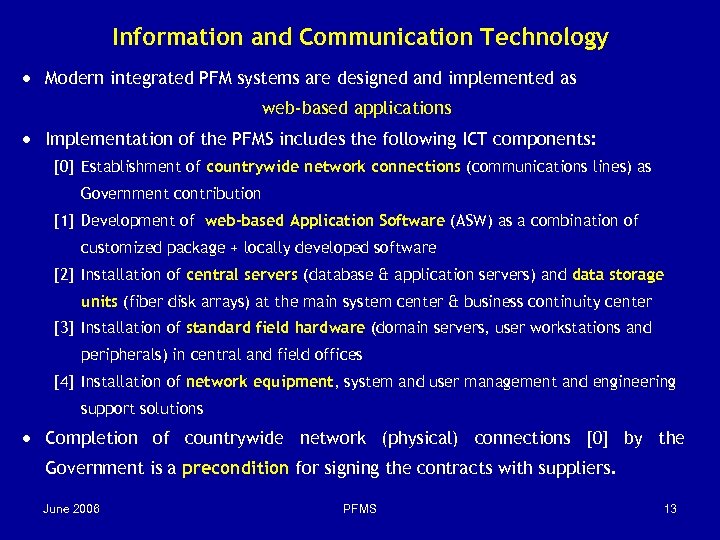
Information and Communication Technology · Modern integrated PFM systems are designed and implemented as web-based applications · Implementation of the PFMS includes the following ICT components: [0] Establishment of countrywide network connections (communications lines) as Government contribution [1] Development of web-based Application Software (ASW) as a combination of customized package + locally developed software [2] Installation of central servers (database & application servers) and data storage units (fiber disk arrays) at the main system center & business continuity center [3] Installation of standard field hardware (domain servers, user workstations and peripherals) in central and field offices [4] Installation of network equipment, system and user management and engineering support solutions · Completion of countrywide network (physical) connections [0] by the Government is a precondition for signing the contracts with suppliers. June 2006 PFMS 13
![Technology Architecture 3 -Tier Web-Based B C C M 1 SC Database Server(s) [2] Technology Architecture 3 -Tier Web-Based B C C M 1 SC Database Server(s) [2]](https://present5.com/presentation/bafd2d565abf35ff9034bd47ba641c9a/image-14.jpg)
Technology Architecture 3 -Tier Web-Based B C C M 1 SC Database Server(s) [2] Central Servers 2 Application Servers [0] [1] Wide Area Network PFMS Application Software Internet Web Server PFMS DB Firewall Mo. F / Treasury District Offices [3] Field Hardware Special DU lines for towns Collection Point (city center) FR line Local Server 3 FR line Virtual Private Network Encryption Tunnelling District Offices PCs / Thin Clients MSC : Main System Center BCC : Business Continuity Center June 2006 [4] Network Equipment District Offices Spending Units PFMS 14
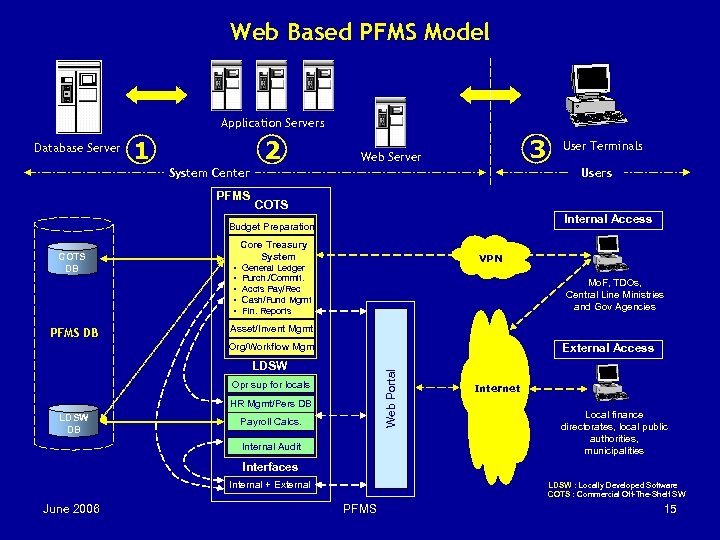
Web Based PFMS Model Application Servers Database Server 1 2 3 Web Server Users System Center PFMS COTS Internal Access Budget Preparation COTS DB PFMS DB Core Treasury System • • • VPN General Ledger Purch. /Commit. Accts Pay/Rec Cash/Fund Mgmt Fin. Reports Mo. F, TDOs, Central Line Ministries and Gov Agencies Asset/Invent Mgmt External Access Org/Workflow Mgm Web Portal LDSW Opr sup for locals HR Mgmt/Pers DB LDSW DB User Terminals Payroll Calcs. Internal Audit Internet Local finance directorates, local public authorities, municipalities Interfaces Internal + External June 2006 LDSW : Locally Developed Software COTS : Commercial Off-The-Shelf SW PFMS 15
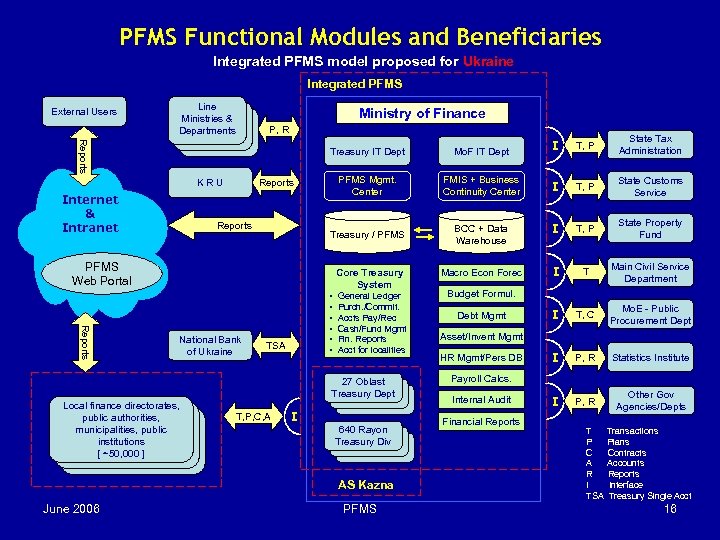
PFMS Functional Modules and Beneficiaries Integrated PFMS model proposed for Ukraine Integrated PFMS External Users Line Ministries & Departments Ministry of Finance P, R I T, P State Tax Administration PFMS Mgmt. Center FMIS + Business Continuity Center I T, P State Customs Service BCC + Data Warehouse I T, P State Property Fund Macro Econ Forec I T Main Civil Service Department I T, C Mo. E - Public Procurement Dept I P, R Statistics Institute I P, R Other Gov Agencies/Depts Reports KRU Internet & Intranet Mo. F IT Dept Treasury / PFMS Reports Treasury IT Dept Reports PFMS Web Portal Core Treasury System Reports National Bank of Ukraine • • • TSA 27 Oblast Treasury Dept Spending Units Local finance directorates, public authorities, municipalities, public institutions [ ~50, 000 ] General Ledger Purch. /Commit. Accts Pay/Rec Cash/Fund Mgmt Fin. Reports Acct for localities T, P, C, A I 640 Rayon Treasury Div AS Kazna June 2006 PFMS Budget Formul. Debt Mgmt Asset/Invent Mgmt HR Mgmt/Pers DB Payroll Calcs. Internal Audit Financial Reports T P C A R I TSA Transactions Plans Contracts Accounts Reports Interface Treasury Single Acct 16
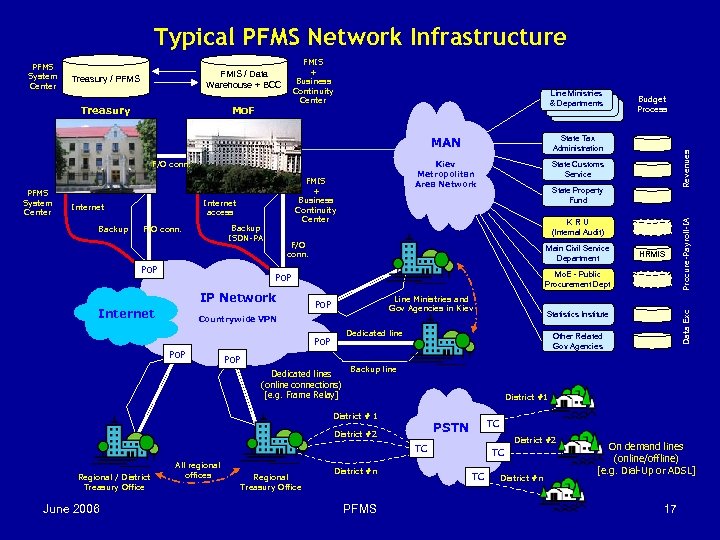
Typical PFMS Network Infrastructure Treasury Mo. F Line Ministries & Departments MAN PFMS System Center Internet access Internet Backup FMIS + Business Continuity Center Backup ISDN-PA F/O conn. Po. P State Tax Administration Kiev Metropolitan Area Network F/O conn. State Customs Service KRU (Internal Audit) Main Civil Service Department Line Ministries and Gov Agencies in Kiev Po. P Dedicated lines (online connections) [e. g. Frame Relay] Other Related Gov Agencies Backup line District #1 District # 1 TC PSTN District #2 TC June 2006 Statistics Institute Countrywide VPN Po. P All regional offices Regional Treasury Office HRMIS Mo. E - Public Procurement Dept Po. P Internet Regional / District Treasury Office State Property Fund F/O conn. IP Network Budget Process Revenues Treasury / PFMS Procure-Payroll-IA FMIS + Business Continuity Center FMIS / Data Warehouse + BCC Data Exc PFMS System Center District #n PFMS TC TC District #n On demand lines (online/offline) [e. g. Dial-Up or ADSL] 17

Information and Communication Technology Central Servers and Field Hardware u Central servers (database and application servers) and main networking equipment located at System Center (SC). u A disaster recovery solution is highly recommended. Treasury head office (system center) can be connected to the Business Continuity Center (BCC) through a separate fiber optic line. u BCC servers can be used to host the Data Warehouse (FMIS) to avoid overloading of operational servers at system center. u Central network and system management tools. u Workstations, servers and peripherals for treasury district offices. June 2006 PFMS 18
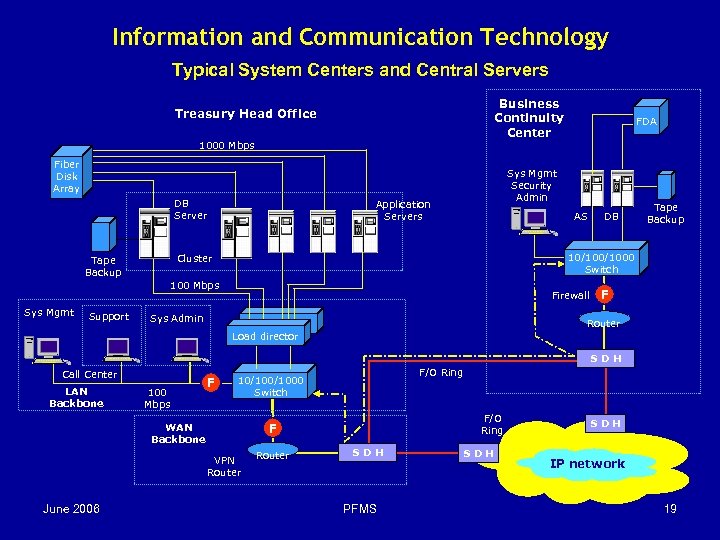
Information and Communication Technology Typical System Centers and Central Servers Business Continuity Center Treasury Head Office 1000 Mbps Fiber Disk Array DB Server Sys Mgmt Security Admin Application Servers AS 100 Mbps Sys Mgmt Support DB Tape Backup 10/1000 Switch Cluster Tape Backup FDA Firewall Sys Admin F Router Load director Director SDH Call Center LAN Backbone 100 Mbps F 10/1000 Switch F/O Ring F WAN Backbone VPN Router June 2006 F/O Ring Router SDH PFMS SDH IP network 19

ICT - Network Treasury/PFM System Network Infrastructure Network solution for a web-based system [on-line operation] All Treasury District Offices (TDOs) are connected to the central Treasury office located at the center (usually within the Mo. F). u A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is established to form a secure intranet in which all public financial data can be transmitted in encrypted format. u This VPN is also used as the main communication platform of the Treasury/Mo. F offices by providing e-mail services, internet access and other utilities. u Voice over IP (Vo. IP) services can be utilized to reduce internal telecommunication costs of the Treasury/Mo. F offices. u Solution for the spending units of line ministries and local gov [off-line / on-demand] u Selected spending units and local gov units can be connected to nearest TDO through off-line or on-demand [e. g. Dial-Up (DU) or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)] connections to enter transactions and to get their financial reports. June 2006 PFMS 20
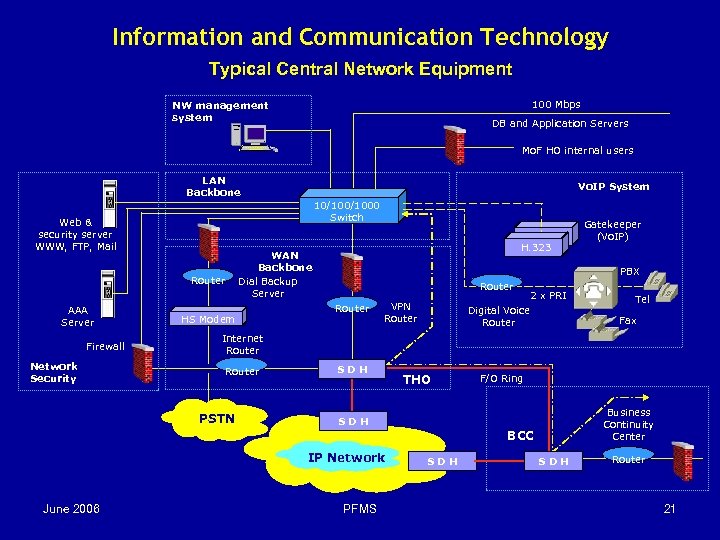
Information and Communication Technology Typical Central Network Equipment 100 Mbps NW management system DB and Application Servers Mo. F HO internal users LAN Backbone 10/1000 Switch Web & security server WWW, FTP, Mail Firewall Network Security H. 323 WAN Backbone Dial Backup Server Router AAA Server Vo. IP System HS Modem PBX Router VPN Router 2 x PRI Digital Voice Router Tel Fax Internet Router PSTN SDH THO F/O Ring Business Continuity Center SDH BCC IP Network June 2006 Gatekeeper (Vo. IP) PFMS SDH Router 21

Observations u Development of the core treasury system is an important milestone for the implementation of a countrywide Public Financial Management System (PFMS), which enables integration and exchange of information available in various systems (e. g. Treasury, Tax, Customs, Central Bank) developed by different agencies. u The Financial Management Information System (FMIS), as the main decision support and monitoring system for public finance, is based on centrally available information gathered from all important components of the PFMS. u Development time for a fully functional treasury system in some transition economies and developing countries varies between 3 to 5 years. Large scale implementations of the treasury systems may take even longer. u Total cost of ownership of treasury system implementation depends on a number of factors, such as institutional capacity, scope, desired functionality, number of users and implementation method. June 2006 PFMS 22
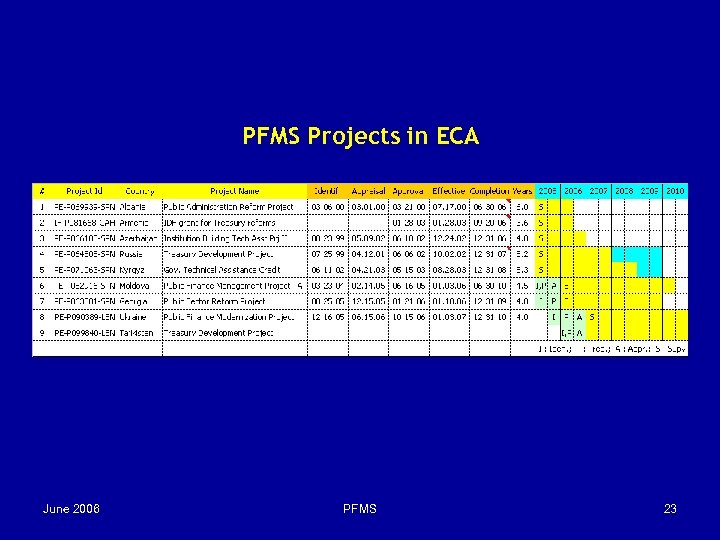
PFMS Projects in ECA June 2006 PFMS 23
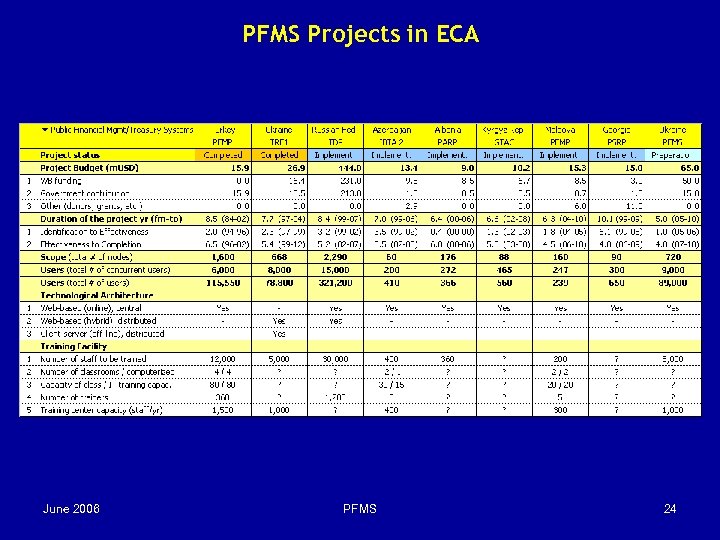
PFMS Projects in ECA June 2006 PFMS 24
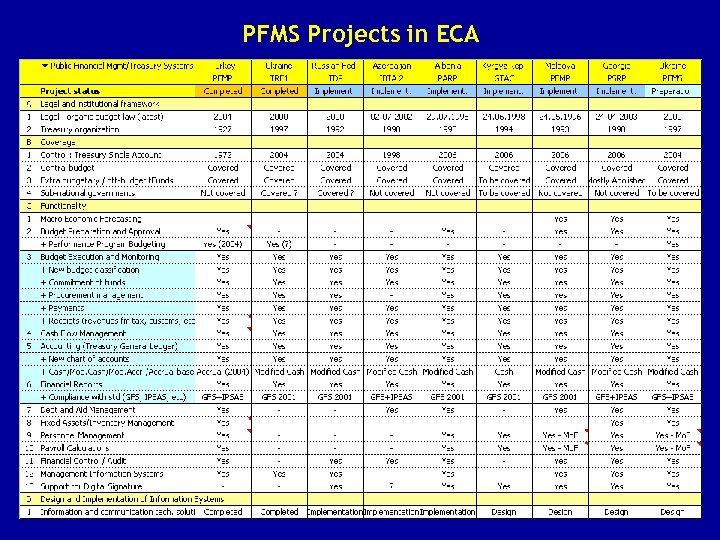
PFMS Projects in ECA June 2006 PFMS 25

Recommendations Development of modern integrated PFMS according to the best practices is a complex task, which should be designed as a separate project. Implementation of such wide spread changes would require: u Government commitment and management support at the highest levels to ensure that the change process is completed smoothly u Inter-agency coordination and user involvement in system design u Building institutional capacity and technical skills starting from the preparation phase u Development of project management and technical support units within the Mo. F/Treasury for implementation and sustainability of new systems June 2006 PFMS 26
bafd2d565abf35ff9034bd47ba641c9a.ppt