e60dc433d6f51154f62cf09f710f8199.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

 What Is Cloud Computing
What Is Cloud Computing
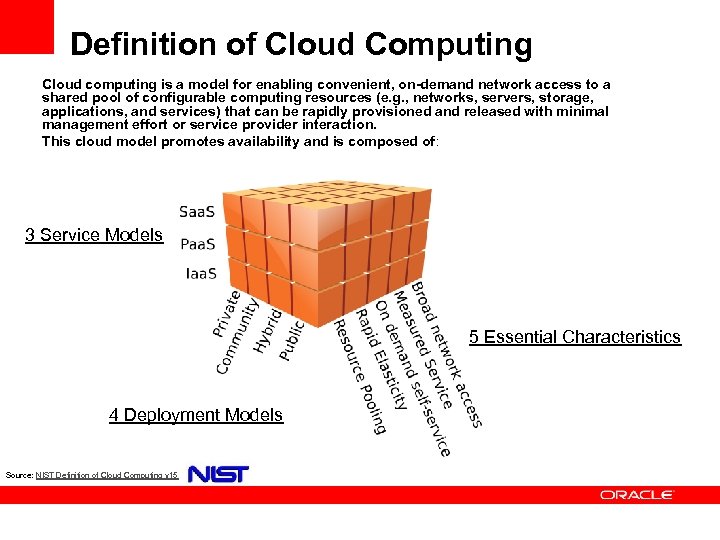 Definition of Cloud Computing Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e. g. , networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of: 3 Service Models 5 Essential Characteristics 4 Deployment Models Source: NIST Definition of Cloud Computing v 15
Definition of Cloud Computing Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e. g. , networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of: 3 Service Models 5 Essential Characteristics 4 Deployment Models Source: NIST Definition of Cloud Computing v 15
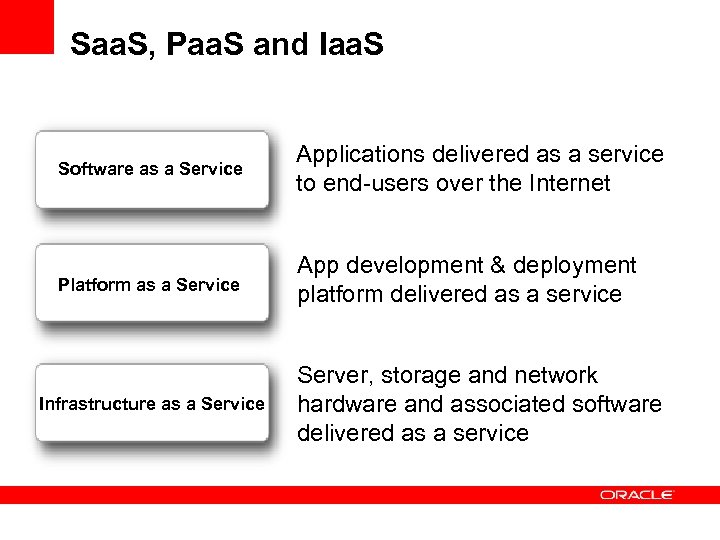 Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S Software as a Service Applications delivered as a service to end-users over the Internet Platform as a Service App development & deployment platform delivered as a service Infrastructure as a Service Server, storage and network hardware and associated software delivered as a service
Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S Software as a Service Applications delivered as a service to end-users over the Internet Platform as a Service App development & deployment platform delivered as a service Infrastructure as a Service Server, storage and network hardware and associated software delivered as a service
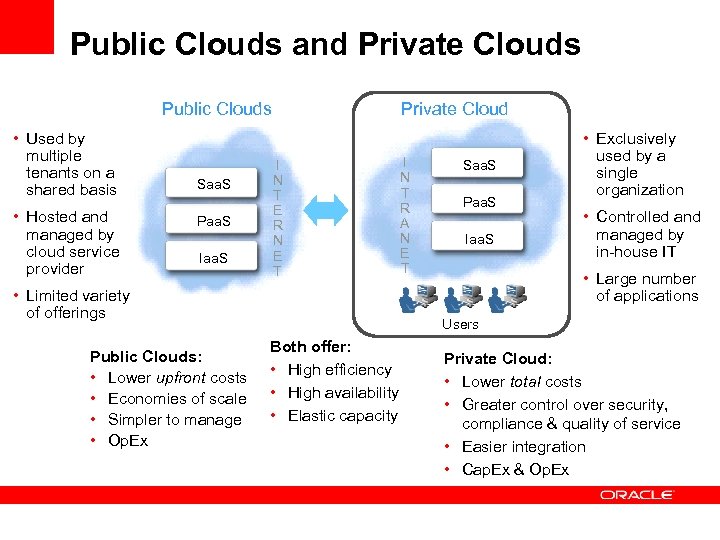 Public Clouds and Private Clouds Private Cloud Public Clouds • Used by multiple tenants on a shared basis • Hosted and managed by cloud service provider Saa. S Paa. S I N T E R N E T • Limited variety of offerings Public Clouds: • Lower upfront costs • Economies of scale • Simpler to manage • Op. Ex I N T R A N E T Saa. S Paa. S Iaa. S • Exclusively used by a single organization • Controlled and managed by in-house IT • Large number of applications Users Both offer: • High efficiency • High availability • Elastic capacity Private Cloud: • Lower total costs • Greater control over security, compliance & quality of service • Easier integration • Cap. Ex & Op. Ex
Public Clouds and Private Clouds Private Cloud Public Clouds • Used by multiple tenants on a shared basis • Hosted and managed by cloud service provider Saa. S Paa. S I N T E R N E T • Limited variety of offerings Public Clouds: • Lower upfront costs • Economies of scale • Simpler to manage • Op. Ex I N T R A N E T Saa. S Paa. S Iaa. S • Exclusively used by a single organization • Controlled and managed by in-house IT • Large number of applications Users Both offer: • High efficiency • High availability • Elastic capacity Private Cloud: • Lower total costs • Greater control over security, compliance & quality of service • Easier integration • Cap. Ex & Op. Ex
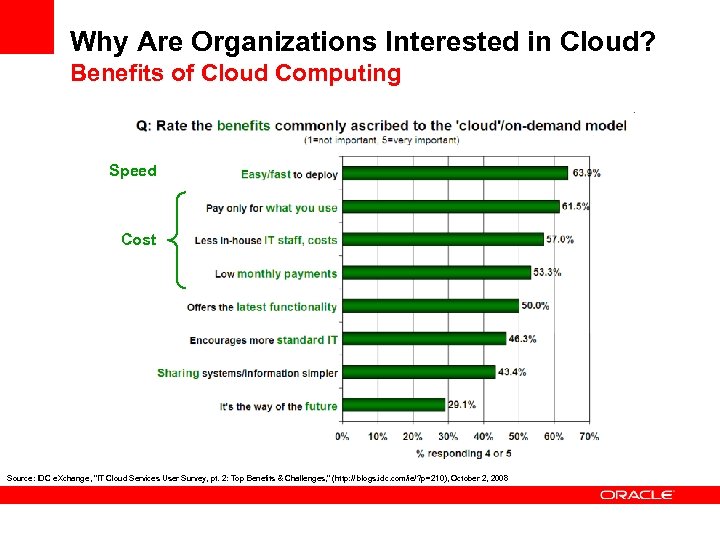 Why Are Organizations Interested in Cloud? Benefits of Cloud Computing Speed Cost Source: IDC e. Xchange, "IT Cloud Services User Survey, pt. 2: Top Benefits & Challenges, " (http: // blogs. idc. com/ie/? p=210), October 2, 2008
Why Are Organizations Interested in Cloud? Benefits of Cloud Computing Speed Cost Source: IDC e. Xchange, "IT Cloud Services User Survey, pt. 2: Top Benefits & Challenges, " (http: // blogs. idc. com/ie/? p=210), October 2, 2008
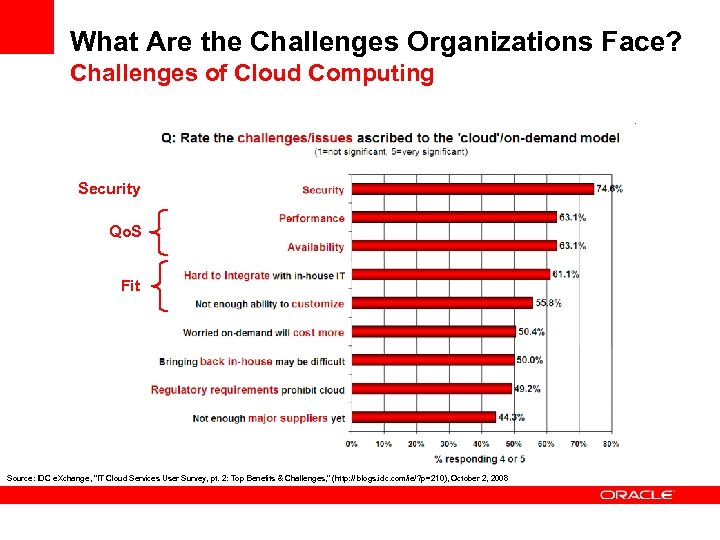 What Are the Challenges Organizations Face? Challenges of Cloud Computing Security Qo. S Fit Source: IDC e. Xchange, "IT Cloud Services User Survey, pt. 2: Top Benefits & Challenges, " (http: // blogs. idc. com/ie/? p=210), October 2, 2008
What Are the Challenges Organizations Face? Challenges of Cloud Computing Security Qo. S Fit Source: IDC e. Xchange, "IT Cloud Services User Survey, pt. 2: Top Benefits & Challenges, " (http: // blogs. idc. com/ie/? p=210), October 2, 2008
 Choose Cloud Strategically
Choose Cloud Strategically
 Is there a G-Cloud? • In G-Cloud we define a “Private Cloud” as an infrastructure dedicated to government most likely amalgam of several compute utilities targeted to improve citizen services. Therefore it is a hybrid cloud comprised of both private and public deployment models.
Is there a G-Cloud? • In G-Cloud we define a “Private Cloud” as an infrastructure dedicated to government most likely amalgam of several compute utilities targeted to improve citizen services. Therefore it is a hybrid cloud comprised of both private and public deployment models.
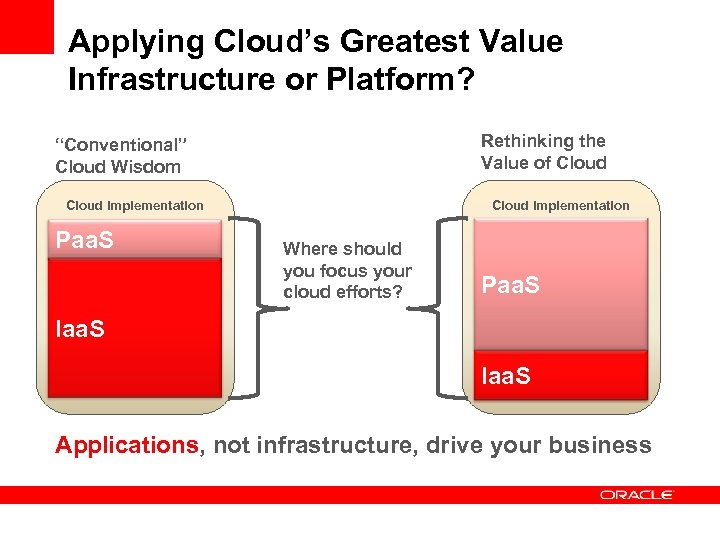 Applying Cloud’s Greatest Value Infrastructure or Platform? Rethinking the Value of Cloud “Conventional” Cloud Wisdom Cloud Implementation Paa. S Cloud Implementation Where should you focus your cloud efforts? Paa. S Iaa. S Applications, not infrastructure, drive your business
Applying Cloud’s Greatest Value Infrastructure or Platform? Rethinking the Value of Cloud “Conventional” Cloud Wisdom Cloud Implementation Paa. S Cloud Implementation Where should you focus your cloud efforts? Paa. S Iaa. S Applications, not infrastructure, drive your business
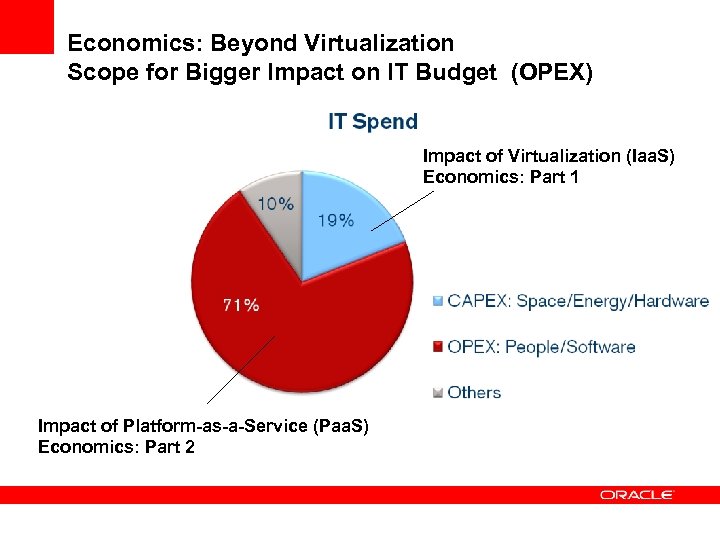 Economics: Beyond Virtualization Scope for Bigger Impact on IT Budget (OPEX) Impact of Virtualization (Iaa. S) Economics: Part 1 Impact of Platform-as-a-Service (Paa. S) Economics: Part 2
Economics: Beyond Virtualization Scope for Bigger Impact on IT Budget (OPEX) Impact of Virtualization (Iaa. S) Economics: Part 1 Impact of Platform-as-a-Service (Paa. S) Economics: Part 2
 Oracle Private Paa. S: What, Why and How
Oracle Private Paa. S: What, Why and How
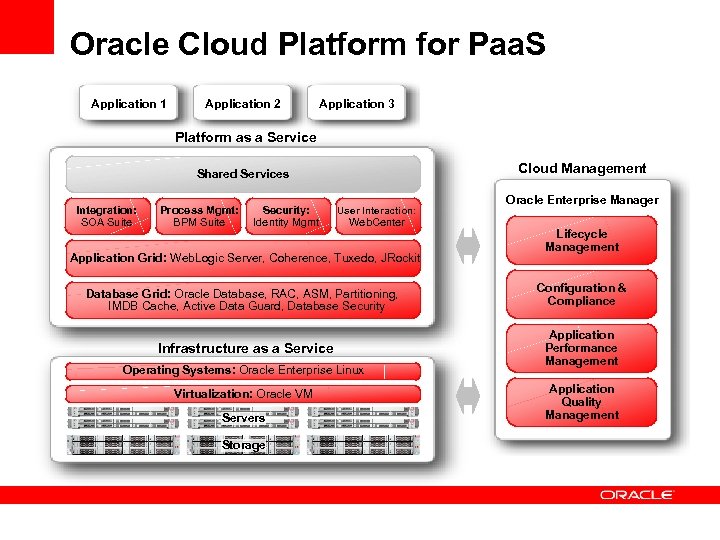 Oracle Cloud Platform for Paa. S Application 1 Application 2 Application 3 Platform as a Service Cloud Management Shared Services Integration: SOA Suite Process Mgmt: BPM Suite Security: Identity Mgmt User Interaction: Web. Center Application Grid: Web. Logic Server, Coherence, Tuxedo, JRockit Database Grid: Oracle Database, RAC, ASM, Partitioning, IMDB Cache, Active Data Guard, Database Security Infrastructure as a Service Operating Systems: Oracle Enterprise Linux Virtualization: Oracle VM Servers Storage Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Configuration & Compliance Application Performance Management Application Quality Management
Oracle Cloud Platform for Paa. S Application 1 Application 2 Application 3 Platform as a Service Cloud Management Shared Services Integration: SOA Suite Process Mgmt: BPM Suite Security: Identity Mgmt User Interaction: Web. Center Application Grid: Web. Logic Server, Coherence, Tuxedo, JRockit Database Grid: Oracle Database, RAC, ASM, Partitioning, IMDB Cache, Active Data Guard, Database Security Infrastructure as a Service Operating Systems: Oracle Enterprise Linux Virtualization: Oracle VM Servers Storage Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Configuration & Compliance Application Performance Management Application Quality Management
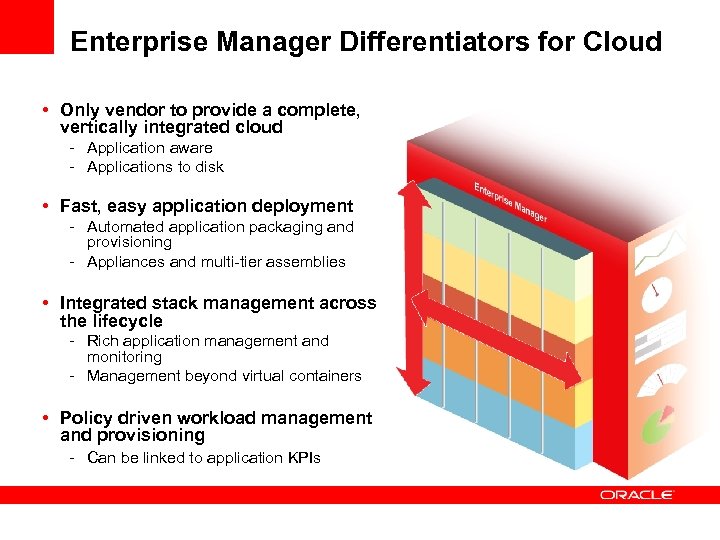 Enterprise Manager Differentiators for Cloud • Only vendor to provide a complete, vertically integrated cloud - Application aware - Applications to disk • Fast, easy application deployment - Automated application packaging and provisioning - Appliances and multi-tier assemblies • Integrated stack management across the lifecycle - Rich application management and monitoring - Management beyond virtual containers • Policy driven workload management and provisioning - Can be linked to application KPIs
Enterprise Manager Differentiators for Cloud • Only vendor to provide a complete, vertically integrated cloud - Application aware - Applications to disk • Fast, easy application deployment - Automated application packaging and provisioning - Appliances and multi-tier assemblies • Integrated stack management across the lifecycle - Rich application management and monitoring - Management beyond virtual containers • Policy driven workload management and provisioning - Can be linked to application KPIs
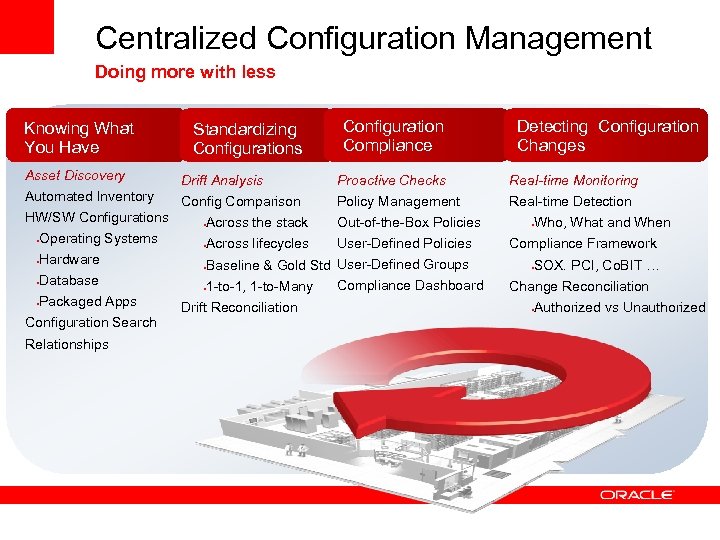 Centralized Configuration Management Doing more with less Knowing What You Have Asset Discovery Automated Inventory HW/SW Configurations Operating Systems Hardware Database Packaged Apps Configuration Search Relationships Standardizing Configurations Configuration Compliance Detecting Configuration Changes Drift Analysis Proactive Checks Real-time Monitoring Config Comparison Policy Management Real-time Detection Across the stack Out-of-the-Box Policies Across lifecycles User-Defined Policies Baseline & Gold Std User-Defined Groups Compliance Dashboard 1 -to-1, 1 -to-Many Drift Reconciliation Who, What and When Compliance Framework SOX. PCI, Co. BIT … Change Reconciliation Authorized vs Unauthorized
Centralized Configuration Management Doing more with less Knowing What You Have Asset Discovery Automated Inventory HW/SW Configurations Operating Systems Hardware Database Packaged Apps Configuration Search Relationships Standardizing Configurations Configuration Compliance Detecting Configuration Changes Drift Analysis Proactive Checks Real-time Monitoring Config Comparison Policy Management Real-time Detection Across the stack Out-of-the-Box Policies Across lifecycles User-Defined Policies Baseline & Gold Std User-Defined Groups Compliance Dashboard 1 -to-1, 1 -to-Many Drift Reconciliation Who, What and When Compliance Framework SOX. PCI, Co. BIT … Change Reconciliation Authorized vs Unauthorized
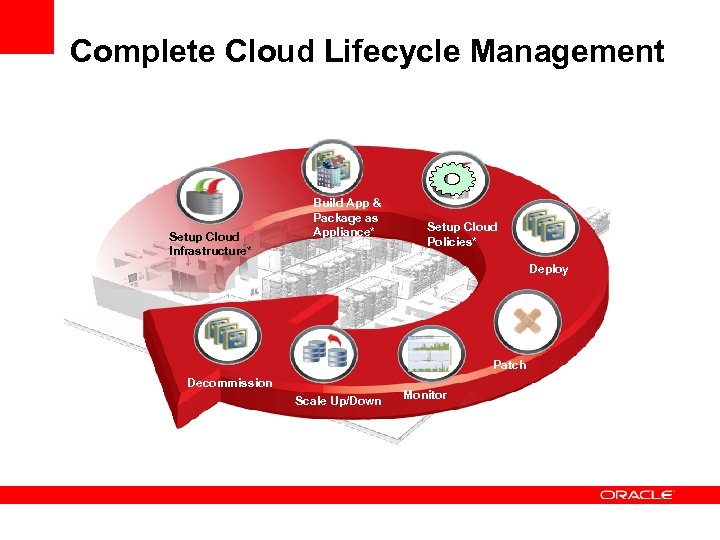 Complete Cloud Lifecycle Management Setup Cloud Infrastructure* Build App & Package as Appliance* Setup Cloud Policies* Deploy Patch Decommission Scale Up/Down Monitor
Complete Cloud Lifecycle Management Setup Cloud Infrastructure* Build App & Package as Appliance* Setup Cloud Policies* Deploy Patch Decommission Scale Up/Down Monitor
 Summary
Summary
 Oracle Cloud Computing Summary • Oracle’s cloud computing strategy is to offer: 1. Technology to build private clouds or run in public clouds 2. Applications deployed in private shared services environment or via public Saa. S • Oracle helps enterprise IT evolve to become private cloud service providers based on our leadership position in grid computing • Oracle offers a comprehensive set of building blocks for building and managing public and private clouds from applications to disk
Oracle Cloud Computing Summary • Oracle’s cloud computing strategy is to offer: 1. Technology to build private clouds or run in public clouds 2. Applications deployed in private shared services environment or via public Saa. S • Oracle helps enterprise IT evolve to become private cloud service providers based on our leadership position in grid computing • Oracle offers a comprehensive set of building blocks for building and managing public and private clouds from applications to disk
 © 2009 Oracle – Proprietary and Confidential 19
© 2009 Oracle – Proprietary and Confidential 19


