e19a7c560e392e55b840c1f1ad3523e0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Instruction & Reinforcement
Instruction & Reinforcement
 Identify a student and using instructional procedures in your book teach a skill: Use at least 4 strategies. Incorporate a technology application into your lesson Graphic organizers Anchoring Tables Mediated Scaffolding Priming Conspicuous Strategies Response Cards Explicit instruction Incorporating Choices Direct instruction (Direct teach) Multiple ways of responding Stating objectives
Identify a student and using instructional procedures in your book teach a skill: Use at least 4 strategies. Incorporate a technology application into your lesson Graphic organizers Anchoring Tables Mediated Scaffolding Priming Conspicuous Strategies Response Cards Explicit instruction Incorporating Choices Direct instruction (Direct teach) Multiple ways of responding Stating objectives
 What is Reinforcement? Refers to the relationship between a behavior (response) and an event or consequence that follows the response The response must increase or be maintained as a result of the consequence Is reinforcement bribery and does it decrease internal motivation?
What is Reinforcement? Refers to the relationship between a behavior (response) and an event or consequence that follows the response The response must increase or be maintained as a result of the consequence Is reinforcement bribery and does it decrease internal motivation?
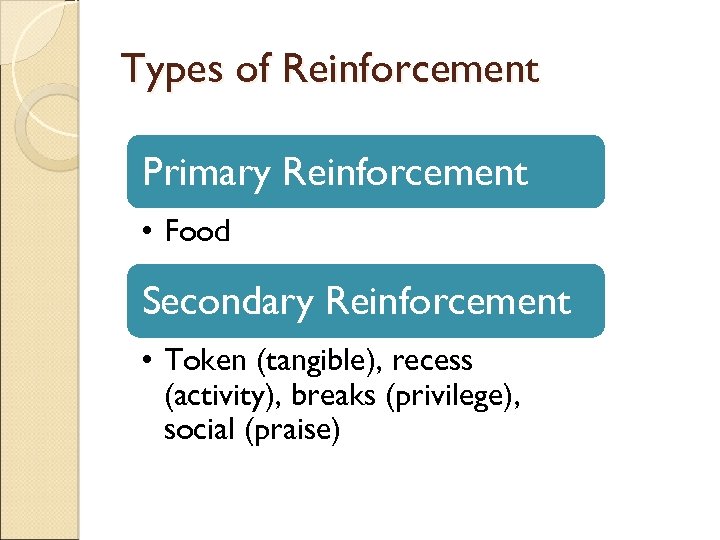 Types of Reinforcement Primary Reinforcement • Food Secondary Reinforcement • Token (tangible), recess (activity), breaks (privilege), social (praise)
Types of Reinforcement Primary Reinforcement • Food Secondary Reinforcement • Token (tangible), recess (activity), breaks (privilege), social (praise)
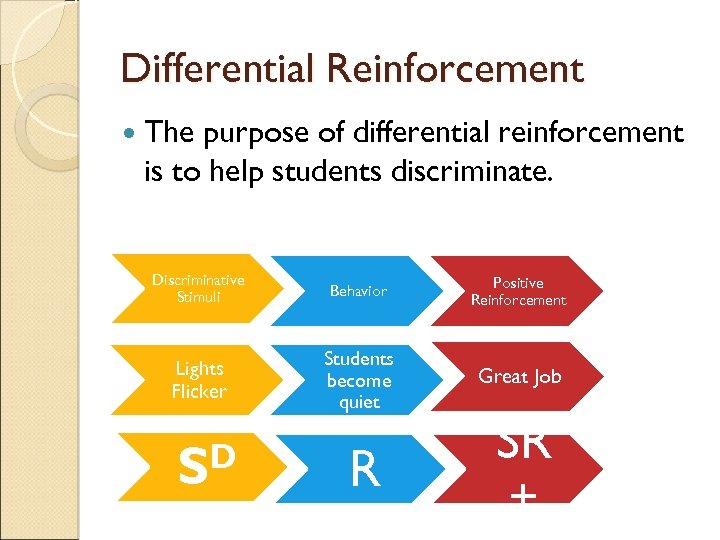 Differential Reinforcement The purpose of differential reinforcement is to help students discriminate. Discriminative Stimuli Behavior Positive Reinforcement Lights Flicker Students become quiet Great Job D S R SR +
Differential Reinforcement The purpose of differential reinforcement is to help students discriminate. Discriminative Stimuli Behavior Positive Reinforcement Lights Flicker Students become quiet Great Job D S R SR +
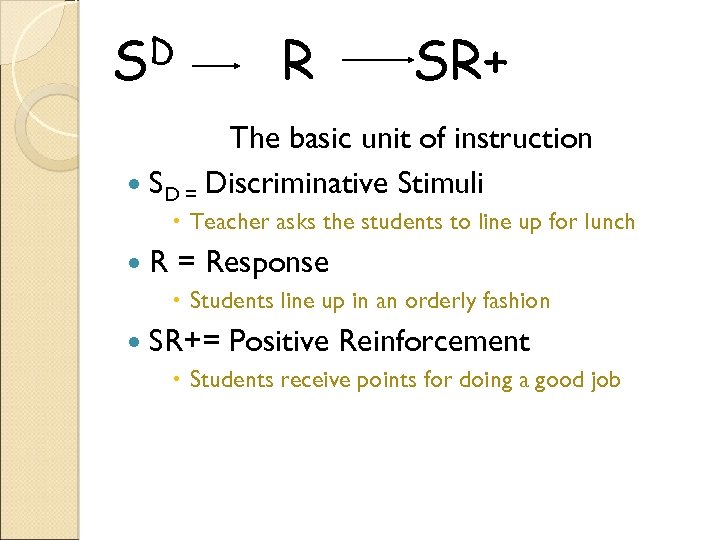 D S R SR+ The basic unit of instruction SD = Discriminative Stimuli Teacher asks the students to line up for lunch R = Response Students line up in an orderly fashion SR+= Positive Reinforcement Students receive points for doing a good job
D S R SR+ The basic unit of instruction SD = Discriminative Stimuli Teacher asks the students to line up for lunch R = Response Students line up in an orderly fashion SR+= Positive Reinforcement Students receive points for doing a good job
 S Isn’t that a new sorority? ? ? S-Delta is a second cue (stimuli or stimulus) that produces the same response but is not reinforced Why is important? When learning to discriminate and SD there are other stimuli (cues) that produce the desired response. But through positive reinforcement we increase the response to the SD because that is what we want the student to respond to. This process is called discrimination training with differential reinforcement
S Isn’t that a new sorority? ? ? S-Delta is a second cue (stimuli or stimulus) that produces the same response but is not reinforced Why is important? When learning to discriminate and SD there are other stimuli (cues) that produce the desired response. But through positive reinforcement we increase the response to the SD because that is what we want the student to respond to. This process is called discrimination training with differential reinforcement
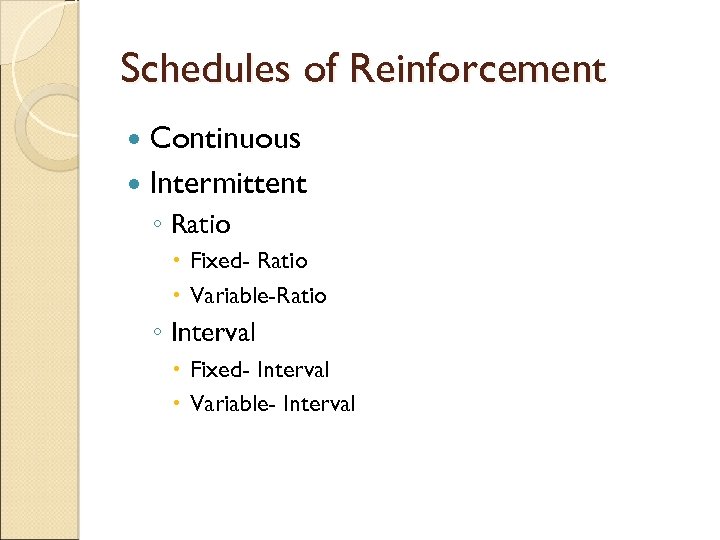 Schedules of Reinforcement Continuous Intermittent ◦ Ratio Fixed- Ratio Variable-Ratio ◦ Interval Fixed- Interval Variable- Interval
Schedules of Reinforcement Continuous Intermittent ◦ Ratio Fixed- Ratio Variable-Ratio ◦ Interval Fixed- Interval Variable- Interval
 Intermittent Schedule of Reinforcement Ratio Schedule: reinforcer delivered per NUMBER ◦ Fixed: Only after a specific number of tasks are completed ◦ Variable: Delivered following an average number of occurrences Interval Schedule: reinforcer delivered per TIME ◦ Fixed: Only after a specific number of minutes have passed ◦ Variable: Delivered following an average number of minutes
Intermittent Schedule of Reinforcement Ratio Schedule: reinforcer delivered per NUMBER ◦ Fixed: Only after a specific number of tasks are completed ◦ Variable: Delivered following an average number of occurrences Interval Schedule: reinforcer delivered per TIME ◦ Fixed: Only after a specific number of minutes have passed ◦ Variable: Delivered following an average number of minutes
 Token Economy Reinforcement Program It is a symbolic reinforcement system where students receive tokens for specific appropriate behaviors, which may be exchanged for objects or activities that have been identified as reinforcing. As students learn to associate the tokens with the purchase of reinforcers, the tokens themselves become reinforcing.
Token Economy Reinforcement Program It is a symbolic reinforcement system where students receive tokens for specific appropriate behaviors, which may be exchanged for objects or activities that have been identified as reinforcing. As students learn to associate the tokens with the purchase of reinforcers, the tokens themselves become reinforcing.
 What students need to know about a token system What students need to know ◦ What do I have to do to get one? ◦ What can I buy with them? ◦ How much does everything cost? ◦ When can I buy something? What teachers need to think about ◦ How you are going to collect the information ◦ How are you going to build in choice ◦ What reinforcers are available at what times
What students need to know about a token system What students need to know ◦ What do I have to do to get one? ◦ What can I buy with them? ◦ How much does everything cost? ◦ When can I buy something? What teachers need to think about ◦ How you are going to collect the information ◦ How are you going to build in choice ◦ What reinforcers are available at what times
 Sample Token System Behavior Required: Raise your hand provide answer or contribution to class discussion…only when called upon. Back up reinforcers: candy Cost: one ticket per piece of candy When can tokens be exchanged? : at the end of class
Sample Token System Behavior Required: Raise your hand provide answer or contribution to class discussion…only when called upon. Back up reinforcers: candy Cost: one ticket per piece of candy When can tokens be exchanged? : at the end of class
 Demonstrate your knowledge of schedules of reinforcement- Develop a reinforcement program and then pose an idea on how you would fade your program Group A: Continuous Group B: Fixed- Ratio Group C: Variable-Ratio Group D: Fixed- Interval Group E: Variable- Interval Ideas for fading: Changing the schedule, selfreinforcement, slowly moving to natural reinforcement
Demonstrate your knowledge of schedules of reinforcement- Develop a reinforcement program and then pose an idea on how you would fade your program Group A: Continuous Group B: Fixed- Ratio Group C: Variable-Ratio Group D: Fixed- Interval Group E: Variable- Interval Ideas for fading: Changing the schedule, selfreinforcement, slowly moving to natural reinforcement


