d1a7a97cc46135e686b8f3d1dbe05ac3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Int’l Submarine Cable Network In KT (Status and Plan) May 25, 2002 “The Value Networking Company”

Table of Contents 1. Introductions 2. International Submarine Cables 3. Korea-Japan Cable Network (KJCN) 4. Benefit of KJCN 5. Future Plan 2

Introductions 1. General Features of Submarine Cable 2. Basic Structure of Submarine Cable 3. Role of Submarine Cable 4. Procedure of Submarine Cable Construction 5. Special Equipments for Construction 3

Introduction General Features of Submarine Cables q Long Distance Transmission Capability - Trans-Pacific and Trans-Atlantic q Big Bandwidth Transmission Capability - Suitable for Internet, Video Streaming q High Reliability - Suitable for international e-commerce business q State of Art Technology - High Quality Service 4
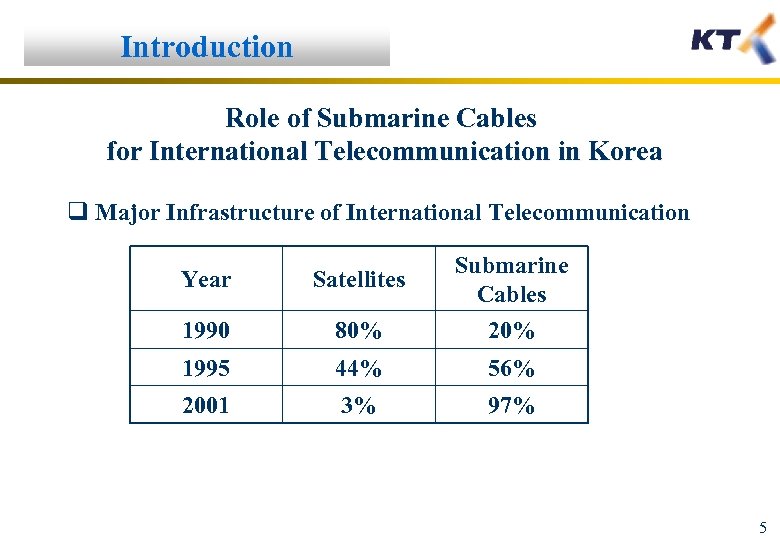
Introduction Role of Submarine Cables for International Telecommunication in Korea q Major Infrastructure of International Telecommunication Year Satellites Submarine Cables 1990 80% 20% 1995 44% 56% 2001 3% 97% 5
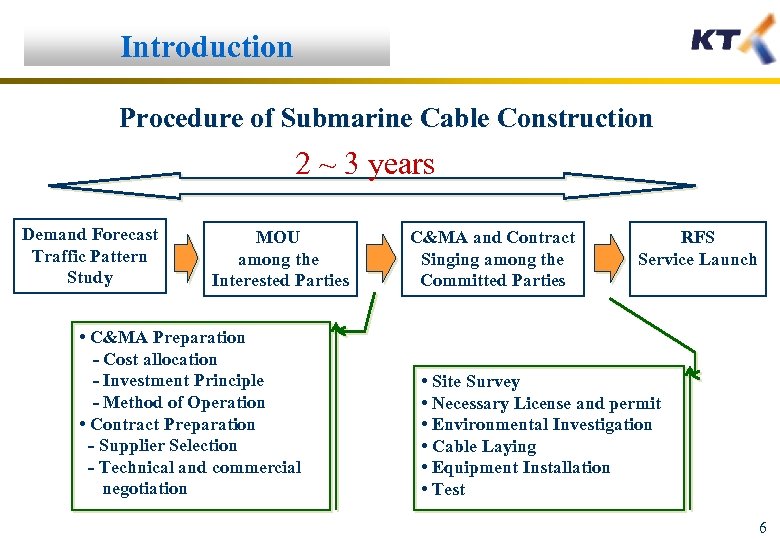
Introduction Procedure of Submarine Cable Construction 2 ~ 3 years Demand Forecast Traffic Pattern Study MOU among the Interested Parties • C&MA Preparation - Cost allocation - Investment Principle - Method of Operation • Contract Preparation - Supplier Selection - Technical and commercial negotiation C&MA and Contract Singing among the Committed Parties RFS Service Launch • Site Survey • Necessary License and permit • Environmental Investigation • Cable Laying • Equipment Installation • Test 6
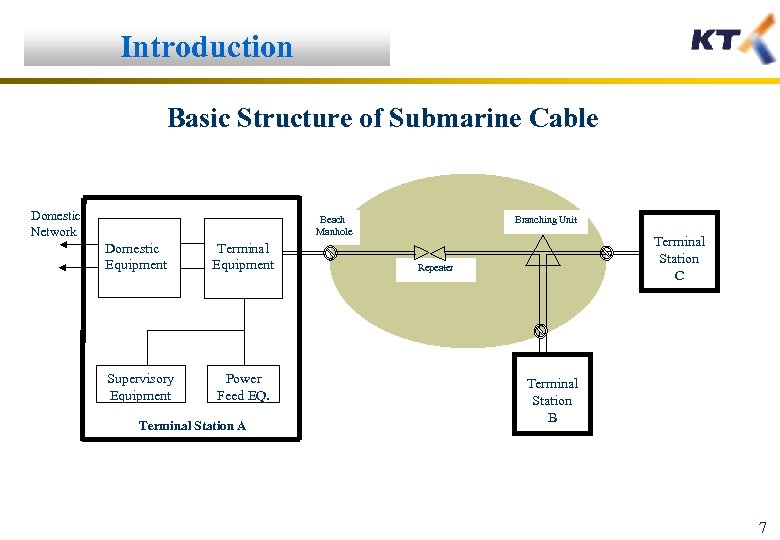
Introduction Basic Structure of Submarine Cable Domestic Network Beach Manhole Domestic Equipment Supervisory Equipment Terminal Equipment Power Feed EQ. Terminal Station A Branching Unit Terminal Station C Repeater Terminal Station B 7

Introduction Special Equipments for Construction (Cableship Segero) Main Particulars - Launch : 1998. 4 - Gross Ton : 8, 300 T - Length : 115. 8 m - Beam : 20 m - Accommodation: 63 - Endurance : 12, 000 nm 8

Introduction Special Equipments for Construction (Plough) The Plough is designed for the installation and burial submarine cables at same time to protect the cable 9

Introduction Special Equipments for Construction (ROV) Remotely operated vehicles (ROV), plough typed vehicle, can be used for the difficult working area like the junction of cables and of re-burial working after repairing the present cables. 10

International Submarine Cable 1. Submarine Cable Maps - World Cable Map - North East Asia Cable Map 2. Submarine Cables Landed in Korea 11

International Submarine Cables in the World 12
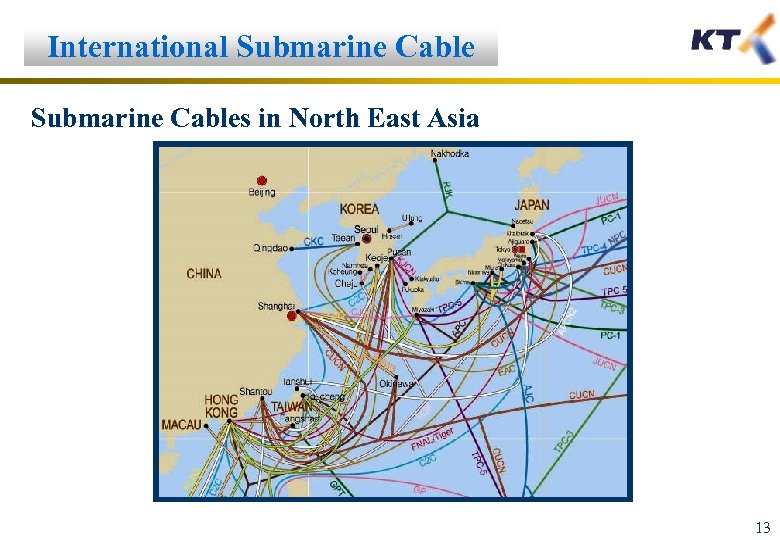
International Submarine Cables in North East Asia 13
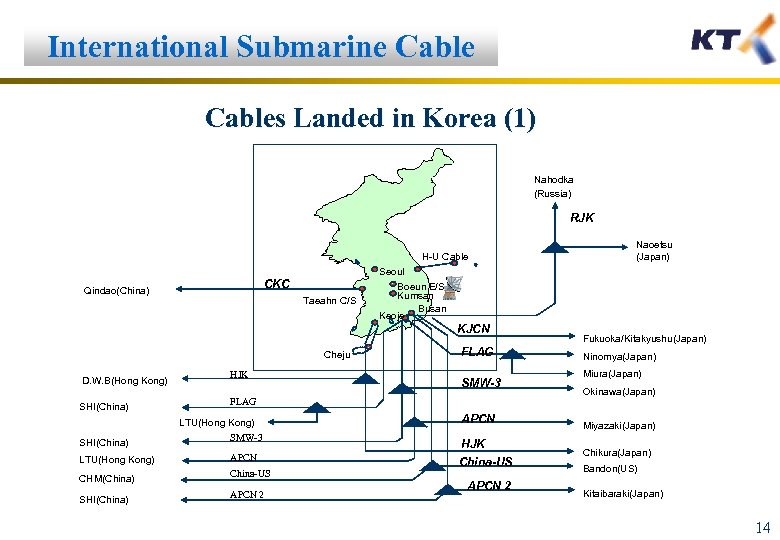
International Submarine Cables Landed in Korea (1) Nahodka (Russia) RJK H-U Cable CKC Qindao(China) Taeahn C/S Seoul Boeun E/S Kumsan Busan Keoje KJCN Cheju D. W. B(Hong Kong) SHI(China) HJK SHI(China) SMW-3 LTU(Hong Kong) APCN CHM(China) China-US SHI(China) FLAG SMW-3 FLAG LTU(Hong Kong) APCN 2 Naoetsu (Japan) APCN HJK China-US APCN 2 Fukuoka/Kitakyushu(Japan) Ninomya(Japan) Miura(Japan) Okinawa(Japan) Miyazaki(Japan) Chikura(Japan) Bandon(US) Kitaibaraki(Japan) 14
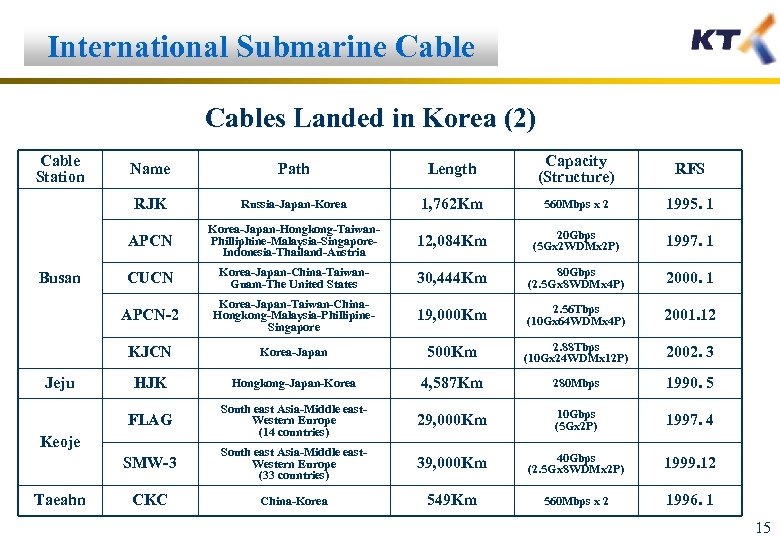
International Submarine Cables Landed in Korea (2) Cable Station Length Capacity (Structure) RFS Russia-Japan-Korea 1, 762 Km 560 Mbps x 2 1995. 1 APCN Korea-Japan-Hongkong-Taiwan. Philliphine-Malaysia-Singapore. Indonesia-Thailand-Austria 12, 084 Km 20 Gbps (5 Gx 2 WDMx 2 P) 1997. 1 CUCN Korea-Japan-China-Taiwan. Guam-The United States 30, 444 Km 80 Gbps (2. 5 Gx 8 WDMx 4 P) 2000. 1 APCN-2 Korea-Japan-Taiwan-China. Hongkong-Malaysia-Phillipine. Singapore 19, 000 Km 2. 56 Tbps (10 Gx 64 WDMx 4 P) 2001. 12 KJCN Korea-Japan 500 Km 2. 88 Tbps (10 Gx 24 WDMx 12 P) 2002. 3 HJK Hongkong-Japan-Korea 4, 587 Km 280 Mbps 1990. 5 FLAG South east Asia-Middle east. Western Europe (14 countries) 29, 000 Km 10 Gbps (5 Gx 2 P) 1997. 4 SMW-3 Jeju Path RJK Busan Name South east Asia-Middle east. Western Europe (33 countries) 39, 000 Km 40 Gbps (2. 5 Gx 8 WDMx 2 P) 1999. 12 CKC China-Korea 549 Km 560 Mbps x 2 1996. 1 Keoje Taeahn 15

Korea-Japan Cable Network 1. KJCN Map 2. KJCN General 3. Advantages of KJCN 16
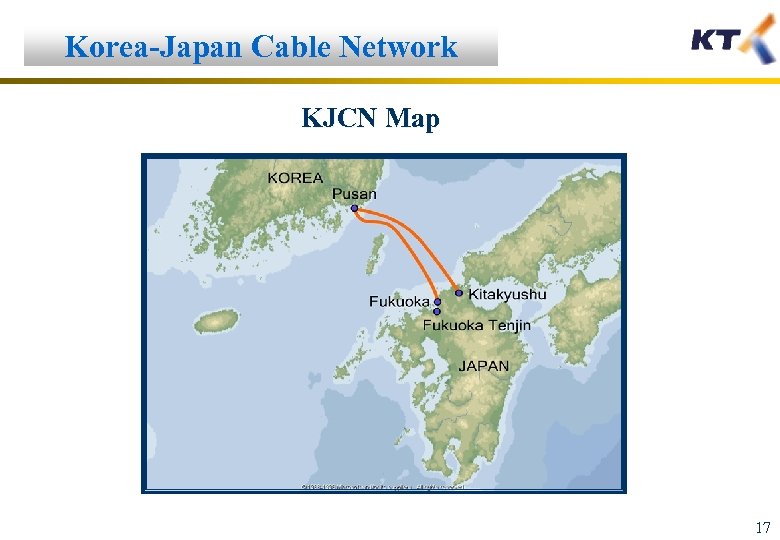
Korea-Japan Cable Network KJCN Map 17
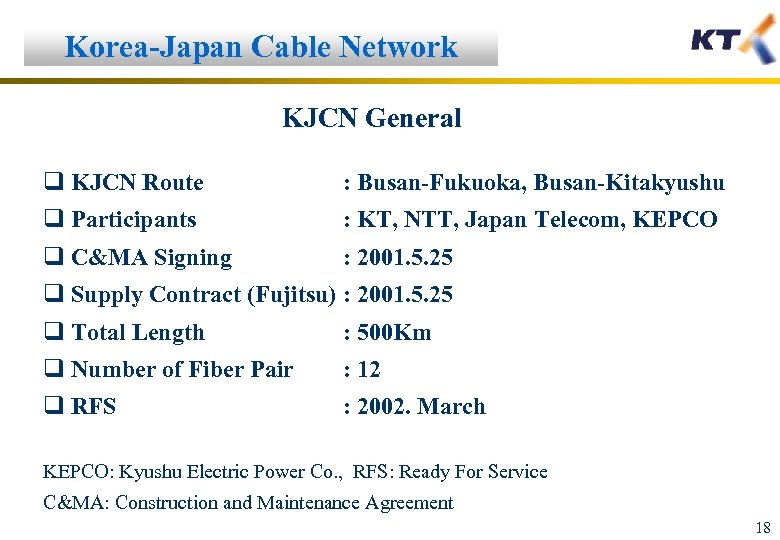
Korea-Japan Cable Network KJCN General q KJCN Route : Busan-Fukuoka, Busan-Kitakyushu q Participants : KT, NTT, Japan Telecom, KEPCO q C&MA Signing : 2001. 5. 25 q Supply Contract (Fujitsu) : 2001. 5. 25 q Total Length : 500 Km q Number of Fiber Pair : 12 q RFS : 2002. March KEPCO: Kyushu Electric Power Co. , RFS: Ready For Service C&MA: Construction and Maintenance Agreement 18

Korea-Japan Cable Network Advantages of KJCN q Continuous Competitiveness of the Network - No need for Repeater due to the Short distance - Applying cutting edge technology is possible at any time q Exclusive connection between Korea and Japan - Cheap Cost - But, high quality and cheap service q Highly stable network by Self-healing function - Stable telecommunication Services - Internet and e-commerce application 19

Future Plan 1. Trends of Submarine Cable Technology 2. Expansion of Submarine Cable Capacity 3. Construction of additional Trans-Pacific Cable Network 4. KT’s International Service 20
Future Plan Trends of Submarine Cable Technology q Development of 10 Gbps/ big bandwidth transmission technology - Commercializing 128 DWDM at Trans-Pacific(9, 000 Km) is possible within 2004 - Under development to apply 40 Gbps/ at Trans-Pacific q Migration to Wavelength access - Optimizing cable network to reduce the cost - Adopting NG-SDH platform, such as MSPP 21
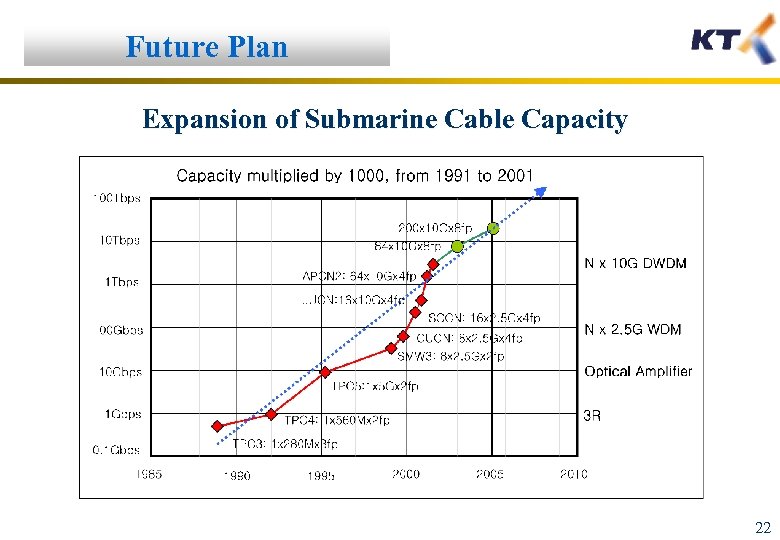
Future Plan Expansion of Submarine Cable Capacity 22

Future Plan Construction of additional Trans-Pacific Cable Network q Next cable project - High demand toward America (Sharp increase of High speed Internet in Asia region) - Under review to participate in new project q Outlook - Unavoidableness of postponement - Decreasing demand by World IT economic slump (except Korea, China, Taiwan, etc. ) 23
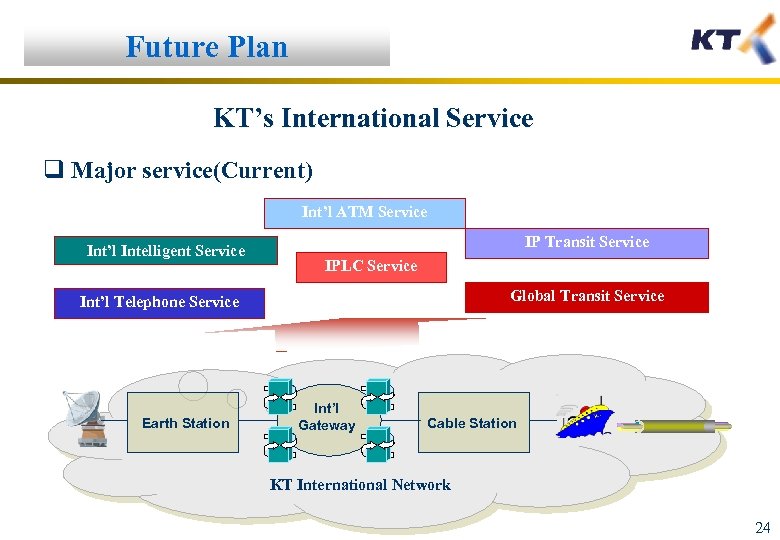
Future Plan KT’s International Service q Major service(Current) Int’l ATM Service Int’l Intelligent Service IP Transit Service IPLC Service Global Transit Service Int’l Telephone Service Earth Station Int’l Gateway Cable Station KT International Network 24
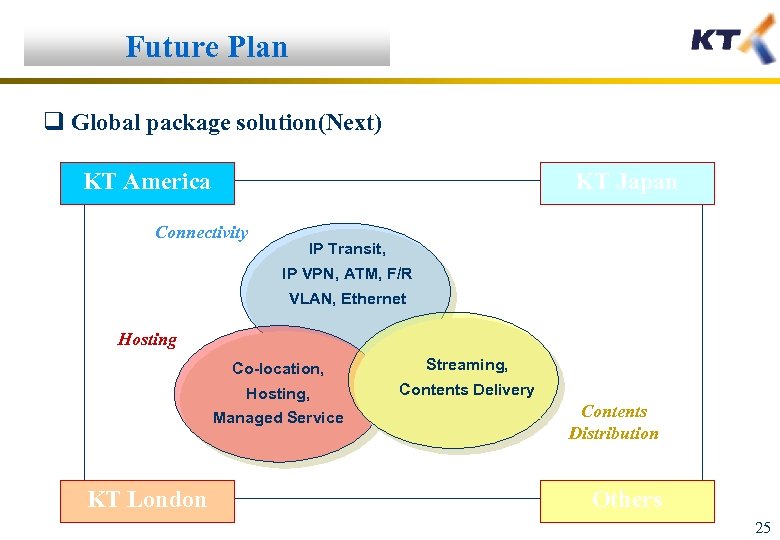
Future Plan q Global package solution(Next) KT America KT Japan Connectivity IP Transit, IP VPN, ATM, F/R VLAN, Ethernet Hosting Co-location, Streaming, Hosting, Contents Delivery Managed Service KT London Contents Distribution Others 25
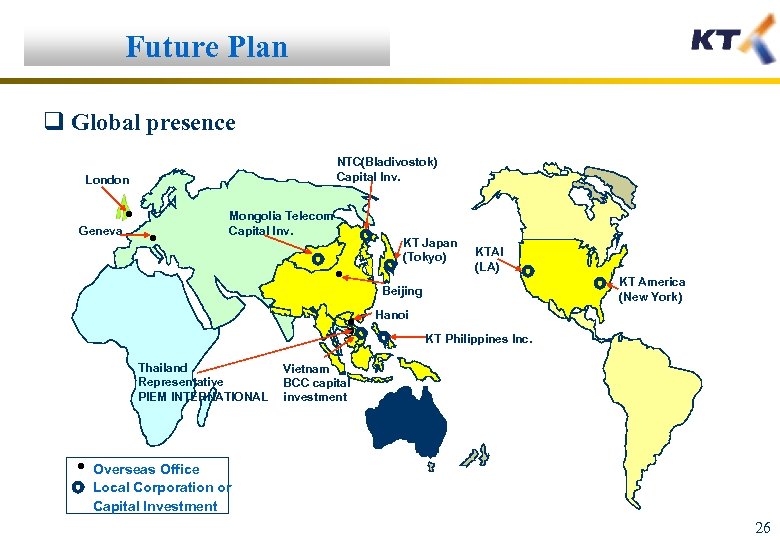
Future Plan q Global presence NTC(Bladivostok) Capital Inv. London Geneva Mongolia Telecom Capital Inv. KT Japan (Tokyo) KTAI (LA) KT America (New York) Beijing Hanoi KT Philippines Inc. Thailand Representative PIEM INTERNATIONAL Vietnam BCC capital investment Overseas Office Local Corporation or Capital Investment 26
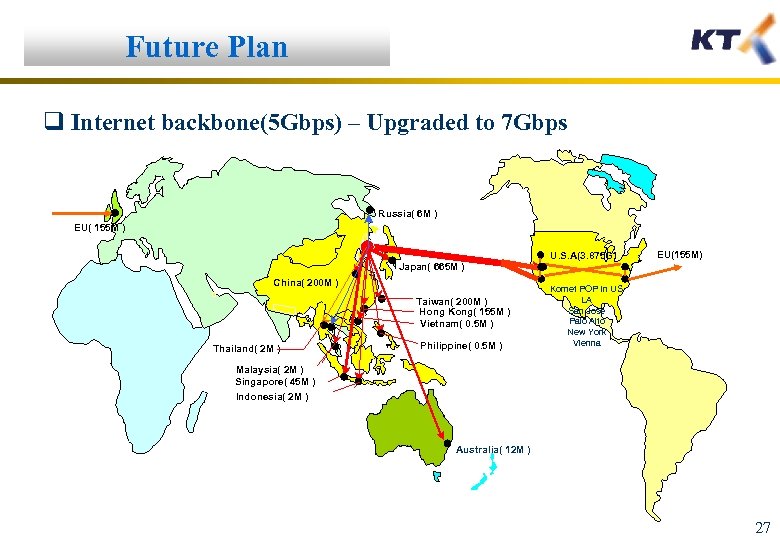
Future Plan q Internet backbone(5 Gbps) – Upgraded to 7 Gbps Russia( 6 M ) EU( 155 M ) Japan( 665 M ) China( 200 M ) Taiwan( 200 M ) Hong Kong( 155 M ) Vietnam( 0. 5 M ) Thailand( 2 M ) Philippine( 0. 5 M ) U. S. A(3. 875 G) EU(155 M) Kornet POP in US LA San Jose Palo Alto New York Vienna Malaysia( 2 M ) Singapore( 45 M ) Indonesia( 2 M ) Australia( 10 M ) 12 M 27
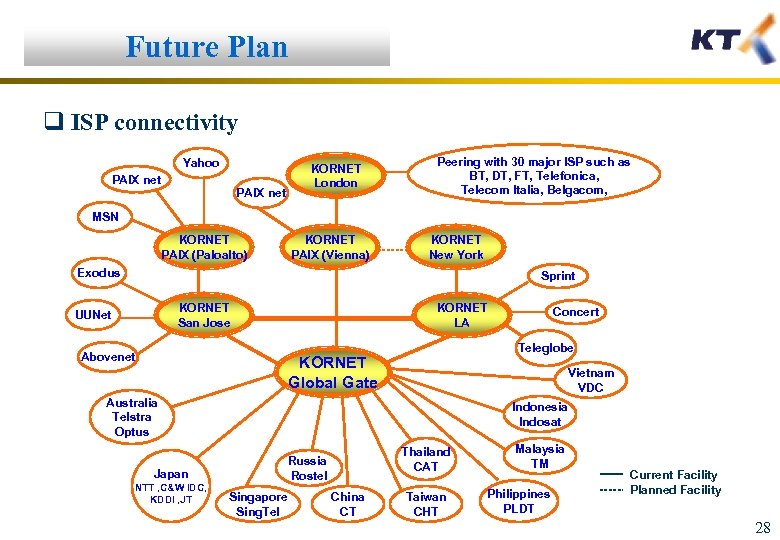
Future Plan q ISP connectivity Yahoo PAIX net KORNET London Peering with 30 major ISP such as BT, DT, FT, Telefonica, Telecom Italia, Belgacom, MSN KORNET PAIX (Paloalto) KORNET PAIX (Vienna) KORNET New York Exodus Sprint KORNET San Jose UUNet Abovenet KORNET LA Teleglobe KORNET Global Gate Vietnam VDC Australia Telstra Optus Indonesia Indosat Thailand CAT Russia Rostel Japan NTT , C&W IDC, KDDI , JT Concert Singapore Sing. Tel China CT Taiwan CHT Malaysia TM Philippines PLDT Current Facility Planned Facility 28

Thank you … Sung-In KIM Manager Int’l Network Planning & Management Team World. Cup/Int’l Telecommunication Business Center Network Planning & Coordination Group KT Corporation Tel: +82 -31 -727 -2532 E-mail: mcgyber@kt. co. kr 29
d1a7a97cc46135e686b8f3d1dbe05ac3.ppt