13a8b1f4b589116fcecba39865aed21a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

Innovative Hackers are Bad for Business Brian O’Higgins CTO, Third Brigade Inc. October 14, 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc.

Outline Evolving Threat Hackers and Targeted Attacks Counter-attack: Host Intrusion Prevention Conclusions © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 2

Outline Evolving Threat Hackers and Targeted Attacks Counter-attack: Host Intrusion Prevention Conclusions © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 3
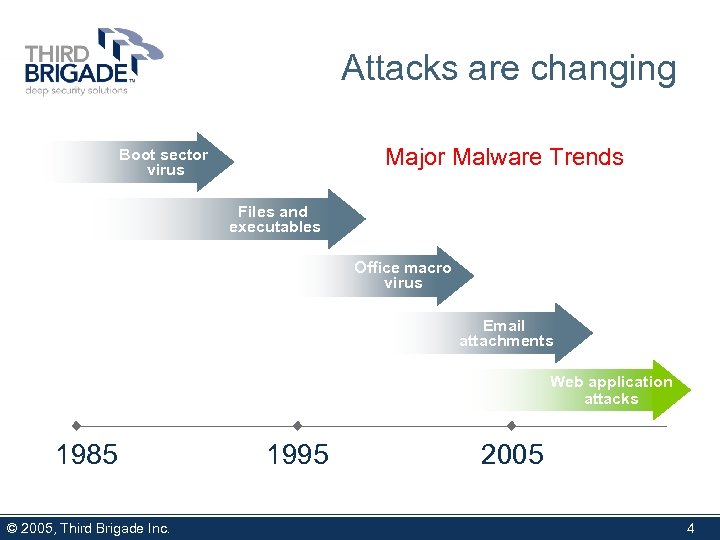
Attacks are changing Major Malware Trends Boot sector virus Files and executables Office macro virus Email attachments Web application attacks 1985 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 1995 2005 4
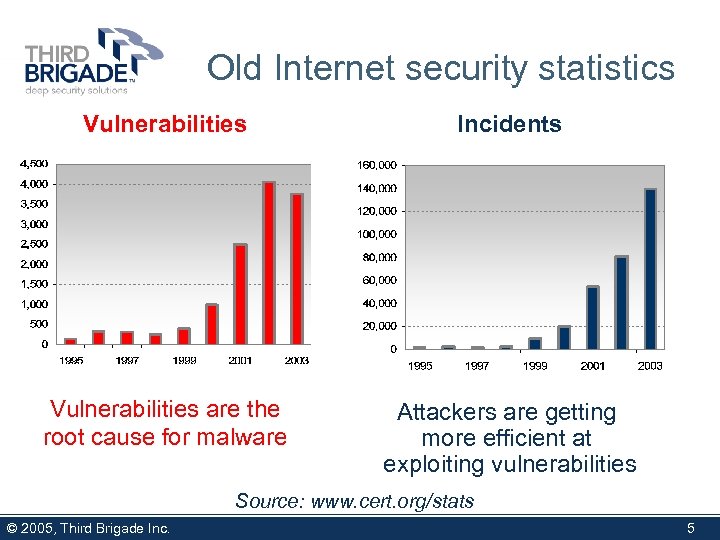
Old Internet security statistics Vulnerabilities Incidents Vulnerabilities are the root cause for malware Attackers are getting more efficient at exploiting vulnerabilities Source: www. cert. org/stats © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 5
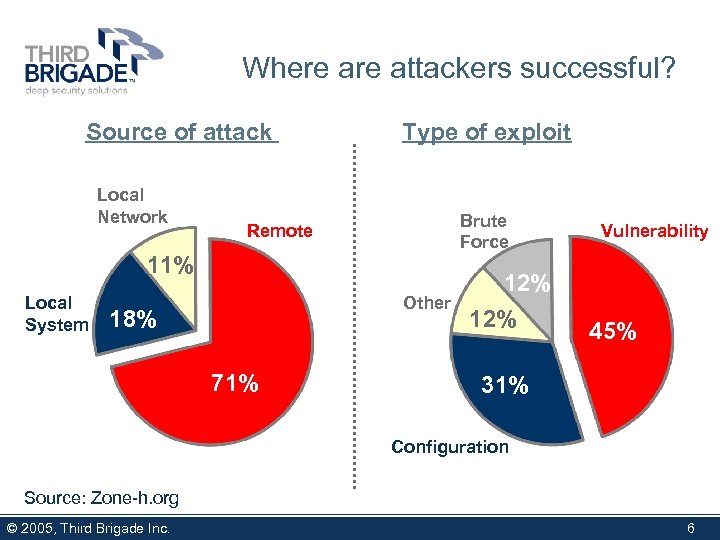
Where attackers successful? Source of attack Local Network Type of exploit Brute Force Remote 11% Local System Other 18% 71% 12% Vulnerability 45% 31% Configuration Source: Zone-h. org © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 6
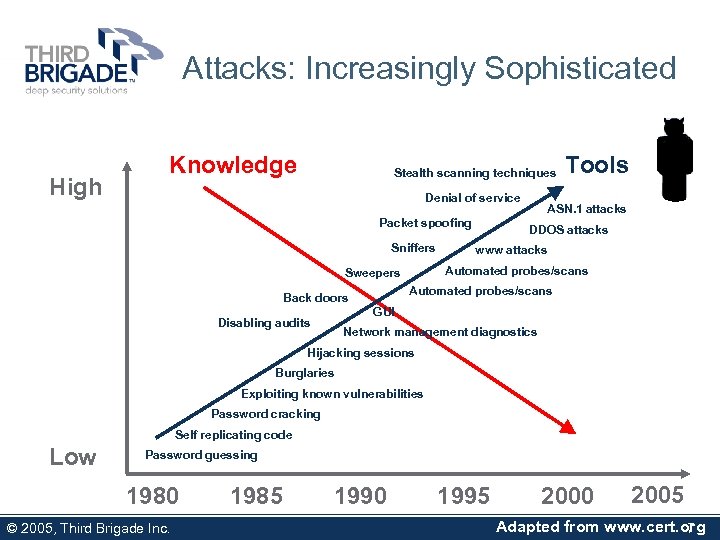
Attacks: Increasingly Sophisticated High Knowledge Stealth scanning techniques Denial of service Packet spoofing Sniffers Tools ASN. 1 attacks DDOS attacks www attacks Automated probes/scans Sweepers Automated probes/scans Back doors GUI Disabling audits Network management diagnostics Hijacking sessions Burglaries Exploiting known vulnerabilities Password cracking Self replicating code Low Password guessing 1980 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Adapted from www. cert. org 7

Automated exploit tools “…The goal is to provide useful information to people who perform penetration testing, IDS signature development, and exploit research. This site was created to fill the gaps in the information publicly available on various exploitation techniques and to create a useful resource for exploit developers. The tools and information on this site are provided for legal penetration testing and research purposes only” © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 8
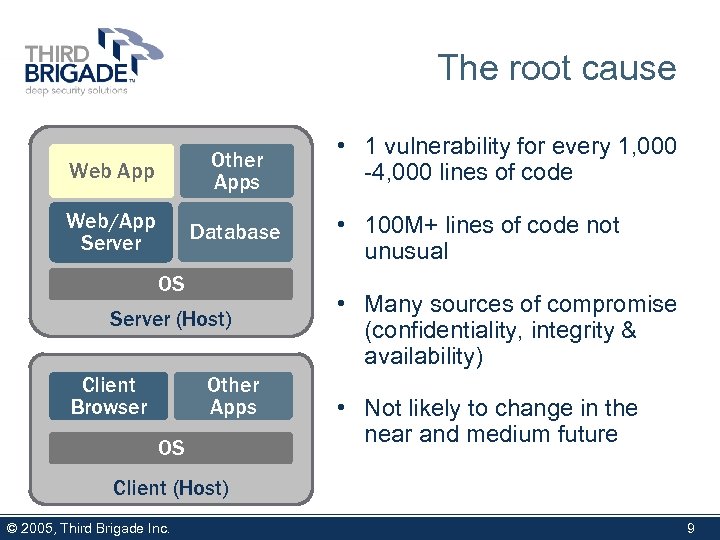
The root cause Web App Other Apps Web/App Server Database OS Server (Host) Other Apps Client Browser OS • 1 vulnerability for every 1, 000 -4, 000 lines of code • 100 M+ lines of code not unusual • Many sources of compromise (confidentiality, integrity & availability) • Not likely to change in the near and medium future Client (Host) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 9

Software vulnerabilities • Symantec Internet Security Report, 1 H 2005 – 1, 862 new vulnerabilities, highest ever – 59% related to web applications • SANS Top 20 list, Q 1 2005 – 600+ new vulnerabilities listed that: 1. Affect large number of users 2. Not patched on substantial number of machines 3. Allow computer to be taken over by remote, nonauthorized user 4. Sufficient details published on the internet 5. Discovered or first patched during Q 1 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 10
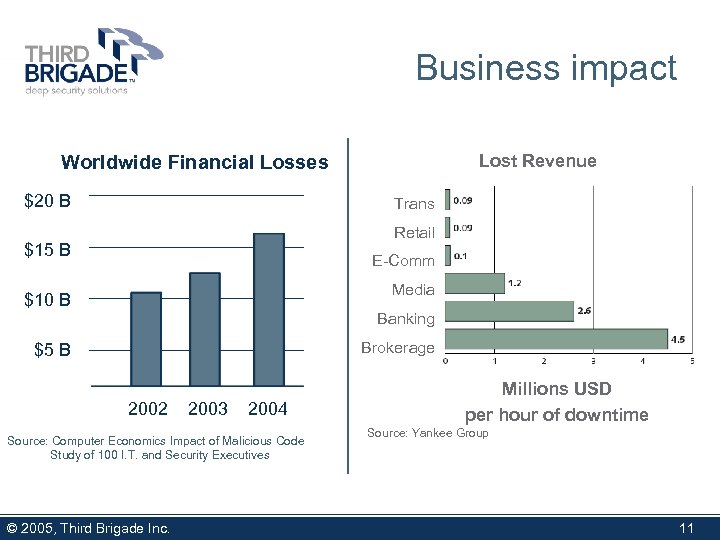
Business impact Lost Revenue Worldwide Financial Losses $20 B Trans Retail $15 B E-Comm Media $10 B Banking Brokerage $5 B 2002 2003 2004 Source: Computer Economics Impact of Malicious Code Study of 100 I. T. and Security Executives © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Millions USD per hour of downtime Source: Yankee Group 11

Outline Evolving Threat Hackers and Targeted Attacks Counter-attack: Host Intrusion Prevention Conclusions © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 12

Hacking is changing $ • Mass nuisance profit motive • Targeted attacks take advantage of s/w vulnerabilities – Can exploit a database without having to compromise any servers © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 13

Bot Nets for hire • “First hour is free” – Infect web servers, then unsuspecting PCs – Change infection after a few thousand downloads to stay under virus signature radar – Call to the mothership for subsequent updates – Password stealing program web site count doubled from June 2005 to July 2005 (www. antiphishing. org) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 14

Popular Web Application Attacks Google hacking $ Buffer overflow Command injection Cross-site scripting Parameter manipulation Session hijacking Improper error handling © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 15

SB 1386 impact • California breach notification legislation – Spreading to other jurisdictions – Notifications and subsequent press are biggest contributor to online fear – Since the Feb 15 2005 Choice. Point breach, 78 notifications have been publicized covering 50 M individuals (www. privacyrights. org) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 16

Consumer confidence erodes • U. S. survey on data security breach notification (sep 25 2005) – Ponemon Institute (www. ponemon. org) survey of 10, 000 victims of data security breach • • 19% of respondents have terminated relationship 40% more said they are thinking about terminating 5% had hired lawyers Businesses using canned communication are 3 X more likely to lose the customer vs. personalized © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 17

Security fears harm e-banking • Forrester Research study of 11, 300 users in the UK – Concludes that 600, 000 from a total of 15 M have quit online banking – 20% of internet users say security fears will stop them from ever banking online – 50% of UK internet users paranoid about online banking security © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 18
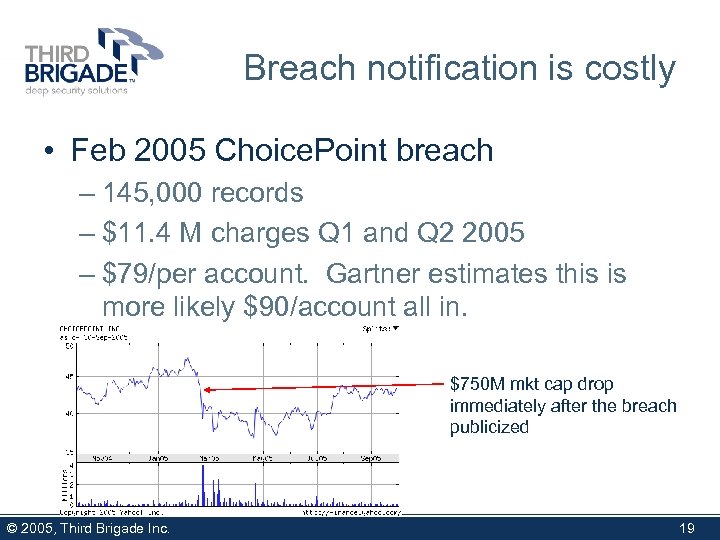
Breach notification is costly • Feb 2005 Choice. Point breach – 145, 000 records – $11. 4 M charges Q 1 and Q 2 2005 – $79/per account. Gartner estimates this is more likely $90/account all in. $750 M mkt cap drop immediately after the breach publicized © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 19
Costs for notification • Smaller numbers, cost per account higher 5, 000 accounts ~ $1, 500 per account • Very large compromises, >1 M accounts, direct costs ~$50 per account. – But this may be the death sentence for the company (Card. Systems 40 M accounts) Source: Gartner, Data Protection is Less Costly Than Data Breaches, 28 Sept 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 20

Business case to protect data • Three recommendations from Garter, and ballpark costs for 100 K accounts 1. Encrypt Stored Data 2. Deploy HIPS on servers 3. More rigorous audits $5/account initial, $1 recurring $6/account initial, $2 recurring $4/account recurring vs. expenditure of $90/customer account exposed in a breach *Source: Gartner, Data Protection is Less Costly Than Data Breaches, 28 Sept 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 21
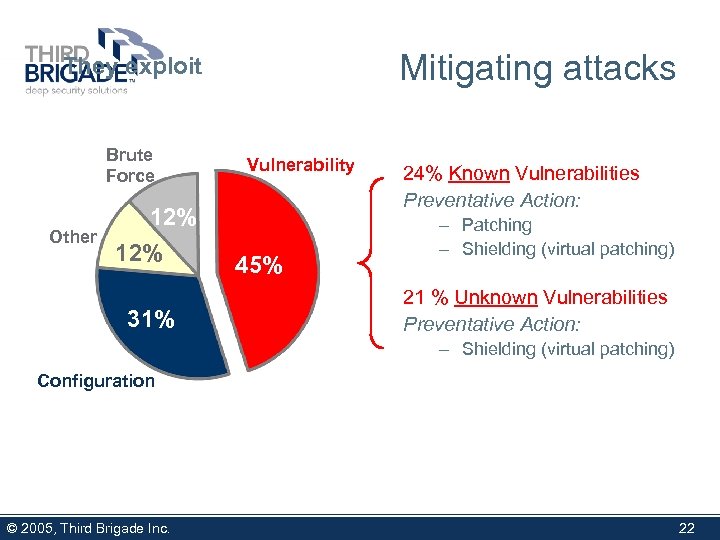
Mitigating attacks They exploit Brute Force Other 12% 31% Vulnerability 45% 24% Known Vulnerabilities Preventative Action: – Patching – Shielding (virtual patching) 21 % Unknown Vulnerabilities Preventative Action: – Shielding (virtual patching) Configuration © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 22
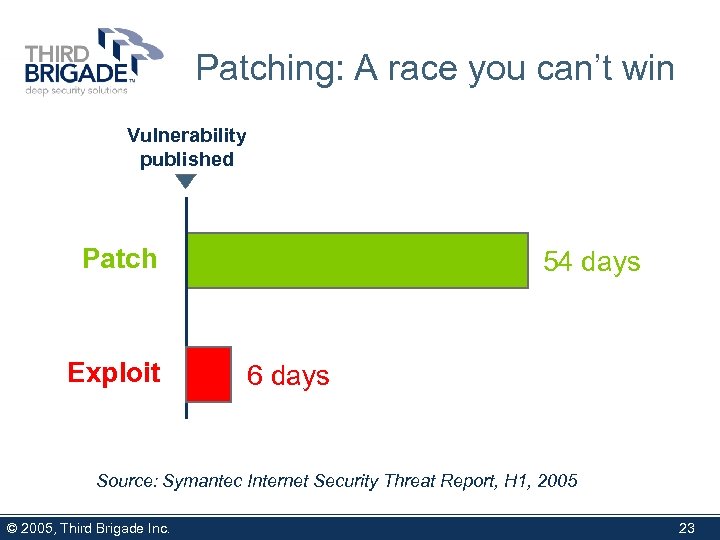
Patching: A race you can’t win Vulnerability published Patch Exploit 54 days 6 days Source: Symantec Internet Security Threat Report, H 1, 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 23
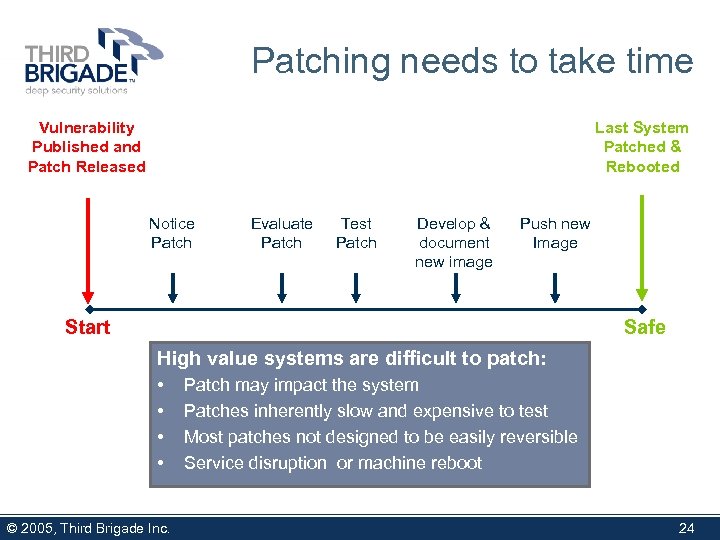
Patching needs to take time Vulnerability Published and Patch Released Last System Patched & Rebooted Notice Patch Evaluate Patch Test Patch Develop & document new image Push new Image Start Safe High value systems are difficult to patch: • • © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Patch may impact the system Patches inherently slow and expensive to test Most patches not designed to be easily reversible Service disruption or machine reboot 24
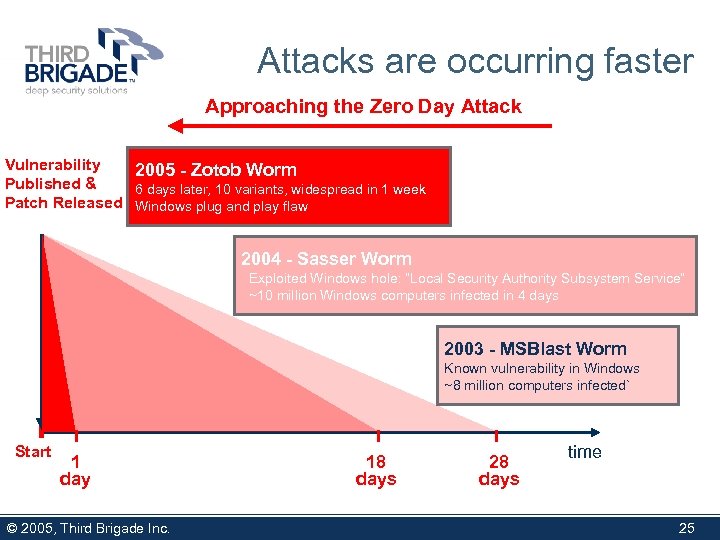
Attacks are occurring faster Approaching the Zero Day Attack Vulnerability 2005 - Zotob Worm Published & 6 days later, 10 variants, widespread in 1 week Patch Released Windows plug and play flaw 2004 - Sasser Worm Exploited Windows hole: “Local Security Authority Subsystem Service” ~10 million Windows computers infected in 4 days 2003 - MSBlast Worm Known vulnerability in Windows ~8 million computers infected` Start 1 day © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 18 days 28 days time 25

Outline Evolving Threat Hackers and Targeted Attacks Counter-attack: Host Intrusion Prevention Conclusions © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 26
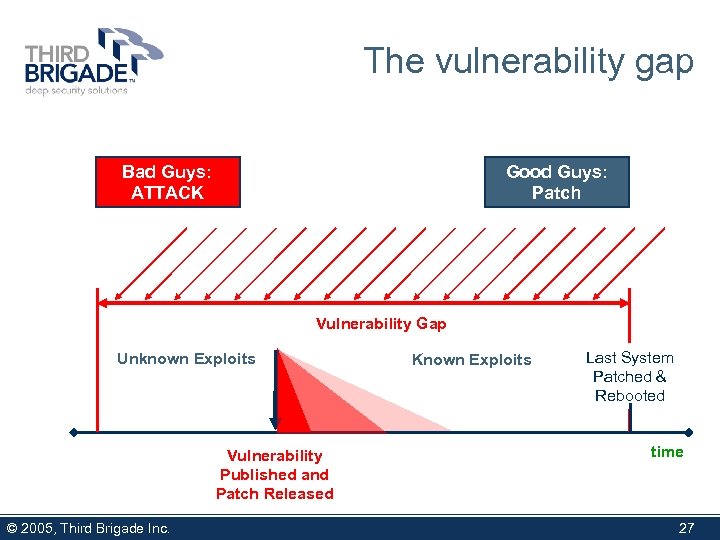
The vulnerability gap Bad Guys: ATTACK Good Guys: Patch Vulnerability Gap Unknown Exploits Vulnerability Published and Patch Released © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Known Exploits Last System Patched & Rebooted time 27
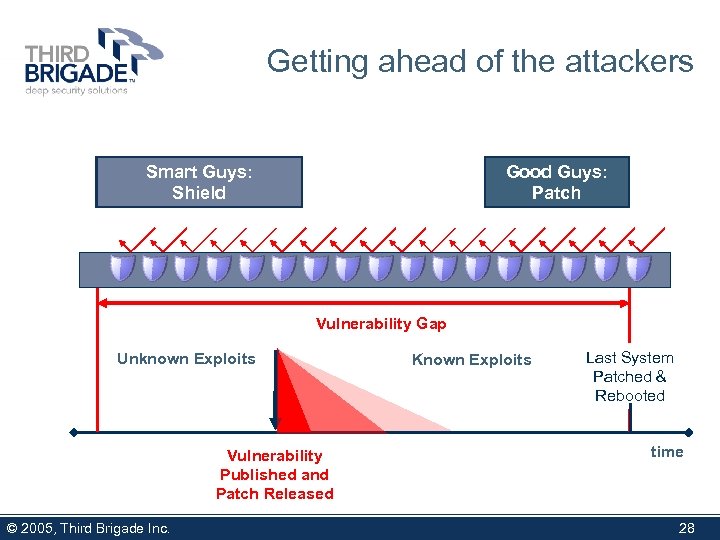
Getting ahead of the attackers Bad Guys: Smart Guys: ATTACK Shield Good Guys: Patch Vulnerability Gap Unknown Exploits Vulnerability Published and Patch Released © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Known Exploits Last System Patched & Rebooted time 28
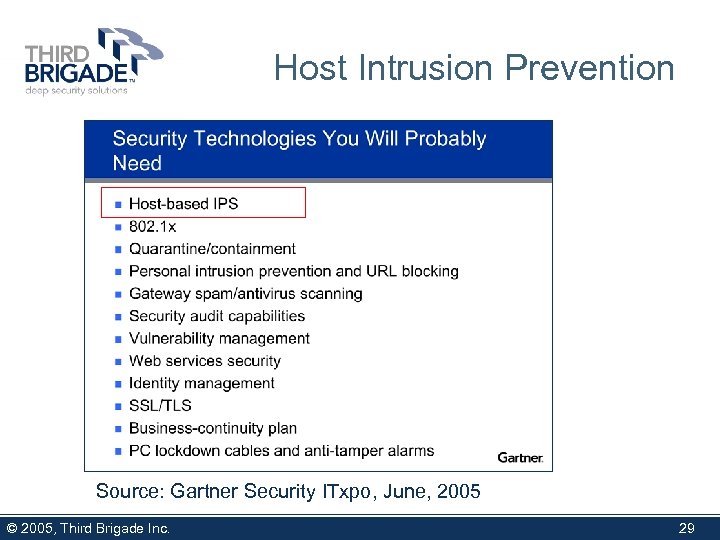
Host Intrusion Prevention Source: Gartner Security ITxpo, June, 2005 © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 29
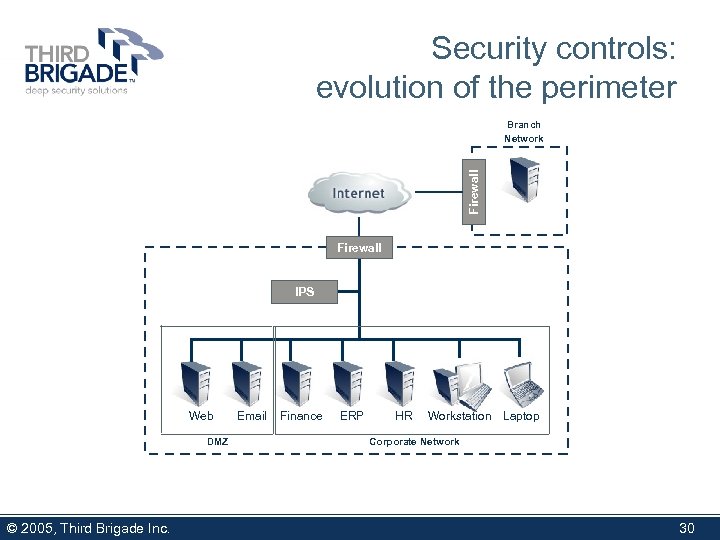
Security controls: evolution of the perimeter Firewall Branch Network Firewall IDS IPS Web DMZ © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Email Finance ERP HR Workstation Laptop Corporate Network 30
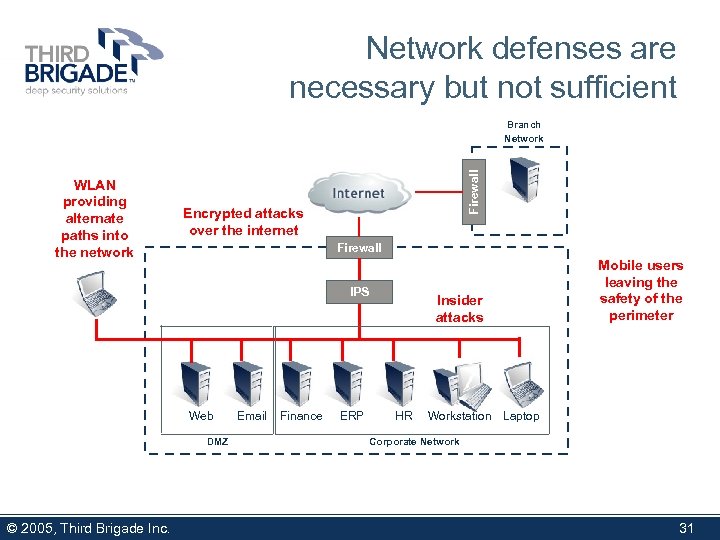
Network defenses are necessary but not sufficient WLAN providing alternate paths into the network Firewall Branch Network Encrypted attacks over the internet Firewall IPS Web DMZ © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Email Finance ERP Insider attacks HR Mobile users leaving the safety of the perimeter Workstation Laptop Corporate Network 31
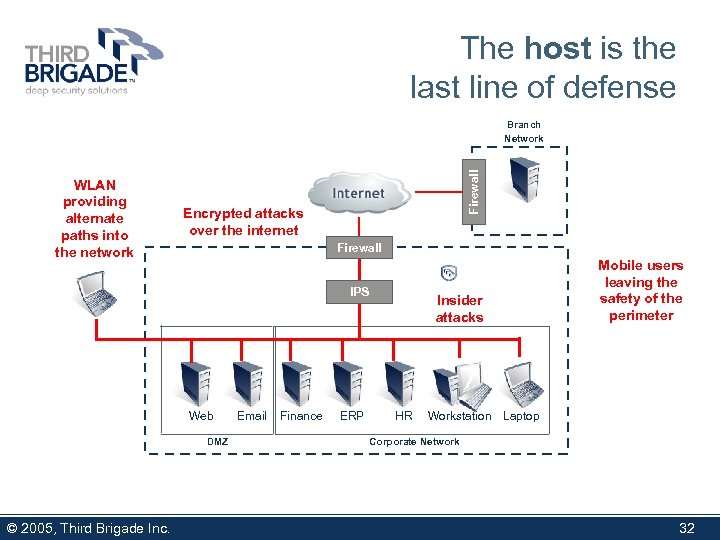
The host is the last line of defense WLAN providing alternate paths into the network Firewall Branch Network Encrypted attacks over the internet Firewall IPS Web DMZ © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Email Finance ERP Insider attacks HR Mobile users leaving the safety of the perimeter Workstation Laptop Corporate Network 32

Experts agree “Firewall-based prevention solutions that function with deep packet inspection techniques are key to effective protection from the growing number of cyber threats” Gartner, Richard Stiennon, Research VP “By 2006, 50% of enterprise servers and 30% of corporate PCs will incorporate host-based security agents (0. 7 probability)” Gartner, John Pescatore, Research VP © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 33
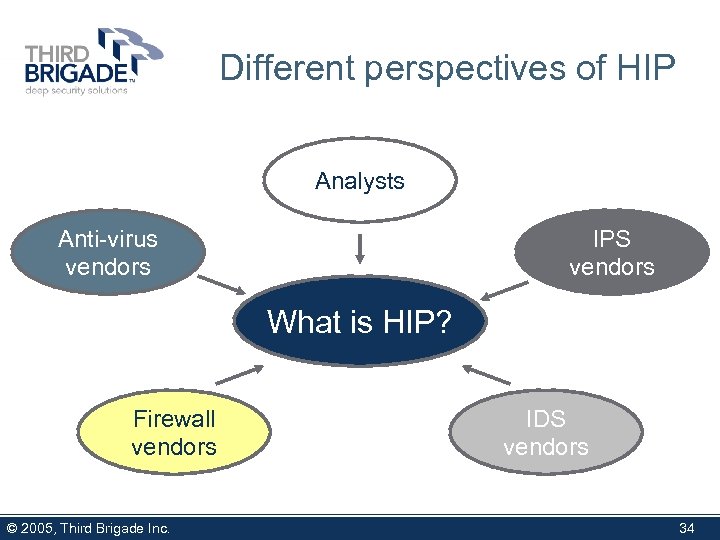
Different perspectives of HIP Analysts Anti-virus vendors IPS vendors What is HIP? Firewall vendors © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. IDS vendors 34
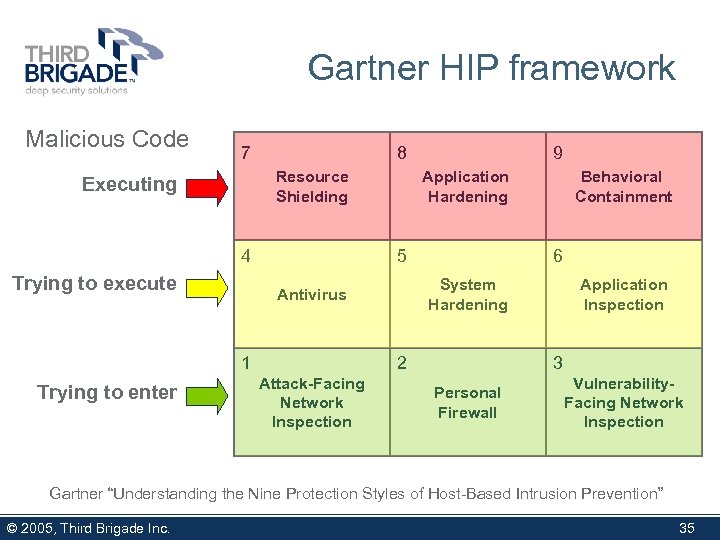
Gartner HIP framework Malicious Code 7 8 Resource Shielding Executing 4 Trying to execute Application Hardening 5 6 2 Attack-Facing Network Inspection Behavioral Containment System Hardening Antivirus 1 Trying to enter 9 Application Inspection 3 Personal Firewall Vulnerability. Facing Network Inspection Gartner “Understanding the Nine Protection Styles of Host-Based Intrusion Prevention” © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 35
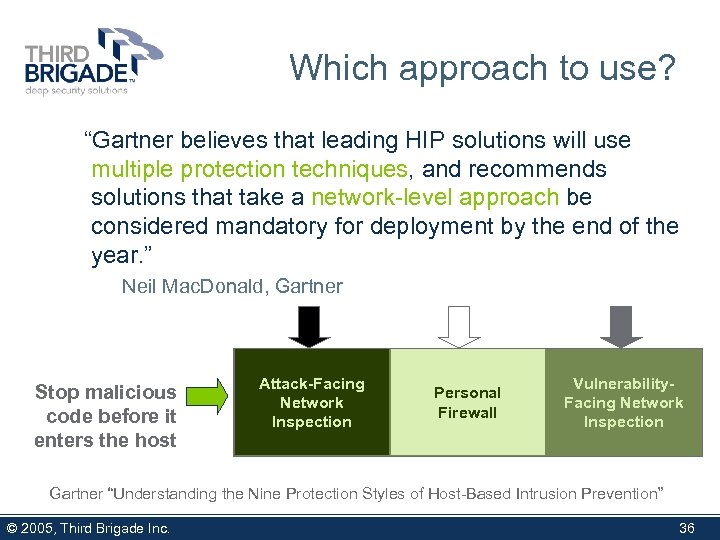
Which approach to use? Known Bad Known Good Unknown “Gartner believes that leading 8 HIP solutions 9 use will 7 multiple protection techniques, and recommends Resource Application Behavioral Shielding Hardening Containment solutions that take a network-level approach be considered mandatory for deployment by the end of the 4 5 6 year. ” Neil Mac. Donald, Gartner Antivirus 1 Stop malicious code before it enters the host System Hardening 2 Attack-Facing Network Inspection Application Inspection 3 Personal Firewall Vulnerability. Facing Network Inspection Gartner “Understanding the Nine Protection Styles of Host-Based Intrusion Prevention” © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 36

Analysts recommend HIP – “The Role of Network Intrusion Prevention in Protecting Medical Devices” (2004) – “Most Important Security Action: Limiting Access to Corporate and Customer Data” (2005) – “Host-Intrusion Prevention is here to Stay” (2004) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 37

HIP: Security best practise Found in security guidelines – “Recommended Security Controls for Federal Information System 800 -53” (2005) – SANS: HIPAA Security Step-by. Step © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 38
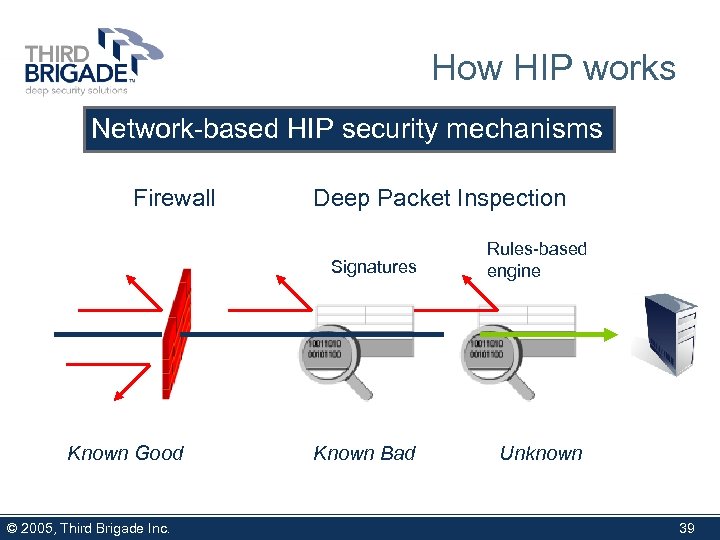
How HIP works Network-based HIP security mechanisms Firewall Deep Packet Inspection Signatures Known Good © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Known Bad Rules-based engine Unknown 39
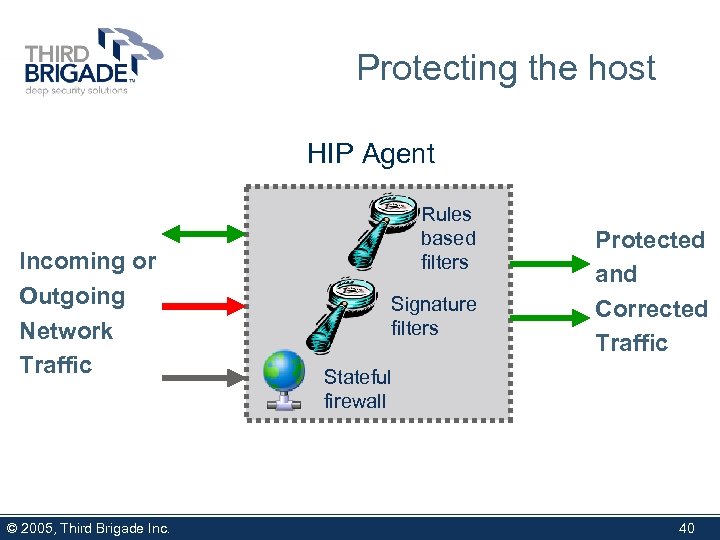
Protecting the host HIP Agent Incoming or Outgoing Network Traffic © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Rules based filters Signature filters Protected and Corrected Traffic Stateful firewall 40
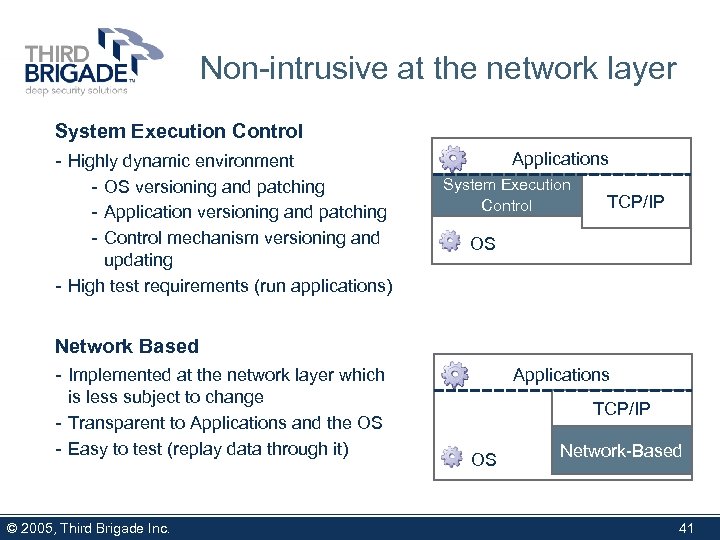
Non-intrusive at the network layer System Execution Control - Highly dynamic environment - OS versioning and patching - Application versioning and patching - Control mechanism versioning and updating - High test requirements (run applications) Applications System Execution Control TCP/IP OS Network Based - Implemented at the network layer which is less subject to change - Transparent to Applications and the OS - Easy to test (replay data through it) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Applications TCP/IP OS Network-Based 41

Software must resist attack • Software agents must be resilient to attack ‘knocking out the security guard’ – Use kernel-mode implementations rather than user-mode – Stateful implementations are resistant to evading deep packet inspection • Manage agents with a central console, not the end user © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 42
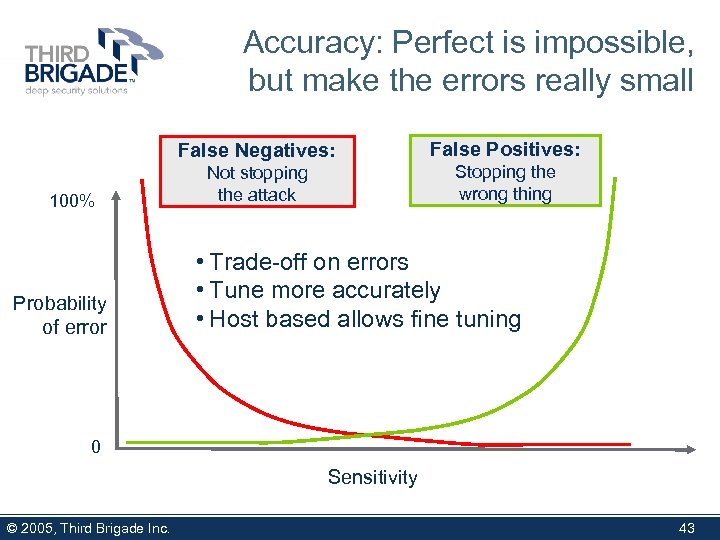
Accuracy: Perfect is impossible, but make the errors really small False Negatives: 100% Probability of error False Positives: Not stopping the attack Stopping the wrong thing • Trade-off on errors • Tune more accurately • Host based allows fine tuning 0 Sensitivity © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 43
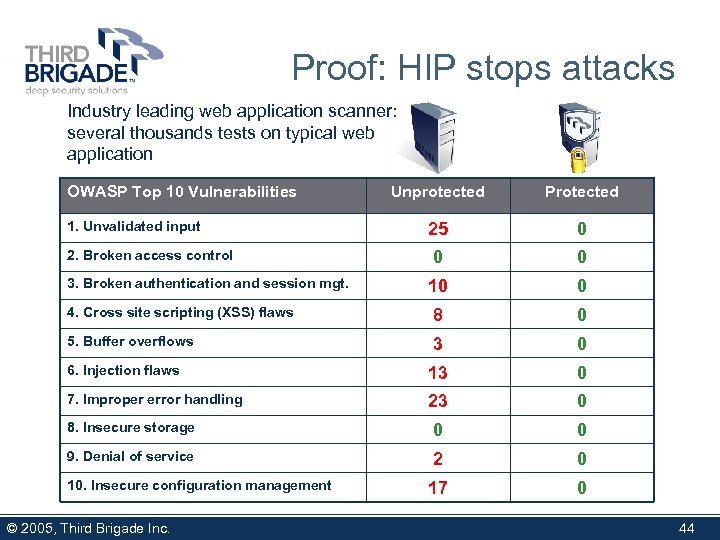
Proof: HIP stops attacks Industry leading web application scanner: several thousands tests on typical web application OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities Unprotected Protected 25 0 0 0 10 0 4. Cross site scripting (XSS) flaws 8 0 5. Buffer overflows 3 0 6. Injection flaws 13 0 7. Improper error handling 23 0 8. Insecure storage 0 0 9. Denial of service 2 0 17 0 1. Unvalidated input 2. Broken access control 3. Broken authentication and session mgt. 10. Insecure configuration management © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 44
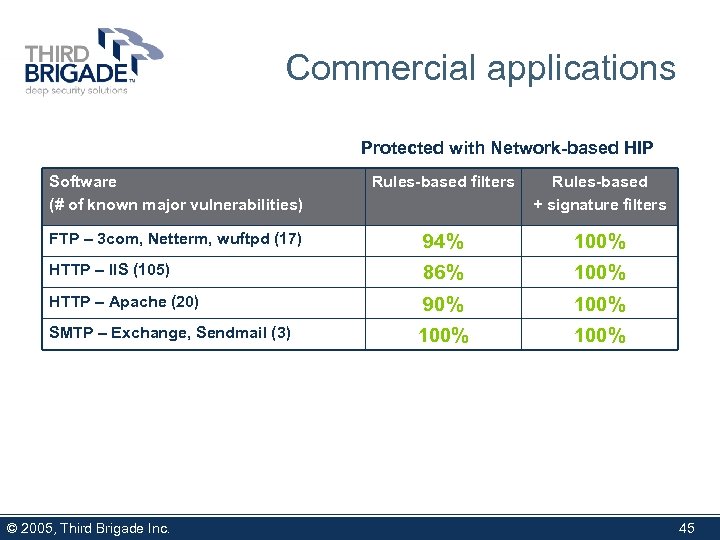
Commercial applications Protected with Network-based HIP Software (# of known major vulnerabilities) Rules-based filters Rules-based + signature filters FTP – 3 com, Netterm, wuftpd (17) 94% 100% HTTP – IIS (105) 86% 100% HTTP – Apache (20) 90% 100% SMTP – Exchange, Sendmail (3) © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 45

Outline Evolving Threat Hackers and Targeted Attacks Counter-attack: Host Intrusion Prevention Conclusions © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 46
Internet, intrusions and HIP everywhere Financial Enterprise Computing Military SCADA © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. Mobile & PDA Telecom Medical Systems Vo. IP 47

Evaluate HIP now • Host Intrusion Prevention technology and products are becoming mainstream by YE 2005. • Organizations need to start evaluating options and testing solutions now. © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 48

Deployment strategy • Incorporate HIP into pilots – Confirm user acceptance (performance, transparency and manageability) – Identify the types of threats these systems are seeing – Demonstrate the effectiveness of HIP in protecting these systems • Deploy applications with confidence – Protect against known and unknown vulnerabilities © 2005, Third Brigade Inc. 49

The End Brian O’Higgins brian. ohiggins@thirdbrigade. com www. thirdbrigade. com © 2005, Third Brigade Inc.
13a8b1f4b589116fcecba39865aed21a.ppt