6a0eeab00353cbba79d833b6c62b4b96.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Israel Hernandez May 20 th, 2004 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Israel Hernandez May 20 th, 2004 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
 Motivation • A Grid computational environment is suitable for parallel applications. In spite of such suitability few users currently execute their parallel applications on Grid. • Mainly reason is that Grid environment has two distinct characteristics: heterogeneous and dynamic. • The Grid Scheduling problem is classified as NP-complete problem and optimal algorithms in polynomial time are known for restricted cases. • We investigate scheduling techniques which respond to dynamic resources availability. A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
Motivation • A Grid computational environment is suitable for parallel applications. In spite of such suitability few users currently execute their parallel applications on Grid. • Mainly reason is that Grid environment has two distinct characteristics: heterogeneous and dynamic. • The Grid Scheduling problem is classified as NP-complete problem and optimal algorithms in polynomial time are known for restricted cases. • We investigate scheduling techniques which respond to dynamic resources availability. A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique The objective of Grid Scheduler is to minimize the completion time of a parallel application by properly allocating the tasks onto processors. A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique The objective of Grid Scheduler is to minimize the completion time of a parallel application by properly allocating the tasks onto processors. A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
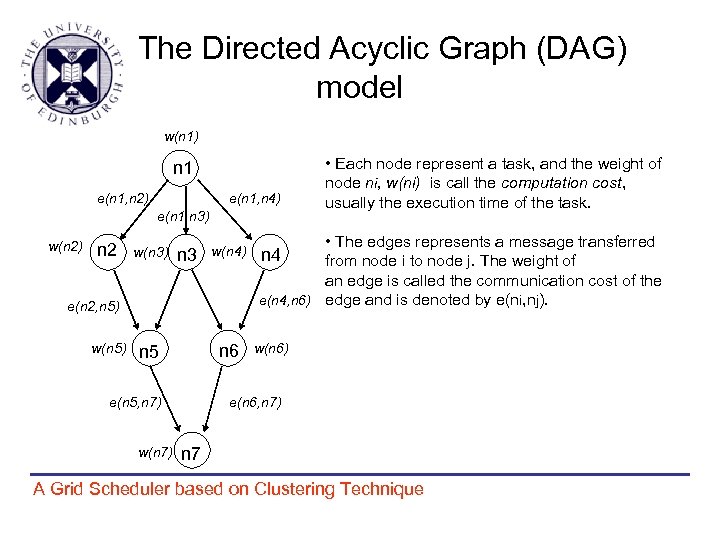 The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) model w(n 1) n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) w(n 2) n 2 w(n 3) n 3 w(n 4) e(n 2, n 5) w(n 5) n 6 n 5 e(n 5, n 7) w(n 7) • Each node represent a task, and the weight of node ni, w(ni) is call the computation cost, usually the execution time of the task. • The edges represents a message transferred n 4 from node i to node j. The weight of an edge is called the communication cost of the e(n 4, n 6) edge and is denoted by e(ni, nj). w(n 6) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) model w(n 1) n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) w(n 2) n 2 w(n 3) n 3 w(n 4) e(n 2, n 5) w(n 5) n 6 n 5 e(n 5, n 7) w(n 7) • Each node represent a task, and the weight of node ni, w(ni) is call the computation cost, usually the execution time of the task. • The edges represents a message transferred n 4 from node i to node j. The weight of an edge is called the communication cost of the e(n 4, n 6) edge and is denoted by e(ni, nj). w(n 6) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
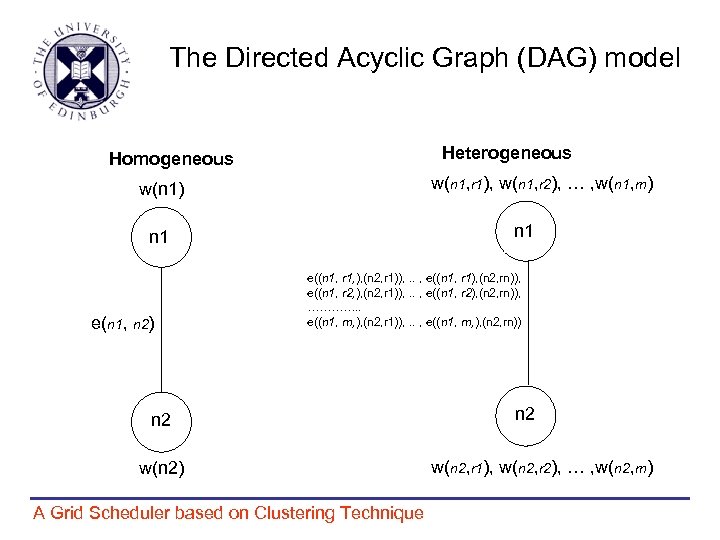 The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) model Heterogeneous Homogeneous w(n 1, r 1), w(n 1, r 2), … , w(n 1, rn) w(n 1) n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e((n 1, r 1, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, r 1), (n 2, rn)), e((n 1, r 2, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, r 2), (n 2, rn)), …………. . e((n 1, rn, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, rn, ), (n 2, rn)) n 2 w(n 2) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique n 2 w(n 2, r 1), w(n 2, r 2), … , w(n 2, rn)
The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) model Heterogeneous Homogeneous w(n 1, r 1), w(n 1, r 2), … , w(n 1, rn) w(n 1) n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e((n 1, r 1, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, r 1), (n 2, rn)), e((n 1, r 2, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, r 2), (n 2, rn)), …………. . e((n 1, rn, ), (n 2, r 1)), . . , e((n 1, rn, ), (n 2, rn)) n 2 w(n 2) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique n 2 w(n 2, r 1), w(n 2, r 2), … , w(n 2, rn)
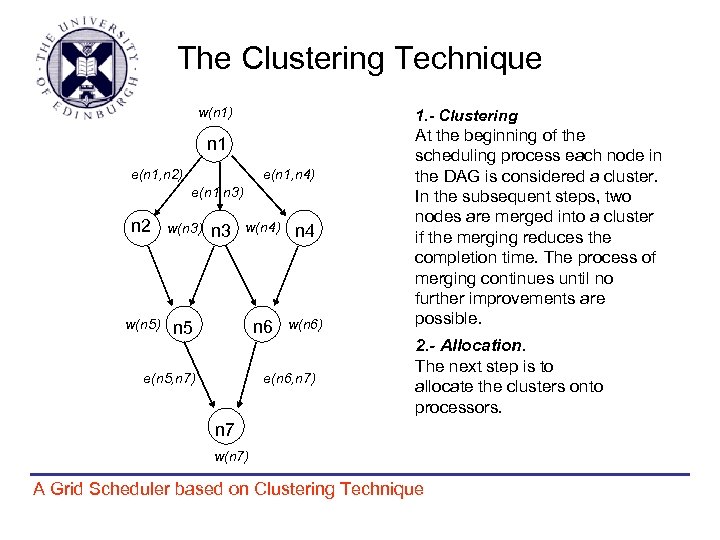 The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. n 7 w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. n 7 w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
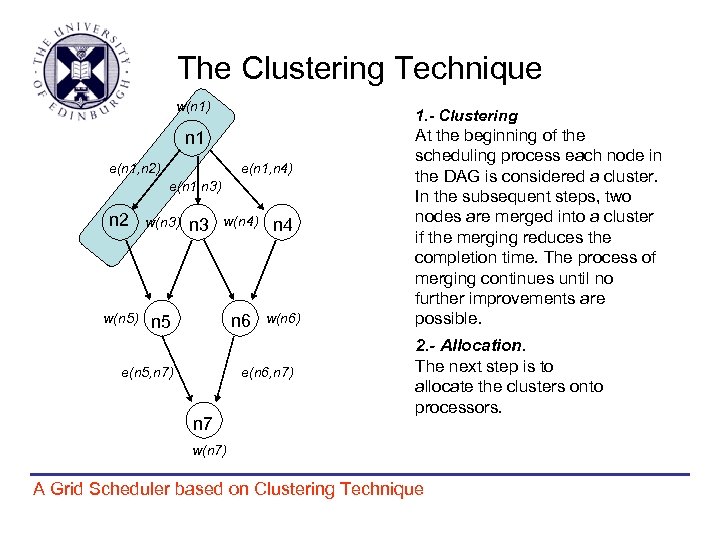 The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
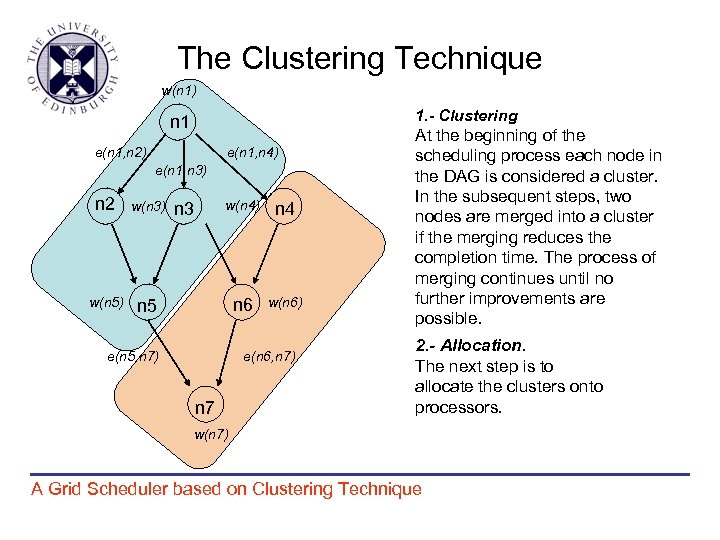 The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
The Clustering Technique w(n 1) 1. - Clustering n 1 e(n 1, n 2) e(n 1, n 4) e(n 1, n 3) n 2 w(n 3) w(n 5) n 5 w(n 4) n 4 n 6 n 3 w(n 6) e(n 5, n 7) e(n 6, n 7) n 7 At the beginning of the scheduling process each node in the DAG is considered a cluster. In the subsequent steps, two nodes are merged into a cluster if the merging reduces the completion time. The process of merging continues until no further improvements are possible. 2. - Allocation. The next step is to allocate the clusters onto processors. w(n 7) A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
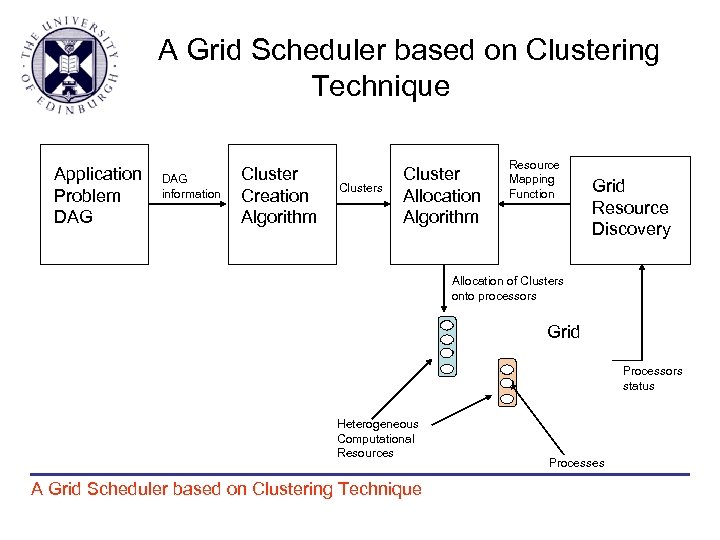 A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Application Problem DAG information Cluster Creation Algorithm Clusters Cluster Allocation Algorithm Resource Mapping Function Grid Resource Discovery Allocation of Clusters onto processors Grid Processors status Heterogeneous Computational Resources A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Processes
A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Application Problem DAG information Cluster Creation Algorithm Clusters Cluster Allocation Algorithm Resource Mapping Function Grid Resource Discovery Allocation of Clusters onto processors Grid Processors status Heterogeneous Computational Resources A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique Processes
 Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh THANKS A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique
Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh THANKS A Grid Scheduler based on Clustering Technique


