d1bffc647c776ee75282bec91d007196.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Wind and Solar – Experiences in Europe and Germany with Selfsufficiency for Electricity Hermann-Josef Wagner Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economy Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany lee@lee. rub. de 34 th USAEE/IAEE North American Conference, Tulsa, Oklahoma/USA 23. -26. October 2016 1
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Wind and Solar – Experiences in Europe and Germany with Selfsufficiency for Electricity Hermann-Josef Wagner Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economy Ruhr-University Bochum, Germany lee@lee. rub. de 34 th USAEE/IAEE North American Conference, Tulsa, Oklahoma/USA 23. -26. October 2016 1
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 2
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 2
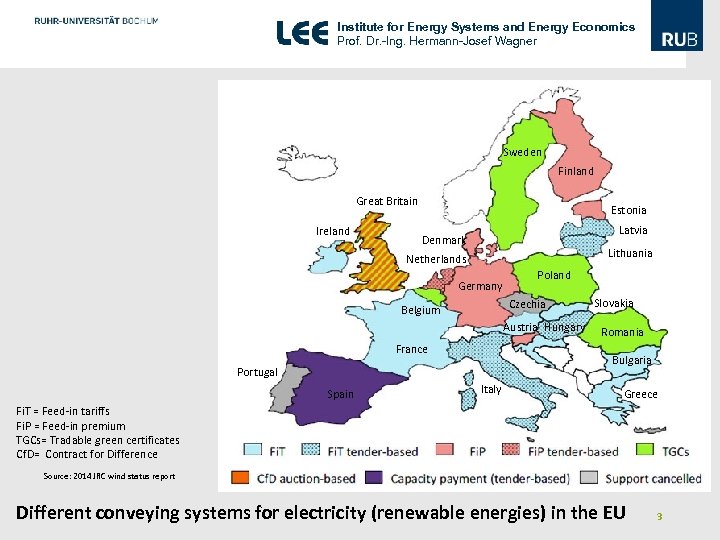 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Sweden Finland Great Britain Ireland Estonia Latvia Denmark Lithuania Netherlands Germany Poland Czechia Belgium Austria Hungary France Romania Bulgaria Portugal Spain Slovakia Italy Greece Fi. T = Feed-in tariffs Fi. P = Feed-in premium TGCs= Tradable green certificates Cf. D= Contract for Difference Source: 2014 JRC wind status report Different conveying systems for electricity (renewable energies) in the EU 3
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Sweden Finland Great Britain Ireland Estonia Latvia Denmark Lithuania Netherlands Germany Poland Czechia Belgium Austria Hungary France Romania Bulgaria Portugal Spain Slovakia Italy Greece Fi. T = Feed-in tariffs Fi. P = Feed-in premium TGCs= Tradable green certificates Cf. D= Contract for Difference Source: 2014 JRC wind status report Different conveying systems for electricity (renewable energies) in the EU 3
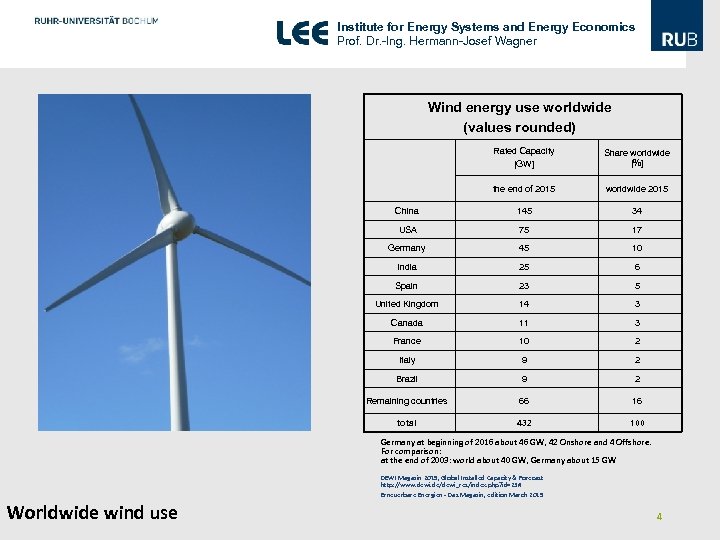 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Wind energy use worldwide (values rounded) Rated Capacity [GW] Share worldwide [%] the end of 2015 worldwide 2015 China 145 34 USA 75 17 Germany 45 10 India 25 6 Spain 23 5 United Kingdom 14 3 Canada 11 3 France 10 2 Italy 9 2 Brazil 9 2 Remaining countries 66 16 total 432 100 Germany at beginning of 2016 about 46 GW, 42 Onshore and 4 Offshore. For comparison: at the end of 2003: world about 40 GW, Germany about 15 GW DEWI Magazin 2015, Global Installed Capacity & Forecast http: //www. dewi. de/dewi_res/index. php? id=23# Erneuerbare Energien - Das Magazin, edition March 2015 Worldwide wind use 4
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Wind energy use worldwide (values rounded) Rated Capacity [GW] Share worldwide [%] the end of 2015 worldwide 2015 China 145 34 USA 75 17 Germany 45 10 India 25 6 Spain 23 5 United Kingdom 14 3 Canada 11 3 France 10 2 Italy 9 2 Brazil 9 2 Remaining countries 66 16 total 432 100 Germany at beginning of 2016 about 46 GW, 42 Onshore and 4 Offshore. For comparison: at the end of 2003: world about 40 GW, Germany about 15 GW DEWI Magazin 2015, Global Installed Capacity & Forecast http: //www. dewi. de/dewi_res/index. php? id=23# Erneuerbare Energien - Das Magazin, edition March 2015 Worldwide wind use 4
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Offshore windfarm alpha ventus 5
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Offshore windfarm alpha ventus 5
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Thermal solar power station „Arenales“ (Spain) • 50 MW • 156 rows of parabolic reflecors, that are able to follow the solar altitude • 510. 000 m² reflector surface • Molten salt storage • The integrated storage enables an electricity production up to seven hours without sunshine Image: www. steag. com Source: „Steag speist erstmalig Strom ins Netz“, BWK, Bd. 65 (2013) Nr. 11/12 Image: www. focus. de Parabolic trough power plant „Arenales“, Spain 6
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Thermal solar power station „Arenales“ (Spain) • 50 MW • 156 rows of parabolic reflecors, that are able to follow the solar altitude • 510. 000 m² reflector surface • Molten salt storage • The integrated storage enables an electricity production up to seven hours without sunshine Image: www. steag. com Source: „Steag speist erstmalig Strom ins Netz“, BWK, Bd. 65 (2013) Nr. 11/12 Image: www. focus. de Parabolic trough power plant „Arenales“, Spain 6
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 7
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 7
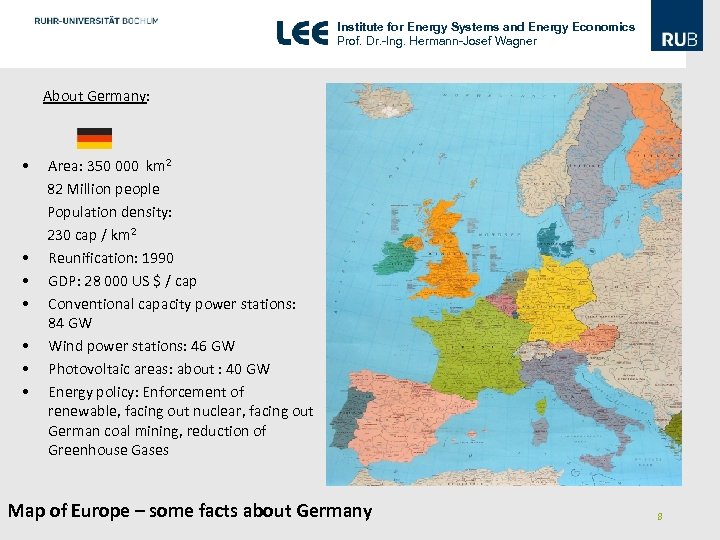 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner About Germany: • Area: 350 000 km 2 82 Million people Population density: 230 cap / km 2 • Reunification: 1990 • GDP: 28 000 US $ / cap • Conventional capacity power stations: 84 GW • Wind power stations: 46 GW • Photovoltaic areas: about : 40 GW • Energy policy: Enforcement of renewable, facing out nuclear, facing out German coal mining, reduction of Greenhouse Gases Map of Europe – some facts about Germany 8
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner About Germany: • Area: 350 000 km 2 82 Million people Population density: 230 cap / km 2 • Reunification: 1990 • GDP: 28 000 US $ / cap • Conventional capacity power stations: 84 GW • Wind power stations: 46 GW • Photovoltaic areas: about : 40 GW • Energy policy: Enforcement of renewable, facing out nuclear, facing out German coal mining, reduction of Greenhouse Gases Map of Europe – some facts about Germany 8
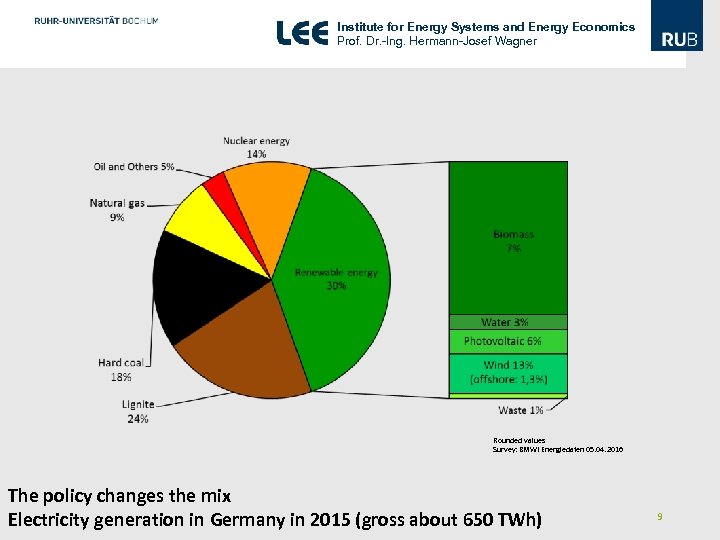 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Rounded values Survey: BMWI Energiedaten 05. 04. 2016 The policy changes the mix Electricity generation in Germany in 2015 (gross about 650 TWh) 9
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Rounded values Survey: BMWI Energiedaten 05. 04. 2016 The policy changes the mix Electricity generation in Germany in 2015 (gross about 650 TWh) 9
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Objective of green electricity: • 2025 (2035): 40 -45 % (55 -60 %) of the electricity consumption should be covered by green energy • Expansion target wind offshore till 2020: 6, 5 GW and till 2025: 11 GW • Limiting the expansion of new wind onshore: 2, 9 GW/year including replacement of old stations • Limiting the expansion of new biogas plants: 150 MW/year (next 3 years) than 200 MW/year • Limiting the annual expansion of new photovoltaic: 2, 5 GW/year Green electricity marketing: • Direct marketing of all new plants with a power output of 750 k. W or more, except biomass 150 k. W or more Reducing of financial support: • Degradation of immoderate promotion and bonus, progressively reducing of support Industrial companies: • Energy-intensive companies have to pay about 15 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy, up to a maximum limit of 4 % of the companies´ gross value added • For large scale consumers, such as aluminum or steel plants, the maximum limit decreases to 0, 5 % Own power consumption: • Existing plants are exempted from the Renewable Energy Act • Electricity, generated by eco-electricity plants, is charged with 40 %, all the rest has to pay the whole amount • Small plants up to 10 k. W (e. g. photovoltaic systems on house roofs) are exempted from the Renewable Energy Act levy Railway: • Payment of 20 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy Private Consumer: • Payment of 100 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy (about 7, 3 €-Ct/k. Wh = 8, 3 US-Ct US Ct/k. Wh)) Source: - VDI Nachrichten, 4. Juli, 2014, Nr. 27/28 - http: //www. bmwi. de/DE/Themen/Energie/Erneuerbare-Energien/eeg-reform. htm -Different internet sources – Status: 5 August 2016 l German Renewable Energy Act (EEG) 2016 (valid from 2017) 10
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Objective of green electricity: • 2025 (2035): 40 -45 % (55 -60 %) of the electricity consumption should be covered by green energy • Expansion target wind offshore till 2020: 6, 5 GW and till 2025: 11 GW • Limiting the expansion of new wind onshore: 2, 9 GW/year including replacement of old stations • Limiting the expansion of new biogas plants: 150 MW/year (next 3 years) than 200 MW/year • Limiting the annual expansion of new photovoltaic: 2, 5 GW/year Green electricity marketing: • Direct marketing of all new plants with a power output of 750 k. W or more, except biomass 150 k. W or more Reducing of financial support: • Degradation of immoderate promotion and bonus, progressively reducing of support Industrial companies: • Energy-intensive companies have to pay about 15 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy, up to a maximum limit of 4 % of the companies´ gross value added • For large scale consumers, such as aluminum or steel plants, the maximum limit decreases to 0, 5 % Own power consumption: • Existing plants are exempted from the Renewable Energy Act • Electricity, generated by eco-electricity plants, is charged with 40 %, all the rest has to pay the whole amount • Small plants up to 10 k. W (e. g. photovoltaic systems on house roofs) are exempted from the Renewable Energy Act levy Railway: • Payment of 20 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy Private Consumer: • Payment of 100 % of the Renewable Energy Act levy (about 7, 3 €-Ct/k. Wh = 8, 3 US-Ct US Ct/k. Wh)) Source: - VDI Nachrichten, 4. Juli, 2014, Nr. 27/28 - http: //www. bmwi. de/DE/Themen/Energie/Erneuerbare-Energien/eeg-reform. htm -Different internet sources – Status: 5 August 2016 l German Renewable Energy Act (EEG) 2016 (valid from 2017) 10
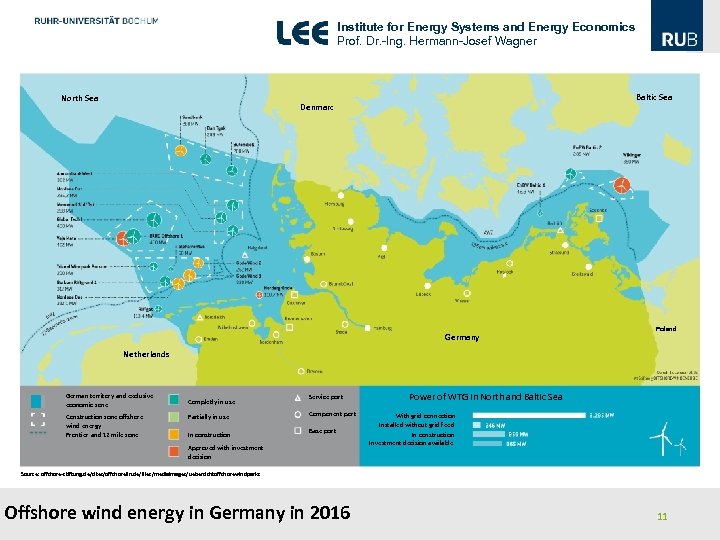 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner North Sea Baltic Sea Denmarc Ø Germany Poland Netherlands German territory and exclusive economic zone Construction zone offshore wind energy Frontier and 12 mile zone Completly in use Partially in use In construction Service port Component port Base port Approved with investment decision Power of WTG in North and Baltic Sea With grid connection Installed without grid feed In construction Investment decision available Source: offshore-stiftung. de/sites/offshorelin. de/files/mediaimages/uebersichtoffshorewindparks Offshore wind energy in Germany in 2016 11
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner North Sea Baltic Sea Denmarc Ø Germany Poland Netherlands German territory and exclusive economic zone Construction zone offshore wind energy Frontier and 12 mile zone Completly in use Partially in use In construction Service port Component port Base port Approved with investment decision Power of WTG in North and Baltic Sea With grid connection Installed without grid feed In construction Investment decision available Source: offshore-stiftung. de/sites/offshorelin. de/files/mediaimages/uebersichtoffshorewindparks Offshore wind energy in Germany in 2016 11
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner pile Tripod sea level bubble curtain Monopile About 0, 2 -0, 4 m 3/min/m air volume Ø reduced noise emission nozzle pipe seabed Source: left: Trianel; right: NVB, Nordhäuser Versorgungsbetriebe, entnommen aus: VDI Ingenieurforum, Ausgabe 2/2012 Bubble curtain as underwater noise protection during pile-driving 12
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner pile Tripod sea level bubble curtain Monopile About 0, 2 -0, 4 m 3/min/m air volume Ø reduced noise emission nozzle pipe seabed Source: left: Trianel; right: NVB, Nordhäuser Versorgungsbetriebe, entnommen aus: VDI Ingenieurforum, Ausgabe 2/2012 Bubble curtain as underwater noise protection during pile-driving 12
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Photo: Helmut Müller; Sonne, Wind und Wärme 4/2012 Repair of corrosion protection 13
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Photo: Helmut Müller; Sonne, Wind und Wärme 4/2012 Repair of corrosion protection 13
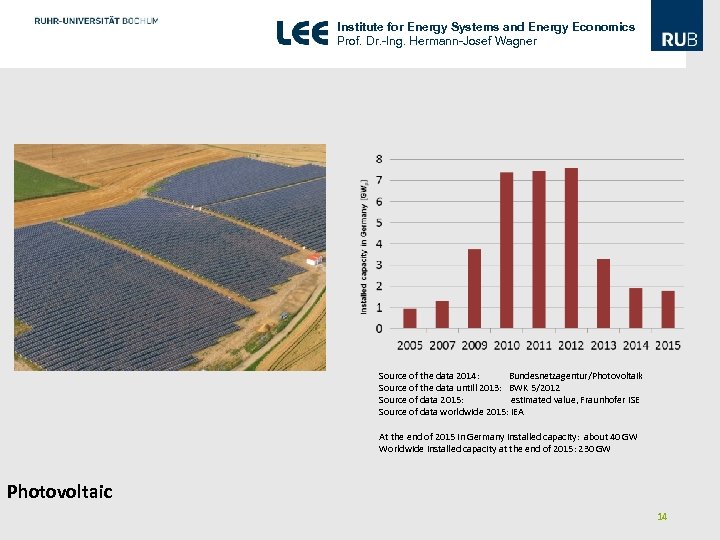 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Source of the data 2014: Bundesnetzagentur/Photovoltaik Source of the data untill 2013: BWK 5/2012 Source of data 2015: estimated value, Fraunhofer ISE Source of data worldwide 2015: IEA At the end of 2015 in Germany installed capacity: about 40 GW Worldwide installed capacity at the end of 2015: 230 GW Photovoltaic 14
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Source of the data 2014: Bundesnetzagentur/Photovoltaik Source of the data untill 2013: BWK 5/2012 Source of data 2015: estimated value, Fraunhofer ISE Source of data worldwide 2015: IEA At the end of 2015 in Germany installed capacity: about 40 GW Worldwide installed capacity at the end of 2015: 230 GW Photovoltaic 14
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 15
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 15
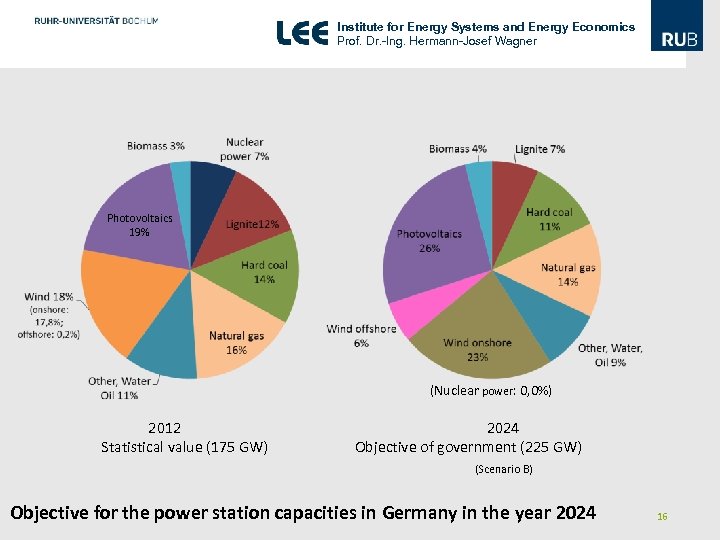 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Photovoltaics 19% (Nuclear power: 0, 0%) 2012 2024 Statistical value (175 GW) Objective of government (225 GW) (Scenario B) Objective for the power station capacities in Germany in the year 2024 16
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Photovoltaics 19% (Nuclear power: 0, 0%) 2012 2024 Statistical value (175 GW) Objective of government (225 GW) (Scenario B) Objective for the power station capacities in Germany in the year 2024 16
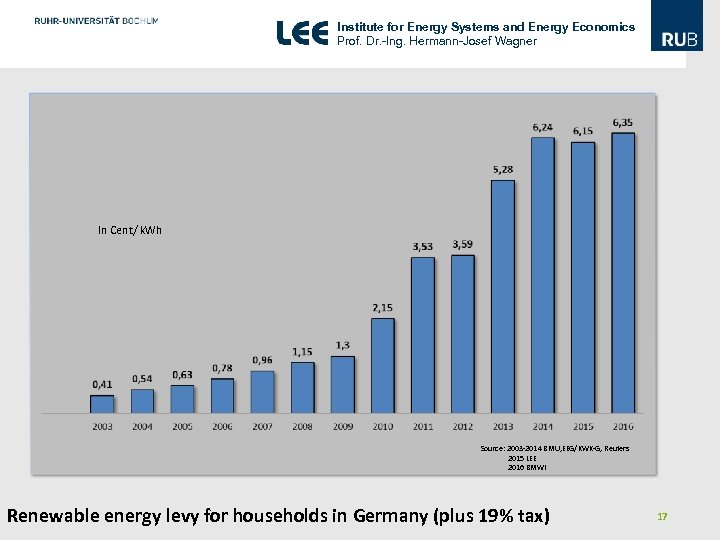 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner In Cent/ k. Wh Source: 2003 -2014 BMU, EEG/KWK-G, Reuters 2015 LEE 2016 BMWI Renewable energy levy for households in Germany (plus 19% tax) 17
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner In Cent/ k. Wh Source: 2003 -2014 BMU, EEG/KWK-G, Reuters 2015 LEE 2016 BMWI Renewable energy levy for households in Germany (plus 19% tax) 17
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Windenergy and liberalisation of markets require bulk transmission capacity 18
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Windenergy and liberalisation of markets require bulk transmission capacity 18
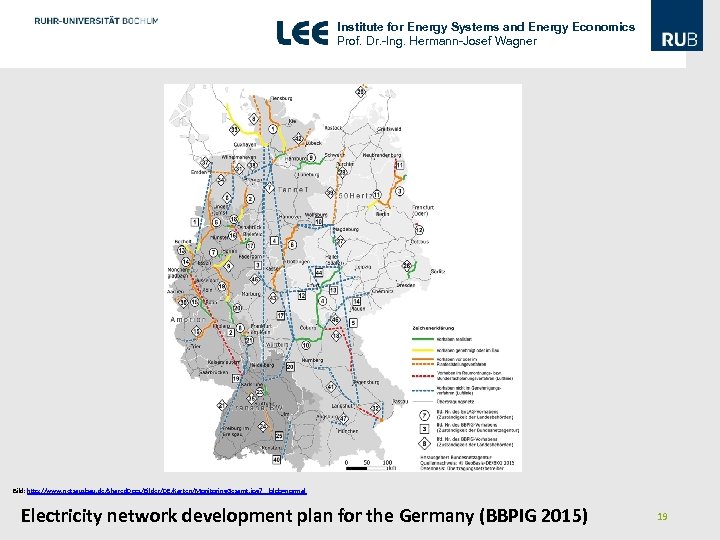 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Bild: http: //www. netzausbau. de/Shared. Docs/Bilder/DE/Karten/Monitoring. Gesamt. jpg? __blob=normal Electricity network development plan for the Germany (BBPIG 2015) 19
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Bild: http: //www. netzausbau. de/Shared. Docs/Bilder/DE/Karten/Monitoring. Gesamt. jpg? __blob=normal Electricity network development plan for the Germany (BBPIG 2015) 19
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 20
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • Electricity production – activities in Europe • German energy way – enforcement of wind and sun • Risk and experiences – high acceptance in policy and population • Conclusion Structure of my presentation 20
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • • Wind energy and photovoltaic use is increasing worldwide Technology is available Off shore wind park's are under construction, they deliver more electricity, but they are expensive In Europe are different support systems: Feed-in tariff, tax incentives, quota Germany: Fixed feet-in regulation for electricity of renewables over 20 years, policy is changing, private consumers are paying 7, 4 €-Cent/k. Wh (8, 3 US-Cent/k. Wh) for introduction and operating of renewables, companies less German government is following an energy concept 2050 CO 2 -certificates are increasing electricity price only a little bit, renewable energies much more Conclusions 21
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner • • Wind energy and photovoltaic use is increasing worldwide Technology is available Off shore wind park's are under construction, they deliver more electricity, but they are expensive In Europe are different support systems: Feed-in tariff, tax incentives, quota Germany: Fixed feet-in regulation for electricity of renewables over 20 years, policy is changing, private consumers are paying 7, 4 €-Cent/k. Wh (8, 3 US-Cent/k. Wh) for introduction and operating of renewables, companies less German government is following an energy concept 2050 CO 2 -certificates are increasing electricity price only a little bit, renewable energies much more Conclusions 21
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Thank you 22 Bild: http: //www. cpmax. com/tl_files/content/leistungen/inspektionen/galerie/100629%20097_klein. jpg
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Thank you 22 Bild: http: //www. cpmax. com/tl_files/content/leistungen/inspektionen/galerie/100629%20097_klein. jpg
 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner For discussion 23
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner For discussion 23
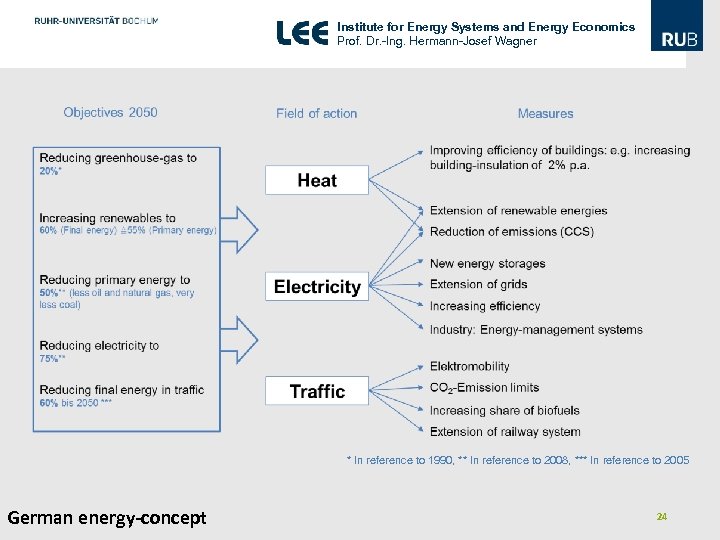 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner * In reference to 1990, ** In reference to 2008, *** In reference to 2005 German energy-concept 24
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner * In reference to 1990, ** In reference to 2008, *** In reference to 2005 German energy-concept 24
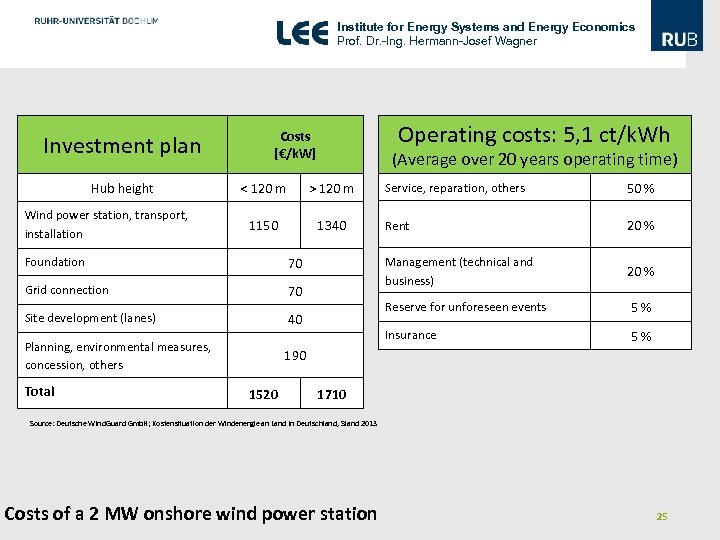 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Investment plan Hub height Wind power station, transport, installation Operating costs: 5, 1 ct/k. Wh Costs [€/k. W] (Average over 20 years operating time) 1340 Foundation 70 Grid connection 70 Site development (lanes) 40 Planning, environmental measures, concession, others Total Rent 20 % 5 % Insurance 1150 50 % Reserve for unforeseen events > 120 m Service, reparation, others Management (technical and business) < 120 m 5 % 190 1520 1710 Source: Deutsche Wind. Guard Gmb. H; Kostensituation der Windenergie an Land in Deutschland, Stand 2013 Costs of a 2 MW onshore wind power station 25
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Investment plan Hub height Wind power station, transport, installation Operating costs: 5, 1 ct/k. Wh Costs [€/k. W] (Average over 20 years operating time) 1340 Foundation 70 Grid connection 70 Site development (lanes) 40 Planning, environmental measures, concession, others Total Rent 20 % 5 % Insurance 1150 50 % Reserve for unforeseen events > 120 m Service, reparation, others Management (technical and business) < 120 m 5 % 190 1520 1710 Source: Deutsche Wind. Guard Gmb. H; Kostensituation der Windenergie an Land in Deutschland, Stand 2013 Costs of a 2 MW onshore wind power station 25
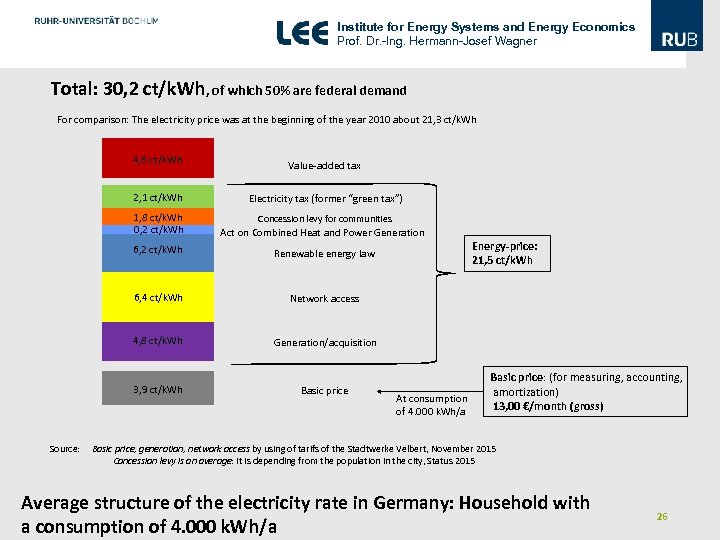 Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Total: 30, 2 ct/k. Wh, of which 50% are federal demand For comparison: The electricity price was at the beginning of the year 2010 about 21, 3 ct/k. Wh 4, 8 ct/k. Wh Value-added tax 2, 1 ct/k. Wh Electricity tax (former “green tax”) 1, 8 ct/k. Wh 0, 2 ct/k. Wh Act on Combined Heat and Power Generation 6, 2 ct/k. Wh Renewable energy law 6, 4 ct/k. Wh Network access 4, 8 ct/k. Wh Generation/acquisition 3, 9 ct/k. Wh Basic price Concession levy for communities Energy-price: 21, 5 ct/k. Wh At consumption of 4. 000 k. Wh/a Basic price: (for measuring, accounting, amortization) 13, 00 €/month (gross) Source: Basic price, generation, network access by using of tarifs of the Stadtwerke Velbert, November 2015 Concession levy is an average: It is depending from the population in the city, Status 2015 Average structure of the electricity rate in Germany: Household with a consumption of 4. 000 k. Wh/a 26
Institute for Energy Systems and Energy Economics Prof. Dr. -Ing. Hermann-Josef Wagner Total: 30, 2 ct/k. Wh, of which 50% are federal demand For comparison: The electricity price was at the beginning of the year 2010 about 21, 3 ct/k. Wh 4, 8 ct/k. Wh Value-added tax 2, 1 ct/k. Wh Electricity tax (former “green tax”) 1, 8 ct/k. Wh 0, 2 ct/k. Wh Act on Combined Heat and Power Generation 6, 2 ct/k. Wh Renewable energy law 6, 4 ct/k. Wh Network access 4, 8 ct/k. Wh Generation/acquisition 3, 9 ct/k. Wh Basic price Concession levy for communities Energy-price: 21, 5 ct/k. Wh At consumption of 4. 000 k. Wh/a Basic price: (for measuring, accounting, amortization) 13, 00 €/month (gross) Source: Basic price, generation, network access by using of tarifs of the Stadtwerke Velbert, November 2015 Concession levy is an average: It is depending from the population in the city, Status 2015 Average structure of the electricity rate in Germany: Household with a consumption of 4. 000 k. Wh/a 26


