0bf15501137c5b459c3ee634e6c6433b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Integrated Human Rights Maturity Model

Context/Background n Canadian Human Rights Commission programs: § Knowledge Management and Dissemination § Discrimination Prevention § Dispute Resolution n One component of the Discrimination Prevention Program is to help employers prevent discrimination in the workplace 2

Context/Background n We negotiate and enter into agreements with organizations to assist them in reducing discrimination in workplaces or service delivery areas n These agreements require significant resources to deliver 3

Context/Background n A set of human rights standards for workplaces may help employers prevent discrimination in the workplace without the need for significant resources n A human rights maturity model will be a set of standards for organizations to enhance their “human rights competence” 4

Context/Background n Knowledge gained from other organizations using maturity models have demonstrated value of this tool for the CHRC n The Integrated Human Rights Maturity Model (IHRMM) integrates multiple CHRC processes (complaints, audits, policy review, training, etc. ) 5

Why develop a Maturity Model? Successful firms will be those most adept at attracting, developing, and retaining individuals with the skills, perspectives, and experience necessary to drive a global business. Ulrich, in People Capability Maturity Model: Guidelines for Improving the Workforce 6

What is a Maturity Model? n A roadmap for implementing workforce practices that continuously improve an organization’s human rights capability n Support for the coordination of multidisciplined activities that might be required to successfully develop a ‘human rights competent’ organization 7

What is a Maturity Model? n Means to emphasize the alignment of human rights objectives with organizational business objectives n A collection of best practices n An integration of multiple processes leading to a self-sustaining human rights culture 8

What does a Maturity Model provide? n n A common language and a shared vision The benefit of employers’ prior experiences A framework for prioritizing activities A way to define what human rights competence means for an organization 9

What does a Maturity Model provide? n A way to recognize success in implementing human rights practices in the workplace (i. e. , CHRC “stamp” of recognition) n A means to evaluate progress toward a selfsustaining human rights culture 10

IHRMM Guiding Principles n n n Focus Integration General Framework Modelling the Model Extensive Consultation/Buy-in Knowledge Transfer 11

Critical Path Progress to Date n General research on “maturity models” has been completed n Initial internal (CHRC) consultations with all sectors has been completed; focus groups are ongoing n External consultation (EAC, CBA, FETCO, other employers) is ongoing 12

Critical Path Progress to Date n General IHRMM outline has been developed n Communications strategy has been prepared n The IHRMM Steering Committee has been established 13
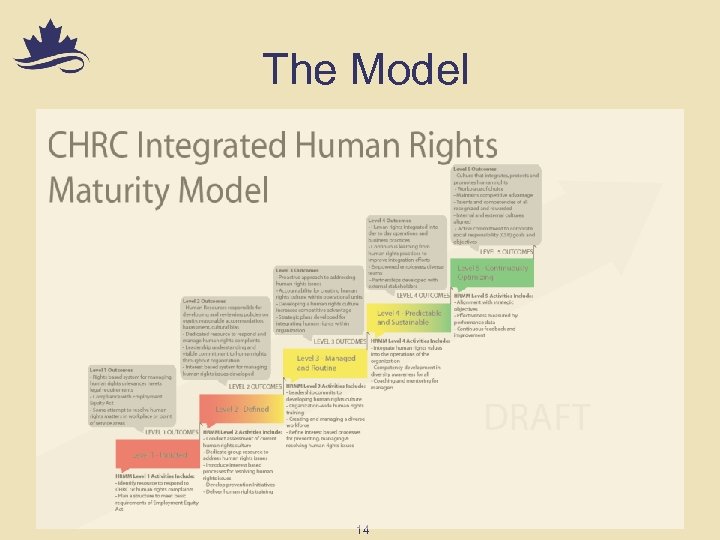
The Model 14

Level 1 – Initiated n An organization at this level of evolution demonstrates an initial recognition that a reactive approach to human rights matters in its workplace and/or its point-of-service areas may not be sufficient in today’s competitive marketplace 15

Level 2 – Defined n Unlike an organization at Level 1, an organization at this level will delegate accountability for creating a human rights culture to its operational units, rather than relying solely on its human resources unit to carry the responsibility n Sample Outcome § Interest-based system for managing human rights issues developed 16

Level 3 – Managed and Routine n An organization at this level of evolution has clearly established policies for a wide range of human rights issues, including harassment and reasonable accommodation, and routinely reviews all policies likely to contain cultural bias (hiring, deployment, training, etc. ) n Sample Outcome § Strategic plans developed for integrating human rights within organization 17

Level 4 – Predictable and Sustainable n An organization at this level of evolution views human rights as an intrinsic value and integral part of the organization n Sample Outcome § Human Rights integrated into day-to-day operations and business practices 18

Level 5 – Continuously Optimizing n An organization at this level of evolution has achieved a culture of human rights in its workplace and point-of-service areas and is constantly striving for continuous improvement n Sample Outcome § Workplace of choice § Active commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals and objectives (“spreading the gospel internationally”) 19

Challenges n Relative to other models in existence, the IHRMM is attempting to provide a standard for over 600 federally regulated employers: § from different sectors (public, private), § from different industries, § with different mandates, and § each with a diverse employee base. 20

Challenges n The IHRMM is not enforceable; buy-in is critical n What employers are hoping the maturity model will provide: § Streamlining administrative reporting § Being recognized as an employer of choice § Performance indicators 21

Next Steps n n n Pilot workshops Implementation in pilot organizations Evaluation of pilots Revision of IHRMM Launching the IHRMM 22
0bf15501137c5b459c3ee634e6c6433b.ppt