6371b52e8f4dc1cbf32e88c5153f9dcc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

Inovácia obsahu a metód vzdelávania prispôsobená potrebám vedomostnej spoločnosti BAUHAUS The Design history VYPRACOVAL: Mgr, Barbora Kravcová jún 2014 „Moderné vzdelávanie pre vedomostnú spoločnosť/Projekt je spolufinancovaný zo zdrojov EÚ“

CONTENT • • Short history Main principles Curriculum Laszlo- Moholy- Nagy: childhood Laszlo- Moholy- Nagy: art Examples of Bauhaus work principles and ideas

HISTORY • literally "house of construction" - was understood as meaning "School of Building". • School in Germany that combined crafts and fine art under one roof. • Founded by Walter Gropius. • Started in Weimar, Germany in 1919, the school moved to Dessau in 1924 and then was forced to close in 1933. • Main principles: simplified forms, rationality, functionality. • The idea that mass production could live in harmony with the artistic spirit of individuality. Laszlo-Moholy-Nagy and L. M. Van der Rohe made significant contributions to the development of graphic design. • Bauhaus taught typography as part of its curriculum. • Developed sans-serif typography, which they favored for its simplified geometric forms.

MAIN PRINCIPLES The building itself was the zenith of all design Art and technology in a new unity. Principles : • RATIONALITY decide wisely what to use and how. • FUNCTIONALITY it should be easily functional for everyone. • MASSPRODUCT WITH ARTISTIC SPIRIT even though it is a mass produced good it must have an aesthetical value.
BAUHAUS CURRICULUM • Theory of form over the function • Strong understanding of basic design • The principles of composition • Colour theory • Craftsmanship in a wide array of disciplines

LASZLO- MOHOLY-NAGY Childhood • Laszlo Moholy-Nagy was born in a small farming town in southern Hungary. • He was brough up by his grandmother. • He left for Budapest in 1913 to study law, but his studies were interrupted when he was drafted into the Army, experienced the horror of war. • Became a painter, photographer and a teacher at Bauhaus.

LASZLO- MOHOLY-NAGY Examples of work

LASZLO- MOHOLY-NAGY Art principles and ideas • Believed that all art disciplines should be joined together and accompany each other. • L-M-Nagy was fascinated by a new age and modern art fields such as typography, photography and graphic design itself. • He was experimenting with photograms • He was interest in qualities of space, time, and light • He made some sculptures of transparent Plexiglas

EXAMPLES OF WORK AT BAUHAUS
BAUHAUS CONTRIBUTIONS • Bauhaus started to establish extensive contact with business, through many small- scale exhibitions • Changed the field of design and education • revolutionized the idea of “pure art” and “applied art” • started so called “factory apprenticeship”, Bauhaus emphasized on the combination of practice and theory. • It also develops modern design theory on architecture design.

QESTIONNAIRE • Who is the man in the photograph? • What do you know about him? • Which art discipline was he fascinated by?

ANSWERS • Laszlo- Moholy-Nagy • A painter, photographer and a teacher at Bauhaus • was fascinated by a new age and modern art fields. such as typography, photography and graphic design itself.
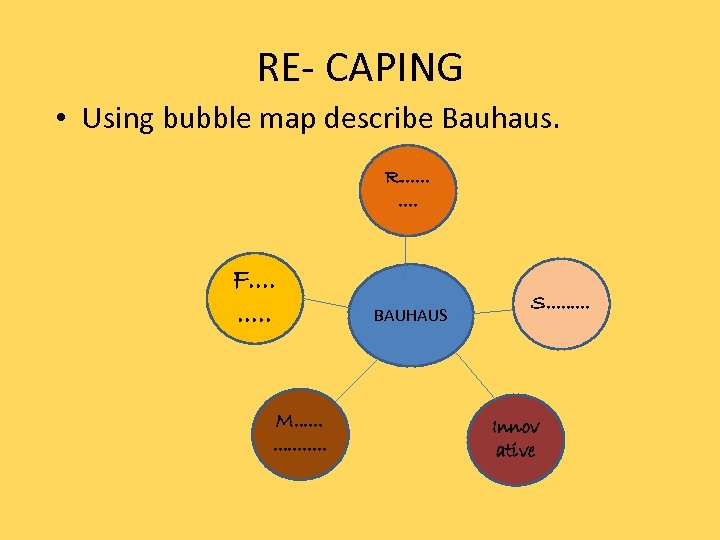
RE- CAPING • Using bubble map describe Bauhaus. R. . F. . M. . . . BAUHAUS S. . Innov ative

SOURCES • • http: //www. designishistory. com/1920/the-bauhaus/ http: //monoskop. org/L%C 3%A 1 szl%C 3%B 3_Moholy-Nagy http: //moholy-nagy. org/ • The Bauhaus and Its Influence, ” 2003. http: //www. spurensuchemidwest. org/a_Bauhaus_english. http: //www. dieselpunks. org/profiles/blogs/laszlo-moholynagy-the-pursuit •
6371b52e8f4dc1cbf32e88c5153f9dcc.ppt