 Insert Manufacturing 1
Insert Manufacturing 1
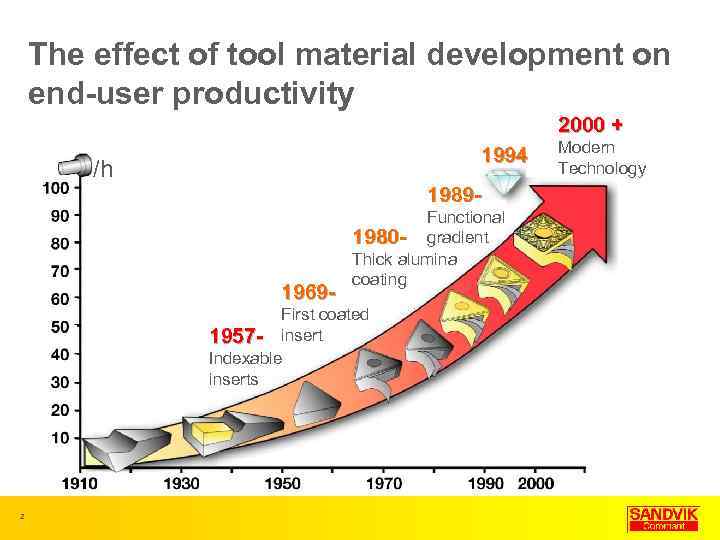 The effect of tool material development on end-user productivity 2000 + 1994 /h 1989 - 1969 - Functional 1980 - gradient Thick alumina coating First coated 1957 - insert Indexable inserts 2 Modern Technology
The effect of tool material development on end-user productivity 2000 + 1994 /h 1989 - 1969 - Functional 1980 - gradient Thick alumina coating First coated 1957 - insert Indexable inserts 2 Modern Technology
 The design of a modern coated cemented carbide Ti. N - wear detection Al 2 O 3 - chemical and thermal wear resistance Ti. CN - mechanical wear resistance Functional gradient- edge fracture resistance Cemented carbide - plastic deformation resistance 3
The design of a modern coated cemented carbide Ti. N - wear detection Al 2 O 3 - chemical and thermal wear resistance Ti. CN - mechanical wear resistance Functional gradient- edge fracture resistance Cemented carbide - plastic deformation resistance 3
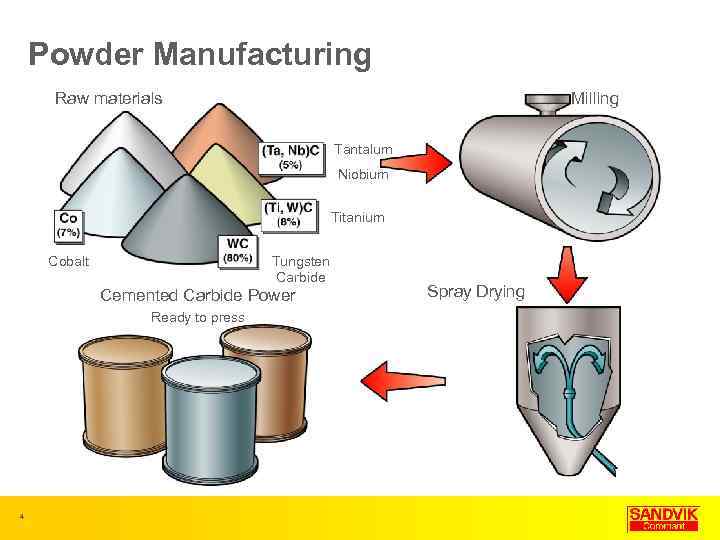 Powder Manufacturing Raw materials Milling Tantalum Niobium Titanium Cobalt Tungsten Carbide Cemented Carbide Power Ready to press 4 Spray Drying
Powder Manufacturing Raw materials Milling Tantalum Niobium Titanium Cobalt Tungsten Carbide Cemented Carbide Power Ready to press 4 Spray Drying
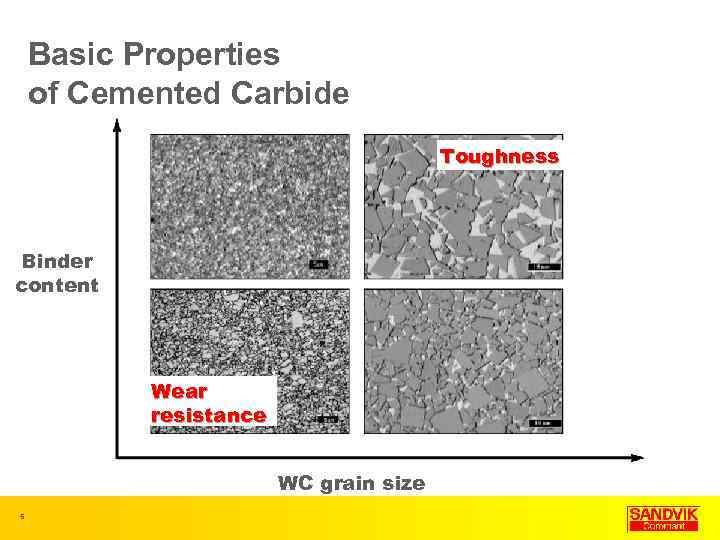 Basic Properties of Cemented Carbide Toughness Binder content Wear resistance WC grain size 5
Basic Properties of Cemented Carbide Toughness Binder content Wear resistance WC grain size 5
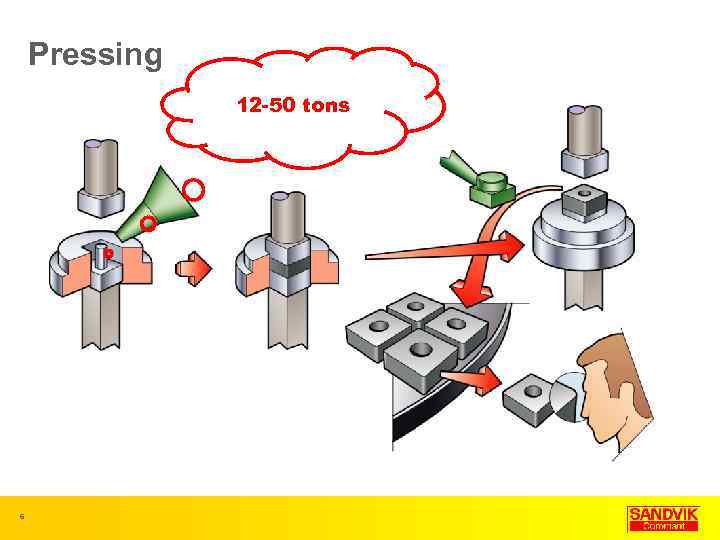 Pressing 12 -50 tons 6
Pressing 12 -50 tons 6
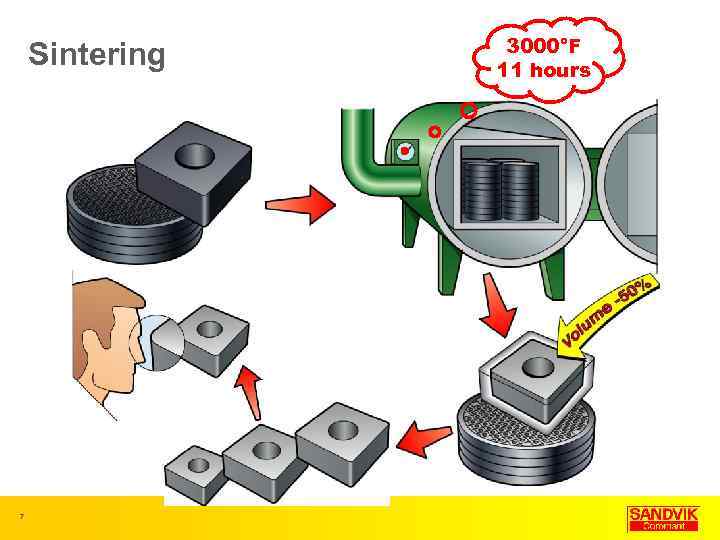 Sintering 7 3000°F 11 hours
Sintering 7 3000°F 11 hours
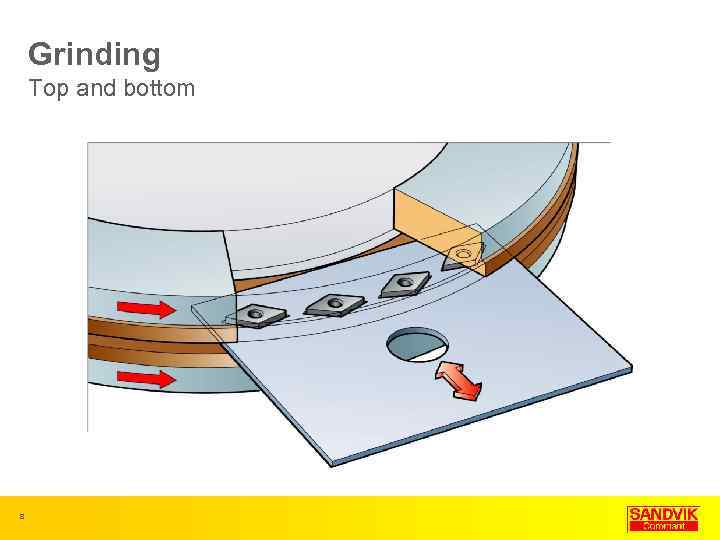 Grinding Top and bottom 8
Grinding Top and bottom 8
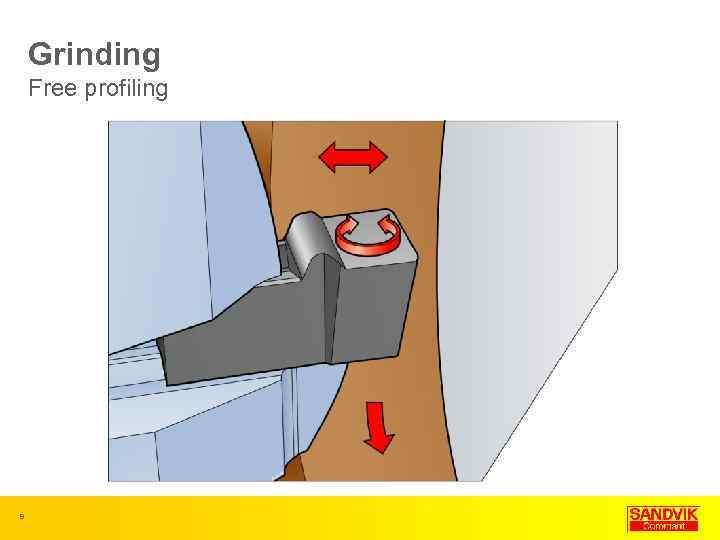 Grinding Free profiling 9
Grinding Free profiling 9
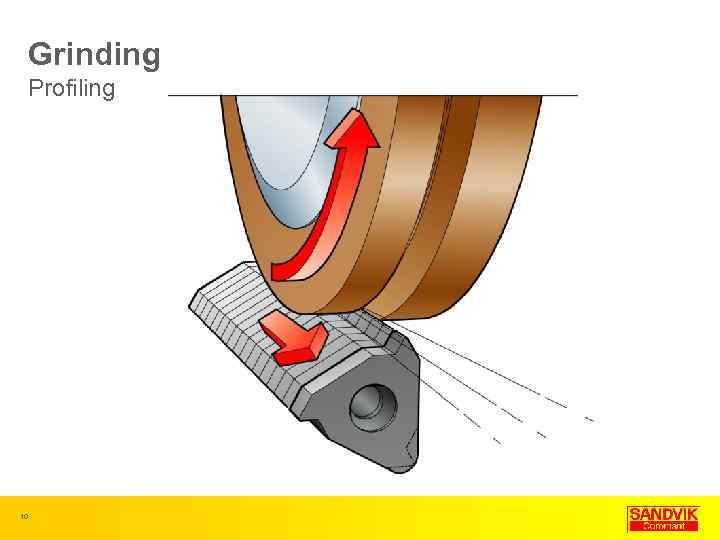 Grinding Profiling 10
Grinding Profiling 10
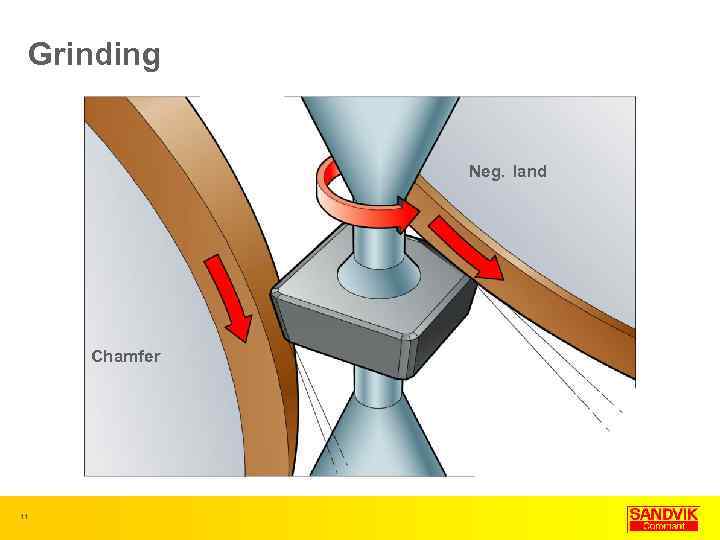 Grinding Neg. land Chamfer 11
Grinding Neg. land Chamfer 11
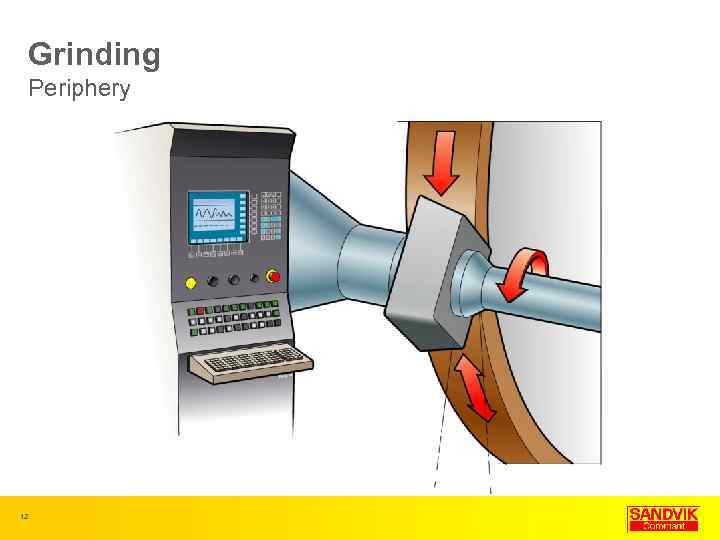 Grinding Periphery 12
Grinding Periphery 12
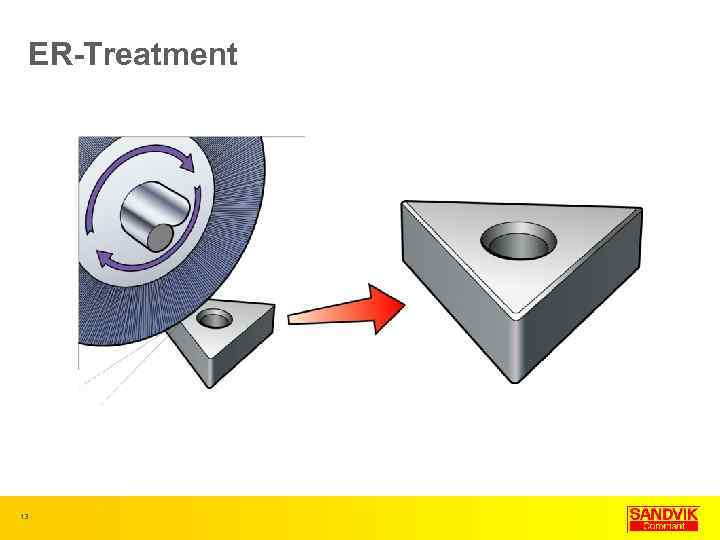 ER-Treatment 13
ER-Treatment 13
 Cleaning 14
Cleaning 14
 The design of a modern coated cemented carbide Ti. N - wear detection Al 2 O 3 - chemical and thermal wear resistance Ti. CN - mechanical wear resistance Functional gradientedge fracture resistance Cemented carbide plastic deformation resistance 15
The design of a modern coated cemented carbide Ti. N - wear detection Al 2 O 3 - chemical and thermal wear resistance Ti. CN - mechanical wear resistance Functional gradientedge fracture resistance Cemented carbide plastic deformation resistance 15
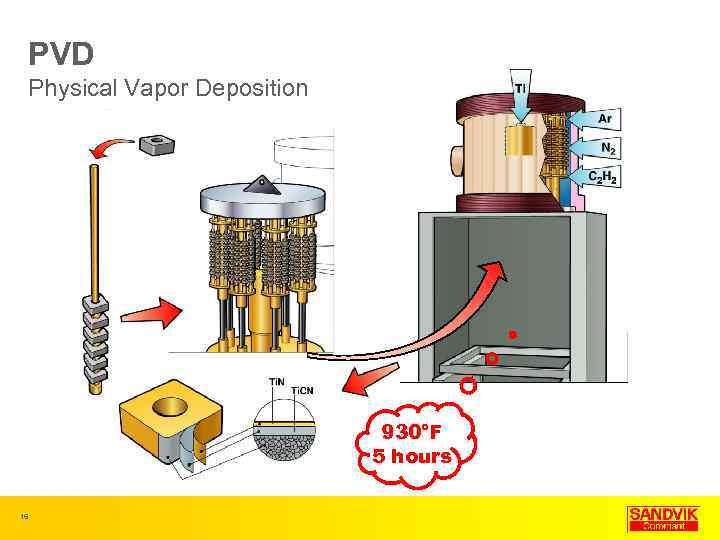 PVD Physical Vapor Deposition 930°F 5 hours 16
PVD Physical Vapor Deposition 930°F 5 hours 16
 PVD Physical Vapor Deposition • PVD coatings are generally tougher than CVD coatings • Thin Coatings • Sharper edge • Ti. C, Ti. CN, Ti. Al. N common • < 2 microns thick 17 most
PVD Physical Vapor Deposition • PVD coatings are generally tougher than CVD coatings • Thin Coatings • Sharper edge • Ti. C, Ti. CN, Ti. Al. N common • < 2 microns thick 17 most
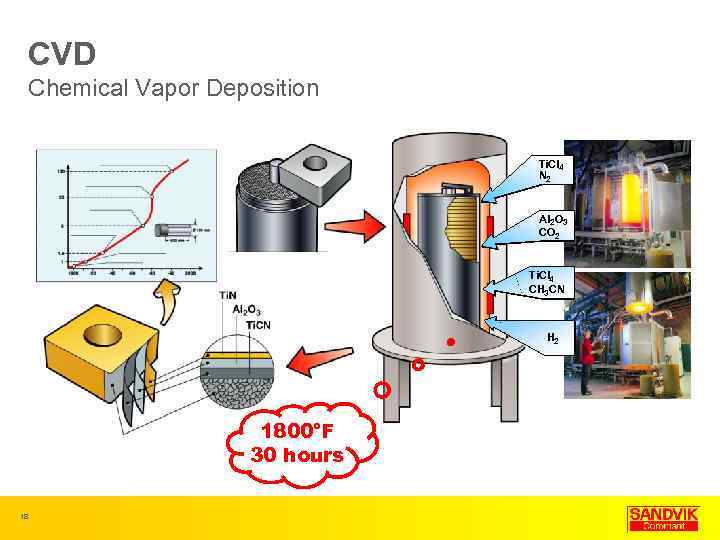 CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition Ti. Cl 4 N 2 Al 2 O 3 CO 2 Ti. Cl 4 CH 3 CN H 2 1800°F 30 hours 18
CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition Ti. Cl 4 N 2 Al 2 O 3 CO 2 Ti. Cl 4 CH 3 CN H 2 1800°F 30 hours 18
 CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition • PVD coatings are generally tougher than CVD coatings • Thicker Coatings • Ti. CN, Al 203, Ti. N most common • 2 -12 microns thick CVD MT-CVD 19
CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition • PVD coatings are generally tougher than CVD coatings • Thicker Coatings • Ti. CN, Al 203, Ti. N most common • 2 -12 microns thick CVD MT-CVD 19
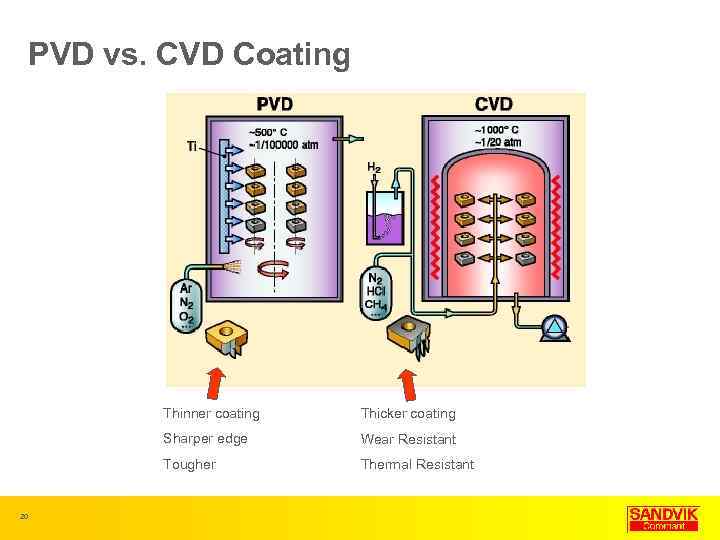 PVD vs. CVD Coating Thinner coating Sharper edge Wear Resistant Tougher 20 Thicker coating Thermal Resistant
PVD vs. CVD Coating Thinner coating Sharper edge Wear Resistant Tougher 20 Thicker coating Thermal Resistant
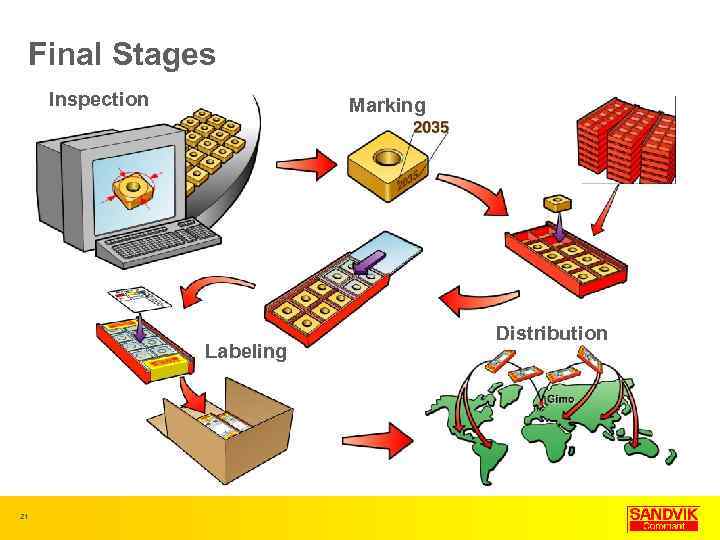 Final Stages Inspection Marking Labeling 21 Distribution
Final Stages Inspection Marking Labeling 21 Distribution
 Insert Manufacturing Video 22
Insert Manufacturing Video 22
 23
23