7002aaf8a996950e44705353c3efb377.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Instability rise-time far above the TMCI threshold: Comparison between simple theory, MOSES and HEADTAIL E. Benedetto, E. Metral Acknowledgements: G. Rumolo, D. Quatraro, B. Salvant (CERN) 19/2/09 CERN/GSI beam dynamics and collective effects collaboration meeting

Outline • Motivation • TMC theory to compute rise-time far above threshold • Simple TMC model, MOSES, HEADTAIL: – Qualitative – Quantitative • Conclusions and discussion E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
Transverse Instability for high-intensity single-bunch beams • In the past, studies have been done for what concerns finding the instability threshold • Different approaches: – – – Beam Break-up TMC theory Coasting beam with peak value post Head-Tail fast blow-up Unified the different approaches and formalisms to compute instability threshold → E. Metral, 2004 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
Transverse Instability for high-intensity single-bunch beams • • Next step: for intensities far above the TMCI intensity threshold i. e. instability risetime much faster then synchrotron period How to evaluate the risetime? Can we still use the concept of modes and modes coupling? → Follow-up discussion with W. Fisher and G. Rumolo at the CARE-HHH workshop (24 -25/11/08, Chavannes-de-Bogis) → E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08, https: //ab-dep-abp. web. cern. ch/ab-depabp/LIS/Minutes/20081201/metral 1. pdf • Interesting for instance near g transition, crossing (PS, RHIC) or isochronous rings (n-factory proton driver accumulator) E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
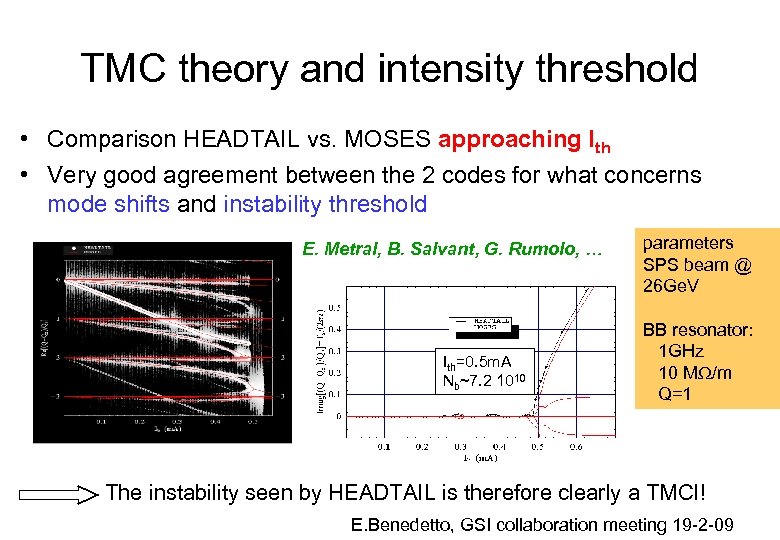
TMC theory and intensity threshold • Comparison HEADTAIL vs. MOSES approaching Ith • Very good agreement between the 2 codes for what concerns mode shifts and instability threshold E. Metral, B. Salvant, G. Rumolo, … Ith=0. 5 m. A Nb~7. 2 1010 parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 The instability seen by HEADTAIL is therefore clearly a TMCI! E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
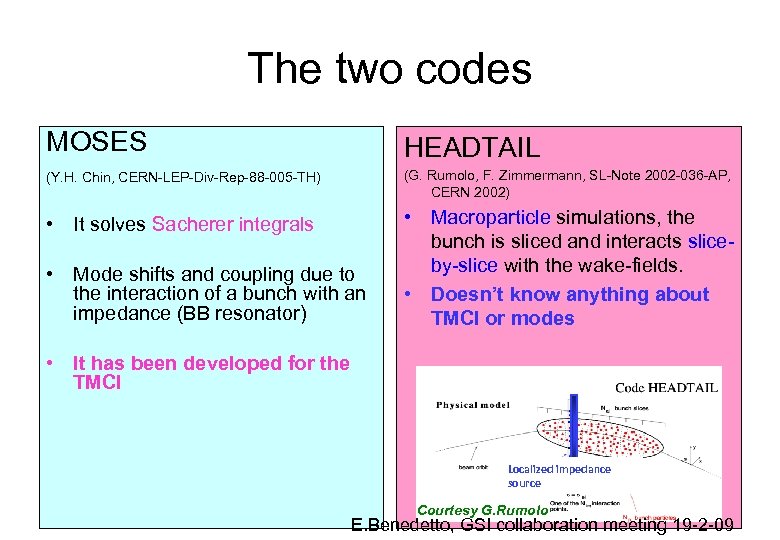
The two codes MOSES HEADTAIL (Y. H. Chin, CERN-LEP-Div-Rep-88 -005 -TH) (G. Rumolo, F. Zimmermann, SL-Note 2002 -036 -AP, CERN 2002) • It solves Sacherer integrals • Macroparticle simulations, the bunch is sliced and interacts sliceby-slice with the wake-fields. • Doesn’t know anything about TMCI or modes • Mode shifts and coupling due to the interaction of a bunch with an impedance (BB resonator) • It has been developed for the TMCI Localized impedance source Courtesy G. Rumolo E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09

TMC theory and intensity threshold • Extension of TMCI theory far above TMCI threshold • Comparison theory - HEADTAIL – MOSES for I>>Ith Courtesy B. Salvant
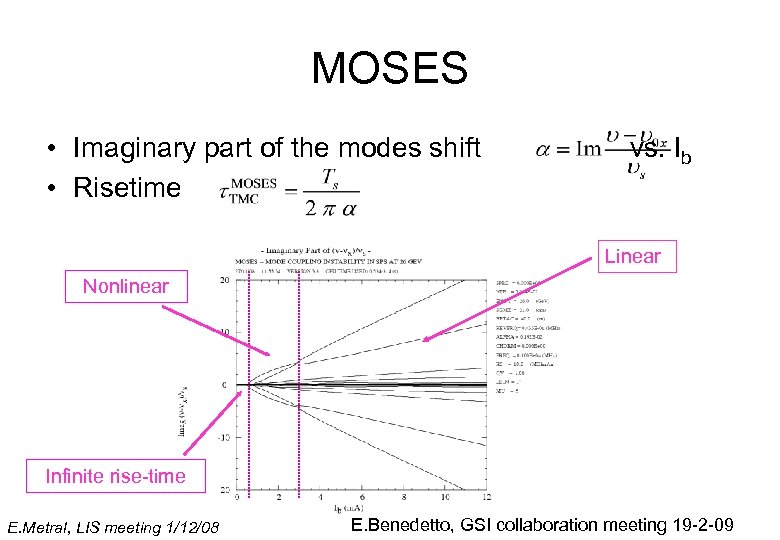
MOSES • Imaginary part of the modes shift • Risetime vs. Ib Linear Nonlinear Infinite rise-time E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09

MOSES parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
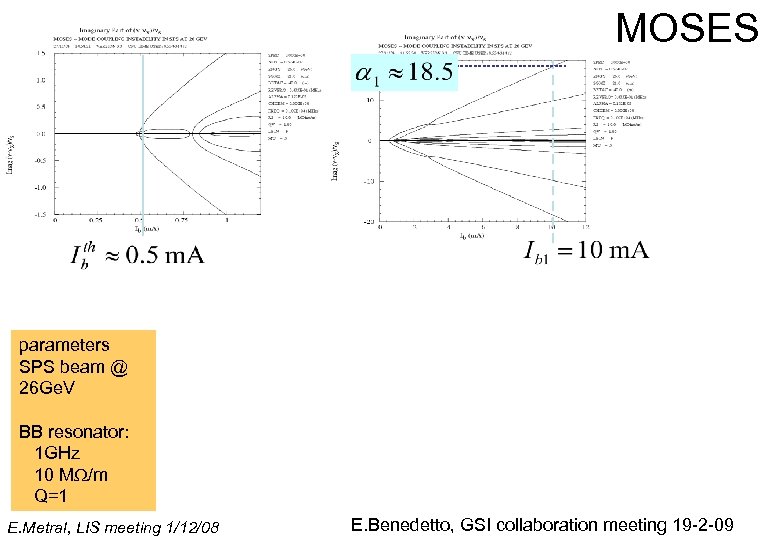
MOSES parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
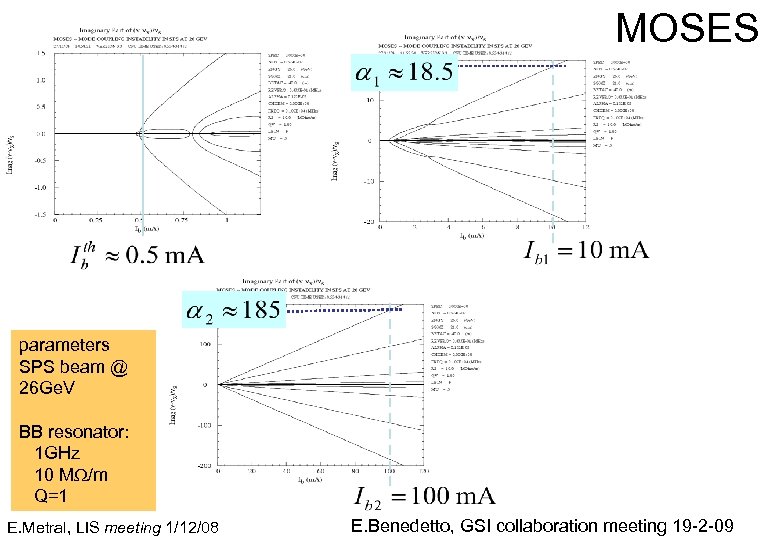
MOSES parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
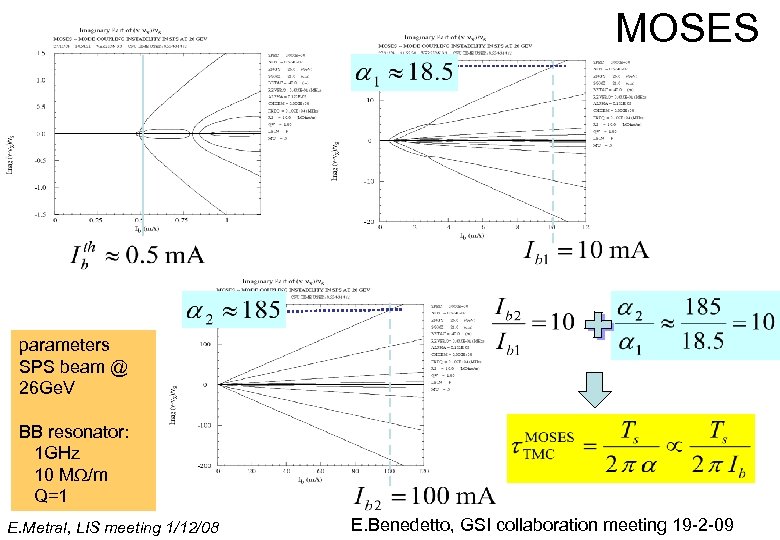
MOSES parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
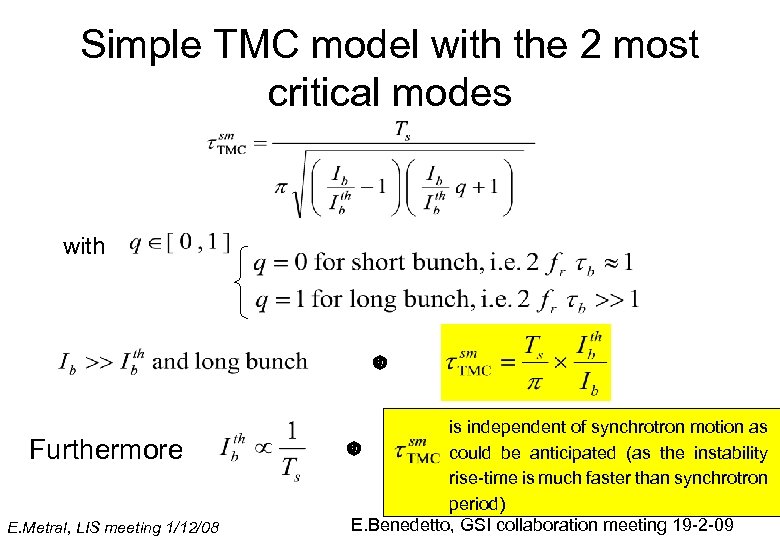
Simple TMC model with the 2 most critical modes with Furthermore E. Metral, LIS meeting 1/12/08 is independent of synchrotron motion as could be anticipated (as the instability rise-time is much faster than synchrotron period) E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
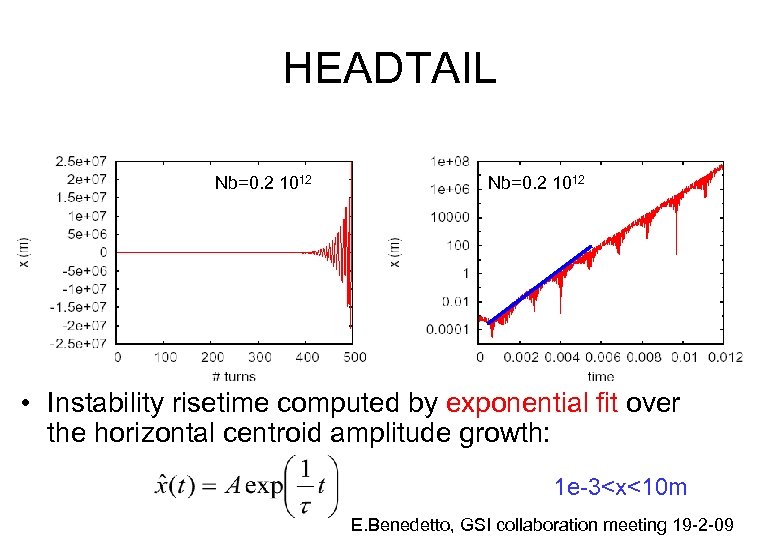
HEADTAIL Nb=0. 2 1012 • Instability risetime computed by exponential fit over the horizontal centroid amplitude growth: 1 e-3<x<10 m E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
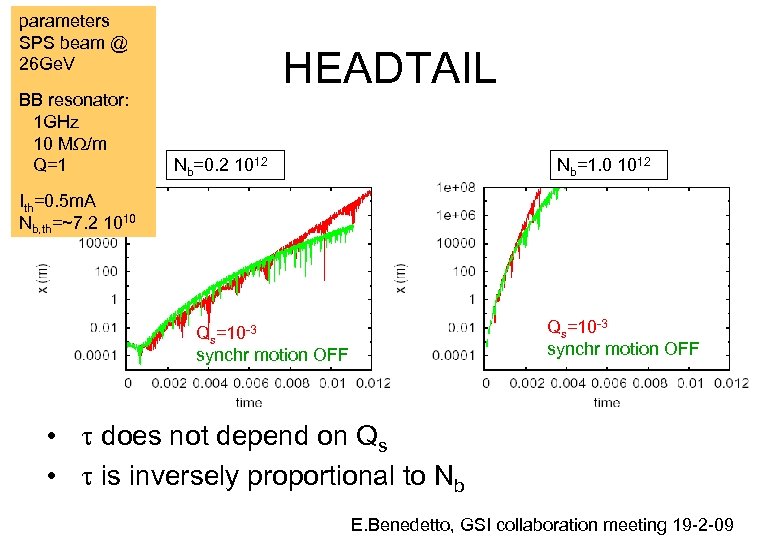
parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 HEADTAIL Nb=0. 2 1012 Nb=1. 0 1012 Ith=0. 5 m. A Nb, th=~7. 2 1010 Qs=10 -3 synchr motion OFF • t does not depend on Qs • t is inversely proportional to Nb E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
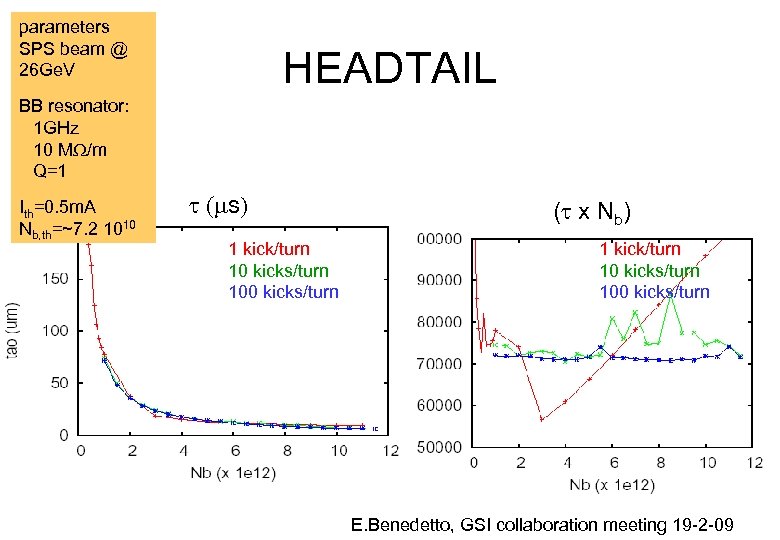
parameters SPS beam @ 26 Ge. V HEADTAIL BB resonator: 1 GHz 10 MW/m Q=1 Ith=0. 5 m. A Nb, th=~7. 2 1010 t (ms) 1 kick/turn 10 kicks/turn 100 kicks/turn (t x Nb) 1 kick/turn 10 kicks/turn 100 kicks/turn E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09

Some numerical values • Let’s consider I=100 m. A • MOSES: • Simple TMC model (2 most critical modes) • HEADTAIL: E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
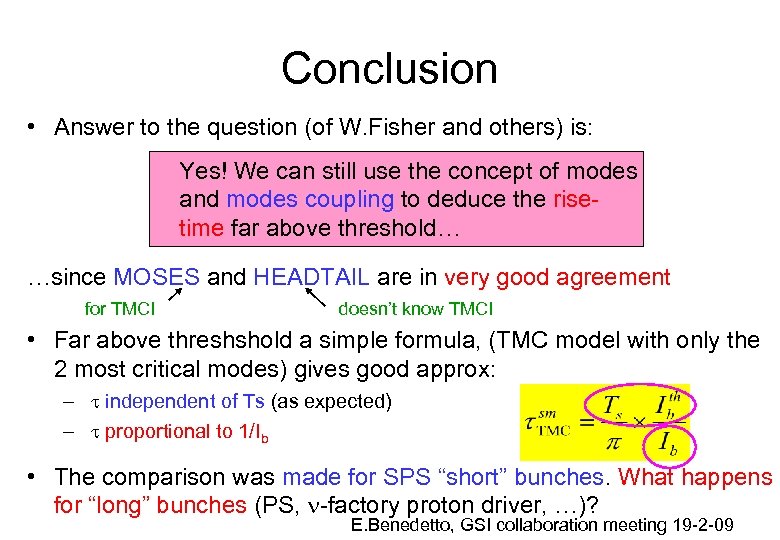
Conclusion • Answer to the question (of W. Fisher and others) is: Yes! We can still use the concept of modes and modes coupling to deduce the risetime far above threshold… …since MOSES and HEADTAIL are in very good agreement for TMCI doesn’t know TMCI • Far above threshshold a simple formula, (TMC model with only the 2 most critical modes) gives good approx: – t independent of Ts (as expected) – t proportional to 1/Ib • The comparison was made for SPS “short” bunches. What happens for “long” bunches (PS, n-factory proton driver, …)? E. Benedetto, GSI collaboration meeting 19 -2 -09
7002aaf8a996950e44705353c3efb377.ppt