1f5dada10d9a711cd9d0812b1915a7ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Integrated Electronics Course Rapid Prototyping 11 th March 2009 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Integrated Electronics Course Rapid Prototyping 11 th March 2009 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
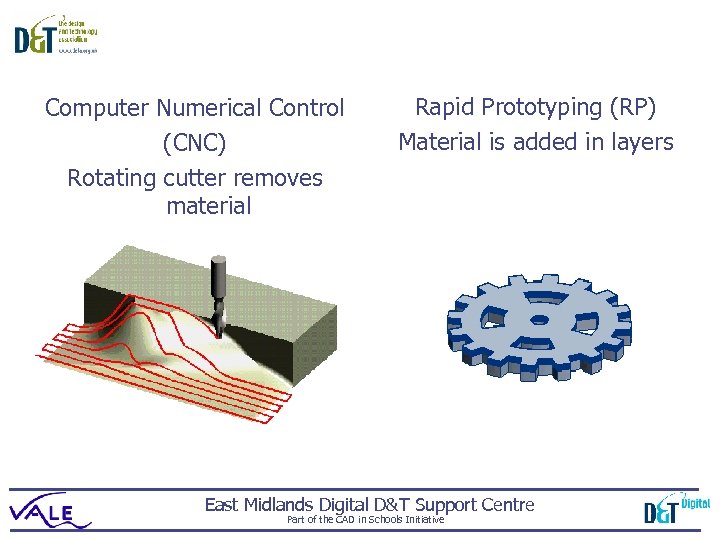 Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Rotating cutter removes material Rapid Prototyping (RP) Material is added in layers East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Rotating cutter removes material Rapid Prototyping (RP) Material is added in layers East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Rapid prototyping is the automatic construction of physical objects using solid freeform fabrication. The first techniques for rapid prototyping became available in the late 1980 s and were used to produce models and prototype parts. Today, they are used for a much wider range of applications and are even used to manufacture production quality parts in relatively small numbers. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Rapid prototyping is the automatic construction of physical objects using solid freeform fabrication. The first techniques for rapid prototyping became available in the late 1980 s and were used to produce models and prototype parts. Today, they are used for a much wider range of applications and are even used to manufacture production quality parts in relatively small numbers. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Rapid Prototyping (RP) SLA - Stereo Lithography LOM - Laminated object manufacture FDM - Fuse deposition modelling SLM - Selective Laser Melting 3 DP - 3 D Printing East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Rapid Prototyping (RP) SLA - Stereo Lithography LOM - Laminated object manufacture FDM - Fuse deposition modelling SLM - Selective Laser Melting 3 DP - 3 D Printing East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
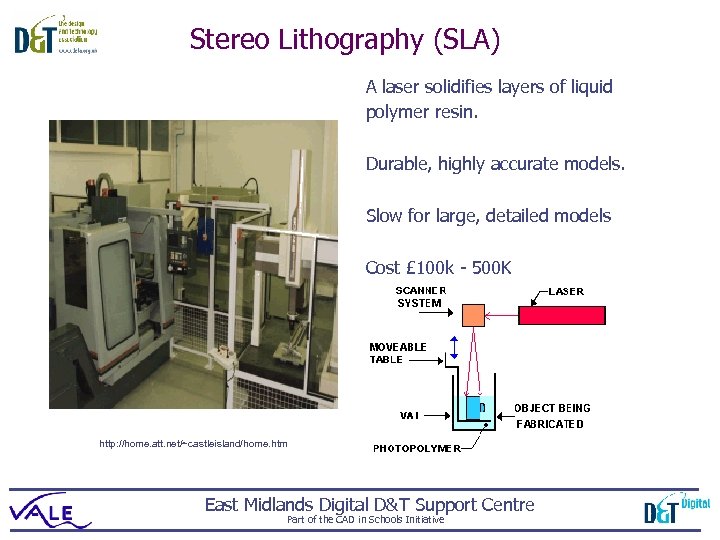 Stereo Lithography (SLA) A laser solidifies layers of liquid polymer resin. Durable, highly accurate models. Slow for large, detailed models Cost £ 100 k - 500 K http: //home. att. net/~castleisland/home. htm East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Stereo Lithography (SLA) A laser solidifies layers of liquid polymer resin. Durable, highly accurate models. Slow for large, detailed models Cost £ 100 k - 500 K http: //home. att. net/~castleisland/home. htm East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Laminated Object Manufacture (LOM) Heavy duty knife cutter creates paper or cardboard layers which are stuck together. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Laminated Object Manufacture (LOM) Heavy duty knife cutter creates paper or cardboard layers which are stuck together. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Fuse Deposition Modelling (FDM) Corn starch powder or plaster Material Adequate detail Machine = £ 14 K+ Quick build time Low cost models Models are fragile East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Fuse Deposition Modelling (FDM) Corn starch powder or plaster Material Adequate detail Machine = £ 14 K+ Quick build time Low cost models Models are fragile East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Selective Laser Melting (SLM) High powered laser melts metal powder to produce solid metal components MCP Technologies - http: //www. mcp-group. com East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) High powered laser melts metal powder to produce solid metal components MCP Technologies - http: //www. mcp-group. com East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
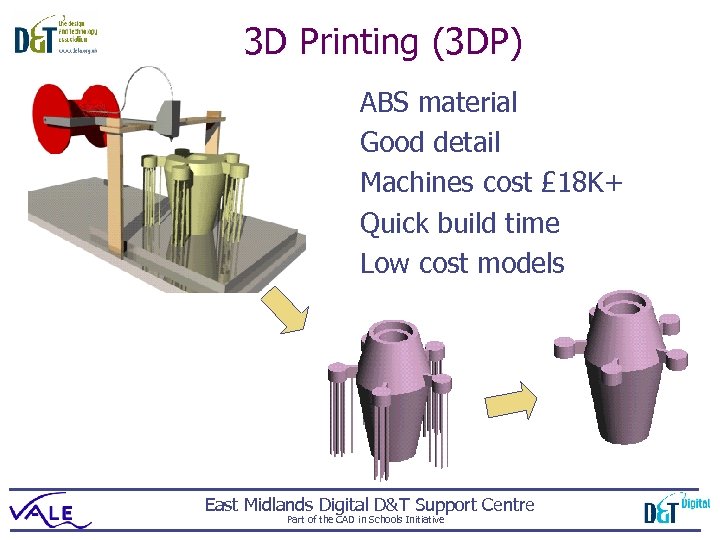 3 D Printing (3 DP) ABS material Good detail Machines cost £ 18 K+ Quick build time Low cost models East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
3 D Printing (3 DP) ABS material Good detail Machines cost £ 18 K+ Quick build time Low cost models East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Dimension 3 D Printers Three-dimensional printing is a type of rapid prototyping. The Dimension printers build functional 3 D models from the bottom up, one layer at a time from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene – ABS – plastic. Files are imported into the printer’s software which slices and orients the parts and creates any necessary support structures. The software plots a precise deposition path that the printer follows. ABS – in filament form within auto-loading cartridges – is fed into an extrusion head, heated to a semi-liquid state and deposited in layers as fine as 0. 010" thick. After completion of the build, support structures are removed. http: //www. dimensionprinting. com/ East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Dimension 3 D Printers Three-dimensional printing is a type of rapid prototyping. The Dimension printers build functional 3 D models from the bottom up, one layer at a time from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene – ABS – plastic. Files are imported into the printer’s software which slices and orients the parts and creates any necessary support structures. The software plots a precise deposition path that the printer follows. ABS – in filament form within auto-loading cartridges – is fed into an extrusion head, heated to a semi-liquid state and deposited in layers as fine as 0. 010" thick. After completion of the build, support structures are removed. http: //www. dimensionprinting. com/ East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
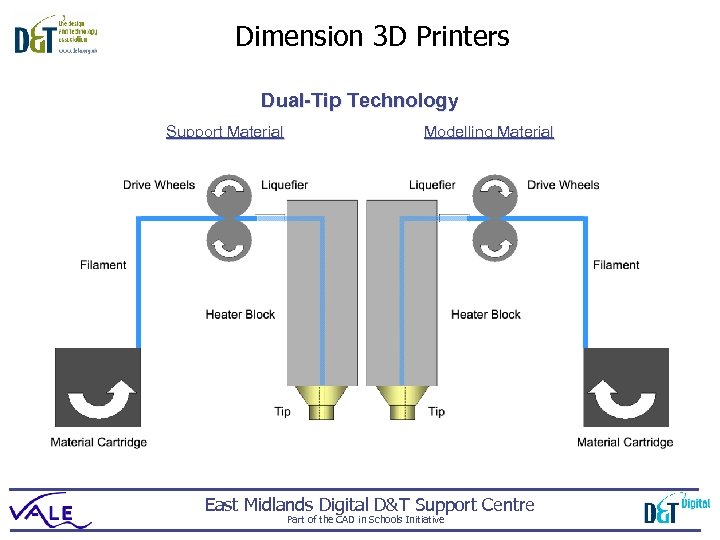 Dimension 3 D Printers Dual-Tip Technology Support Material Modelling Material East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Dimension 3 D Printers Dual-Tip Technology Support Material Modelling Material East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Case design Cases and enclosures for electronic circuits can be designed with any 3 D software capable of exporting STL files Pro. Desktop Pro. Engineer Solid. Works etc. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Case design Cases and enclosures for electronic circuits can be designed with any 3 D software capable of exporting STL files Pro. Desktop Pro. Engineer Solid. Works etc. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
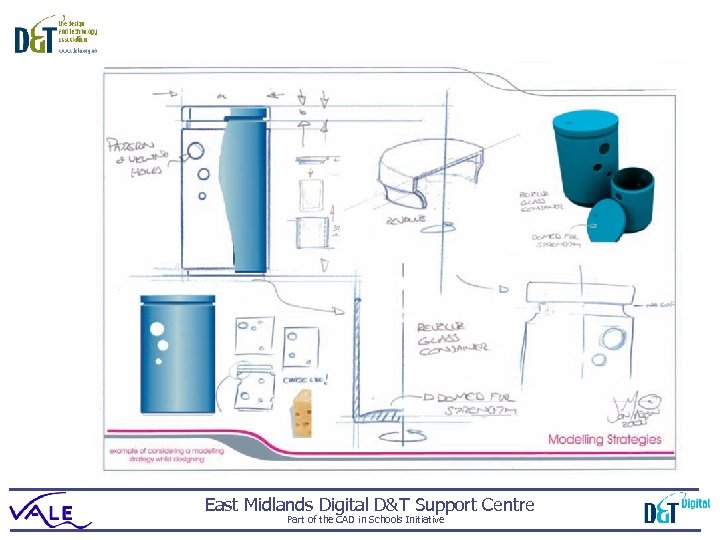
 Case design Modelling strategies Top-down: starts with a concept or overall form before moving to the detail of components that can create that form, eg car design starts with the finished vehicle and works down to consider the details that it will be made up of. Bottom-Up: involves several components or sub-systems in a product being designed or redesigned and then packaged together into an overall product e. g. a computer. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Case design Modelling strategies Top-down: starts with a concept or overall form before moving to the detail of components that can create that form, eg car design starts with the finished vehicle and works down to consider the details that it will be made up of. Bottom-Up: involves several components or sub-systems in a product being designed or redesigned and then packaged together into an overall product e. g. a computer. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Case design Modelling strategies Part family design: Reverse enginering: involves the creation of a master model and the final product is one of a series of different designs that vary from that master only in their dimensions (eg a set of gears). is the creation of a new model or product from an existing one. The new model will be based on the old one but have some number of alterations eg a computer mouse developed from a previous design. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Case design Modelling strategies Part family design: Reverse enginering: involves the creation of a master model and the final product is one of a series of different designs that vary from that master only in their dimensions (eg a set of gears). is the creation of a new model or product from an existing one. The new model will be based on the old one but have some number of alterations eg a computer mouse developed from a previous design. East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Case design Why are modelling strategies useful to us as designers? You need not worry too much about having a definite strategy for your CAD model as it is not always possible to plan this right from the start. For example, we may have a loose idea so cannot fully decide what it is we want to model. You can however start considering your modelling strategy whilst designing. What is important is that you understand that a good modelling strategy, or an awareness of modelling strategies, should enable you to: • model your design ideas more quickly • make changes more easily • produce a CAD model which is appropriate for the post processes you wish to apply to it (ie what you do with it at later stages) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Case design Why are modelling strategies useful to us as designers? You need not worry too much about having a definite strategy for your CAD model as it is not always possible to plan this right from the start. For example, we may have a loose idea so cannot fully decide what it is we want to model. You can however start considering your modelling strategy whilst designing. What is important is that you understand that a good modelling strategy, or an awareness of modelling strategies, should enable you to: • model your design ideas more quickly • make changes more easily • produce a CAD model which is appropriate for the post processes you wish to apply to it (ie what you do with it at later stages) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
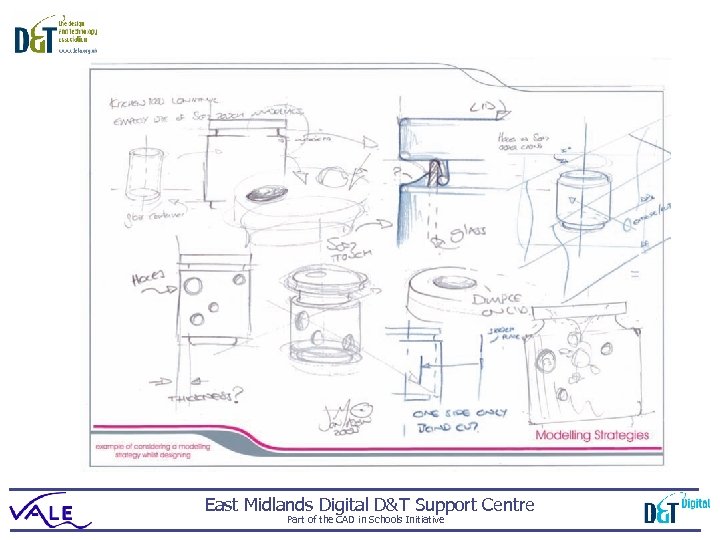 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
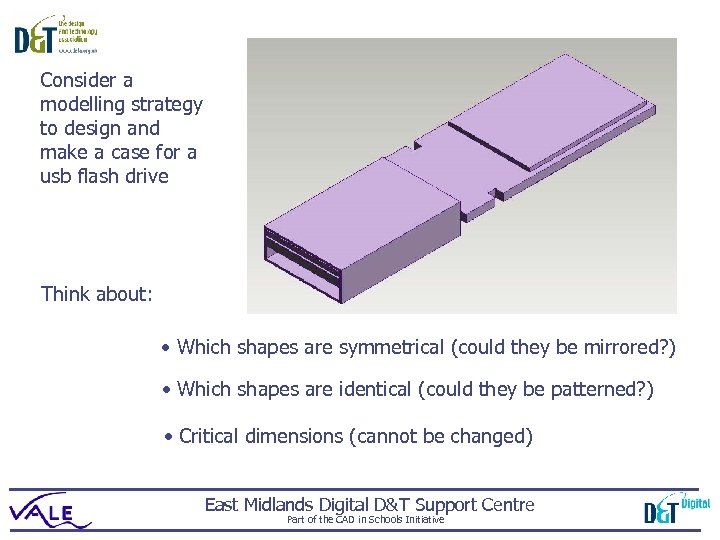 Consider a modelling strategy to design and make a case for a usb flash drive Think about: • Which shapes are symmetrical (could they be mirrored? ) • Which shapes are identical (could they be patterned? ) • Critical dimensions (cannot be changed) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Consider a modelling strategy to design and make a case for a usb flash drive Think about: • Which shapes are symmetrical (could they be mirrored? ) • Which shapes are identical (could they be patterned? ) • Critical dimensions (cannot be changed) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
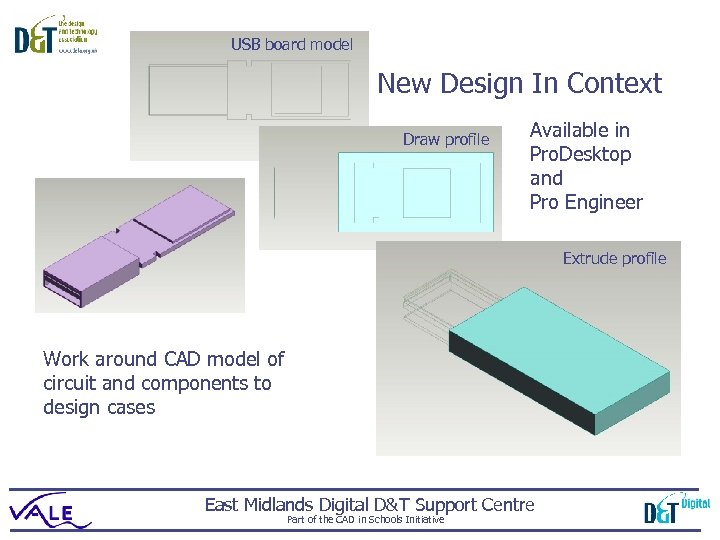 USB board model New Design In Context Draw profile Available in Pro. Desktop and Pro Engineer Extrude profile Work around CAD model of circuit and components to design cases East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
USB board model New Design In Context Draw profile Available in Pro. Desktop and Pro Engineer Extrude profile Work around CAD model of circuit and components to design cases East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
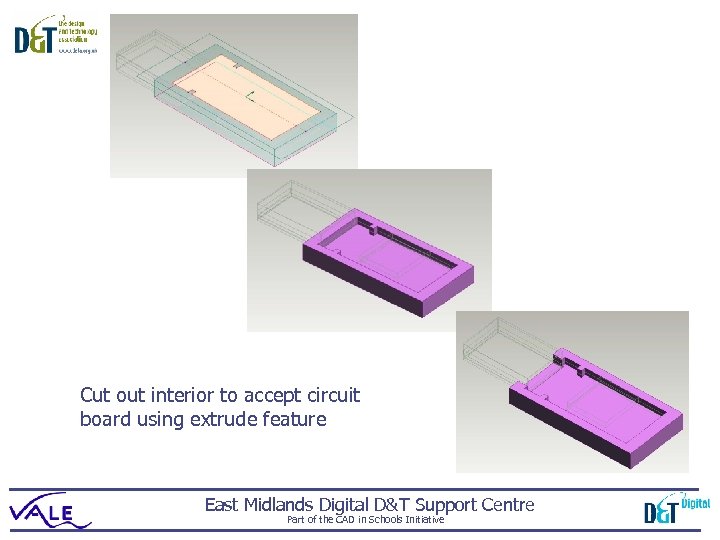 Cut out interior to accept circuit board using extrude feature East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Cut out interior to accept circuit board using extrude feature East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
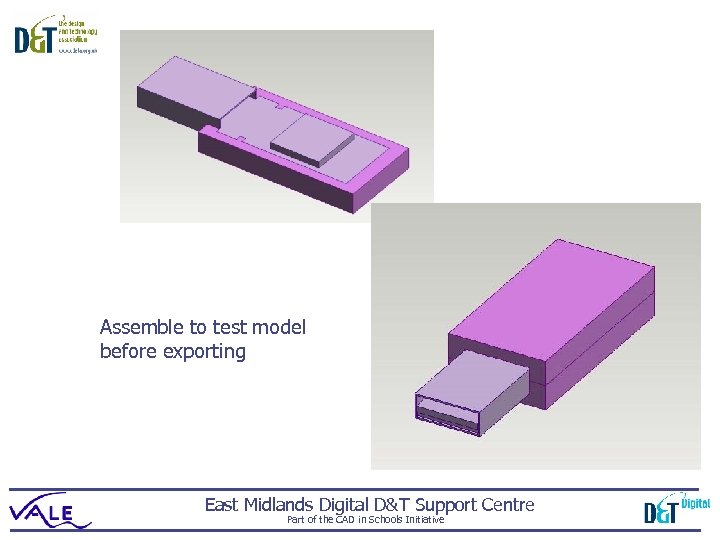 Assemble to test model before exporting East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Assemble to test model before exporting East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Important considerations when designing for 3 D printing. Size matters! • Wall thicknesses must not be less than 1. 5 mm. • Keep models as small/compact as possible ABS modelling material is expensive - £ 250 per kilo! (multiply the amount used by 0. 25 to work out the cost) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Important considerations when designing for 3 D printing. Size matters! • Wall thicknesses must not be less than 1. 5 mm. • Keep models as small/compact as possible ABS modelling material is expensive - £ 250 per kilo! (multiply the amount used by 0. 25 to work out the cost) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Creating and exporting an STL file In order to create physical models from CAD models we need to export them to an. stl format that machines can understand. This universal format allows the machine to recognise the model’s geometry and manufacture it. An. stl file works by tessellating a series of triangles over the form of the model to reproduce it exactly. These triangles are often referred to as facets. For example, a simple cube may look something like this: East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Creating and exporting an STL file In order to create physical models from CAD models we need to export them to an. stl format that machines can understand. This universal format allows the machine to recognise the model’s geometry and manufacture it. An. stl file works by tessellating a series of triangles over the form of the model to reproduce it exactly. These triangles are often referred to as facets. For example, a simple cube may look something like this: East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Creating and exporting an STL file The number of facets created within an. stl file controls how accurately the file reflects the original model and the level of detail in what is manufactured by the RP machine. The smaller the number of triangles or facets the less detail/accuracy there will be in the. stl file. Alternatively The larger the number of triangles or facets the more detailed the output from the. stl file. This is shown in examples on the right East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Creating and exporting an STL file The number of facets created within an. stl file controls how accurately the file reflects the original model and the level of detail in what is manufactured by the RP machine. The smaller the number of triangles or facets the less detail/accuracy there will be in the. stl file. Alternatively The larger the number of triangles or facets the more detailed the output from the. stl file. This is shown in examples on the right East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Creating and exporting an STL file Therefore, when exporting an. stl file we need to control the number of facets (triangles) by setting the chord height and the angle values to control the level of detail in the final model. In Pro. DESKTOP select: file > export > Stereo Lithography File Name the file appropriately and Save in a location you can easily retrieve it from. Set the Chordal (mm) value to 0. 005 Set the Angular (deg) value to 1 and Select: OK East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Creating and exporting an STL file Therefore, when exporting an. stl file we need to control the number of facets (triangles) by setting the chord height and the angle values to control the level of detail in the final model. In Pro. DESKTOP select: file > export > Stereo Lithography File Name the file appropriately and Save in a location you can easily retrieve it from. Set the Chordal (mm) value to 0. 005 Set the Angular (deg) value to 1 and Select: OK East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
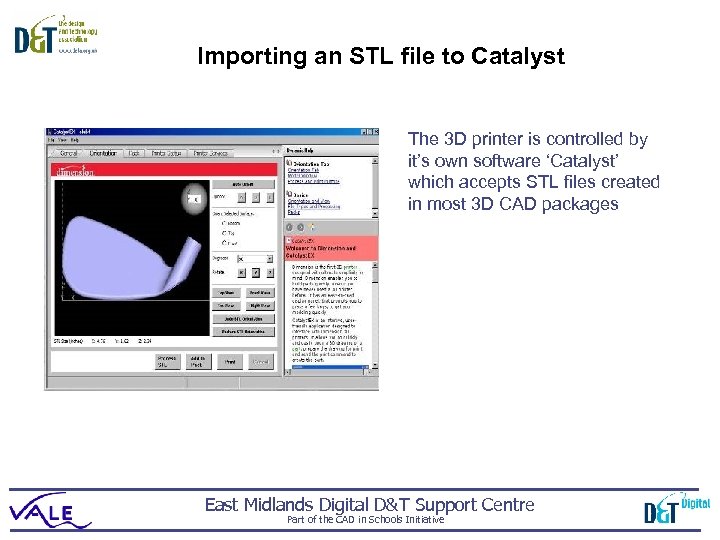 Importing an STL file to Catalyst The 3 D printer is controlled by it’s own software ‘Catalyst’ which accepts STL files created in most 3 D CAD packages East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Importing an STL file to Catalyst The 3 D printer is controlled by it’s own software ‘Catalyst’ which accepts STL files created in most 3 D CAD packages East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 Finishing RP Models • The most important thing with rapid prototypes is spending enough time to remove excess support material once they have been moulded • Take care not to lose any detail created in your model just by not being careful enough at the finishing stage. • Spray with filler primer (available from most car accessory shops eg Halfords) • Allow to dry between coats and rub down with wet & dry paper • Spray with colour spray paint (ideally car body paint) • Finish with polish or rubbing compound (Solvol-Autosol works) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
Finishing RP Models • The most important thing with rapid prototypes is spending enough time to remove excess support material once they have been moulded • Take care not to lose any detail created in your model just by not being careful enough at the finishing stage. • Spray with filler primer (available from most car accessory shops eg Halfords) • Allow to dry between coats and rub down with wet & dry paper • Spray with colour spray paint (ideally car body paint) • Finish with polish or rubbing compound (Solvol-Autosol works) East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
 East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative
East Midlands Digital D&T Support Centre Part of the CAD in Schools Initiative


