24dd0c075cd71c8f2e14d3654b873e34.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
Insulin Pumps Kyle Gildea BME 181

Diabetes Statistics • • 23. 6 million children and adults in the United States ~ 8% of the population—have diabetes. 10. 9 million, or 26. 9% of all people age 65 or older have diabetes 231, 404 deaths in 2007 Diabetes is the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 20– 74 years.

What is Diabetes ? • • • Diabetes is a condition where the body is unable to regulate levels of glucose (a sugar) in the blood, resulting in excess glucose being present in the blood. Glucose is the main sugar digested from our foods Blood glucose levels are regulated by insulin

Insulin • • • Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels Insulin enables the body to use Glucose First discovered in 1921 Before the discovery children with diabetes were expected to live for under a year Diabetics cant produce insulin so it must be given to their body
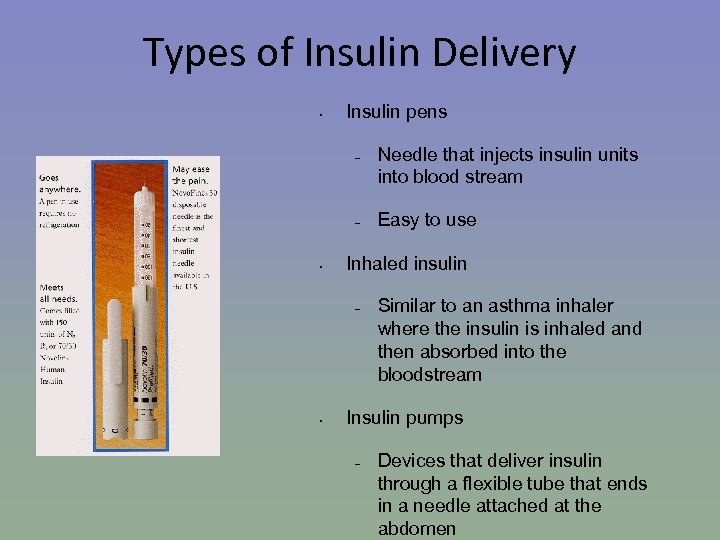
Types of Insulin Delivery • Insulin pens – – • Easy to use Inhaled insulin – • Needle that injects insulin units into blood stream Similar to an asthma inhaler where the insulin is inhaled and then absorbed into the bloodstream Insulin pumps – Devices that deliver insulin through a flexible tube that ends in a needle attached at the abdomen

History of the Insulin pump • • • The first insulin pump was developed in 1963 by Dr. Arnold Kadish 1976 Dean Kamen invented the first wearable insulin pump 1980’s insulin pumps start to enter the market – • • Minimed and Disetronic Mini. Med 502 first popular insulin pump 2003 Mini. Med 512 first insulin pump to monitor glucose levels

Using an Insulin Pump • • Insert needle anywhere into body typically the abdomen Three programmable ways to deliver insulin – – Bolus doses – • Basal rates Correctional doses Then press ok

Modern Insulin pump • Minimed ® Paradigm Revel ™ Insulin Pump – Quick release features – 108 g – 300 unit of insulin – – Predicts/Alerts Insulin needs Graphs glucose use over last 3, 6, 12, 24 Will give constant insulin rates as low as. 025 units per hour $10, 710

Advantages • • • Eliminates individual insulin injections Deliver insulin more accurately and regularly Allows for exercise without having to eat a lot of carbs Makes diabetes management easier Better control

Disadvantages • • Can cause weight gain Needle can fall out leading to no insulin • Expensive • Requires training • Constantly need to be attached to pump
Future for Insulin • Projected growth rate between 2011 – 2015 is 9% • Insulin Patch • Implantable insulin pumps • A buccal spray • An artificial pancreas

Works Cited • • • Jerreat, Lynne. Diabetes for Nurses. London: Whurr, 1999. Print. IOH Diabetes Treatment - Insulin Delivery Devices. " Diabetes Assistance Programs for Diabetes, Diabetes Laws, Insurance Laws. 11 Mar. 2006. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. isletsofhope. com/diabetes/treatment/insulin_devices_1. html>. Sattley, Melissa. "The History of Diabetes - Diabetes Health. " Diabetes Health Investigate, Inform, Inspire. 17 Dec. 2008. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. diabeteshealth. com/read/2008/12/17/715/the-history-of-diabetes/>. Richard. "History Of Insulin Pumps. " Diabetes | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes. 17 Apr. 2008. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. dlife. com/diabetesforum/viewtopic. php? f=22&t=10964&start=0&sid=46065 bf 7 bcb 0 a 2 ec 5 f 38 f 0 a 3 b 95 ed 5 42&view=print>. Mini. Med. "Minimed ® Paradigm Revel ™ Insulin Pump MMDMMT 523 B. " Medical Supplies - Discount Home Medical Supply & Equipment Store. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. onlinemedicalsupply. com/DIABETIC/INSULIN_PRODUCTS/MMDMMT 5 23 B/product. aspx>.

Works Cited • • • Noida. "Global Insulin Pumps Market Set for Stupendous Upsurge by 2015. " Press Release Distribution, Public Relations Services | SBWire. 16 Feb. 2011. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. sbwire. com/press-releases/sbwire-79053. htm>. Reuters. "Artificial Pancreas Shows Promise in Pregnancy| Reuters. " Business & Financial News, Breaking US & International News | Reuters. com. Reuters, 30 Jan. 2011. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. reuters. com/article/2011/01/31/us-pancreasdiabetes-id. USTRE 70 U 00 N 20110131>. American Diabetes Association. "How Do Insulin Pumps Work? " American Diabetes Association Home Page - American Diabetes Association. Web. 24 Feb. 2011. <http: //www. diabetes. org/living-with-diabetes/treatment-andcare/medication/insulin-pumps-how-do-insulin. html>.
24dd0c075cd71c8f2e14d3654b873e34.ppt