e1bb9c14c885cc2e7f9d78aed8bbde18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Insecticides 632 Lecture 6 - Application of cellular neuroscience to a practical problem
Insecticides 632 Lecture 6 - Application of cellular neuroscience to a practical problem
 Cellular Neuroscience Revision n Resting potential n Action potential n Channels: u voltage gated, u ligand gated, ionotropic & metabotropic n Chemical synaptic transmission
Cellular Neuroscience Revision n Resting potential n Action potential n Channels: u voltage gated, u ligand gated, ionotropic & metabotropic n Chemical synaptic transmission
 Aims of lecture n to know problems of effective application of insecticides n to know the main types of insecticides n to know their site(s) of action n possible mechanisms of resistance
Aims of lecture n to know problems of effective application of insecticides n to know the main types of insecticides n to know their site(s) of action n possible mechanisms of resistance
 Reading Matters n Web see http: //biolpc 22. york. ac. uk/632 n Book: u Tomlin, CD S (1997) The pesticide manual n Papers u u u Narahashi T (1996) Neuronal ion channels as the target sites of insecticides Pharmacology & Toxicology 79: 1 -14 ffrench-Constant, RH et al (1998) Why are there so few resistanceassociated mutations in insecticide target genes? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 353 1685 -1693 Matsuda et al (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors Trends pharm. 11: 573 -580
Reading Matters n Web see http: //biolpc 22. york. ac. uk/632 n Book: u Tomlin, CD S (1997) The pesticide manual n Papers u u u Narahashi T (1996) Neuronal ion channels as the target sites of insecticides Pharmacology & Toxicology 79: 1 -14 ffrench-Constant, RH et al (1998) Why are there so few resistanceassociated mutations in insecticide target genes? Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 353 1685 -1693 Matsuda et al (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors Trends pharm. 11: 573 -580
 Delivering insecticide effectively? n rapidity n specificity u to target species u side effects n stability u light & air (oxygen) u not too persistent n solubility n cheap
Delivering insecticide effectively? n rapidity n specificity u to target species u side effects n stability u light & air (oxygen) u not too persistent n solubility n cheap
![Main targets n development u ecdysis [moulting] specific to insects u cuticle specific to Main targets n development u ecdysis [moulting] specific to insects u cuticle specific to](https://present5.com/presentation/e1bb9c14c885cc2e7f9d78aed8bbde18/image-6.jpg) Main targets n development u ecdysis [moulting] specific to insects u cuticle specific to insects n respiration n CNS
Main targets n development u ecdysis [moulting] specific to insects u cuticle specific to insects n respiration n CNS
 Why Knockdown n resting insects have low metabolic demand u unlike mammals u general respiratory or muscular poisons not so good? n knockdown insecticides u disable insect quickly u OK to kill slowly u target CNS
Why Knockdown n resting insects have low metabolic demand u unlike mammals u general respiratory or muscular poisons not so good? n knockdown insecticides u disable insect quickly u OK to kill slowly u target CNS
 Main classes n organochlorine (1940 s) n cyclodiene n organophosphorus n pyrethroids (1975 -) n Imidacloprid (1990 s) n phenyl pyrazoles
Main classes n organochlorine (1940 s) n cyclodiene n organophosphorus n pyrethroids (1975 -) n Imidacloprid (1990 s) n phenyl pyrazoles
 Organophosphorus n example: malathion n carbamates have similar action n more toxic to insects n phosphorylate acetylcholinesterase n raises [ACh], so use atropine as antidote if humans are poisoned
Organophosphorus n example: malathion n carbamates have similar action n more toxic to insects n phosphorylate acetylcholinesterase n raises [ACh], so use atropine as antidote if humans are poisoned
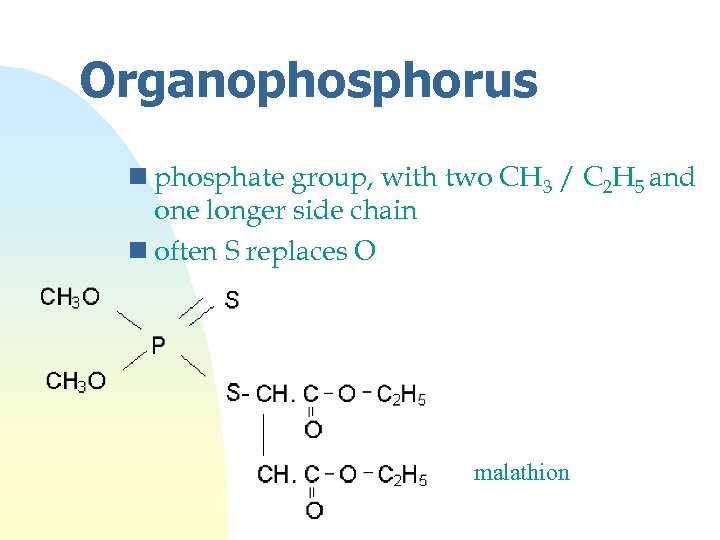 Organophosphorus n phosphate group, with two CH 3 / C 2 H 5 and one longer side chain n often S replaces O malathion
Organophosphorus n phosphate group, with two CH 3 / C 2 H 5 and one longer side chain n often S replaces O malathion
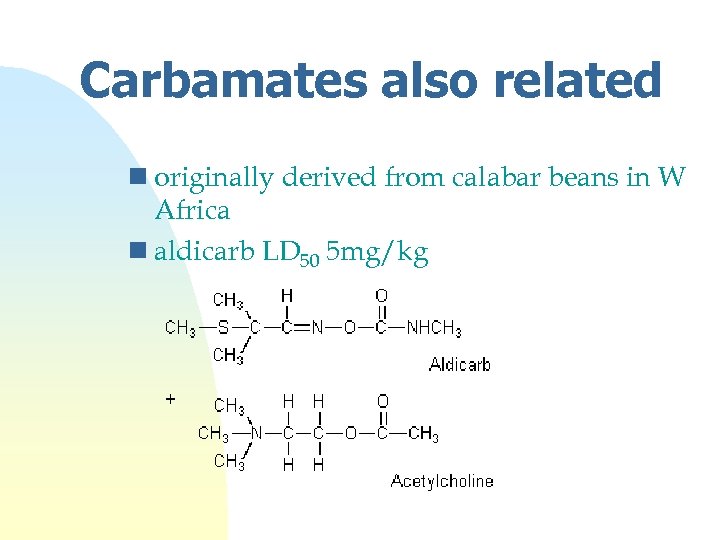 Carbamates also related n originally derived from calabar beans in W Africa n aldicarb LD 50 5 mg/kg
Carbamates also related n originally derived from calabar beans in W Africa n aldicarb LD 50 5 mg/kg
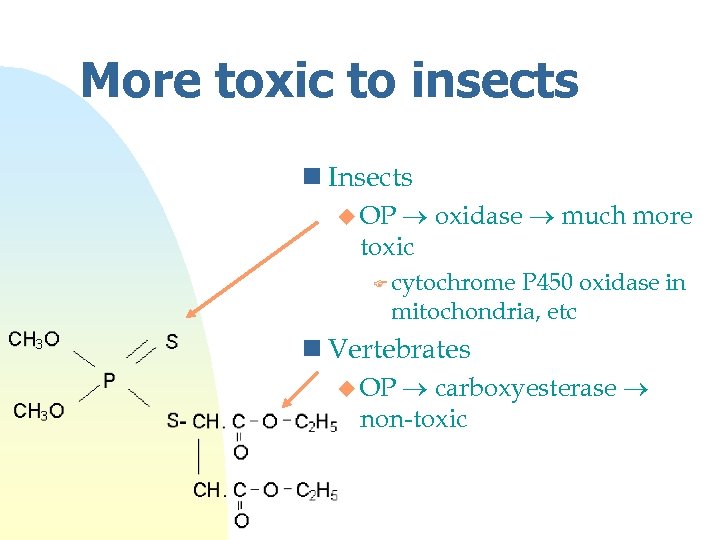 More toxic to insects n Insects oxidase much more toxic u OP F cytochrome P 450 oxidase in mitochondria, etc n Vertebrates carboxyesterase non-toxic u OP
More toxic to insects n Insects oxidase much more toxic u OP F cytochrome P 450 oxidase in mitochondria, etc n Vertebrates carboxyesterase non-toxic u OP
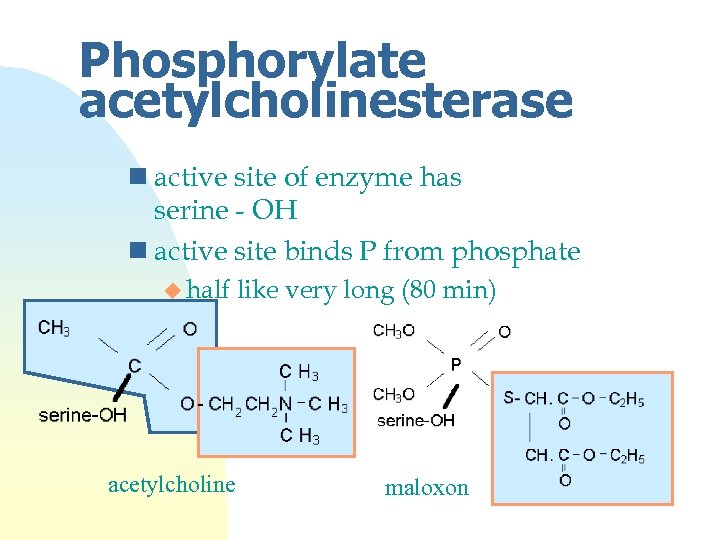 Phosphorylate acetylcholinesterase n active site of enzyme has serine - OH n active site binds P from phosphate u half acetylcholine like very long (80 min) maloxon
Phosphorylate acetylcholinesterase n active site of enzyme has serine - OH n active site binds P from phosphate u half acetylcholine like very long (80 min) maloxon
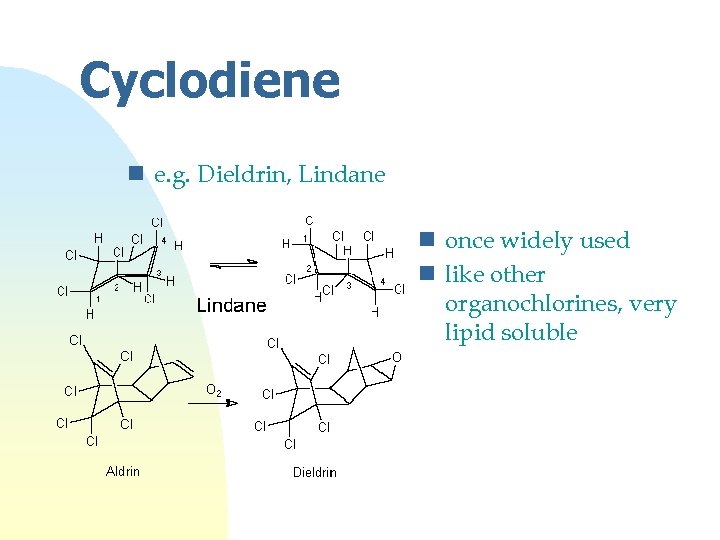 Cyclodiene n e. g. Dieldrin, Lindane n once widely used n like other organochlorines, very lipid soluble
Cyclodiene n e. g. Dieldrin, Lindane n once widely used n like other organochlorines, very lipid soluble
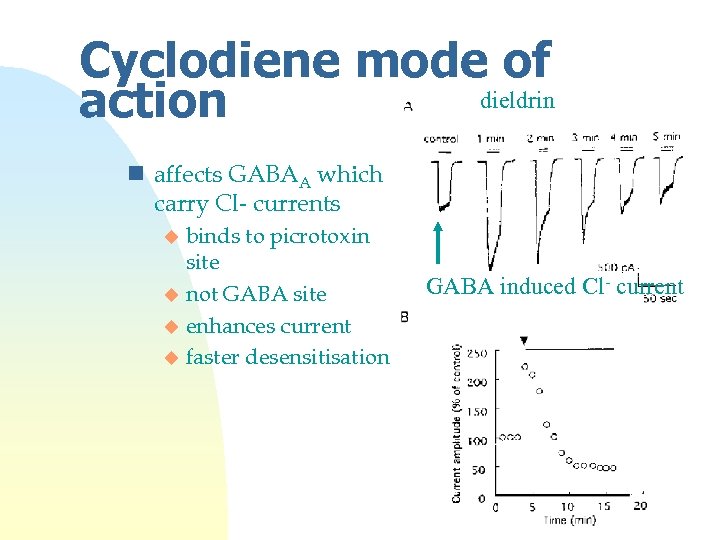 Cyclodiene mode of dieldrin action n affects GABAA which carry Cl- currents binds to picrotoxin site u not GABA site u enhances current u faster desensitisation u GABA induced Cl- current
Cyclodiene mode of dieldrin action n affects GABAA which carry Cl- currents binds to picrotoxin site u not GABA site u enhances current u faster desensitisation u GABA induced Cl- current
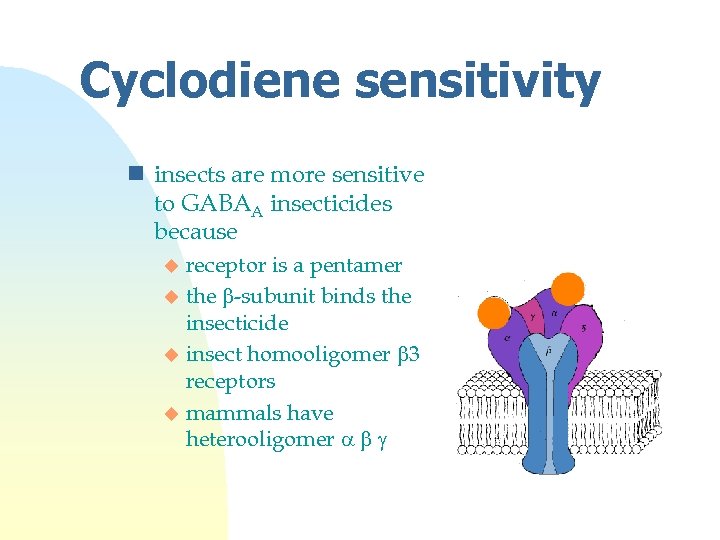 Cyclodiene sensitivity n insects are more sensitive to GABAA insecticides because receptor is a pentamer u the b-subunit binds the insecticide u insect homooligomer b 3 receptors u mammals have heterooligomer a b g u
Cyclodiene sensitivity n insects are more sensitive to GABAA insecticides because receptor is a pentamer u the b-subunit binds the insecticide u insect homooligomer b 3 receptors u mammals have heterooligomer a b g u
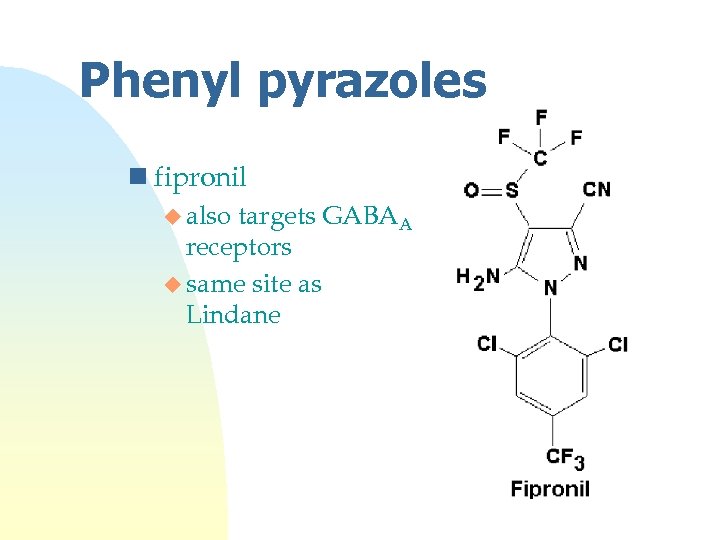 Phenyl pyrazoles n fipronil u also targets GABAA receptors u same site as Lindane
Phenyl pyrazoles n fipronil u also targets GABAA receptors u same site as Lindane
 Organochlorine n DDT n low solubility in water, high in lipids n at main peak of use, Americans ate 0. 18 mg/day u human mass 80 kg n Na Channel effect n more toxic to insects
Organochlorine n DDT n low solubility in water, high in lipids n at main peak of use, Americans ate 0. 18 mg/day u human mass 80 kg n Na Channel effect n more toxic to insects
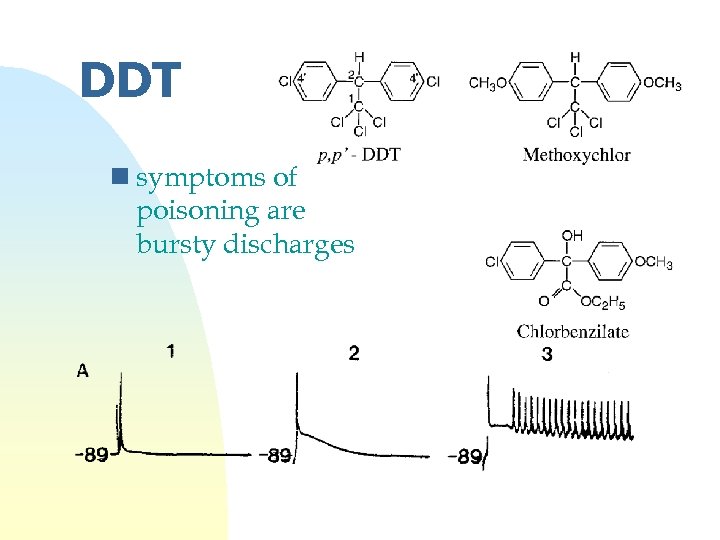 DDT n symptoms of poisoning are bursty discharges
DDT n symptoms of poisoning are bursty discharges
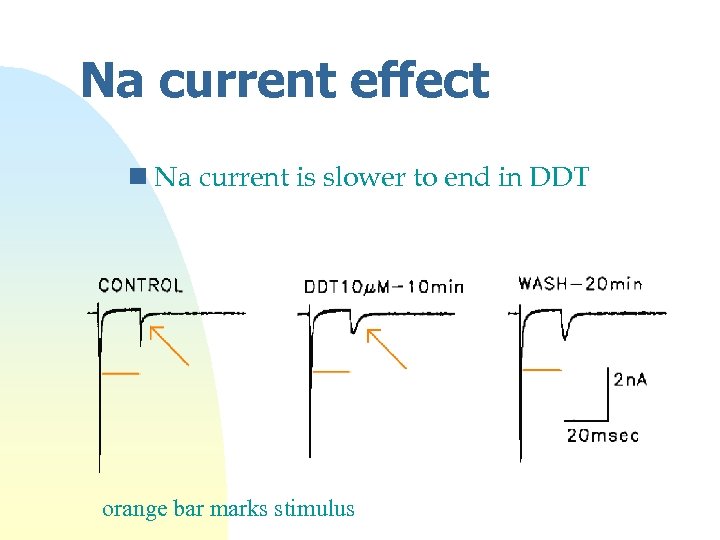 Na current effect n Na current is slower to end in DDT orange bar marks stimulus
Na current effect n Na current is slower to end in DDT orange bar marks stimulus
 Pyrethroids n very quick knockdown n need an oxidase inhibitor n photostable and effective u 30 g/hectare (1% of previous insecticides)
Pyrethroids n very quick knockdown n need an oxidase inhibitor n photostable and effective u 30 g/hectare (1% of previous insecticides)
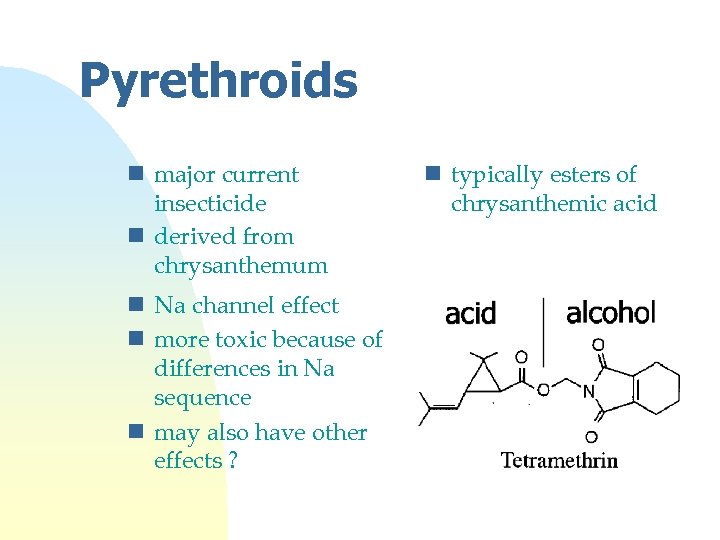 Pyrethroids n major current insecticide n derived from chrysanthemum n Na channel effect n more toxic because of differences in Na sequence n may also have other effects ? n typically esters of chrysanthemic acid
Pyrethroids n major current insecticide n derived from chrysanthemum n Na channel effect n more toxic because of differences in Na sequence n may also have other effects ? n typically esters of chrysanthemic acid
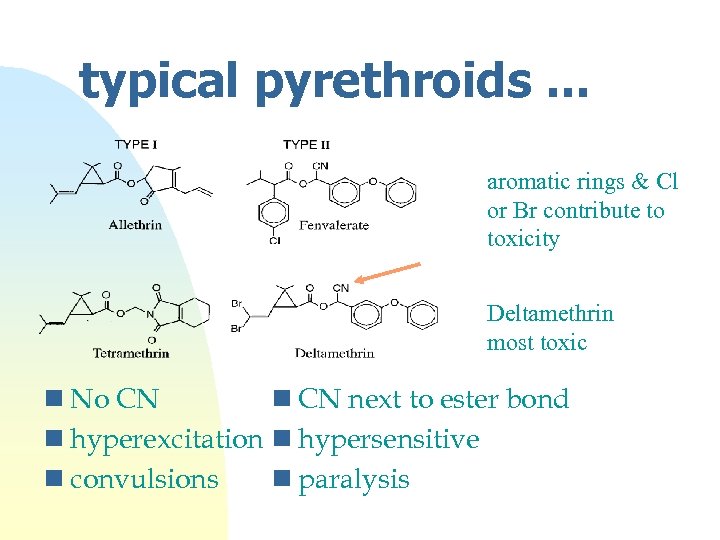 typical pyrethroids. . . aromatic rings & Cl or Br contribute to toxicity Deltamethrin most toxic n No CN next to ester bond n hyperexcitation n hypersensitive n convulsions n paralysis
typical pyrethroids. . . aromatic rings & Cl or Br contribute to toxicity Deltamethrin most toxic n No CN next to ester bond n hyperexcitation n hypersensitive n convulsions n paralysis
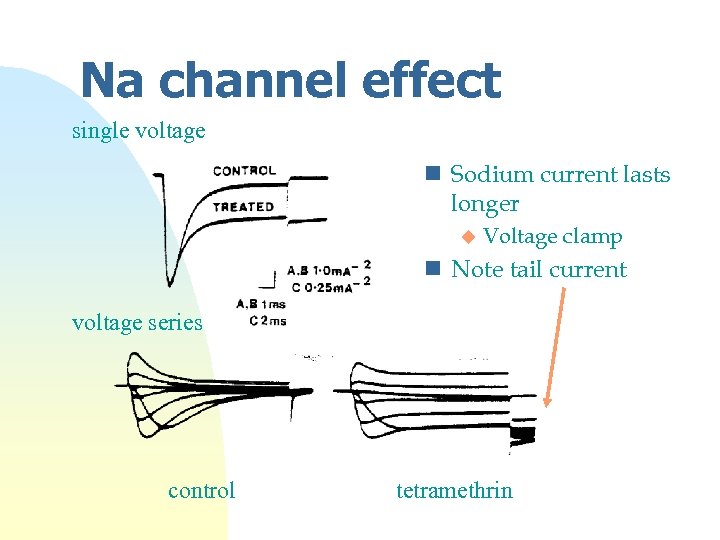 Na channel effect single voltage n Sodium current lasts longer u Voltage clamp n Note tail current voltage series control tetramethrin
Na channel effect single voltage n Sodium current lasts longer u Voltage clamp n Note tail current voltage series control tetramethrin
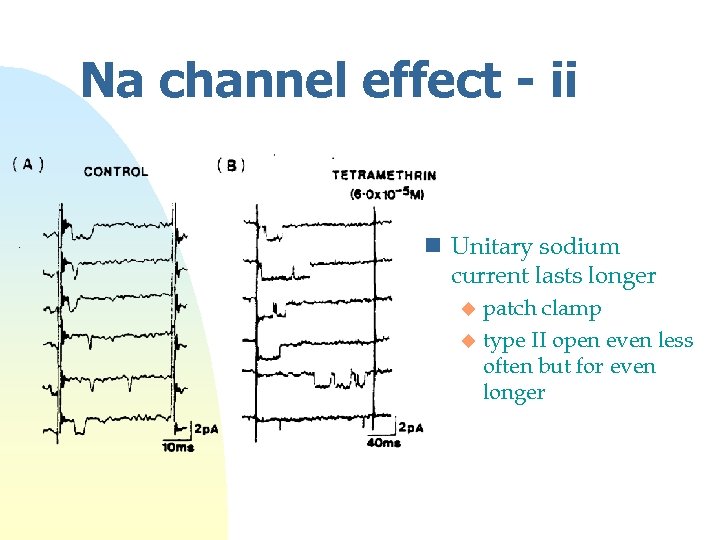 Na channel effect - ii n Unitary sodium current lasts longer patch clamp u type II open even less often but for even longer u
Na channel effect - ii n Unitary sodium current lasts longer patch clamp u type II open even less often but for even longer u
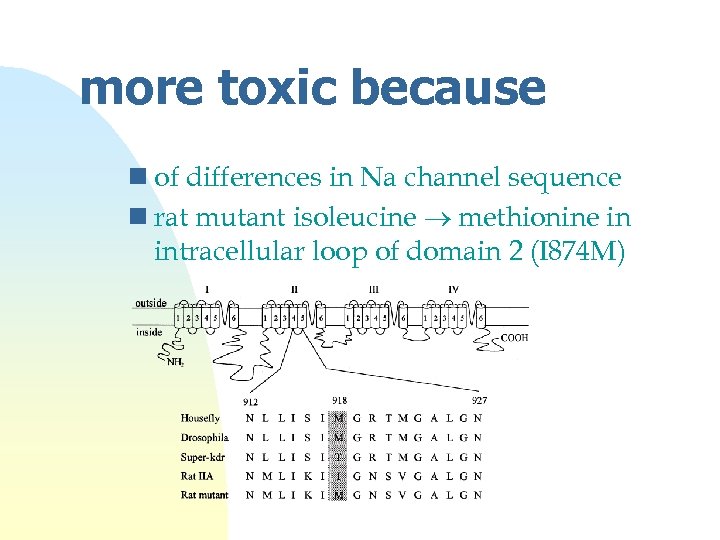 more toxic because n of differences in Na channel sequence n rat mutant isoleucine methionine in intracellular loop of domain 2 (I 874 M)
more toxic because n of differences in Na channel sequence n rat mutant isoleucine methionine in intracellular loop of domain 2 (I 874 M)
 other effects ? n Pyrethroids have been reported to affect u calcium channels u GABA, ACh, glutamate receptors
other effects ? n Pyrethroids have been reported to affect u calcium channels u GABA, ACh, glutamate receptors
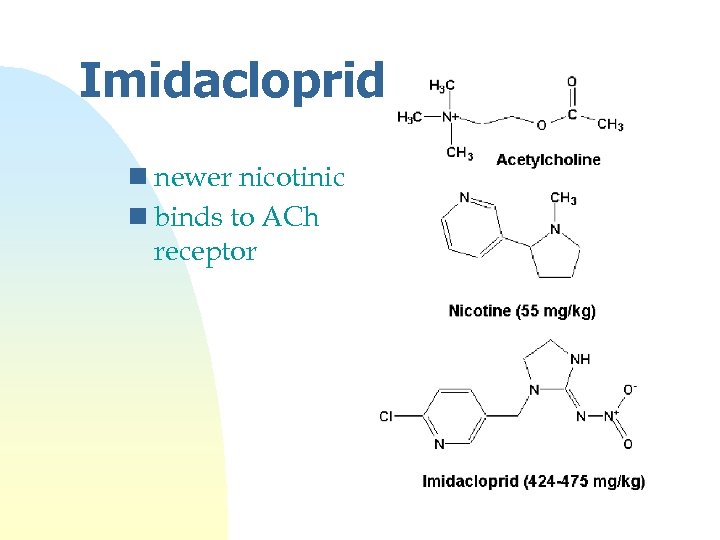 Imidacloprid n newer nicotinic n binds to ACh receptor
Imidacloprid n newer nicotinic n binds to ACh receptor
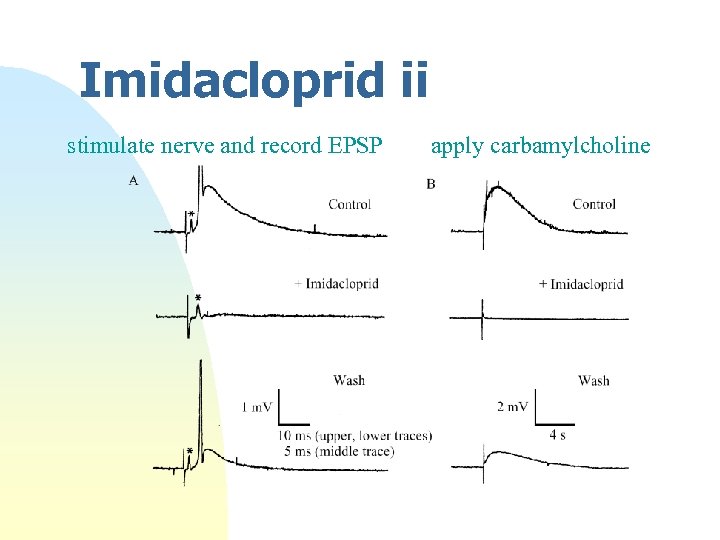 Imidacloprid ii stimulate nerve and record EPSP apply carbamylcholine
Imidacloprid ii stimulate nerve and record EPSP apply carbamylcholine
 Summary so far n Na+ channels targets of DDT, pyrethroids n ACh. Esterase targets of OPs n ACh receptor target of Imidacloprid n GABAA receptor target of cyclodienes & fipronil
Summary so far n Na+ channels targets of DDT, pyrethroids n ACh. Esterase targets of OPs n ACh receptor target of Imidacloprid n GABAA receptor target of cyclodienes & fipronil
 Problem of Resistance n resistance means that the insects survive! n some species never develop, u e. g. tsetse flies - few offspring n most very quick u e. g. mosquitoes - rapid life, many offspring n cross resistance, e. g. to DDT and pyrethroids because same target is used. n [behavioural resistance]
Problem of Resistance n resistance means that the insects survive! n some species never develop, u e. g. tsetse flies - few offspring n most very quick u e. g. mosquitoes - rapid life, many offspring n cross resistance, e. g. to DDT and pyrethroids because same target is used. n [behavioural resistance]
 Resistance mechanisms n organophosphates n organochlorine n cyclodiene n pyrethroids n see Ann Rev Entomology 2000
Resistance mechanisms n organophosphates n organochlorine n cyclodiene n pyrethroids n see Ann Rev Entomology 2000
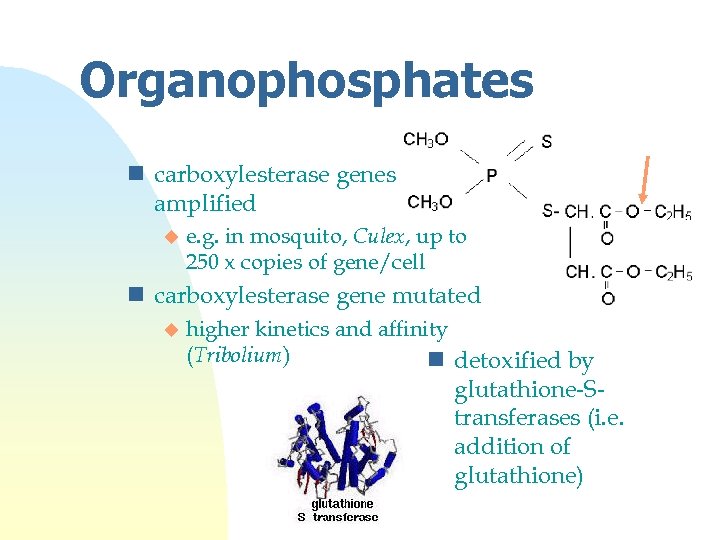 Organophosphates n carboxylesterase genes amplified u e. g. in mosquito, Culex, up to 250 x copies of gene/cell n carboxylesterase gene mutated u higher kinetics and affinity (Tribolium) n detoxified by glutathione-Stransferases (i. e. addition of glutathione)
Organophosphates n carboxylesterase genes amplified u e. g. in mosquito, Culex, up to 250 x copies of gene/cell n carboxylesterase gene mutated u higher kinetics and affinity (Tribolium) n detoxified by glutathione-Stransferases (i. e. addition of glutathione)
 Organochlorine n DDT detoxified by glutathione-Stransferases (i. e. addition of glutathione) n Na channel resistance
Organochlorine n DDT detoxified by glutathione-Stransferases (i. e. addition of glutathione) n Na channel resistance
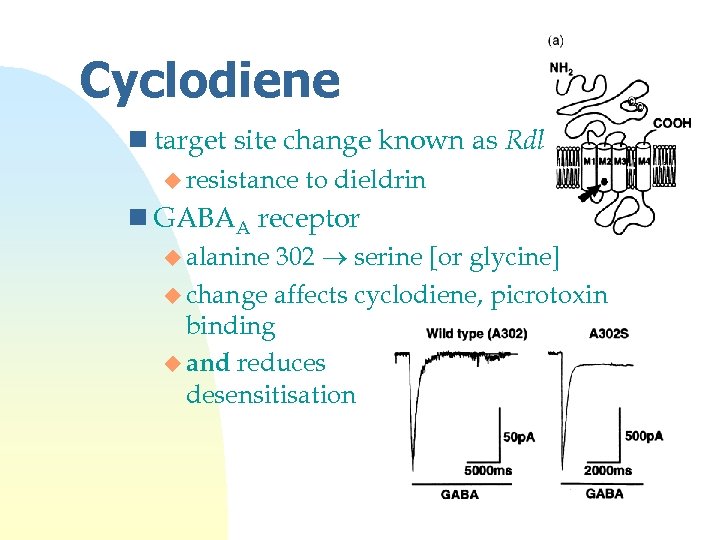 Cyclodiene n target site change known as Rdl u resistance to dieldrin n GABAA receptor 302 serine [or glycine] u change affects cyclodiene, picrotoxin binding u and reduces desensitisation u alanine
Cyclodiene n target site change known as Rdl u resistance to dieldrin n GABAA receptor 302 serine [or glycine] u change affects cyclodiene, picrotoxin binding u and reduces desensitisation u alanine
 Pyrethroids n non-target resistance P 450 oxidase u more transcription giving more expression u leads to cross-resistance to organophosphates & carbamates n target resistance Na+ channel
Pyrethroids n non-target resistance P 450 oxidase u more transcription giving more expression u leads to cross-resistance to organophosphates & carbamates n target resistance Na+ channel
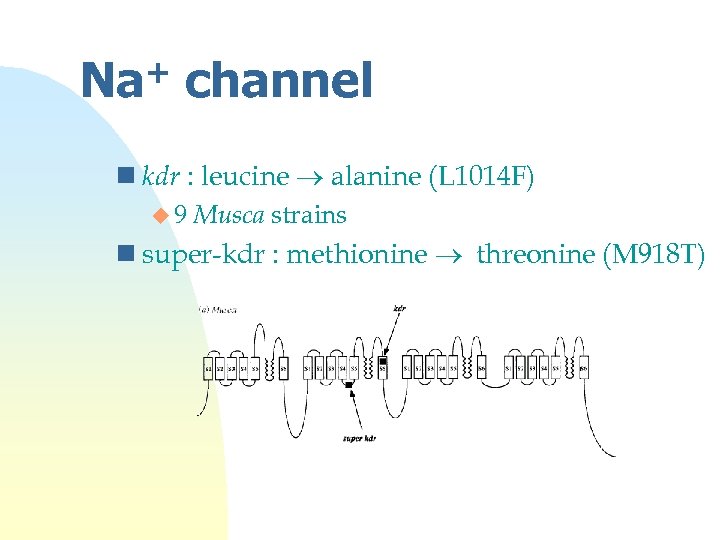 + Na channel n kdr : leucine alanine (L 1014 F) u 9 Musca strains n super-kdr : methionine threonine (M 918 T)
+ Na channel n kdr : leucine alanine (L 1014 F) u 9 Musca strains n super-kdr : methionine threonine (M 918 T)
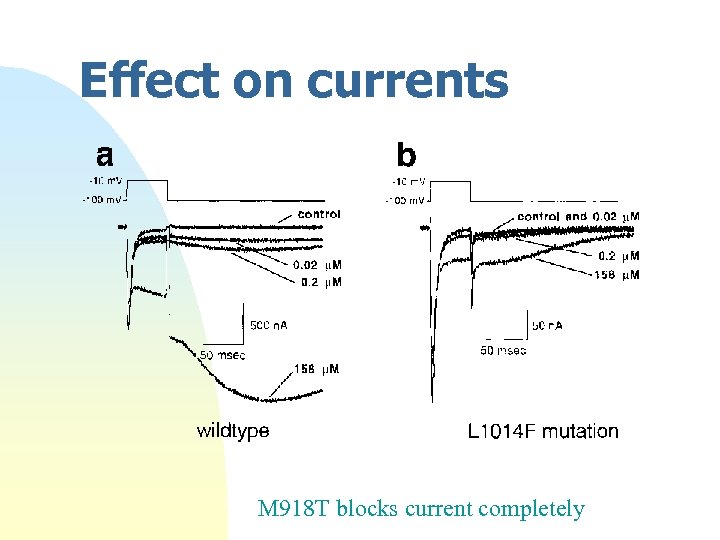 Effect on currents M 918 T blocks current completely
Effect on currents M 918 T blocks current completely
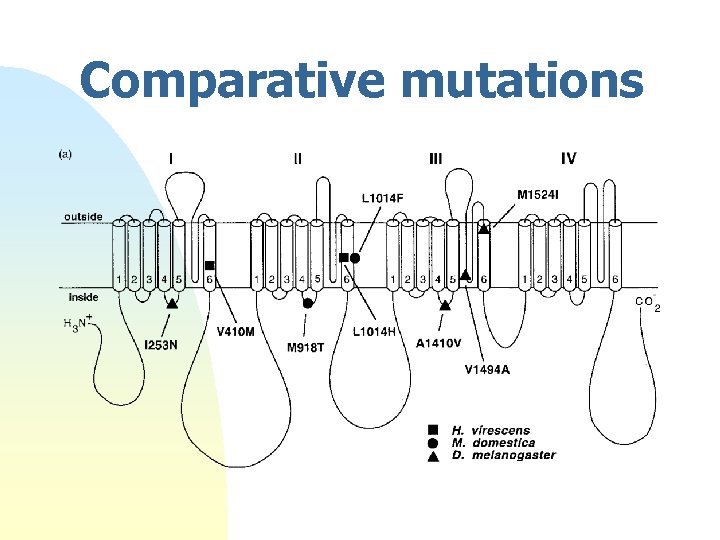 Comparative mutations
Comparative mutations
 Conclusions n Cellular neuroscience helps understand many insecticide actions n binding to channel proteins u ligand-gated u voltage gated n mutation leads to resistance u target site u enzymatic degradation n Web page u http: //biolpc 22. york. ac. uk/632/
Conclusions n Cellular neuroscience helps understand many insecticide actions n binding to channel proteins u ligand-gated u voltage gated n mutation leads to resistance u target site u enzymatic degradation n Web page u http: //biolpc 22. york. ac. uk/632/


