be030333c7a01955039dce1b1d79a7bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 171
 Instructional Coaching Institute Lisa Wyatt Education Service Center Region XIII
Instructional Coaching Institute Lisa Wyatt Education Service Center Region XIII
 The Mom
The Mom
 Housekeeping Cell phones n Restroom Breaks n Lunch n Items
Housekeeping Cell phones n Restroom Breaks n Lunch n Items
 Vacation Partners n Find a person for each vacation destination on your form. Be sure to write their name under that destination.
Vacation Partners n Find a person for each vacation destination on your form. Be sure to write their name under that destination.
 What will we cover? n Why instructional coaching? n Overview of instructional coaching. n Roles of coaches. n Dealing with change. n Communication is key. n Tools
What will we cover? n Why instructional coaching? n Overview of instructional coaching. n Roles of coaches. n Dealing with change. n Communication is key. n Tools
 What is Instructional Coaching? n Definition: – Instructional coaches are on-site professional developers who teach educators how to use proven instructional methods. To be successful in this role, coaches must be skilled in a variety of roles, including public relations guru, communicator extraordinaire, master organizer and, of course, expert educator.
What is Instructional Coaching? n Definition: – Instructional coaches are on-site professional developers who teach educators how to use proven instructional methods. To be successful in this role, coaches must be skilled in a variety of roles, including public relations guru, communicator extraordinaire, master organizer and, of course, expert educator.
 Natalie Gilbert – National Anthem n What does this athletic coach do that you think is similar to what an Instructional Coach should do?
Natalie Gilbert – National Anthem n What does this athletic coach do that you think is similar to what an Instructional Coach should do?
 So, why coaching?
So, why coaching?
 A Look at Education Reform
A Look at Education Reform
 Ellwood Cubberly, 1934 n One of the nation’s foremost educational thinkers of his time: – The public schools of the United States are, in a sense, a manufactory. – Students were the “raw” material. Teachers would “pour” in math, then the next subject, etc.
Ellwood Cubberly, 1934 n One of the nation’s foremost educational thinkers of his time: – The public schools of the United States are, in a sense, a manufactory. – Students were the “raw” material. Teachers would “pour” in math, then the next subject, etc.
 In their defense… n Schools at that time were not intended to educate large numbers of students to a high level. In 1893, less than 3% of American students graduated high school. n Even as late as 1950, majority of students dropped of out high school before graduation.
In their defense… n Schools at that time were not intended to educate large numbers of students to a high level. In 1893, less than 3% of American students graduated high school. n Even as late as 1950, majority of students dropped of out high school before graduation.
 Today n All students must master rigorous content, learn how to learn, pursue productive employment, and compete in a global economy.
Today n All students must master rigorous content, learn how to learn, pursue productive employment, and compete in a global economy.
 Did you know?
Did you know?
 At your table: Discuss any aha moments from the film. 2. Why is this information important for us? 1.
At your table: Discuss any aha moments from the film. 2. Why is this information important for us? 1.
 What researchers say about the best path for sustained organizational improvement: n Only the organizations that have a passion for learning will have an enduring influence. (Covey, 1996, p. 149) n The most successful corporation of the future will be a learning organization. (Senge, 1990, p. 4)
What researchers say about the best path for sustained organizational improvement: n Only the organizations that have a passion for learning will have an enduring influence. (Covey, 1996, p. 149) n The most successful corporation of the future will be a learning organization. (Senge, 1990, p. 4)
 n Research and experts are all saying the same thing n Our kids must be prepared for the 21 st Century Global Economy n They must know HOW TO LEARN n The #1 indicator of student success is… TEACHER QUALITY
n Research and experts are all saying the same thing n Our kids must be prepared for the 21 st Century Global Economy n They must know HOW TO LEARN n The #1 indicator of student success is… TEACHER QUALITY
 Need for a Collaborative Culture Throughout our ten-year study, whenever we found an effective school or an effective department within a school, without exception that school or department has been a part of a collaborative professional learning community. --Mc. Laughlin and Talbert (2001)
Need for a Collaborative Culture Throughout our ten-year study, whenever we found an effective school or an effective department within a school, without exception that school or department has been a part of a collaborative professional learning community. --Mc. Laughlin and Talbert (2001)
 Why Should We Collaborate? Gains in student achievement Higher quality solutions to problems Increased confidence among all staff Teachers able to support one another’s strengths and accommodate weaknesses n Ability to test new ideas n More support for new teachers n Expanded pool of ideas, materials, and methods --Judith Warren Little (1990) n n
Why Should We Collaborate? Gains in student achievement Higher quality solutions to problems Increased confidence among all staff Teachers able to support one another’s strengths and accommodate weaknesses n Ability to test new ideas n More support for new teachers n Expanded pool of ideas, materials, and methods --Judith Warren Little (1990) n n
 “Quality teaching is the most critical means by which to improve student learning and to close achievement gaps. You achieve student success through teacher success. ” Harry Wong
“Quality teaching is the most critical means by which to improve student learning and to close achievement gaps. You achieve student success through teacher success. ” Harry Wong
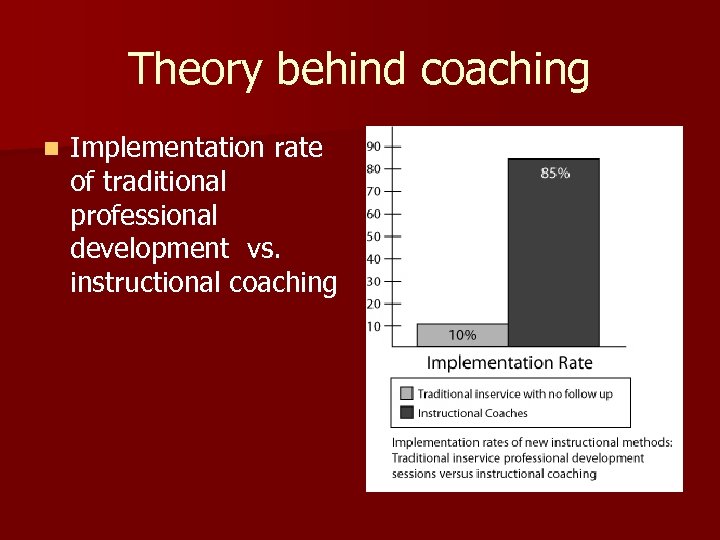 Theory behind coaching n Implementation rate of traditional professional development vs. instructional coaching
Theory behind coaching n Implementation rate of traditional professional development vs. instructional coaching
 The #1 way to improve student success, it to increase teacher quality. n Education has spent all of their money and time on systems change, programs, etc. n Where has it gotten us? n The classroom is where everything happens: – The teacher is the #1 indicator of how a student will progress. – This is where the focus should be.
The #1 way to improve student success, it to increase teacher quality. n Education has spent all of their money and time on systems change, programs, etc. n Where has it gotten us? n The classroom is where everything happens: – The teacher is the #1 indicator of how a student will progress. – This is where the focus should be.
 “Decades of research clearly demonstrate that a quality teacher, more than any other factor, enables students to overcome obstacles to learning like poverty and can even erase the achievement gap. ” Alliance for Education, 2006
“Decades of research clearly demonstrate that a quality teacher, more than any other factor, enables students to overcome obstacles to learning like poverty and can even erase the achievement gap. ” Alliance for Education, 2006
 Percentage of Children Who Achieve Success with Varying Levels of Home and Classroom Support High Home Support Low Home Support High Classroom Support 100% Mixed Classroom Support 100% 25% 60% 0% Low Classroom Support Snow, C. (1991). Unfulfilled Expectations. Harvard University Press
Percentage of Children Who Achieve Success with Varying Levels of Home and Classroom Support High Home Support Low Home Support High Classroom Support 100% Mixed Classroom Support 100% 25% 60% 0% Low Classroom Support Snow, C. (1991). Unfulfilled Expectations. Harvard University Press
 Teaching without learning isn’t teaching at all. It’s just presenting a lesson!
Teaching without learning isn’t teaching at all. It’s just presenting a lesson!
 What is Instructional Coaching?
What is Instructional Coaching?

 What is an Instructional Coach? an on-site professional developer who partners with educators to identify and assist with implementation of proven teaching methods
What is an Instructional Coach? an on-site professional developer who partners with educators to identify and assist with implementation of proven teaching methods
 NTLB n No Teacher Left Behind!
NTLB n No Teacher Left Behind!
 An instructional coach… n Must BUILD leadership among the teachers. n Don’t become the leader.
An instructional coach… n Must BUILD leadership among the teachers. n Don’t become the leader.
 Instructional Coaches n n n n Enroll Identify Explain Model (You watch me) Observe (I watch you) Explore (Collaborative Exploration of Data) Support Reflect
Instructional Coaches n n n n Enroll Identify Explain Model (You watch me) Observe (I watch you) Explore (Collaborative Exploration of Data) Support Reflect
 Enroll teachers n. Large-group presentation n. Small-group presentation n. Interviews n. Informal conversations n. Principal (or other) referral
Enroll teachers n. Large-group presentation n. Small-group presentation n. Interviews n. Informal conversations n. Principal (or other) referral

 Identify n The Big Four: – Behavior – Content – Instruction – Assessment
Identify n The Big Four: – Behavior – Content – Instruction – Assessment
 Explaining interventions n Instructional Coach – Breaks down the instructor’s materials – Lays out the step-by-step procedures – Suggests what teacher should watch for during the model lessons – Does everything possible to make it easier for teachers to implement – Asks about and addresses collaborating teacher’s concerns – Co-constructs Observation Form with teachers
Explaining interventions n Instructional Coach – Breaks down the instructor’s materials – Lays out the step-by-step procedures – Suggests what teacher should watch for during the model lessons – Does everything possible to make it easier for teachers to implement – Asks about and addresses collaborating teacher’s concerns – Co-constructs Observation Form with teachers

 Model Lessons You watch me! Goal: To show a teacher exactly how to implement a particular intervention n Be fully aware of need to model critical teaching practices you knows the purpose Ensure that teacher of the model lesson n Provide concrete description of what you’ll be doing n Clarify roles for behavioral management n n Co-construct an observation form n Ensure your collaborating teacher form knows how to use the
Model Lessons You watch me! Goal: To show a teacher exactly how to implement a particular intervention n Be fully aware of need to model critical teaching practices you knows the purpose Ensure that teacher of the model lesson n Provide concrete description of what you’ll be doing n Clarify roles for behavioral management n n Co-construct an observation form n Ensure your collaborating teacher form knows how to use the
 Observe “I watch you” n Coach uses the observation form to watch for data related to: – Critical teaching behaviors – Fidelity to scientifically proven practices – Student behavior and performance – Additional specific teacher concerns
Observe “I watch you” n Coach uses the observation form to watch for data related to: – Critical teaching behaviors – Fidelity to scientifically proven practices – Student behavior and performance – Additional specific teacher concerns
 Collaborative Exploration of Data n Based on the partnership principles n Involves observations to open up dialogue, rather than to state a single truth n Should be – constructive, but provisional – empathetic and respectful n Coach and teacher identify what data will be gathered
Collaborative Exploration of Data n Based on the partnership principles n Involves observations to open up dialogue, rather than to state a single truth n Should be – constructive, but provisional – empathetic and respectful n Coach and teacher identify what data will be gathered
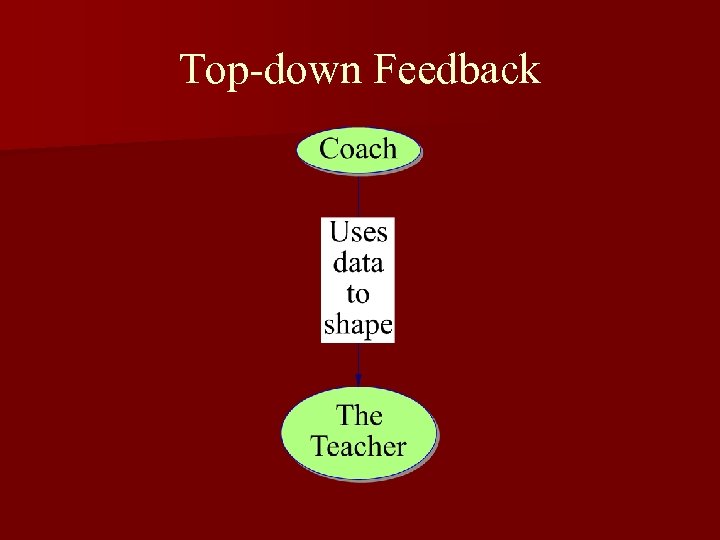 Top-down Feedback
Top-down Feedback
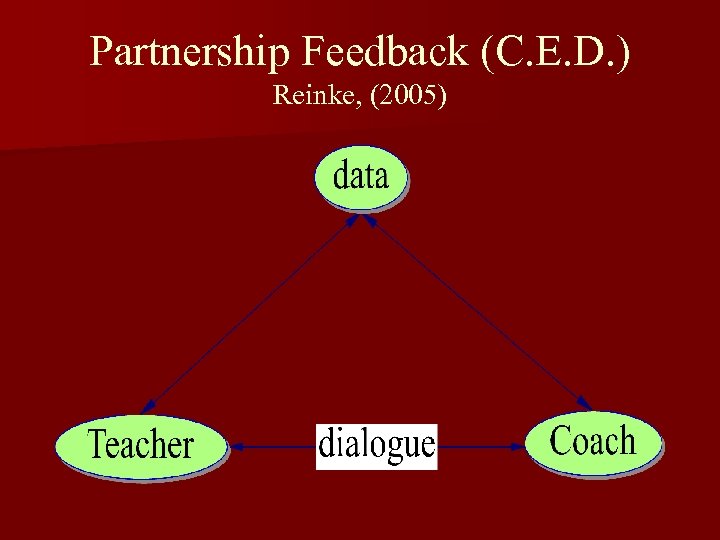 Partnership Feedback (C. E. D. ) Reinke, (2005)
Partnership Feedback (C. E. D. ) Reinke, (2005)
 Partnership Principles n Equality n Praxis n Dialogue n Choice n Voice n Reflection n Reciprocity
Partnership Principles n Equality n Praxis n Dialogue n Choice n Voice n Reflection n Reciprocity
 Your “jigsaw” learning experience n Step one: Settle in with your new group of learning partners n Step two: Read the section you’ve been given from the Partnership Learning manual n Step three: Together with your group, create a graphic organizer on a poster that captures the essential characteristics of the principle n Step four: Attach your poster to the wall, and wait for further instructions
Your “jigsaw” learning experience n Step one: Settle in with your new group of learning partners n Step two: Read the section you’ve been given from the Partnership Learning manual n Step three: Together with your group, create a graphic organizer on a poster that captures the essential characteristics of the principle n Step four: Attach your poster to the wall, and wait for further instructions
 Activity n In your new groups, move to your poster. n The person who helped create the poster explains the concept to the group. n When the music starts, move to the next poster (clockwise) n When the music stops, start discussing the new poster
Activity n In your new groups, move to your poster. n The person who helped create the poster explains the concept to the group. n When the music starts, move to the next poster (clockwise) n When the music stops, start discussing the new poster
 Praxis n Reflection and n Creative inquiry n Not banking education n But creative inquiry
Praxis n Reflection and n Creative inquiry n Not banking education n But creative inquiry
 Dialogue n Respectful, energizing conversation n The developing conversation is more important than being right n Involves suspending opinions & authentic listening n Thinking together
Dialogue n Respectful, energizing conversation n The developing conversation is more important than being right n Involves suspending opinions & authentic listening n Thinking together
 Choice n Command control fosters resistance or external commitment n Choice fosters internal commitment
Choice n Command control fosters resistance or external commitment n Choice fosters internal commitment
 Voice n Build trust n Make it easy for people to say what they think n Give people words, concepts, and tools that help them express who they are--help them find their voice!
Voice n Build trust n Make it easy for people to say what they think n Give people words, concepts, and tools that help them express who they are--help them find their voice!
 Reflection n On action n In action n For action
Reflection n On action n In action n For action
 Reciprocity n Everyone benefits when one person learns n Teachers learn from students as much as students learn from teachers n Every learning situation is a chance for learning
Reciprocity n Everyone benefits when one person learns n Teachers learn from students as much as students learn from teachers n Every learning situation is a chance for learning
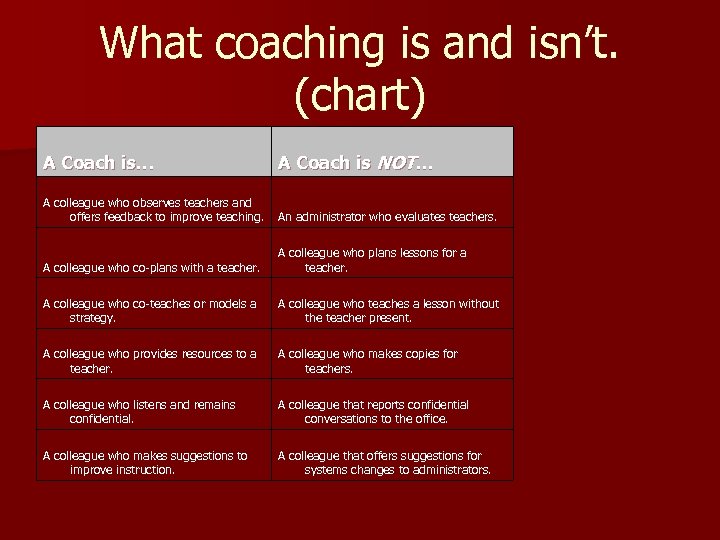 What coaching is and isn’t. (chart) A Coach is… A Coach is NOT… A colleague who observes teachers and offers feedback to improve teaching. An administrator who evaluates teachers. A colleague who co-plans with a teacher. A colleague who plans lessons for a teacher. A colleague who co-teaches or models a strategy. A colleague who teaches a lesson without the teacher present. A colleague who provides resources to a teacher. A colleague who makes copies for teachers. A colleague who listens and remains confidential. A colleague that reports confidential conversations to the office. A colleague who makes suggestions to improve instruction. A colleague that offers suggestions for systems changes to administrators.
What coaching is and isn’t. (chart) A Coach is… A Coach is NOT… A colleague who observes teachers and offers feedback to improve teaching. An administrator who evaluates teachers. A colleague who co-plans with a teacher. A colleague who plans lessons for a teacher. A colleague who co-teaches or models a strategy. A colleague who teaches a lesson without the teacher present. A colleague who provides resources to a teacher. A colleague who makes copies for teachers. A colleague who listens and remains confidential. A colleague that reports confidential conversations to the office. A colleague who makes suggestions to improve instruction. A colleague that offers suggestions for systems changes to administrators.
 Our goals as coaches: n Meet teachers where they are and take teachers to the next step. n Goal-oriented n Evaluative – our program (must show impact) n Ultimate: Impact student learning!
Our goals as coaches: n Meet teachers where they are and take teachers to the next step. n Goal-oriented n Evaluative – our program (must show impact) n Ultimate: Impact student learning!
 Continuum of Coaching visual n Different n Varies! levels of support.
Continuum of Coaching visual n Different n Varies! levels of support.
 Evaluator n Supervises teacher n Tells teacher what to do n Possible growth plan
Evaluator n Supervises teacher n Tells teacher what to do n Possible growth plan
 Consultant n Tells how to do it n Shows how to do it
Consultant n Tells how to do it n Shows how to do it
 Mentor (Consultant/Coach) n New teachers n Tell how to do it n Shows how to do it n Driven more by coach
Mentor (Consultant/Coach) n New teachers n Tell how to do it n Shows how to do it n Driven more by coach
 Coach n Uses questioning n Brings out the best in teacher n Teacher drives the discussion n Teacher drives the area to work on
Coach n Uses questioning n Brings out the best in teacher n Teacher drives the discussion n Teacher drives the area to work on
 Collaborator n Sharing ideas n Equal partnership (no expert) n Reflective dialogue
Collaborator n Sharing ideas n Equal partnership (no expert) n Reflective dialogue
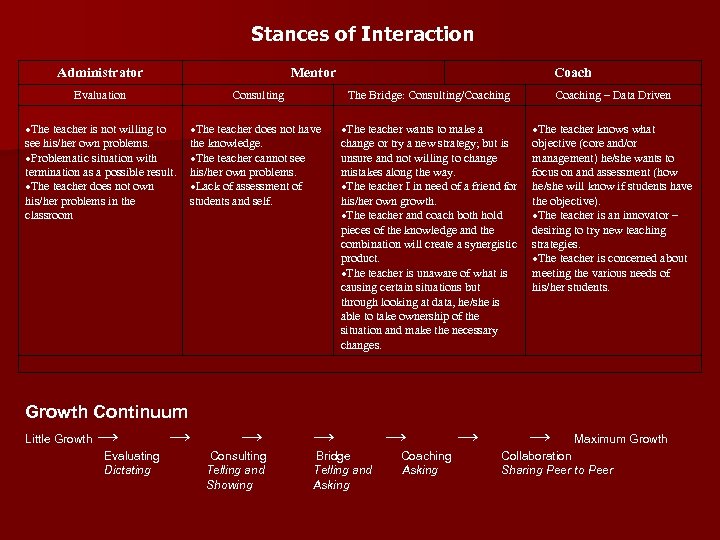 Stances of Interaction Administrator Mentor Coach Evaluation Consulting The Bridge: Consulting/Coaching – Data Driven The teacher is not willing to see his/her own problems. Problematic situation with termination as a possible result. The teacher does not own his/her problems in the classroom The teacher does not have the knowledge. The teacher cannot see his/her own problems. Lack of assessment of students and self. The teacher wants to make a change or try a new strategy; but is unsure and not willing to change mistakes along the way. The teacher I in need of a friend for his/her own growth. The teacher and coach both hold pieces of the knowledge and the combination will create a synergistic product. The teacher is unaware of what is causing certain situations but through looking at data, he/she is able to take ownership of the situation and make the necessary changes. The teacher knows what objective (core and/or management) he/she wants to focus on and assessment (how he/she will know if students have the objective). The teacher is an innovator – desiring to try new teaching strategies. The teacher is concerned about meeting the various needs of his/her students. Growth Continuum Little Growth → Evaluating Dictating → → Consulting Telling and Showing → Bridge Telling and Asking → Coaching Asking → → Maximum Growth Collaboration Sharing Peer to Peer
Stances of Interaction Administrator Mentor Coach Evaluation Consulting The Bridge: Consulting/Coaching – Data Driven The teacher is not willing to see his/her own problems. Problematic situation with termination as a possible result. The teacher does not own his/her problems in the classroom The teacher does not have the knowledge. The teacher cannot see his/her own problems. Lack of assessment of students and self. The teacher wants to make a change or try a new strategy; but is unsure and not willing to change mistakes along the way. The teacher I in need of a friend for his/her own growth. The teacher and coach both hold pieces of the knowledge and the combination will create a synergistic product. The teacher is unaware of what is causing certain situations but through looking at data, he/she is able to take ownership of the situation and make the necessary changes. The teacher knows what objective (core and/or management) he/she wants to focus on and assessment (how he/she will know if students have the objective). The teacher is an innovator – desiring to try new teaching strategies. The teacher is concerned about meeting the various needs of his/her students. Growth Continuum Little Growth → Evaluating Dictating → → Consulting Telling and Showing → Bridge Telling and Asking → Coaching Asking → → Maximum Growth Collaboration Sharing Peer to Peer
 Consultant Teacher CONSULT (80% consultant/20% teacher) ● Inform regarding process and protocols ● Advise based on well-develop expertise; share the reason why a specific strategy is important: offer the “expert” frame before the idea. ● Advocate for particular choices and actions. COACH (20% coach/80% teacher) ● Nonjudgmental mediation of thinking and decision making ● Presumes the other person is giving ideas Coach Teacher COLLABORATE (80% teacher/80% teacher) ● Participate in planning, reflecting and problem solving ● It is important not to offer solutions. Teacher
Consultant Teacher CONSULT (80% consultant/20% teacher) ● Inform regarding process and protocols ● Advise based on well-develop expertise; share the reason why a specific strategy is important: offer the “expert” frame before the idea. ● Advocate for particular choices and actions. COACH (20% coach/80% teacher) ● Nonjudgmental mediation of thinking and decision making ● Presumes the other person is giving ideas Coach Teacher COLLABORATE (80% teacher/80% teacher) ● Participate in planning, reflecting and problem solving ● It is important not to offer solutions. Teacher
 Continuum Checklist n. Think of a person you are currently working with. n. Check each statement that applies to the individual. n. Tally your shapes.
Continuum Checklist n. Think of a person you are currently working with. n. Check each statement that applies to the individual. n. Tally your shapes.
 Continuum Checklist Scoring Guide ♣ Cluster One (Evaluate): Evaluations and directives are based upon approved standards. ○ Cluster Two (Consult): Differentiated professional development is designed and delivered to meet teachers’ individual needs. ○■ The Bridge (Coach and Consult): Coaching occurs prior to the observation and data based consulting occurs after the observation. ■ Cluster Three (Coach): The topic and timing of coaching are the teacher’s agenda. ▲ Cluster Four (Collaborate): Collaboration is a stretching interaction that occurs with a consistent group on a consistent time schedule.
Continuum Checklist Scoring Guide ♣ Cluster One (Evaluate): Evaluations and directives are based upon approved standards. ○ Cluster Two (Consult): Differentiated professional development is designed and delivered to meet teachers’ individual needs. ○■ The Bridge (Coach and Consult): Coaching occurs prior to the observation and data based consulting occurs after the observation. ■ Cluster Three (Coach): The topic and timing of coaching are the teacher’s agenda. ▲ Cluster Four (Collaborate): Collaboration is a stretching interaction that occurs with a consistent group on a consistent time schedule.
 The Roles of Coaches The continuum is the level of support you provide. Roles are the different duties you perform.
The Roles of Coaches The continuum is the level of support you provide. Roles are the different duties you perform.
 You use different skills depending on which role you’re taking. (What are you wearing? )
You use different skills depending on which role you’re taking. (What are you wearing? )
 Resource Provider Function: Provides articles Summarizes strategies for teachers Provides lesson materials
Resource Provider Function: Provides articles Summarizes strategies for teachers Provides lesson materials
 Resource Provider Knowledge and Skills: n Know what resources are available and how to locate. n Synthesis Skills
Resource Provider Knowledge and Skills: n Know what resources are available and how to locate. n Synthesis Skills
 Resource Provider Challenges: n Easy and non-threatening (use too much) n Need to move to areas that affect more change.
Resource Provider Challenges: n Easy and non-threatening (use too much) n Need to move to areas that affect more change.
 Data Coach
Data Coach

 n Data conversation is more important than data analysis!
n Data conversation is more important than data analysis!
 Data Coach n Function: – Data Analysis
Data Coach n Function: – Data Analysis
 Data Coach n Knowledge and Skills: – Thorough understanding of data – Set up blame-free environment – *****Assist teachers in next step for instruction based on data******
Data Coach n Knowledge and Skills: – Thorough understanding of data – Set up blame-free environment – *****Assist teachers in next step for instruction based on data******
 Data Coach n Challenges: – Creating data displays – Understanding the data – Asking the right questions – plan ahead! – Creating a non-threatening environment
Data Coach n Challenges: – Creating data displays – Understanding the data – Asking the right questions – plan ahead! – Creating a non-threatening environment
 Curriculum Specialist n Function: – Ensure implementation of curriculum
Curriculum Specialist n Function: – Ensure implementation of curriculum
 Curriculum Specialist n Knowledge and Skills: – Deep understanding of curriculum, standards, etc.
Curriculum Specialist n Knowledge and Skills: – Deep understanding of curriculum, standards, etc.
 Curriculum Specialist n Challenges: – Can get bogged down with curriculum requirements – Teacher can know curriculum well, but still not implement effective instructional practices
Curriculum Specialist n Challenges: – Can get bogged down with curriculum requirements – Teacher can know curriculum well, but still not implement effective instructional practices
 Instructional Specialist n Function: – Ensure teachers are implementing researchbased instructional strategies
Instructional Specialist n Function: – Ensure teachers are implementing researchbased instructional strategies
 Instructional Specialist n Knowledge and Skills: – Must keep current on research-based instructional strategies
Instructional Specialist n Knowledge and Skills: – Must keep current on research-based instructional strategies
 Instructional Specialist n Challenges: – Convincing teachers to actually use strategies on consistent basis
Instructional Specialist n Challenges: – Convincing teachers to actually use strategies on consistent basis
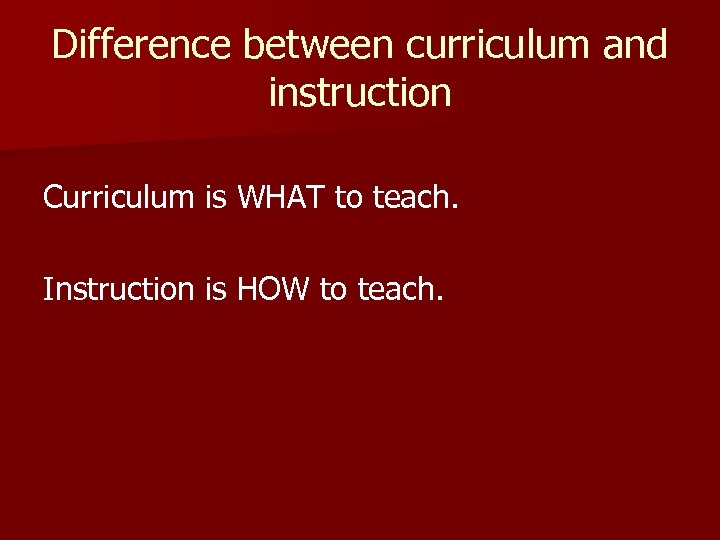 Difference between curriculum and instruction Curriculum is WHAT to teach. Instruction is HOW to teach.
Difference between curriculum and instruction Curriculum is WHAT to teach. Instruction is HOW to teach.
 Classroom Supporter n Function: – Modeling/coaching inside the classroom – Co-teach in classroom – Observe and give feedback
Classroom Supporter n Function: – Modeling/coaching inside the classroom – Co-teach in classroom – Observe and give feedback
 Classroom Supporter n Knowledge and Skills: – Knowledge of content – Stepping on toes – Fostering independence
Classroom Supporter n Knowledge and Skills: – Knowledge of content – Stepping on toes – Fostering independence
 Classroom Supporter n Challenges: – Getting stuck in showing how to do it – In-service setting at most schools
Classroom Supporter n Challenges: – Getting stuck in showing how to do it – In-service setting at most schools
 Mentor n Function: – New teachers around induction process – Improve skills of novice teacher
Mentor n Function: – New teachers around induction process – Improve skills of novice teacher
 Mentor n Knowledge and Skills: – Building relationships – Know best practices
Mentor n Knowledge and Skills: – Building relationships – Know best practices
 Mentor n Challenges: – Stereotypes coaches – veterans think “I’m not new…I don’t need a coach”
Mentor n Challenges: – Stereotypes coaches – veterans think “I’m not new…I don’t need a coach”
 Learning Facilitator n Function: – Provide professional development – Team Meetings – Dept. Meetings – 1 on 1 support
Learning Facilitator n Function: – Provide professional development – Team Meetings – Dept. Meetings – 1 on 1 support
 Learning Facilitator n Knowledge and Skills: – Constant need to be updated on research – Know how adults learn – Know how to assess need – Value collaboration
Learning Facilitator n Knowledge and Skills: – Constant need to be updated on research – Know how adults learn – Know how to assess need – Value collaboration
 Learning Facilitator n Challenges: – Providing opportunity to quickly affect change – Provide teachers choice
Learning Facilitator n Challenges: – Providing opportunity to quickly affect change – Provide teachers choice
 School Leader n Function: – School improvement committees – Set of eyes for principal for what professional development is needed
School Leader n Function: – School improvement committees – Set of eyes for principal for what professional development is needed
 School Leader n Knowledge and Skills: – Understanding of the change process – Knowing at least 1 school improvement model – 1 st and 2 nd order of change
School Leader n Knowledge and Skills: – Understanding of the change process – Knowing at least 1 school improvement model – 1 st and 2 nd order of change
 School Leader n Challenges: – Creating buy-in – In the middle between teachers and leaders
School Leader n Challenges: – Creating buy-in – In the middle between teachers and leaders
 Catalyst for Change n Function: – Actually pushing the school, staff, district to change the way they do their work
Catalyst for Change n Function: – Actually pushing the school, staff, district to change the way they do their work
 Catalyst for Change n Knowledge and Skills: – Introduce alternatives or refinements – Make observations about current practice – Ask hard questions about current practices – Engage teachers in Evaluative Think
Catalyst for Change n Knowledge and Skills: – Introduce alternatives or refinements – Make observations about current practice – Ask hard questions about current practices – Engage teachers in Evaluative Think
 Catalyst for Change n Challenges: – Willing to challenge the status quo – Delicate balance between challenge and support – Be ready to act when opportunity arises – Live with uncertainty and ambiguity – Be okay with just “planting the seed”
Catalyst for Change n Challenges: – Willing to challenge the status quo – Delicate balance between challenge and support – Be ready to act when opportunity arises – Live with uncertainty and ambiguity – Be okay with just “planting the seed”
 Learner n Function: – You are learning all the time – Be the model learner – Be clear on what you need to learn – Application of learning – Reflect on how you’re doing as a learner
Learner n Function: – You are learning all the time – Be the model learner – Be clear on what you need to learn – Application of learning – Reflect on how you’re doing as a learner
 Learner n Knowledge and Skills: – How to process – How to integrate what you’re learning
Learner n Knowledge and Skills: – How to process – How to integrate what you’re learning
 Learner n Challenges: – Time – Being right – Know what you need to learn – Always talk last
Learner n Challenges: – Time – Being right – Know what you need to learn – Always talk last
 Pie Chart Draw a large circle on your purple paper n Create a pie chart showing how much time you spend on these roles. n You don’t have to use all of them. n n n Resource Provider Data Coach Curriculum Specialist Instructional Specialist Classroom Supporter Mentor Learning Facilitator School Leader Catalyst for Change Learner
Pie Chart Draw a large circle on your purple paper n Create a pie chart showing how much time you spend on these roles. n You don’t have to use all of them. n n n Resource Provider Data Coach Curriculum Specialist Instructional Specialist Classroom Supporter Mentor Learning Facilitator School Leader Catalyst for Change Learner
 Go to New York! Find your New York partner. n Share and discuss your pie chart with them. n
Go to New York! Find your New York partner. n Share and discuss your pie chart with them. n
 Evaluation/Survey for Day #1
Evaluation/Survey for Day #1
 Instructional Coaching Institute Day 2 Lisa Wyatt Education Service Center Region XIII
Instructional Coaching Institute Day 2 Lisa Wyatt Education Service Center Region XIII
 National Anthem
National Anthem
 Housekeeping Cell phones n Restroom Breaks n Lunch n Items
Housekeeping Cell phones n Restroom Breaks n Lunch n Items
 Vacation Partners n Find a person for each vacation destination on your form. Be sure to write their name under that destination.
Vacation Partners n Find a person for each vacation destination on your form. Be sure to write their name under that destination.
 What will we cover? n Why instructional coaching? n Overview of instructional coaching. n Roles of coaches. n Dealing with change. n Communication is key. n Tools
What will we cover? n Why instructional coaching? n Overview of instructional coaching. n Roles of coaches. n Dealing with change. n Communication is key. n Tools
 Do you know what quality instruction looks like?
Do you know what quality instruction looks like?
 The History of Engagement
The History of Engagement
 BERC Group n Duane Baker n Research: – Extensive studies have been done through teacher surveys and classroom observations, etc. to identify the essential components of Powerful Teaching and Learning that are aligned with educational reform goals – Has the largest data base on classroom instruction – Observed over 3000 classrooms
BERC Group n Duane Baker n Research: – Extensive studies have been done through teacher surveys and classroom observations, etc. to identify the essential components of Powerful Teaching and Learning that are aligned with educational reform goals – Has the largest data base on classroom instruction – Observed over 3000 classrooms
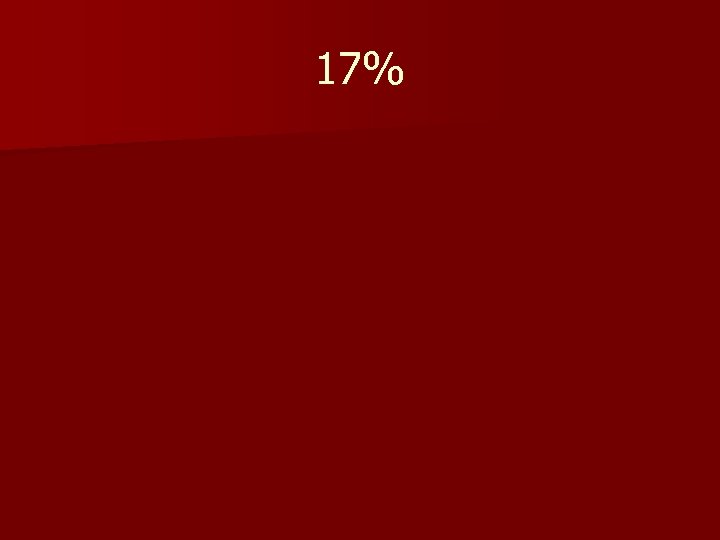
 Percentage of classrooms aligned with Powerful Teaching and Learning? n 3000 classroom observations
Percentage of classrooms aligned with Powerful Teaching and Learning? n 3000 classroom observations
 17%
17%
 Powerful Teaching and Learning n Rigor: Skills and/or knowledge are manifested as students develop conceptual understanding, not just recall n Reflection: Thinking is evident b/c teachers provide opportunities for students to respond to open-ended questions, explain their thinking processes, and reflect to create personal meaning.
Powerful Teaching and Learning n Rigor: Skills and/or knowledge are manifested as students develop conceptual understanding, not just recall n Reflection: Thinking is evident b/c teachers provide opportunities for students to respond to open-ended questions, explain their thinking processes, and reflect to create personal meaning.
 n Relevance: Application of skills, knowledge, and thinking in relevant and/or real-world contexts is essential for engaging students in their learning and for helping students make connections that lead to understanding.
n Relevance: Application of skills, knowledge, and thinking in relevant and/or real-world contexts is essential for engaging students in their learning and for helping students make connections that lead to understanding.
 n Relationships: Relationships are positive and are essential for establishing optimal conditions for learning and include high expectations around challenging work, student social support for learning, and differentiation of instruction based on student needs.
n Relationships: Relationships are positive and are essential for establishing optimal conditions for learning and include high expectations around challenging work, student social support for learning, and differentiation of instruction based on student needs.
 3 Things n Conceptualization n Socialization n Application
3 Things n Conceptualization n Socialization n Application
 Why I’m not a Brain Surgeon!
Why I’m not a Brain Surgeon!
 n Conceptualization n Socialization n Application n (Inspiration)
n Conceptualization n Socialization n Application n (Inspiration)
 Lance Armstrong
Lance Armstrong
 Oprah
Oprah
 Miss Piggy
Miss Piggy
 n How What are you passionate about? do you transfer that passion to your teachers? How do you help them transfer their passion to their students?
n How What are you passionate about? do you transfer that passion to your teachers? How do you help them transfer their passion to their students?
 What about resistance?
What about resistance?

 Understanding Educational Change is Paradoxical
Understanding Educational Change is Paradoxical
 Stuck on an escalator! What does this have to do with us?
Stuck on an escalator! What does this have to do with us?
 Instructional Coaches are Leaders of Change n It’s not easy to lead change!
Instructional Coaches are Leaders of Change n It’s not easy to lead change!
 Go to Hawaii n Think of a change you’ve gone through that was successful and another that was unsuccessful. n What accounts for the difference? n Share your thoughts with your partner.
Go to Hawaii n Think of a change you’ve gone through that was successful and another that was unsuccessful. n What accounts for the difference? n Share your thoughts with your partner.
 Resistance to Change: Reasons and Strategies by Michael Fullan n Review the article with your partner. n Think of a teacher that is resistant to change. Help your partner select the reason on the list that you think could be their justification. n Help your partner choose the strategy you can use to work on that resistance.
Resistance to Change: Reasons and Strategies by Michael Fullan n Review the article with your partner. n Think of a teacher that is resistant to change. Help your partner select the reason on the list that you think could be their justification. n Help your partner choose the strategy you can use to work on that resistance.
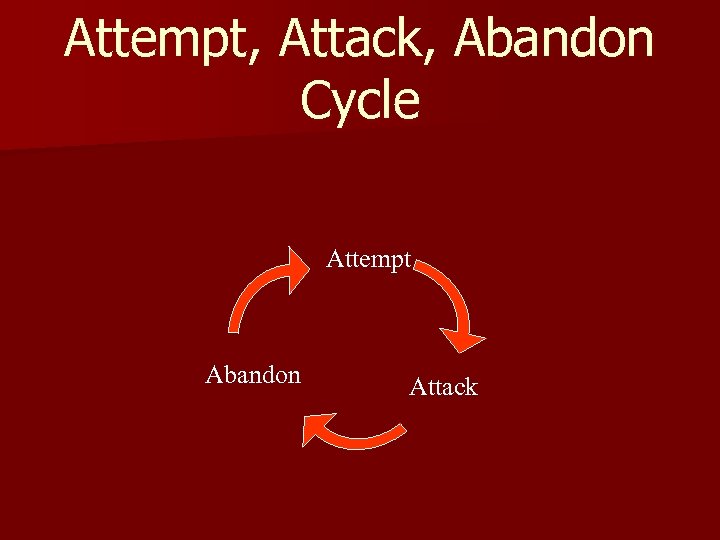 Attempt, Attack, Abandon Cycle Attempt Abandon Attack
Attempt, Attack, Abandon Cycle Attempt Abandon Attack
 Effective change is paradoxical • • Top-down AND bottom-up Easy AND powerful Self-organizing AND tightly managed Gaining commitment by not demanding commitment
Effective change is paradoxical • • Top-down AND bottom-up Easy AND powerful Self-organizing AND tightly managed Gaining commitment by not demanding commitment
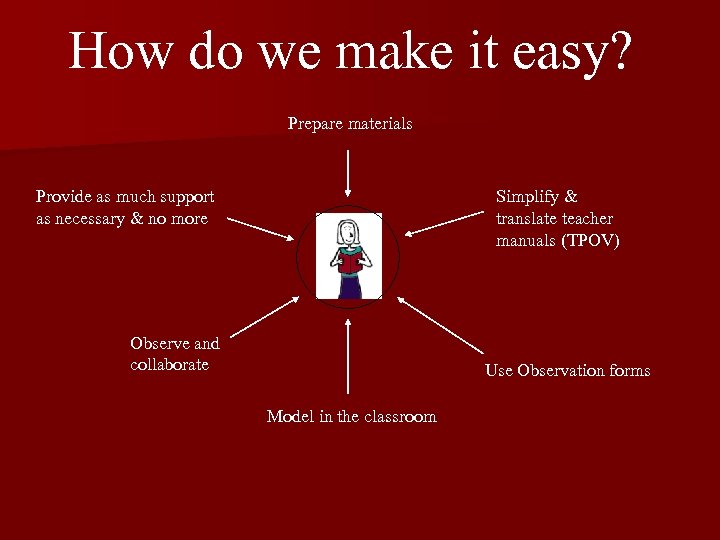 How do we make it easy? Prepare materials Provide as much support as necessary & no more Simplify & translate teacher manuals (TPOV) Observe and collaborate Use Observation forms Model in the classroom
How do we make it easy? Prepare materials Provide as much support as necessary & no more Simplify & translate teacher manuals (TPOV) Observe and collaborate Use Observation forms Model in the classroom
 Prochaska’s Stages of Change n Pre-contemplation (don’t see the need) n Contemplation (weigh pros/cons) n Preparation (prepare for the change) n Activation (Actively participation in the change) n Maintenance (Trying not to go back) n Termination/Integration (now part of normal life)
Prochaska’s Stages of Change n Pre-contemplation (don’t see the need) n Contemplation (weigh pros/cons) n Preparation (prepare for the change) n Activation (Actively participation in the change) n Maintenance (Trying not to go back) n Termination/Integration (now part of normal life)
 Go to Costa Rica n Complete the chart with your partner.
Go to Costa Rica n Complete the chart with your partner.
 The Influencer n Feed their moral purpose!
The Influencer n Feed their moral purpose!

 Get with your New York partner n Read the “Appeal to the Heart” article n Discuss ways you can use this information with your resistant staff.
Get with your New York partner n Read the “Appeal to the Heart” article n Discuss ways you can use this information with your resistant staff.
 A “Day-in-the-Life” Scenario n Answer the questions n Discuss your answers and your “day-in-the -life” with your partner.
A “Day-in-the-Life” Scenario n Answer the questions n Discuss your answers and your “day-in-the -life” with your partner.
 Find out what other coaches visit your school(s)! n If you don’t collaborate, why should your teachers? n Nobody will do it for you.
Find out what other coaches visit your school(s)! n If you don’t collaborate, why should your teachers? n Nobody will do it for you.
 Communication is KEY!
Communication is KEY!
 How does communication proceed? n n n Speaker Message Listener Interference Perceived Message Feedback
How does communication proceed? n n n Speaker Message Listener Interference Perceived Message Feedback
 Frasier What is the communication problem?
Frasier What is the communication problem?
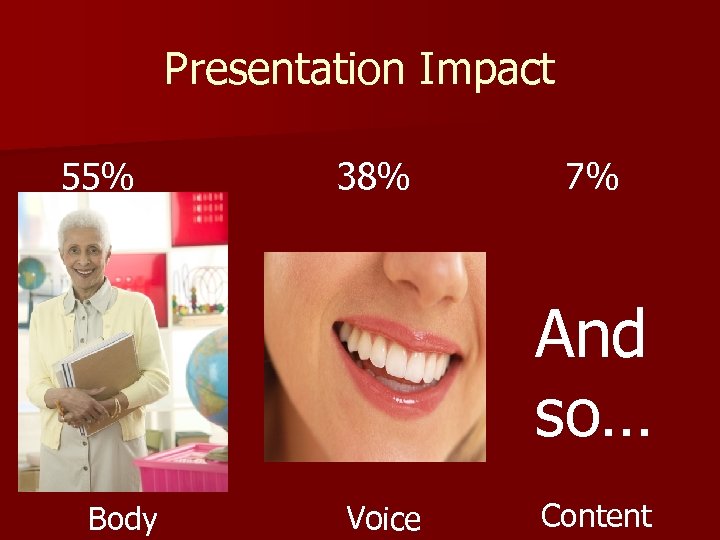 Presentation Impact 55% 38% 7% And so… Body Voice Content
Presentation Impact 55% 38% 7% And so… Body Voice Content
 Responsive Turns (Kolb & Williams (2000) The shadow negotiation) n Interrupt an encounter to change it’s momentum n Name an encounter to make its nature and consequences more obvious n Correct an encounter to provide an explanation for what is taking place and to rectify understandings and assumptions n Divert an encounter to the interaction in a different direction
Responsive Turns (Kolb & Williams (2000) The shadow negotiation) n Interrupt an encounter to change it’s momentum n Name an encounter to make its nature and consequences more obvious n Correct an encounter to provide an explanation for what is taking place and to rectify understandings and assumptions n Divert an encounter to the interaction in a different direction
 Responsive Turns Interrupt Name Correct Divert Cutting off negative conversation before it begins Describing what’s going on so everyone can see it Clarifying that a statement is not true “Oh crap, I’m late; I’ve gotta go. ” Moving the conversation in a different direction “Speaking of Tom, when does basketball season start this year? ” “I thought we agreed we weren’t going to gossip” “Mr. Smith was actually opposed to the plan. ”
Responsive Turns Interrupt Name Correct Divert Cutting off negative conversation before it begins Describing what’s going on so everyone can see it Clarifying that a statement is not true “Oh crap, I’m late; I’ve gotta go. ” Moving the conversation in a different direction “Speaking of Tom, when does basketball season start this year? ” “I thought we agreed we weren’t going to gossip” “Mr. Smith was actually opposed to the plan. ”
 Your chance to play “stop the gossip” n Team up with a partner n One of you gets to be the gossip n One of you gets to be the good guy or girl n The gossip starts with an innocent conversation and then slides in some very interesting gossip n The good person practices using responsive turns to move out of the gossip
Your chance to play “stop the gossip” n Team up with a partner n One of you gets to be the gossip n One of you gets to be the good guy or girl n The gossip starts with an innocent conversation and then slides in some very interesting gossip n The good person practices using responsive turns to move out of the gossip
 Body Language Communicates n Love or hate n Control or submission n Interest or boredom n Trust or suspicion
Body Language Communicates n Love or hate n Control or submission n Interest or boredom n Trust or suspicion
 Trust/Rapport n Ten minutes of our complete and focused attention is worth much more in terms of maintaining a relationship and supporting learning than thirty minutes with distractions. -Wellman and Lipton
Trust/Rapport n Ten minutes of our complete and focused attention is worth much more in terms of maintaining a relationship and supporting learning than thirty minutes with distractions. -Wellman and Lipton
 Types of Listening n. Non-listening n. Selective listening n. Evaluative listening n. Active listening
Types of Listening n. Non-listening n. Selective listening n. Evaluative listening n. Active listening
 Listening Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Developing inner silence Listening for what contradicts our assumptions Clarifying Communicating our understanding Practicing every day Practicing with terrible listeners Developing a routine
Listening Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Developing inner silence Listening for what contradicts our assumptions Clarifying Communicating our understanding Practicing every day Practicing with terrible listeners Developing a routine

 Go to Washington DC Work with a learning partner – Decide who will be speaker and who will coach – The speaker explains a conflict they’re having with another person – The coach listens (duh!) and tries to figure out possible “stories” that might explain the other person’s behavior-why do they act like that – Work from the assumption that the other person is a good person n After this discussion, reverse roles and repeat n
Go to Washington DC Work with a learning partner – Decide who will be speaker and who will coach – The speaker explains a conflict they’re having with another person – The coach listens (duh!) and tries to figure out possible “stories” that might explain the other person’s behavior-why do they act like that – Work from the assumption that the other person is a good person n After this discussion, reverse roles and repeat n
 Coach & principal … n Need to be on the same page n Do the coach and principal – Understand all of the interventions? – Have a shared understanding of all teachers needs? – Have a shared vision about school improvement?
Coach & principal … n Need to be on the same page n Do the coach and principal – Understand all of the interventions? – Have a shared understanding of all teachers needs? – Have a shared vision about school improvement?
 In most cases, if the principal does not support the coach, the coach will not be effective
In most cases, if the principal does not support the coach, the coach will not be effective
 How can the principal show support n n n Communicate support for the coach Arrange staff development Lead study groups Co-facilitate staff development Learning about what the coach has to offer Make time to meet frequently with the coach
How can the principal show support n n n Communicate support for the coach Arrange staff development Lead study groups Co-facilitate staff development Learning about what the coach has to offer Make time to meet frequently with the coach
 What must the coach do? n Be super-organized – Work from an agenda § Principal concerns § Problem solve § Review actions since last week § Discussing interventions
What must the coach do? n Be super-organized – Work from an agenda § Principal concerns § Problem solve § Review actions since last week § Discussing interventions
 What must the coach do? n Respect their time – Be very prepared – Create one-page summaries – Keep the meetings short (less than 30 minutes if possible) – Stay on track
What must the coach do? n Respect their time – Be very prepared – Create one-page summaries – Keep the meetings short (less than 30 minutes if possible) – Stay on track
 What must the coach do? n Provide solutions, not more problems – This is not a time for a stress-relieving conversation – Make each meeting valuable enough that the principal will want to work with you
What must the coach do? n Provide solutions, not more problems – This is not a time for a stress-relieving conversation – Make each meeting valuable enough that the principal will want to work with you
 What approach must the coach take? n Work from the partnership perspective n Be aware of identity issues n Use questions to confront the brutal facts n Stay focused on student outcomes n Separate people from the issue
What approach must the coach take? n Work from the partnership perspective n Be aware of identity issues n Use questions to confront the brutal facts n Stay focused on student outcomes n Separate people from the issue
 Principal Film
Principal Film
 Discuss with your partner What can you do next week to start turning this paradoxical idea into an action?
Discuss with your partner What can you do next week to start turning this paradoxical idea into an action?
 Coaching Clips
Coaching Clips
 Loyalty means… not that I agree with everything you say, or that I believe you are always right. Loyalty means that I share a common ideal with you and that, regardless of minor differences, we strive for it, shoulder to shoulder, confident in one another’s good faith, trust, constancy and affection. -Dr. Karl Menninger
Loyalty means… not that I agree with everything you say, or that I believe you are always right. Loyalty means that I share a common ideal with you and that, regardless of minor differences, we strive for it, shoulder to shoulder, confident in one another’s good faith, trust, constancy and affection. -Dr. Karl Menninger
 How to get movies
How to get movies
 Instructional Coaching Network Monthly Meetings n Discount Codes n Districts that have joined network: n – – – – Leander Round Rock Manor University Charter Bastrop San Marcos Hutto
Instructional Coaching Network Monthly Meetings n Discount Codes n Districts that have joined network: n – – – – Leander Round Rock Manor University Charter Bastrop San Marcos Hutto
 1 st Meeting – Next Tuesday 9/23 n Working Together: The Art of Collaboration and Communication – Presenters: Me and Angela Isenberg
1 st Meeting – Next Tuesday 9/23 n Working Together: The Art of Collaboration and Communication – Presenters: Me and Angela Isenberg
 Instruction Workshops
Instruction Workshops
 Region XIII Catalogues
Region XIII Catalogues
 Dallas ISD Convocation
Dallas ISD Convocation
 Go to the People, Live among them, Love them. Start with what they know, Build on what they have. But of the best leaders, when their task is accomplished, Their work is done, The people will remark, “We have done it ourselves. ” -Ancient Chinese Proverb
Go to the People, Live among them, Love them. Start with what they know, Build on what they have. But of the best leaders, when their task is accomplished, Their work is done, The people will remark, “We have done it ourselves. ” -Ancient Chinese Proverb
 Surveys
Surveys
 Contact Info. n Lisa Wyatt n 512 -919 -5163 n Lisa. Wyatt@esc 13. txed. net
Contact Info. n Lisa Wyatt n 512 -919 -5163 n Lisa. Wyatt@esc 13. txed. net


