f9a88e2b37fc16dad8b2801b2f1b204d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 INSTITUTIONALISATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES DATA MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (NRDMS) IN THE DISTRICT DECISION MAKING SYSTEM OF BANKURA -P. K. Mishra -B. Barat Govt. of West Bengal
INSTITUTIONALISATION OF NATURAL RESOURCES DATA MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (NRDMS) IN THE DISTRICT DECISION MAKING SYSTEM OF BANKURA -P. K. Mishra -B. Barat Govt. of West Bengal
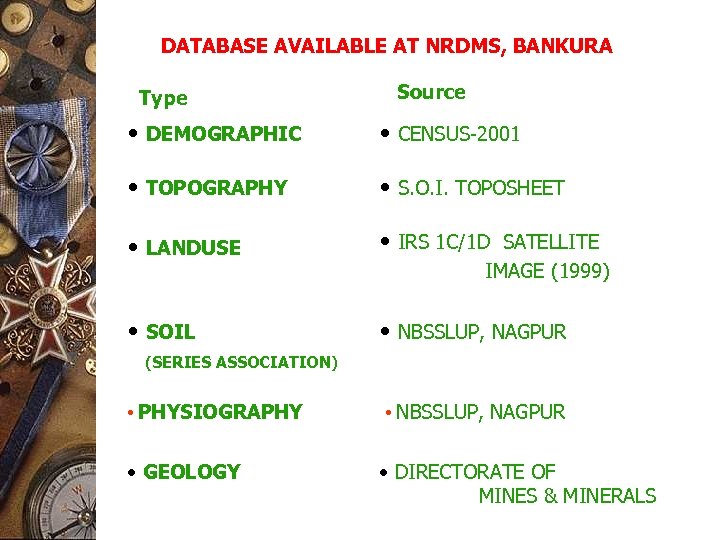 DATABASE AVAILABLE AT NRDMS, BANKURA Type Source • DEMOGRAPHIC • CENSUS-2001 • TOPOGRAPHY • S. O. I. TOPOSHEET • LANDUSE • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE • SOIL • NBSSLUP, NAGPUR IMAGE (1999) (SERIES ASSOCIATION) • PHYSIOGRAPHY • GEOLOGY • NBSSLUP, NAGPUR • DIRECTORATE OF MINES & MINERALS
DATABASE AVAILABLE AT NRDMS, BANKURA Type Source • DEMOGRAPHIC • CENSUS-2001 • TOPOGRAPHY • S. O. I. TOPOSHEET • LANDUSE • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE • SOIL • NBSSLUP, NAGPUR IMAGE (1999) (SERIES ASSOCIATION) • PHYSIOGRAPHY • GEOLOGY • NBSSLUP, NAGPUR • DIRECTORATE OF MINES & MINERALS
 DATABASE AVAILABLE AT NRDMS, BANKURA (Continued) Type Source • MINERAL RESOURCE • DIRECTORATE OF MINES & MINERALS • WASTE LAND • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE • FOREST LAND • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE IMAGE (1999) • HYDROLOGY • SWID, BANKURA • SURFACE WATER • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE IMAGE (1999) • SURFACE WATER BODIES • S. O. I. TOPOSHEET
DATABASE AVAILABLE AT NRDMS, BANKURA (Continued) Type Source • MINERAL RESOURCE • DIRECTORATE OF MINES & MINERALS • WASTE LAND • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE • FOREST LAND • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE IMAGE (1999) • HYDROLOGY • SWID, BANKURA • SURFACE WATER • IRS 1 C/1 D SATELLITE IMAGE (1999) • SURFACE WATER BODIES • S. O. I. TOPOSHEET
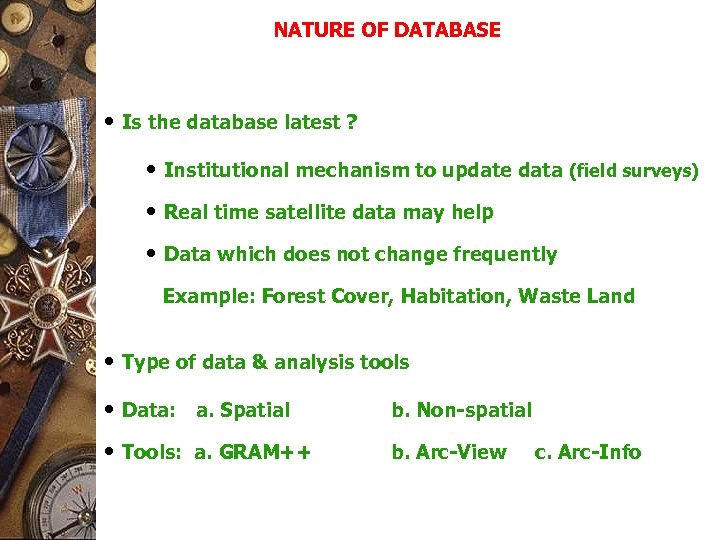 NATURE OF DATABASE • Is the database latest ? • Institutional mechanism to update data (field surveys) • Real time satellite data may help • Data which does not change frequently Example: Forest Cover, Habitation, Waste Land • Type of data & analysis tools • Data: a. Spatial b. Non-spatial • Tools: a. GRAM++ b. Arc-View c. Arc-Info
NATURE OF DATABASE • Is the database latest ? • Institutional mechanism to update data (field surveys) • Real time satellite data may help • Data which does not change frequently Example: Forest Cover, Habitation, Waste Land • Type of data & analysis tools • Data: a. Spatial b. Non-spatial • Tools: a. GRAM++ b. Arc-View c. Arc-Info
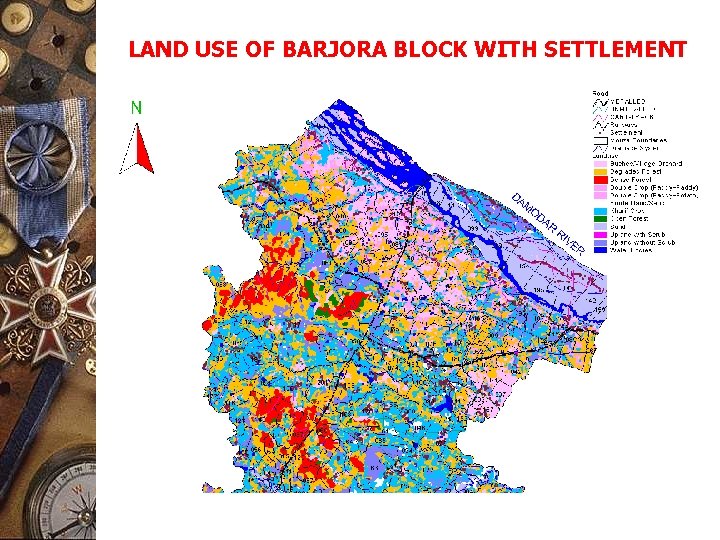 LAND USE OF BARJORA BLOCK WITH SETTLEMENT
LAND USE OF BARJORA BLOCK WITH SETTLEMENT
 APPLICATIONS PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) (CORE NET WORK) Objective : To optimise the road network while serving maximum population Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Road Net Work (field Survey) Population data (Census-2001) Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Drainage System (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Cross Drainage (field Survey) Height Contour (SOI Topo-sheet) Amenities like Market, Health Centres, Bank etc. (field Survey)
APPLICATIONS PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) (CORE NET WORK) Objective : To optimise the road network while serving maximum population Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Road Net Work (field Survey) Population data (Census-2001) Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Drainage System (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Cross Drainage (field Survey) Height Contour (SOI Topo-sheet) Amenities like Market, Health Centres, Bank etc. (field Survey)
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) (CORE NET WORK) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : Output: : 1 Month 5 months Road net work for 22 blocks along with utilities Decision support available: 1. Optimal selection of roads 2. Identification of habitation unconnected by roads and its prioritization 3. Identification of utilities unconnected by road
APPLICATIONS (Continued) PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) (CORE NET WORK) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : Output: : 1 Month 5 months Road net work for 22 blocks along with utilities Decision support available: 1. Optimal selection of roads 2. Identification of habitation unconnected by roads and its prioritization 3. Identification of utilities unconnected by road
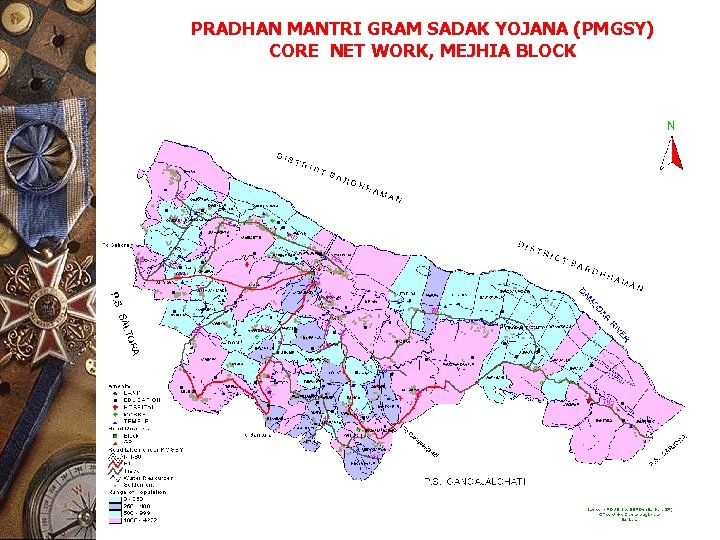 PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) CORE NET WORK, MEJHIA BLOCK
PRADHAN MANTRI GRAM SADAK YOJANA (PMGSY) CORE NET WORK, MEJHIA BLOCK
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF HEALTH SUB-CENTRES Objective : To achieve more effective health care services & its delivery in an equitable manner Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Health Sub-Centres (field survey) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 2 months
APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF HEALTH SUB-CENTRES Objective : To achieve more effective health care services & its delivery in an equitable manner Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Health Sub-Centres (field survey) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Topo-sheet) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 2 months
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF HEALTH SUB-CENTRES Output: To optimally reallocate command area of existing Sub centres’ within Gram Panchayat Boundary considering size of population, distance and road connectivity Decision support available: 1. Outreach centres are identified and action plan prepared accordingly 3. To know the present status of different health programme and to prepare action plan on priority basis
APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF HEALTH SUB-CENTRES Output: To optimally reallocate command area of existing Sub centres’ within Gram Panchayat Boundary considering size of population, distance and road connectivity Decision support available: 1. Outreach centres are identified and action plan prepared accordingly 3. To know the present status of different health programme and to prepare action plan on priority basis
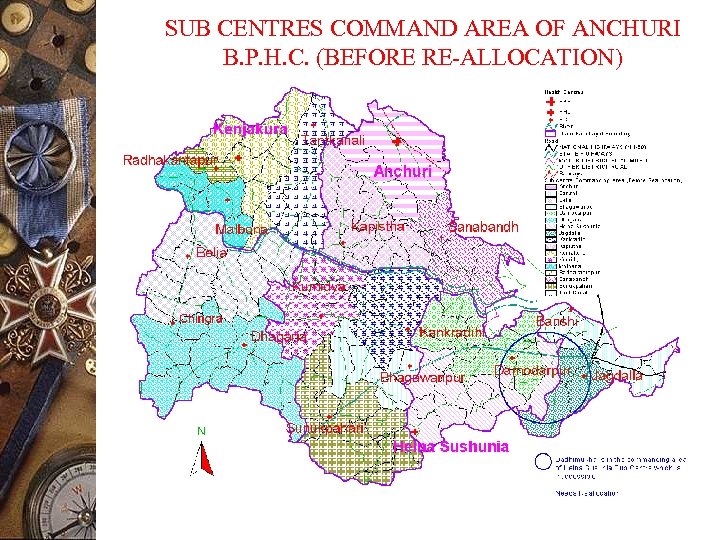 SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (BEFORE RE-ALLOCATION)
SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (BEFORE RE-ALLOCATION)
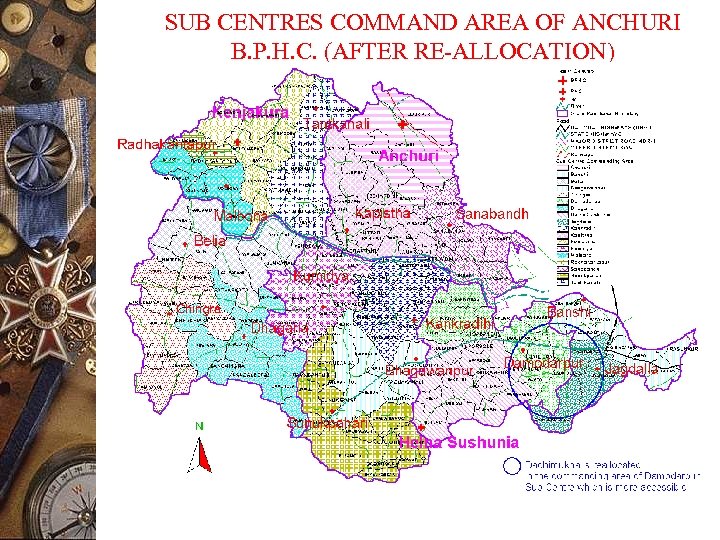 SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (AFTER RE-ALLOCATION)
SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (AFTER RE-ALLOCATION)
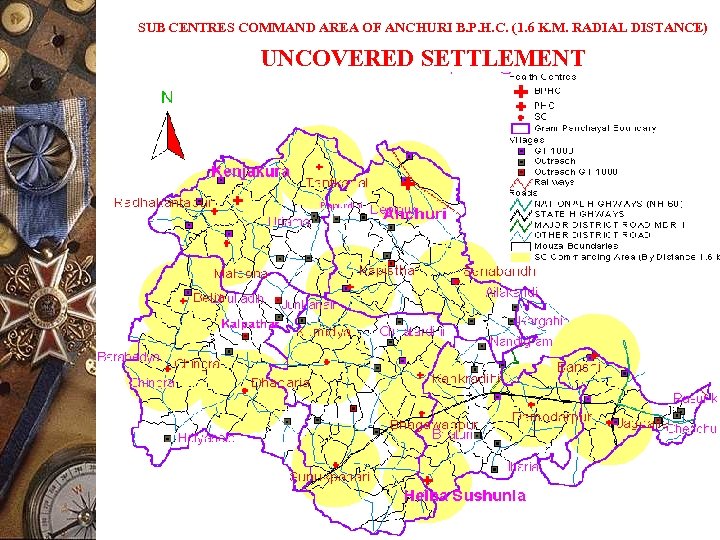 SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (1. 6 K. M. RADIAL DISTANCE) UNCOVERED SETTLEMENT
SUB CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF ANCHURI B. P. H. C. (1. 6 K. M. RADIAL DISTANCE) UNCOVERED SETTLEMENT
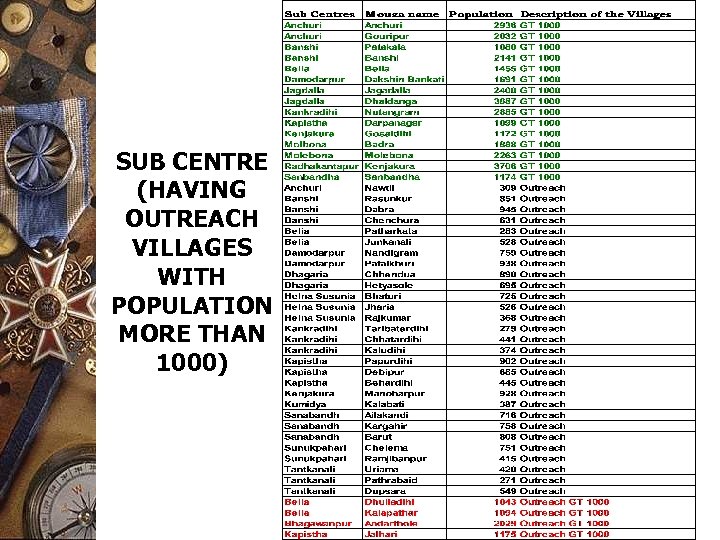 SUB CENTRE (HAVING OUTREACH VILLAGES WITH POPULATION MORE THAN 1000)
SUB CENTRE (HAVING OUTREACH VILLAGES WITH POPULATION MORE THAN 1000)
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF ANGANWADI CENTRES Objective : Optimal identification of location for setting up of a new anganwadi centre Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Anganwadi Centres (field survey) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) ITDP Mouzas (BCW Department) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 2 months
APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF ANGANWADI CENTRES Objective : Optimal identification of location for setting up of a new anganwadi centre Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Anganwadi Centres (field survey) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) ITDP Mouzas (BCW Department) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 2 months
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF ANGANWADI CENTRES Output: Command area with respect to existing Anganwadi Centres of Gangajalghati Project. Decision support available: 1. Determine unserved area which will be taken in next plan on prioratization 2. The villages far away from the Anganwadi centres could be identified for take home ration. 3. The materials supplied to the AWCs could be distributed in a planned way incurring less expenditure.
APPLICATIONS (Continued) ADMINISTRATION OF ANGANWADI CENTRES Output: Command area with respect to existing Anganwadi Centres of Gangajalghati Project. Decision support available: 1. Determine unserved area which will be taken in next plan on prioratization 2. The villages far away from the Anganwadi centres could be identified for take home ration. 3. The materials supplied to the AWCs could be distributed in a planned way incurring less expenditure.
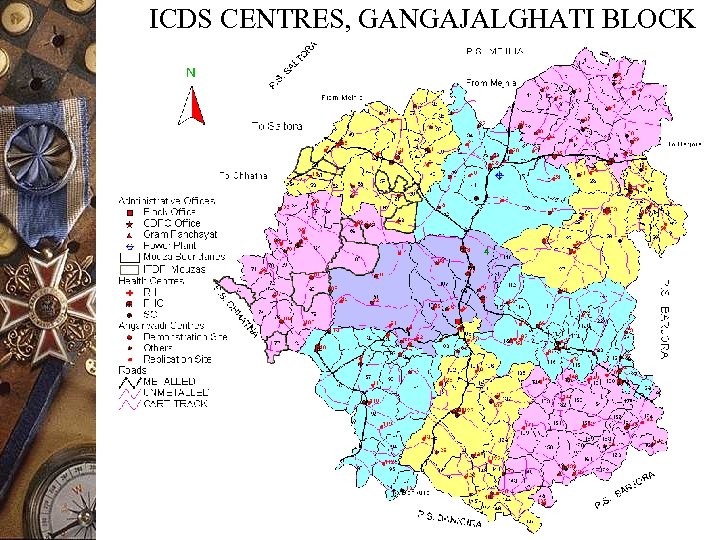 ICDS CENTRES, GANGAJALGHATI BLOCK
ICDS CENTRES, GANGAJALGHATI BLOCK
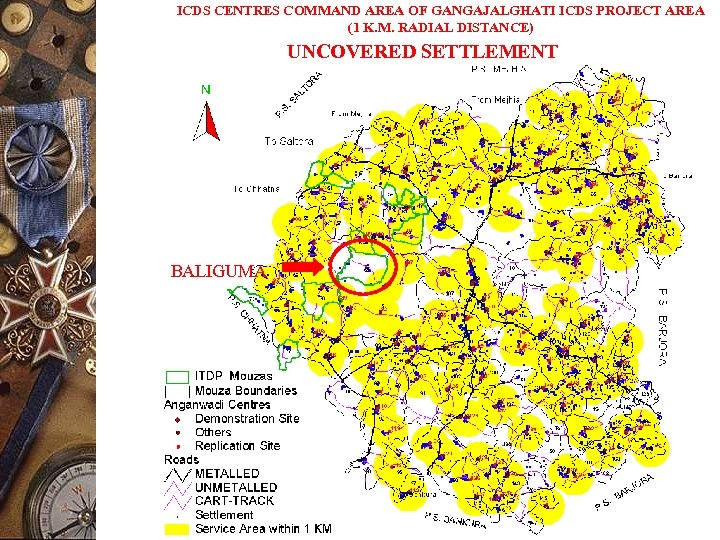 ICDS CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF GANGAJALGHATI ICDS PROJECT AREA (1 K. M. RADIAL DISTANCE) UNCOVERED SETTLEMENT BALIGUMA
ICDS CENTRES COMMAND AREA OF GANGAJALGHATI ICDS PROJECT AREA (1 K. M. RADIAL DISTANCE) UNCOVERED SETTLEMENT BALIGUMA
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) MICROWATERSHED FOR RASHTRIYA SAM VIKAS YOJANA (RSVY) Objective : To select appropriate microwatershed under RSVY Input data and its source: 1. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) 2. Population data (Census-2001) 3. Microwatershed Boundary developed by IIT, Delhi 4. Road Net Work (field survey) 5. Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) 6. Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) 7. Backward Mouzas (P&RD Deptt) 8. Land use (IRS-1 C 1999 Satellite Image) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 3 Months 3 months
APPLICATIONS (Continued) MICROWATERSHED FOR RASHTRIYA SAM VIKAS YOJANA (RSVY) Objective : To select appropriate microwatershed under RSVY Input data and its source: 1. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) 2. Population data (Census-2001) 3. Microwatershed Boundary developed by IIT, Delhi 4. Road Net Work (field survey) 5. Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) 6. Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) 7. Backward Mouzas (P&RD Deptt) 8. Land use (IRS-1 C 1999 Satellite Image) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 3 Months 3 months
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) MICROWATERSHED FOR RASHTRIYA SAM VIKAS YOJANA (RSVY) Output: Delineation of micro-watershed, listing of mouza and identification of plots for land treatment Decision support available: 1. Determination of area of micro-watershed treatment 2. Identification of ponds for re-excavation and sites for check dams.
APPLICATIONS (Continued) MICROWATERSHED FOR RASHTRIYA SAM VIKAS YOJANA (RSVY) Output: Delineation of micro-watershed, listing of mouza and identification of plots for land treatment Decision support available: 1. Determination of area of micro-watershed treatment 2. Identification of ponds for re-excavation and sites for check dams.
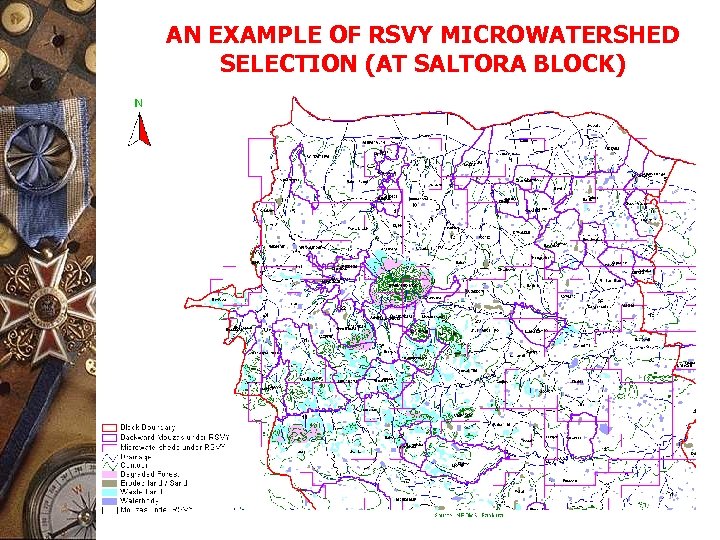 AN EXAMPLE OF RSVY MICROWATERSHED SELECTION (AT SALTORA BLOCK)
AN EXAMPLE OF RSVY MICROWATERSHED SELECTION (AT SALTORA BLOCK)
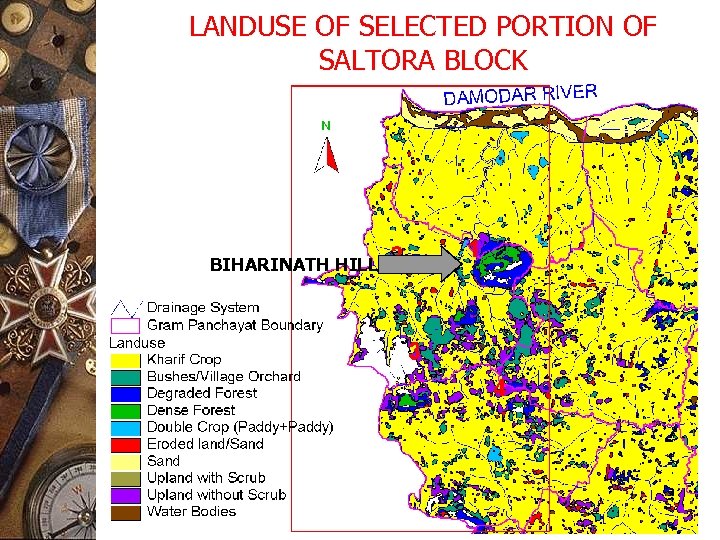 LANDUSE OF SELECTED PORTION OF SALTORA BLOCK BIHARINATH HILL
LANDUSE OF SELECTED PORTION OF SALTORA BLOCK BIHARINATH HILL
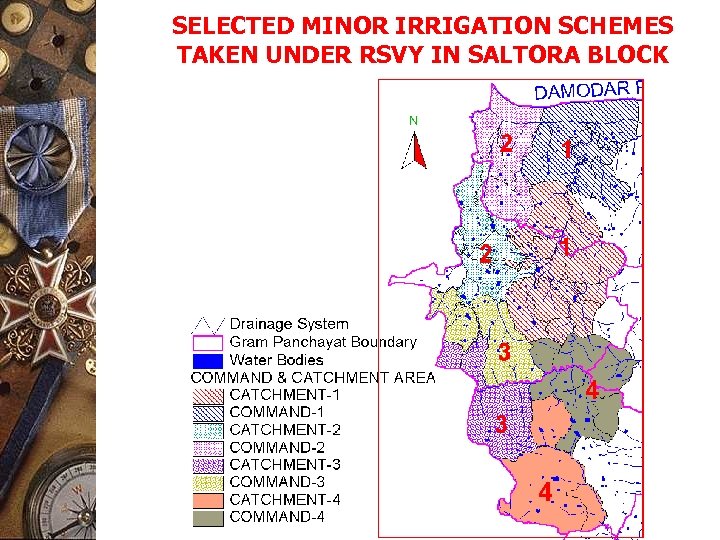 SELECTED MINOR IRRIGATION SCHEMES TAKEN UNDER RSVY IN SALTORA BLOCK
SELECTED MINOR IRRIGATION SCHEMES TAKEN UNDER RSVY IN SALTORA BLOCK
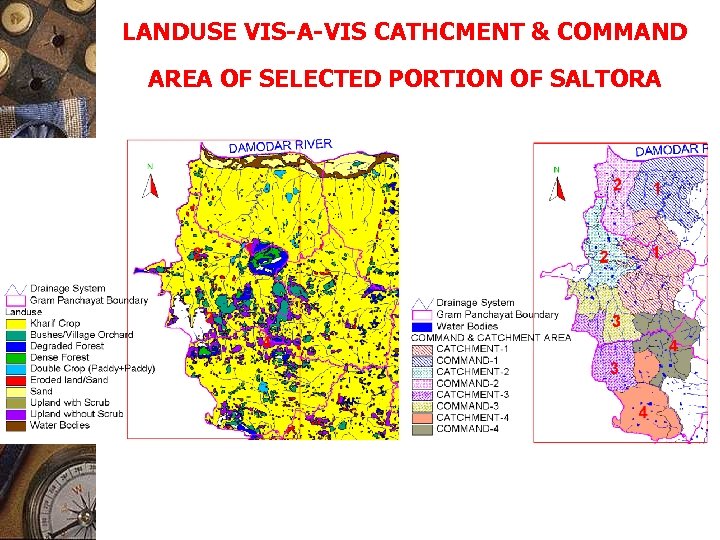 LANDUSE VIS-A-VIS CATHCMENT & COMMAND AREA OF SELECTED PORTION OF SALTORA
LANDUSE VIS-A-VIS CATHCMENT & COMMAND AREA OF SELECTED PORTION OF SALTORA
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) PONDS TO BE TAKEN UP UNDER FOOD FOR WORK PROGRAMME (FFWP) Objective : Selection of Ponds under FFWP Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Water Bodies (IRS-1 C 1999 Satellite Image) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) Backward Mouzas (P&RD Deptt) Canal (S. O. I. Toposheet)
APPLICATIONS (Continued) PONDS TO BE TAKEN UP UNDER FOOD FOR WORK PROGRAMME (FFWP) Objective : Selection of Ponds under FFWP Input data and its source: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) Population data (Census-2001) Water Bodies (IRS-1 C 1999 Satellite Image) Road Net Work (field survey) Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) Backward Mouzas (P&RD Deptt) Canal (S. O. I. Toposheet)
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) PONDS FOR FOOD FOR WORK PROGRAMME Output: Identifying ponds perennial in nature and adjacent to canals Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 3 months Decision support available: • Area of pond planned for excavation and its cost estimation
APPLICATIONS (Continued) PONDS FOR FOOD FOR WORK PROGRAMME Output: Identifying ponds perennial in nature and adjacent to canals Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 2 Months 3 months Decision support available: • Area of pond planned for excavation and its cost estimation
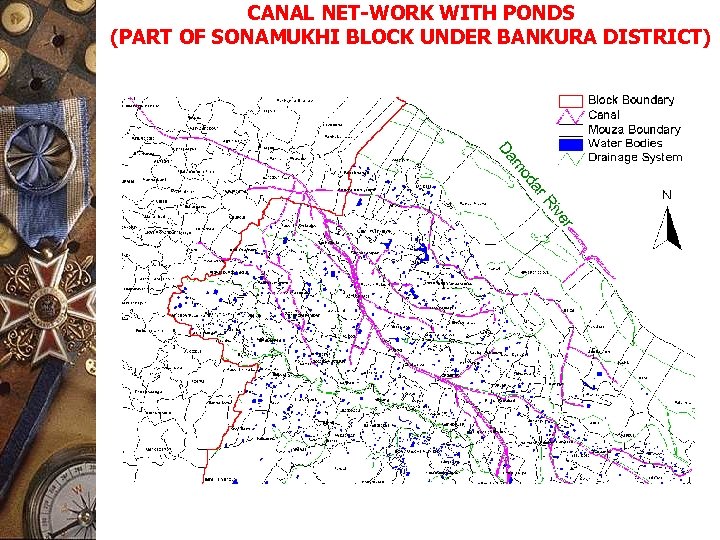 CANAL NET-WORK WITH PONDS (PART OF SONAMUKHI BLOCK UNDER BANKURA DISTRICT)
CANAL NET-WORK WITH PONDS (PART OF SONAMUKHI BLOCK UNDER BANKURA DISTRICT)
 APPLICATIONS (Continued) DELINEATION OF ASSEMBLY CONSTITUENCIES Objective : Optimal delineation of Assembly Constituencies Input data and its source: 1. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) 2. Population data (Census-2001) 3. Road Net Work (field survey) 4. Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) 5. Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 1 Month
APPLICATIONS (Continued) DELINEATION OF ASSEMBLY CONSTITUENCIES Objective : Optimal delineation of Assembly Constituencies Input data and its source: 1. Mouza Boundaries (Census-2001) 2. Population data (Census-2001) 3. Road Net Work (field survey) 4. Habitation (S. O. I. Toposheet) 5. Drainage System (S. O. I. Toposheet) Time Frame: 1. Actual data entry and processing 2. Data Collection : : 1 Month
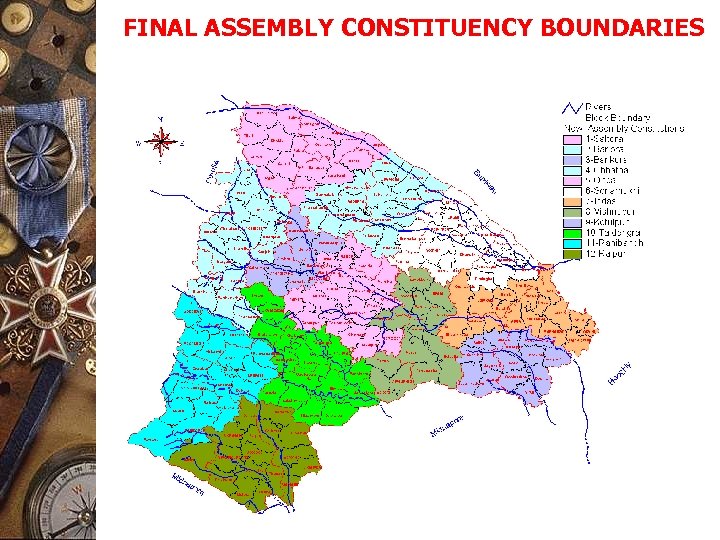 FINAL ASSEMBLY CONSTITUENCY BOUNDARIES
FINAL ASSEMBLY CONSTITUENCY BOUNDARIES
 DECISISON MAKERS (BANKURA) • Office of the District Magistrate & Subordinate offices • Three tiers Structure of Panchayat Raj Institutions • Municipal bodies • Line Departments
DECISISON MAKERS (BANKURA) • Office of the District Magistrate & Subordinate offices • Three tiers Structure of Panchayat Raj Institutions • Municipal bodies • Line Departments
 LIMITATIONS IN THE PRESENT DECISION MAKING PROCESS • Incorrect resource allocation • Slower decisions (time and cost overrun) • Non optimal solutions • Decisions not on objective parameters • High cost of decision making
LIMITATIONS IN THE PRESENT DECISION MAKING PROCESS • Incorrect resource allocation • Slower decisions (time and cost overrun) • Non optimal solutions • Decisions not on objective parameters • High cost of decision making
 THE NEED FOR INSTITUTIONALIZATION • Making it individual neutral • Better and faster decisions • Decision based on objective parameters (situations: flood, drought) • Outsourcing - not a solution • Sustainability
THE NEED FOR INSTITUTIONALIZATION • Making it individual neutral • Better and faster decisions • Decision based on objective parameters (situations: flood, drought) • Outsourcing - not a solution • Sustainability
 HOW TO ISTITUTIONALIZE ? • A centralized place where it can be shared • Patient implementation (building up of knowledge base takes time) • 73 rd & 74 th amendment – decision on transferred subjects by the Zilla Panchayat and Municipal bodies (linking up the committees with NRDMS database) • Lower tiers or panchayats need not be taken up (higher cost without adequate benefit) • Decisions at centralized level; data collection and implementation at local level • Identification of business process (on a case to case basis) ; input – output matrix identification and implementation
HOW TO ISTITUTIONALIZE ? • A centralized place where it can be shared • Patient implementation (building up of knowledge base takes time) • 73 rd & 74 th amendment – decision on transferred subjects by the Zilla Panchayat and Municipal bodies (linking up the committees with NRDMS database) • Lower tiers or panchayats need not be taken up (higher cost without adequate benefit) • Decisions at centralized level; data collection and implementation at local level • Identification of business process (on a case to case basis) ; input – output matrix identification and implementation
 COST BENEFIT • Quantification of benefits in monetary terms – not always possible • Primarily a capacity building effort • Cost of a model unit: a. Hardware b. Software c. Manpower d. Site preparation : : 2, 62, 000 3, 10, 000 2, 88, 000 50, 000 • Total cost for (say) West Bengal: 1, 72, 90, 000
COST BENEFIT • Quantification of benefits in monetary terms – not always possible • Primarily a capacity building effort • Cost of a model unit: a. Hardware b. Software c. Manpower d. Site preparation : : 2, 62, 000 3, 10, 000 2, 88, 000 50, 000 • Total cost for (say) West Bengal: 1, 72, 90, 000
 CONCLUSION • A vision needed to tap its potential • Updation of data • Technology • Integration with Panchayat decision making system • Capacity building (a slow process) • Local wisdom to be integrated
CONCLUSION • A vision needed to tap its potential • Updation of data • Technology • Integration with Panchayat decision making system • Capacity building (a slow process) • Local wisdom to be integrated
 THE END
THE END


