dffb774fb14246cf2065671391864b54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37


 The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle.
The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle.
 Agenda • Information explosion • Oracle Universal Records Management • Demo • Case study – Great River Energy • Summary • Q&A
Agenda • Information explosion • Oracle Universal Records Management • Demo • Case study – Great River Energy • Summary • Q&A
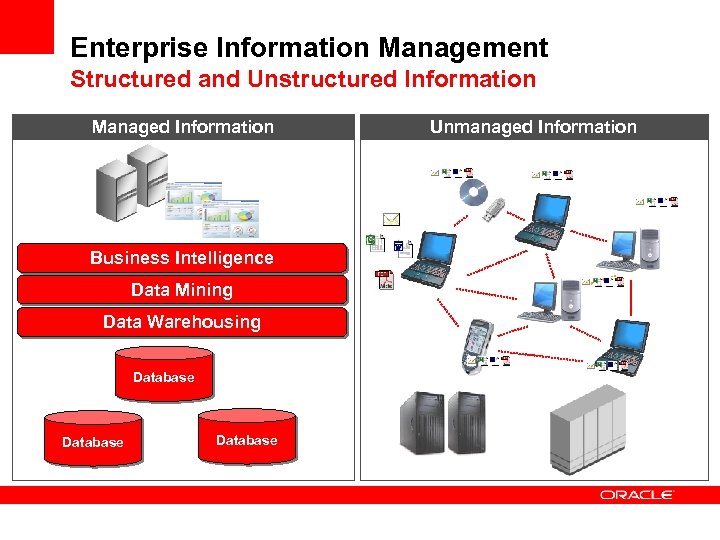 Enterprise Information Management Structured and Unstructured Information Managed Information Business Intelligence Data Mining Data Warehousing Database Unmanaged Information
Enterprise Information Management Structured and Unstructured Information Managed Information Business Intelligence Data Mining Data Warehousing Database Unmanaged Information
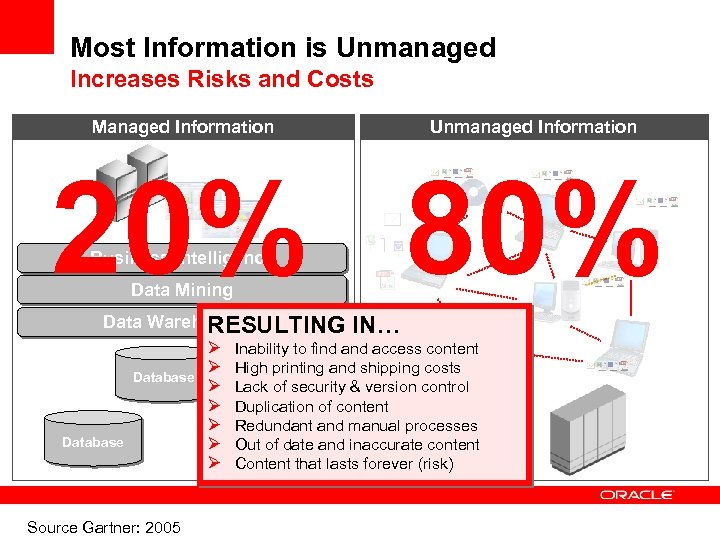 Most Information is Unmanaged Increases Risks and Costs Managed Information Unmanaged Information 20% 80% Business Intelligence Data Mining Data Warehousing RESULTING IN… Ø Inability to find access content Ø High printing and shipping costs Database Ø Lack of security & version control Ø Duplication of content Ø Redundant and manual processes Database Ø Out of date and inaccurate content Ø Content that lasts forever (risk) Source Gartner: 2005
Most Information is Unmanaged Increases Risks and Costs Managed Information Unmanaged Information 20% 80% Business Intelligence Data Mining Data Warehousing RESULTING IN… Ø Inability to find access content Ø High printing and shipping costs Database Ø Lack of security & version control Ø Duplication of content Ø Redundant and manual processes Database Ø Out of date and inaccurate content Ø Content that lasts forever (risk) Source Gartner: 2005
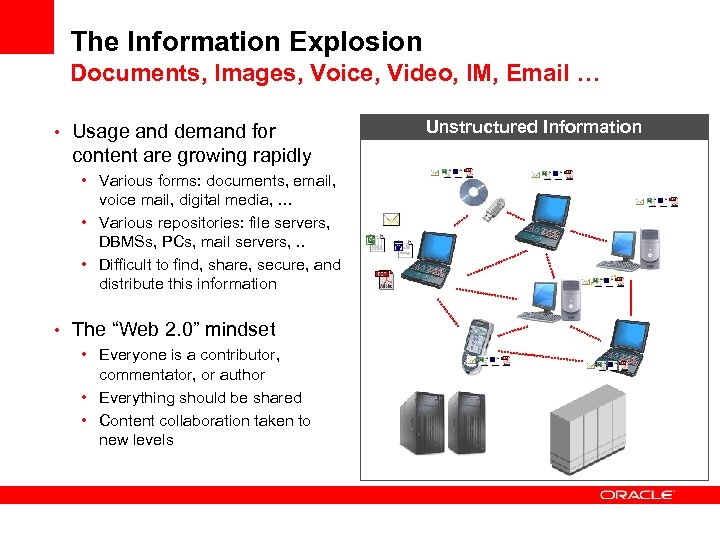 The Information Explosion Documents, Images, Voice, Video, IM, Email … • Usage and demand for content are growing rapidly • Various forms: documents, email, voice mail, digital media, … • Various repositories: file servers, DBMSs, PCs, mail servers, . . • Difficult to find, share, secure, and distribute this information • The “Web 2. 0” mindset • Everyone is a contributor, commentator, or author • Everything should be shared • Content collaboration taken to new levels Unstructured Information
The Information Explosion Documents, Images, Voice, Video, IM, Email … • Usage and demand for content are growing rapidly • Various forms: documents, email, voice mail, digital media, … • Various repositories: file servers, DBMSs, PCs, mail servers, . . • Difficult to find, share, secure, and distribute this information • The “Web 2. 0” mindset • Everyone is a contributor, commentator, or author • Everything should be shared • Content collaboration taken to new levels Unstructured Information
 The Information Explosion Situation Today • Content growth • Content volume issues • Content discovery • Litigation preparedness
The Information Explosion Situation Today • Content growth • Content volume issues • Content discovery • Litigation preparedness
 The Information Explosion Content Growth • Companies are generating tremendous amounts of content … • And those growth rates are themselves growing – – – Email Instant Messaging Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, Power. Point, etc. ) Web Content Reports Collaborative content • Most of the content is (at best) redundant, and (more likely) outdated or counterproductive
The Information Explosion Content Growth • Companies are generating tremendous amounts of content … • And those growth rates are themselves growing – – – Email Instant Messaging Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, Power. Point, etc. ) Web Content Reports Collaborative content • Most of the content is (at best) redundant, and (more likely) outdated or counterproductive
 The Information Explosion Content Volume Issues • Issues for Users – Workers spend large amounts of time searching for content – Outdated or uncontrolled content can lead to poor decisions • Issues for IT – Large amounts of money are spent finding and implementing technologies to cope • Search • Storage • Enterprise Content Management • Archiving / Backup – Labor is spent managing and implementing these technologies, and handling requests for content – IT is often designing content retention policies, and shouldn’t be
The Information Explosion Content Volume Issues • Issues for Users – Workers spend large amounts of time searching for content – Outdated or uncontrolled content can lead to poor decisions • Issues for IT – Large amounts of money are spent finding and implementing technologies to cope • Search • Storage • Enterprise Content Management • Archiving / Backup – Labor is spent managing and implementing these technologies, and handling requests for content – IT is often designing content retention policies, and shouldn’t be
 The Information Explosion Content Volume Issues (cont. ) • Issues for Legal – Discovery is extremely costly – The cost of discovery is (roughly) proportional to the volume of content – From a discovery perspective, it is risky to keep information that should be eliminated
The Information Explosion Content Volume Issues (cont. ) • Issues for Legal – Discovery is extremely costly – The cost of discovery is (roughly) proportional to the volume of content – From a discovery perspective, it is risky to keep information that should be eliminated
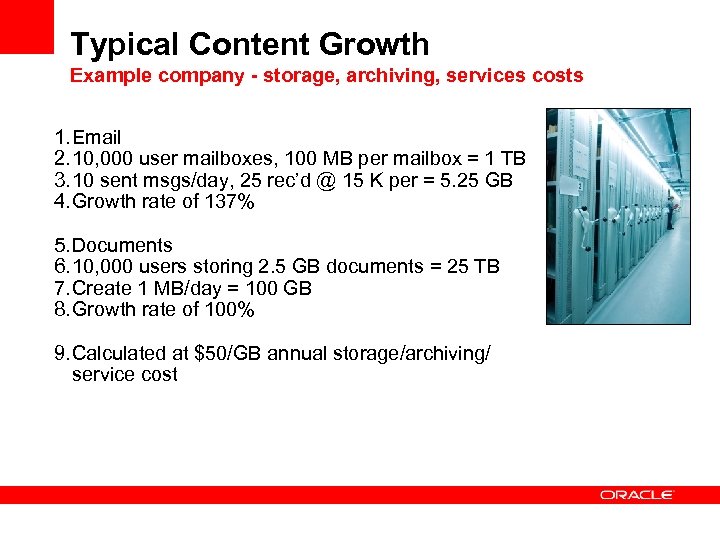 Typical Content Growth Example company - storage, archiving, services costs 1. Email 2. 10, 000 user mailboxes, 100 MB per mailbox = 1 TB 3. 10 sent msgs/day, 25 rec’d @ 15 K per = 5. 25 GB 4. Growth rate of 137% 5. Documents 6. 10, 000 users storing 2. 5 GB documents = 25 TB 7. Create 1 MB/day = 100 GB 8. Growth rate of 100% 9. Calculated at $50/GB annual storage/archiving/ service cost
Typical Content Growth Example company - storage, archiving, services costs 1. Email 2. 10, 000 user mailboxes, 100 MB per mailbox = 1 TB 3. 10 sent msgs/day, 25 rec’d @ 15 K per = 5. 25 GB 4. Growth rate of 137% 5. Documents 6. 10, 000 users storing 2. 5 GB documents = 25 TB 7. Create 1 MB/day = 100 GB 8. Growth rate of 100% 9. Calculated at $50/GB annual storage/archiving/ service cost
 The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable – “Today it is black letter law that computerized data is discoverable if relevant. " Anti-Monopoly, Inc. v. Hasbro, Inc. , No. 94 CIV 2120, 1995 U. S. Dist. LEXIS 16355 (S. D. N. Y. 1995)
The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable – “Today it is black letter law that computerized data is discoverable if relevant. " Anti-Monopoly, Inc. v. Hasbro, Inc. , No. 94 CIV 2120, 1995 U. S. Dist. LEXIS 16355 (S. D. N. Y. 1995)
 The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse – “Deficiencies in the retrieval system… cannot be sufficient to defeat a good faith request to examine relevant information. ” “If a party chooses an electronic storage method, the necessity for a retrieval program or method is an ordinary and foreseeable risk. ” Kaufman v. Kinko’s Inc. , 2002 WL 32123851 (Del. Ch. 2002)
The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse – “Deficiencies in the retrieval system… cannot be sufficient to defeat a good faith request to examine relevant information. ” “If a party chooses an electronic storage method, the necessity for a retrieval program or method is an ordinary and foreseeable risk. ” Kaufman v. Kinko’s Inc. , 2002 WL 32123851 (Del. Ch. 2002)
 The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse • Discovery cost is generally not a valid excuse – Plaintiff sought 800 backup tapes from Toshiba claimed cost of processing tape (analyzing data, identifying and restoring files, searching, producing specified data) would have been $1. 5 to $1. 9 million. Toshiba asked plaintiff to split or cover the cost. Trial court ordered Toshiba to produce at their own expense. Toshiba v. Superior Court of Santa Clara County, 124 Cal. App. 4 th 72 (Cal App. 2004).
The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse • Discovery cost is generally not a valid excuse – Plaintiff sought 800 backup tapes from Toshiba claimed cost of processing tape (analyzing data, identifying and restoring files, searching, producing specified data) would have been $1. 5 to $1. 9 million. Toshiba asked plaintiff to split or cover the cost. Trial court ordered Toshiba to produce at their own expense. Toshiba v. Superior Court of Santa Clara County, 124 Cal. App. 4 th 72 (Cal App. 2004).
 The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse • Discovery cost is generally not a valid excuse • Spoliation can be extremely—even fatally—costly – Adverse inference instruction contributed to $1. 45 billion judgment against Morgan Stanley. Finding Morgan Stanley grossly negligent in failing to produce Emails, overwriting Emails after twelve months in violation of an SEC order, failing to conduct proper searches for back-up tapes that may have contained Emails, and failing to notify plaintiff or the Court when it discovered new Emails. Coleman Holdings v. Morgan Stanley & Co. , No. CA 003 -5045 AI, 2005 WL 674885, at *9 -10 (Fla. Cir. Ct. March 23, 2005).
The Information Explosion Discovery • Almost everything electronic is discoverable • Discovery difficulty is not a valid excuse • Discovery cost is generally not a valid excuse • Spoliation can be extremely—even fatally—costly – Adverse inference instruction contributed to $1. 45 billion judgment against Morgan Stanley. Finding Morgan Stanley grossly negligent in failing to produce Emails, overwriting Emails after twelve months in violation of an SEC order, failing to conduct proper searches for back-up tapes that may have contained Emails, and failing to notify plaintiff or the Court when it discovered new Emails. Coleman Holdings v. Morgan Stanley & Co. , No. CA 003 -5045 AI, 2005 WL 674885, at *9 -10 (Fla. Cir. Ct. March 23, 2005).
 Restoration Costs The Cost to IT • What would it cost to find everywhere content exists in your organization – file system, email, applications, repositories, desktop, archives, backup tapes. • What would it cost you to restore this content for review? Projected Content Restoration Costs Managed Storage Savings 2007 26, 000 $15, 843, 750 26, 000 $0 2008 53, 365 $32, 519, 297 40, 365 $7, 921, 875 2009 80, 730 $49, 194, 844 47, 548 $20, 220, 586 Total $97, 557, 891 $28, 142, 461
Restoration Costs The Cost to IT • What would it cost to find everywhere content exists in your organization – file system, email, applications, repositories, desktop, archives, backup tapes. • What would it cost you to restore this content for review? Projected Content Restoration Costs Managed Storage Savings 2007 26, 000 $15, 843, 750 26, 000 $0 2008 53, 365 $32, 519, 297 40, 365 $7, 921, 875 2009 80, 730 $49, 194, 844 47, 548 $20, 220, 586 Total $97, 557, 891 $28, 142, 461
 The Information Explosion Litigation Preparedness • In case of litigation, it is important to have strong control over your content • Know what evidence you have • Quickly search it for relevant information • Present organized data at discovery meetings • Catalog of content, per new Civil Rules of Federal Procedure
The Information Explosion Litigation Preparedness • In case of litigation, it is important to have strong control over your content • Know what evidence you have • Quickly search it for relevant information • Present organized data at discovery meetings • Catalog of content, per new Civil Rules of Federal Procedure
 Knowing Hand • Organizations can instantly review their information to assess their position in litigation, enabling decisions such as whether or not to settle a case: • Average number of lawsuits for U. S. companies with over $1 billion in • • • revenue: 147 lawsuits Average cost of lawsuits for companies with over $1 billion in revenue: $1. 5 million 25% of lawsuits settled earlier based on “knowing hand” and immediate access to evidence (140 lawsuits x 25% = 35). Estimated savings approximated at 20% per early settled lawsuit ($1. 5 million average lawsuit cost x 20% = $300, 000). • Year 1 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. • Year 2 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. • Year 3 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. Total Savings 3 Years: 105 lawsuits settled early at a settlement savings of $31. 5 million. Now add savings of discovery costs, attorneys fees, etc.
Knowing Hand • Organizations can instantly review their information to assess their position in litigation, enabling decisions such as whether or not to settle a case: • Average number of lawsuits for U. S. companies with over $1 billion in • • • revenue: 147 lawsuits Average cost of lawsuits for companies with over $1 billion in revenue: $1. 5 million 25% of lawsuits settled earlier based on “knowing hand” and immediate access to evidence (140 lawsuits x 25% = 35). Estimated savings approximated at 20% per early settled lawsuit ($1. 5 million average lawsuit cost x 20% = $300, 000). • Year 1 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. • Year 2 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. • Year 3 Savings: 35 lawsuits settled early at a savings of $10. 5 million. Total Savings 3 Years: 105 lawsuits settled early at a settlement savings of $31. 5 million. Now add savings of discovery costs, attorneys fees, etc.
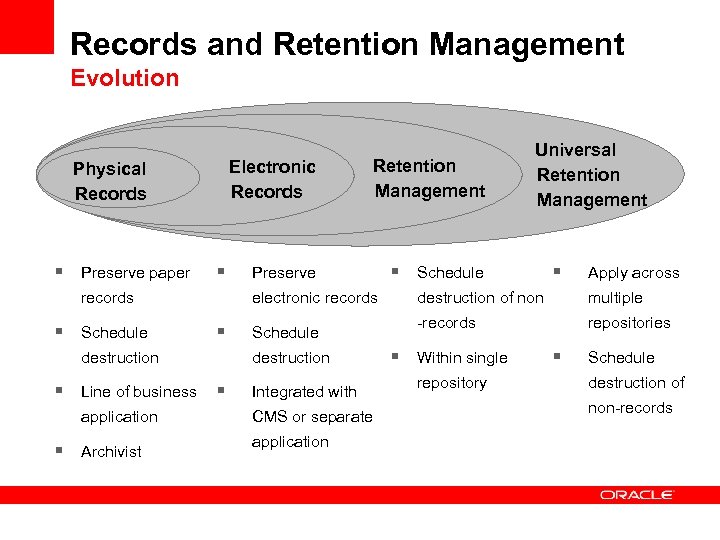 Records and Retention Management Evolution Physical Records § Preserve paper Electronic Records § records § Schedule § § Line of business § § Archivist Preserve electronic records destruction application Retention Management Schedule destruction Integrated with CMS or separate application Universal Retention Management § Schedule § Apply across destruction of non multiple -records repositories § Within single repository § Schedule destruction of non-records
Records and Retention Management Evolution Physical Records § Preserve paper Electronic Records § records § Schedule § § Line of business § § Archivist Preserve electronic records destruction application Retention Management Schedule destruction Integrated with CMS or separate application Universal Retention Management § Schedule § Apply across destruction of non multiple -records repositories § Within single repository § Schedule destruction of non-records

 Oracle Universal Records Management provides a single console to create and administer information lifecycle management functions such as retention, disposition, holds and discovery on both physical and electronic information, with a framework for extending to any repository
Oracle Universal Records Management provides a single console to create and administer information lifecycle management functions such as retention, disposition, holds and discovery on both physical and electronic information, with a framework for extending to any repository
 Oracle Universal Records Management • Single console to create and administer • Retention and disposition rules • Holds and discovery • Electronic and Physical records • Retention management of information across enterprise • A framework that extends records management practices to any repository • In-place management of content • Hot-pluggable support for Oracle and third-party repositories, security solutions and enterprise applications • Proven, defensible system provides full audit trail and certificates of destruction
Oracle Universal Records Management • Single console to create and administer • Retention and disposition rules • Holds and discovery • Electronic and Physical records • Retention management of information across enterprise • A framework that extends records management practices to any repository • In-place management of content • Hot-pluggable support for Oracle and third-party repositories, security solutions and enterprise applications • Proven, defensible system provides full audit trail and certificates of destruction
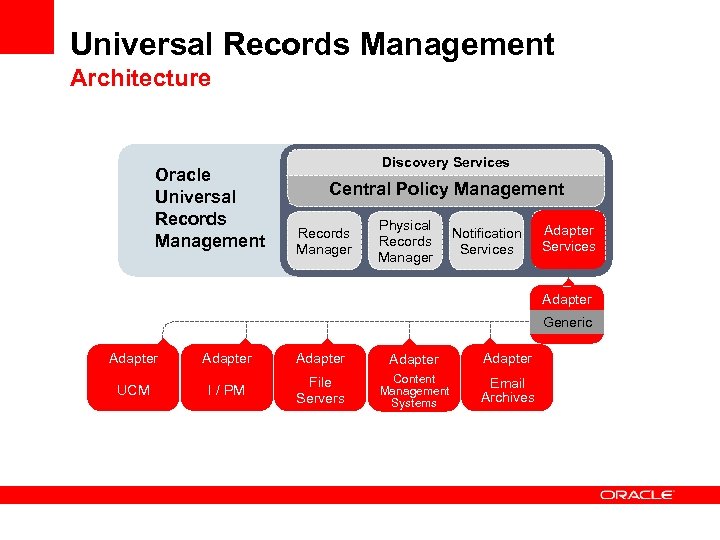 Universal Records Management Architecture Oracle Universal Records Management Discovery Services Central Policy Management Records Manager Physical Records Manager Notification Services Adapter Generic Adapter Adapter UCM I / PM File Servers Content Management Systems Email Archives
Universal Records Management Architecture Oracle Universal Records Management Discovery Services Central Policy Management Records Manager Physical Records Manager Notification Services Adapter Generic Adapter Adapter UCM I / PM File Servers Content Management Systems Email Archives
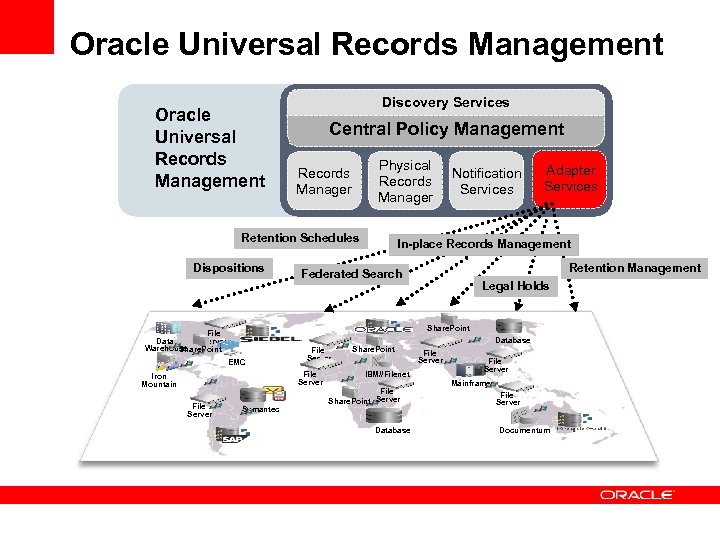 Oracle Universal Records Management Discovery Services Central Policy Management Physical Records Manager Retention Schedules Dispositions Adapter Services In-place Records Management Retention Management Federated Search Legal Holds Share. Point File Data Server Warehouse Share. Point Database EMC File Server Iron Mountain File Server Notification Services Symantec Share. Point IBM//Filenet File Share. Point Server Database File Server Mainframes File Server Documentum
Oracle Universal Records Management Discovery Services Central Policy Management Physical Records Manager Retention Schedules Dispositions Adapter Services In-place Records Management Retention Management Federated Search Legal Holds Share. Point File Data Server Warehouse Share. Point Database EMC File Server Iron Mountain File Server Notification Services Symantec Share. Point IBM//Filenet File Share. Point Server Database File Server Mainframes File Server Documentum
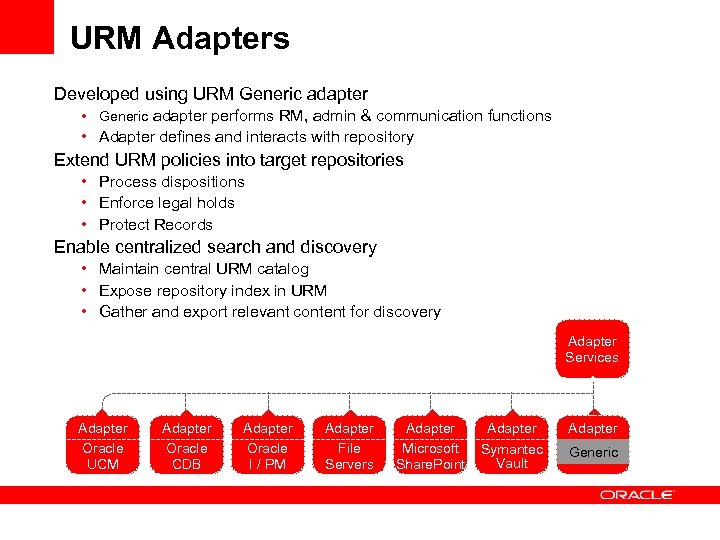 URM Adapters Developed using URM Generic adapter • Generic adapter performs RM, admin & communication functions • Adapter defines and interacts with repository Extend URM policies into target repositories • Process dispositions • Enforce legal holds • Protect Records Enable centralized search and discovery • Maintain central URM catalog • Expose repository index in URM • Gather and export relevant content for discovery Adapter Services Adapter Oracle UCM Adapter Oracle CDB Adapter Oracle I / PM Adapter File Servers Adapter Microsoft Share. Point Adapter Symantec Generic Services Vault
URM Adapters Developed using URM Generic adapter • Generic adapter performs RM, admin & communication functions • Adapter defines and interacts with repository Extend URM policies into target repositories • Process dispositions • Enforce legal holds • Protect Records Enable centralized search and discovery • Maintain central URM catalog • Expose repository index in URM • Gather and export relevant content for discovery Adapter Services Adapter Oracle UCM Adapter Oracle CDB Adapter Oracle I / PM Adapter File Servers Adapter Microsoft Share. Point Adapter Symantec Generic Services Vault
 Customer Scenario Email Archiving • Customer wants to control retention of email archiving system such as Universal Online Archive • Connects URM to Email Archive, sets rules to classify emails as records: • CEO emails are kept 7 years • In case of discovery, URM can search and find any applicable records for litigation • Records can be instantly placed on hold along with content found in other repositories • Content that is deleted has a full audit trail and certificate of destruction to show it is according to policy
Customer Scenario Email Archiving • Customer wants to control retention of email archiving system such as Universal Online Archive • Connects URM to Email Archive, sets rules to classify emails as records: • CEO emails are kept 7 years • In case of discovery, URM can search and find any applicable records for litigation • Records can be instantly placed on hold along with content found in other repositories • Content that is deleted has a full audit trail and certificate of destruction to show it is according to policy
 Customer Scenario Share. Point • Customer wants to control retention of Share. Point content and • • • libraries/sites Connects URM to Share. Point instances, identifies content based upon metadata, and matches the content to retention policies Libraries can be monitored for regular review of activity – libraries or sites that have become inactive can be archived or deleted In case of discovery, URM can search and find any applicable content for litigation across all Share. Point sites Relevant content across all Share. Point sites can be instantly placed on hold along with content found in other repositories Content that is deleted has a full audit trail and certificate of destruction to show it is according to policy
Customer Scenario Share. Point • Customer wants to control retention of Share. Point content and • • • libraries/sites Connects URM to Share. Point instances, identifies content based upon metadata, and matches the content to retention policies Libraries can be monitored for regular review of activity – libraries or sites that have become inactive can be archived or deleted In case of discovery, URM can search and find any applicable content for litigation across all Share. Point sites Relevant content across all Share. Point sites can be instantly placed on hold along with content found in other repositories Content that is deleted has a full audit trail and certificate of destruction to show it is according to policy


 The “Ideal” Solution Don’t just cope, fix it • Universal: Address the root cause by cataloging, applying retention policies, and applying holds to all content – Regardless of location – Regardless of whether it is a record or not – Regardless of whether it is electronic or physical • In-place: Apply holds and retention management actions in- place – Minimize impact on users – Reduce issues associated with moving electronic content – Leverage existing applications • Flexible: Provide features needed to address all content, not just records – Retention triggers based on calendar, event, usage, revision – Retention actions: Delete, move, alert, create
The “Ideal” Solution Don’t just cope, fix it • Universal: Address the root cause by cataloging, applying retention policies, and applying holds to all content – Regardless of location – Regardless of whether it is a record or not – Regardless of whether it is electronic or physical • In-place: Apply holds and retention management actions in- place – Minimize impact on users – Reduce issues associated with moving electronic content – Leverage existing applications • Flexible: Provide features needed to address all content, not just records – Retention triggers based on calendar, event, usage, revision – Retention actions: Delete, move, alert, create
 The “Ideal” Solution Benefits • Reduce the risk of keeping too much or too little • • information Reduce costs of storage, restoration, discovery and litigation Support regulatory requirements Reduce clutter so that users can do their jobs more effectively …All while applying legal holds
The “Ideal” Solution Benefits • Reduce the risk of keeping too much or too little • • information Reduce costs of storage, restoration, discovery and litigation Support regulatory requirements Reduce clutter so that users can do their jobs more effectively …All while applying legal holds

 Next Steps • See a Universal Records Management demo viewlet - www. oracle. com/goto/urm • Read the white paper “Lowering e-Discovery Costs Through Enterprise Records and Retention Management” www. oracle. com/goto/urm • Get more information on Oracle Universal Content Management - http: //www. oracle. com/products/middleware/contentmanagement/index. html • Subscribe to the Content Management Newsletter www. oracle. com/newsletters
Next Steps • See a Universal Records Management demo viewlet - www. oracle. com/goto/urm • Read the white paper “Lowering e-Discovery Costs Through Enterprise Records and Retention Management” www. oracle. com/goto/urm • Get more information on Oracle Universal Content Management - http: //www. oracle. com/products/middleware/contentmanagement/index. html • Subscribe to the Content Management Newsletter www. oracle. com/newsletters




