c5b06a36e7ae923ab7aa20581c6fc6cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

INNOVATION MANAGEMENT Strategies, Implementation and Profits Authored By: Allan Afuah Presented By : Abhinava Chanda Roll No : 313

From Invention to Innovation While invention depends upon creativity, successful technological innovation requires integrating new knowledge with multiple business functions.

Innovation – What is it? The creation of new ideas/processes which will lead to change in an enterprise’s economic or social potential [P. Drucker, ‘The Discipline of Innovation’, Harvard Business Review, Nov-Dec, 1998, 149]
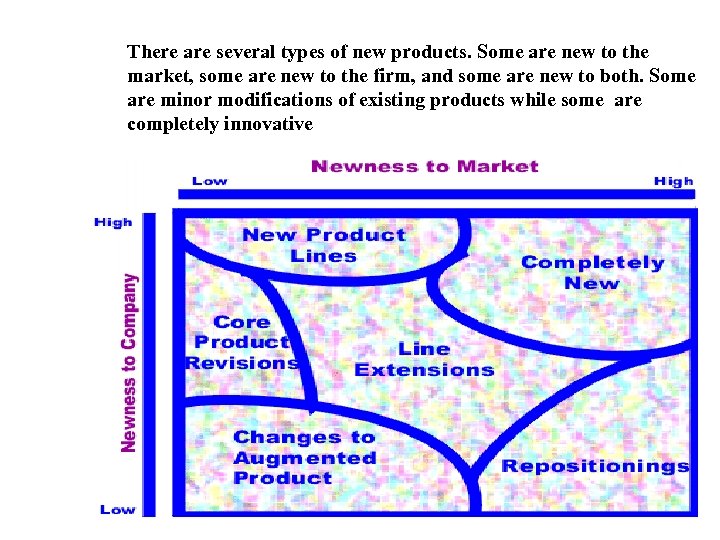
There are several types of new products. Some are new to the market, some are new to the firm, and some are new to both. Some are minor modifications of existing products while some are completely innovative The Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) Division of WIPO
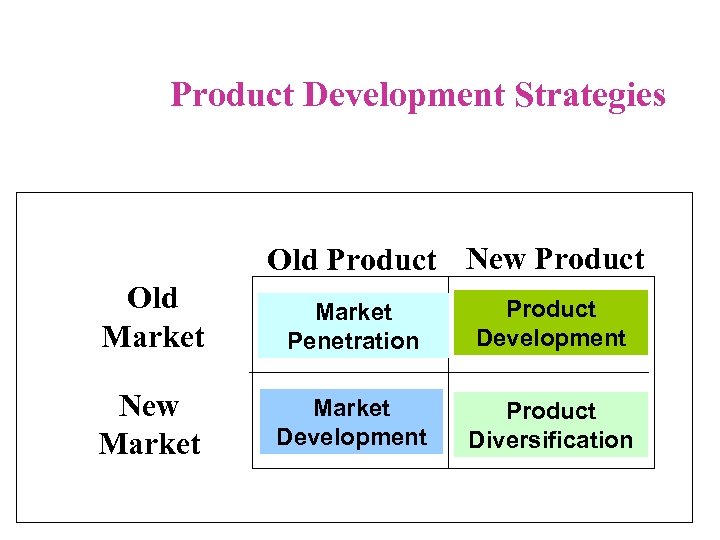
Product Development Strategies Old Product New Product Old Market Penetration Product Development New Market Development Product Diversification
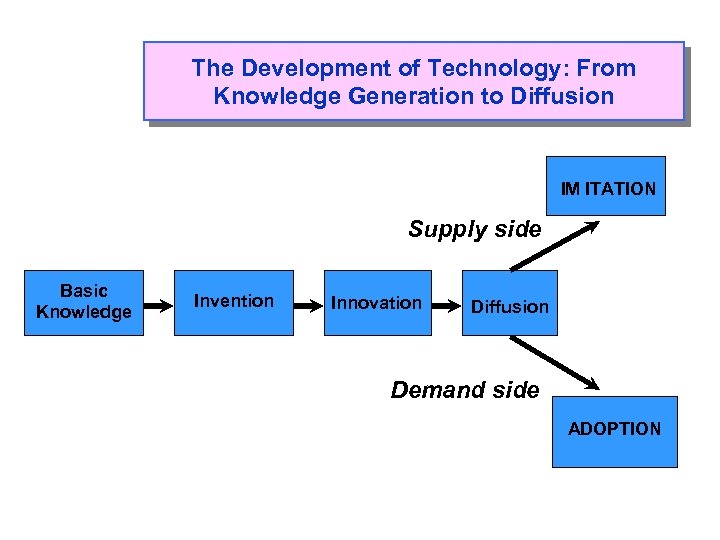
The Development of Technology: From Knowledge Generation to Diffusion IM ITATION Supply side Basic Knowledge Invention Innovation Diffusion Demand side ADOPTION
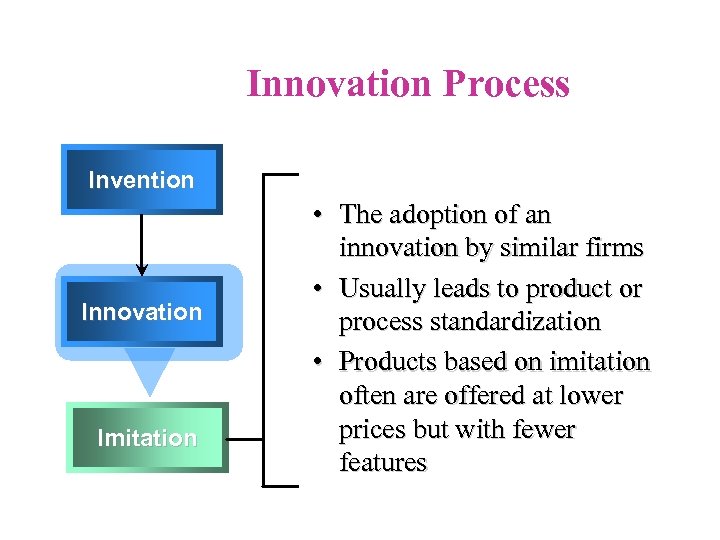
Innovation Process Invention Innovation Imitation • The adoption of an innovation by similar firms • Usually leads to product or process standardization • Products based on imitation often are offered at lower prices but with fewer features
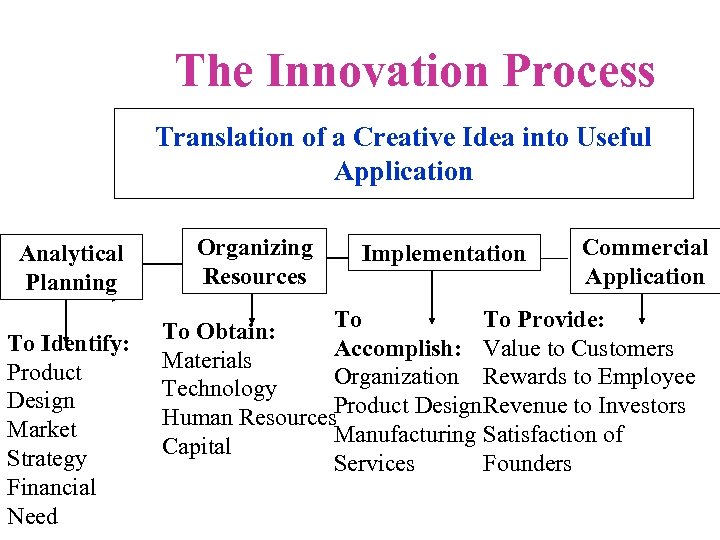
The Innovation Process Translation of a Creative Idea into Useful Application Analytical Planning To Identify: Product Design Market Strategy Financial Need Organizing Resources Implementation Commercial Application To To Provide: To Obtain: Accomplish: Value to Customers Materials Organization Rewards to Employee Technology Human Resources. Product Design Revenue to Investors Manufacturing Satisfaction of Capital Services Founders
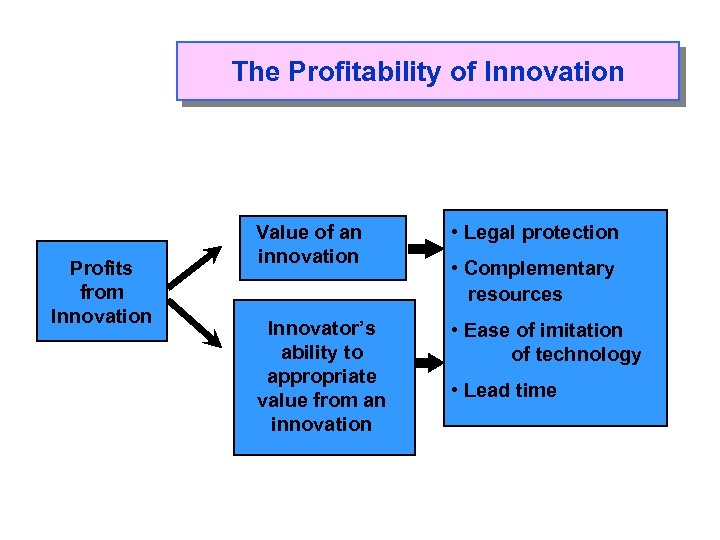
The Profitability of Innovation Profits from Innovation Value of an innovation • Legal protection Innovator’s ability to appropriate value from an innovation • Ease of imitation of technology • Complementary resources • Lead time
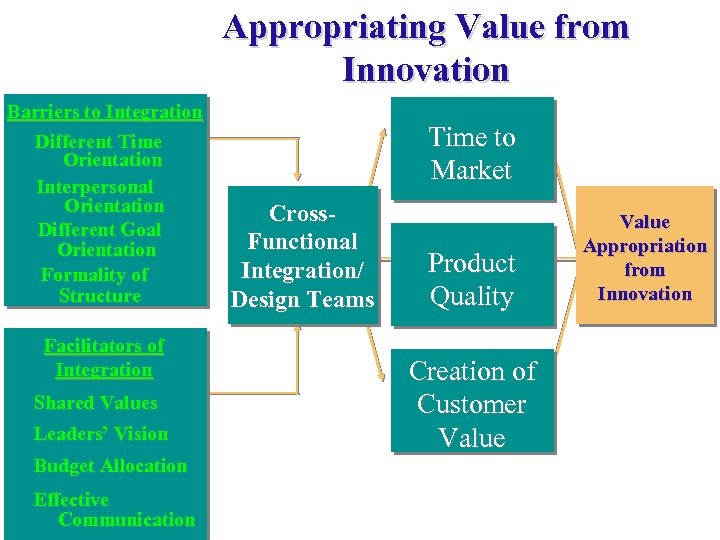
Appropriating Value from Innovation Barriers to Integration Different Time Orientation Interpersonal Orientation Different Goal Orientation Formality of Structure Facilitators of Integration Shared Values Leaders’ Vision Budget Allocation Effective Communication Time to Market Cross. Functional Integration/ Design Teams Product Quality Creation of Customer Value Appropriation from Innovation
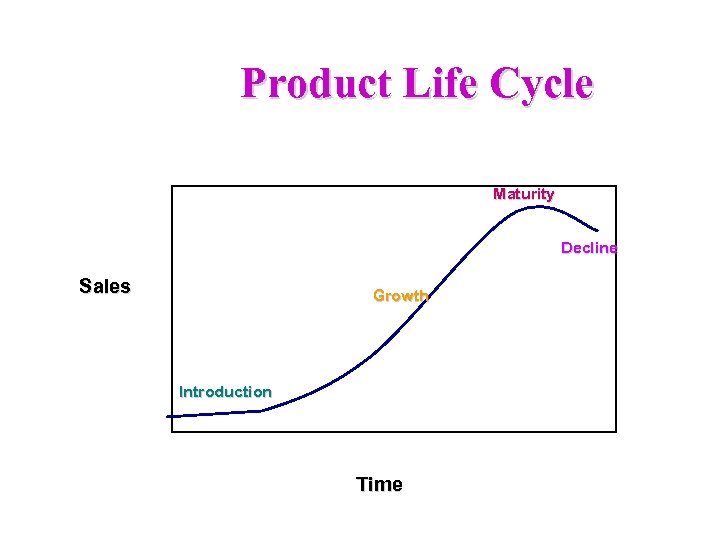
Product Life Cycle Maturity Decline Sales Growth Introduction Time
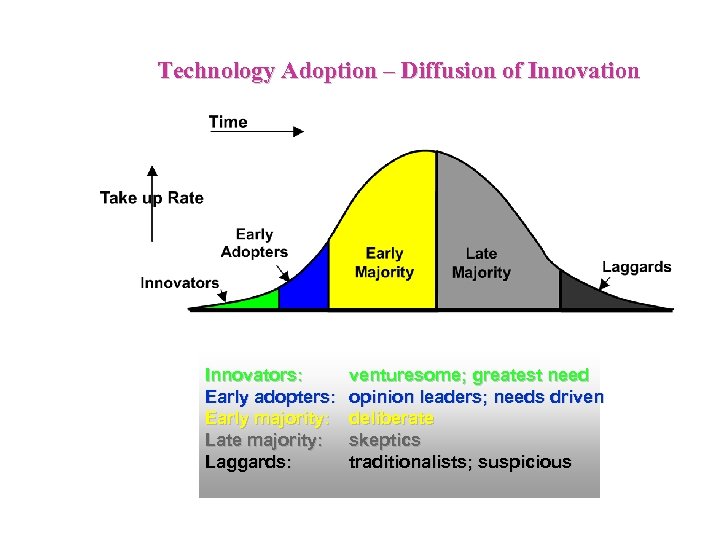
Technology Adoption – Diffusion of Innovation Innovators: Early adopters: Early majority: Late majority: Laggards: venturesome; greatest need opinion leaders; needs driven deliberate skeptics traditionalists; suspicious
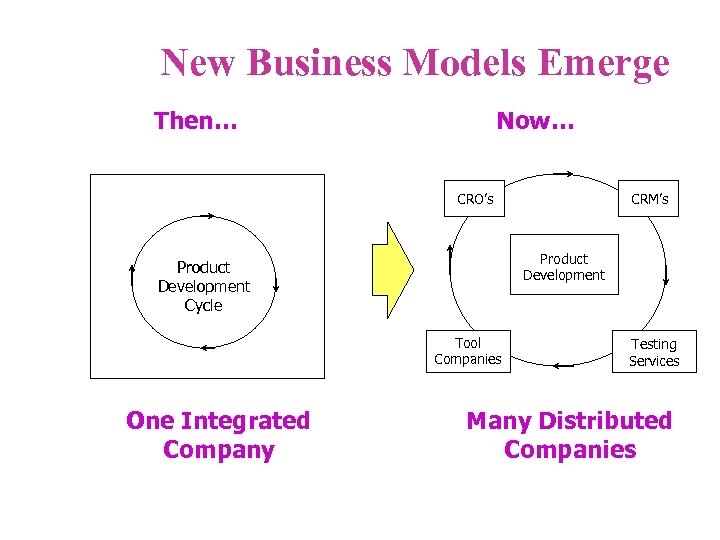
New Business Models Emerge Then… Now… CRM’s CRO’s Product Development Cycle Tool Companies One Integrated Company Testing Services Many Distributed Companies
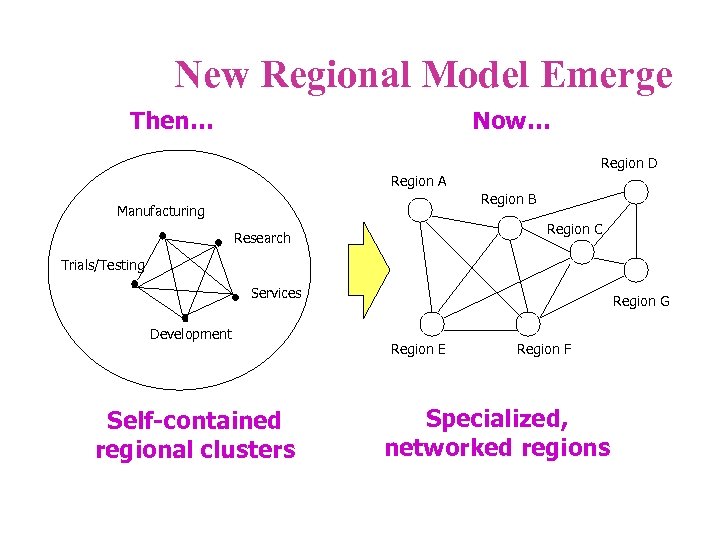
New Regional Model Emerge Then… Now… Region D Region A Region B Manufacturing Region C Research Trials/Testing Services Development Self-contained regional clusters Region G Region E Region F Specialized, networked regions
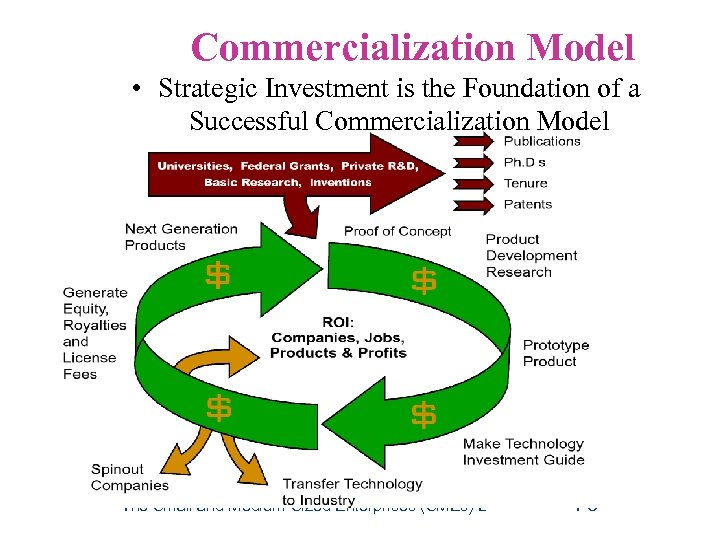
Commercialization Model • Strategic Investment is the Foundation of a Successful Commercialization Model The Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) Division of WIPO
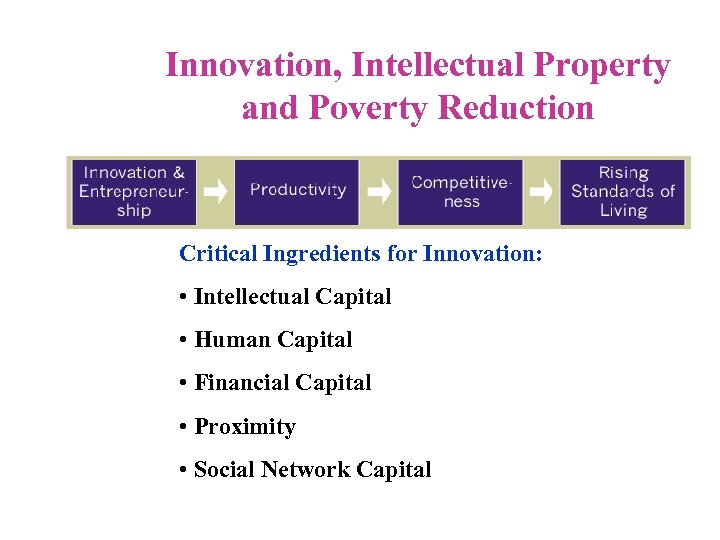
Innovation, Intellectual Property and Poverty Reduction Critical Ingredients for Innovation: • Intellectual Capital • Human Capital • Financial Capital • Proximity • Social Network Capital
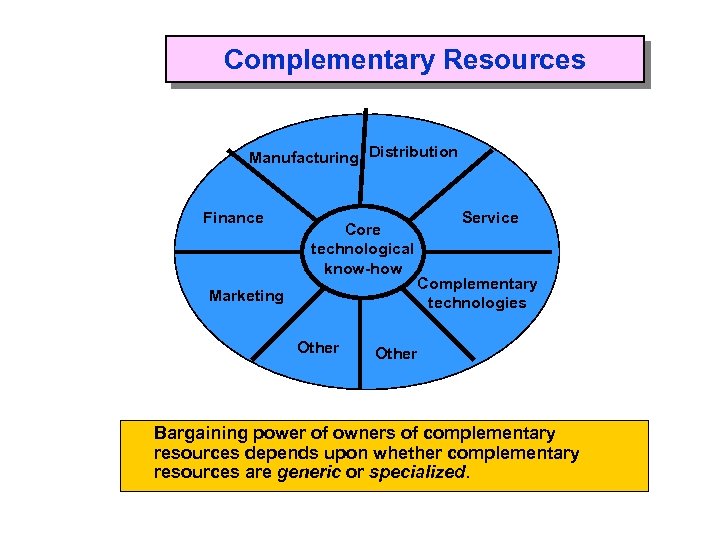
Complementary Resources Manufacturing Distribution Finance Core technological know-how Marketing Other Service Complementary technologies Other Bargaining power of owners of complementary resources depends upon whether complementary resources are generic or specialized.
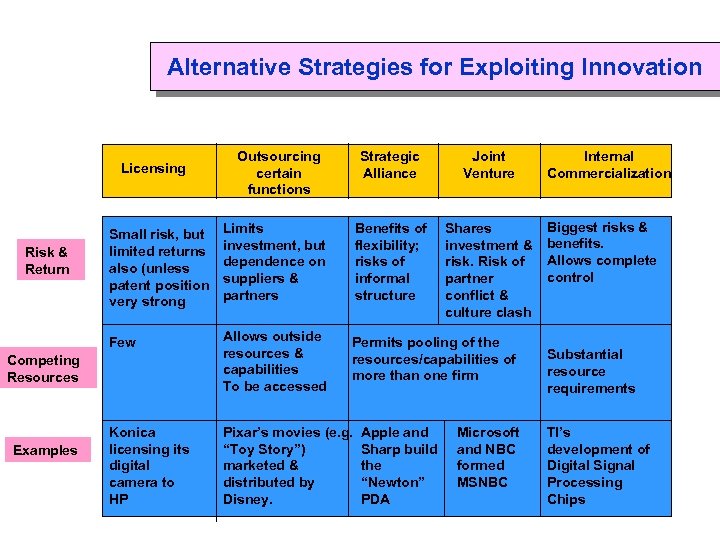
Alternative Strategies for Exploiting Innovation Licensing Outsourcing certain functions Strategic Alliance Joint Venture Shares investment & risk. Risk of partner conflict & culture clash Limits investment, but dependence on suppliers & partners Benefits of flexibility; risks of informal structure Few Risk & Return Small risk, but limited returns also (unless patent position very strong Allows outside resources & capabilities To be accessed Permits pooling of the resources/capabilities of more than one firm Konica licensing its digital camera to HP Pixar’s movies (e. g. “Toy Story”) marketed & distributed by Disney. Competing Resources Examples Apple and Sharp build the “Newton” PDA Microsoft and NBC formed MSNBC Internal Commercialization Biggest risks & benefits. Allows complete control Substantial resource requirements TI’s development of Digital Signal Processing Chips The Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) Division of WIPO
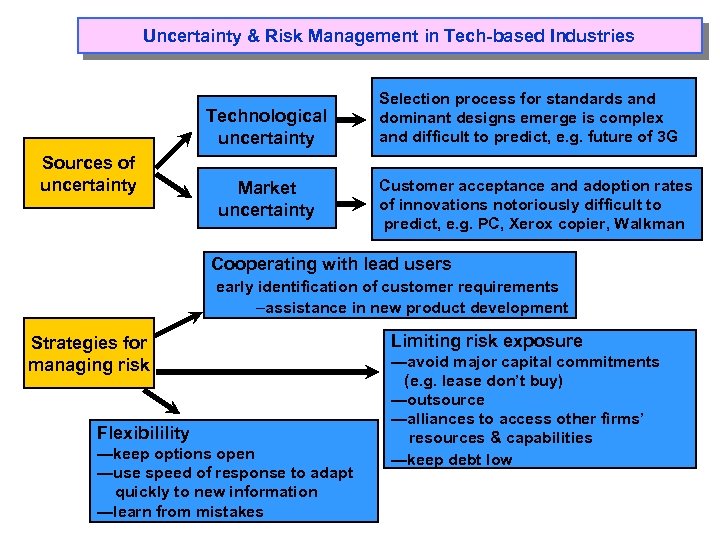
Uncertainty & Risk Management in Tech-based Industries Technological uncertainty Sources of uncertainty Market uncertainty Selection process for standards and dominant designs emerge is complex and difficult to predict, e. g. future of 3 G Customer acceptance and adoption rates of innovations notoriously difficult to predict, e. g. PC, Xerox copier, Walkman Cooperating with lead users early identification of customer requirements –assistance in new product development Strategies for managing risk Flexibilility —keep options open —use speed of response to adapt quickly to new information —learn from mistakes Limiting risk exposure —avoid major capital commitments (e. g. lease don’t buy) —outsource —alliances to access other firms’ resources & capabilities —keep debt low
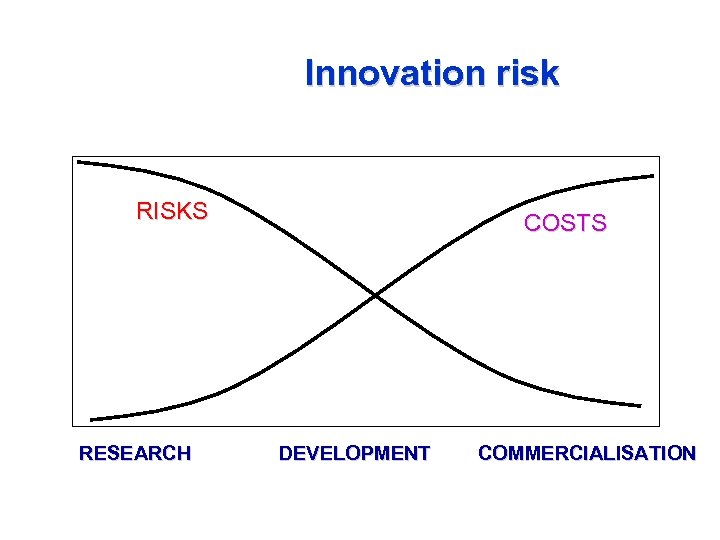
Innovation risk RISKS RESEARCH COSTS DEVELOPMENT COMMERCIALISATION
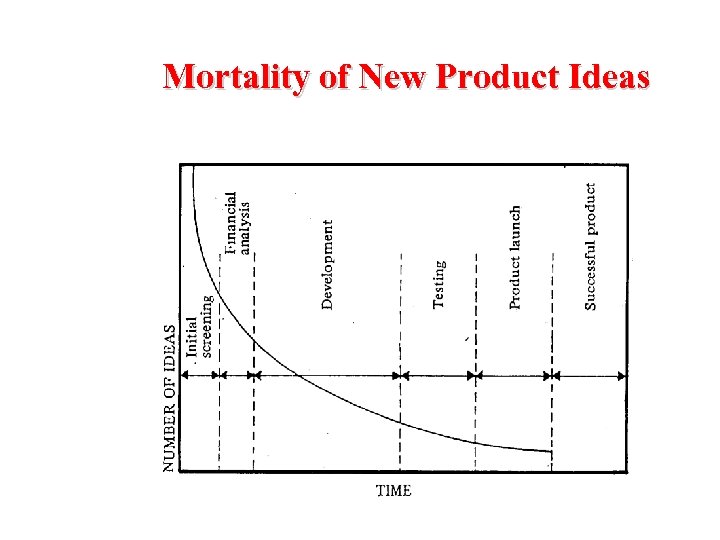
Mortality of New Product Ideas
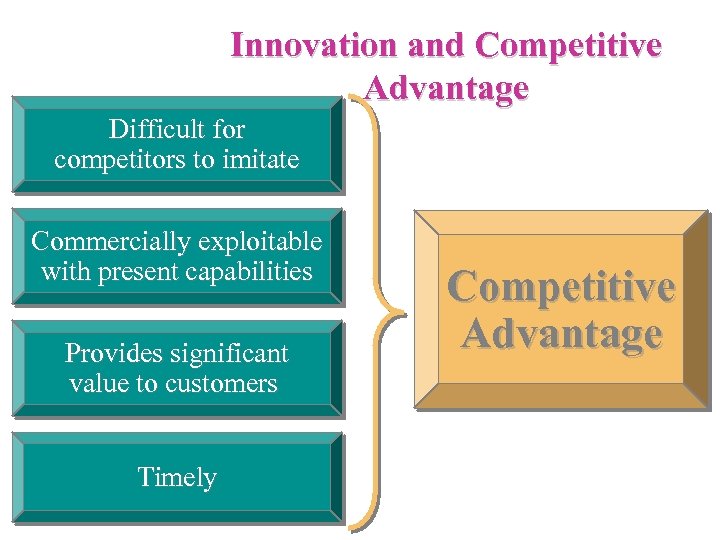
Innovation and Competitive Advantage Difficult for competitors to imitate Commercially exploitable with present capabilities Provides significant value to customers Timely Competitive Advantage

Competitive Advantage Criteria… Low cost producer Product differentiation Niche market
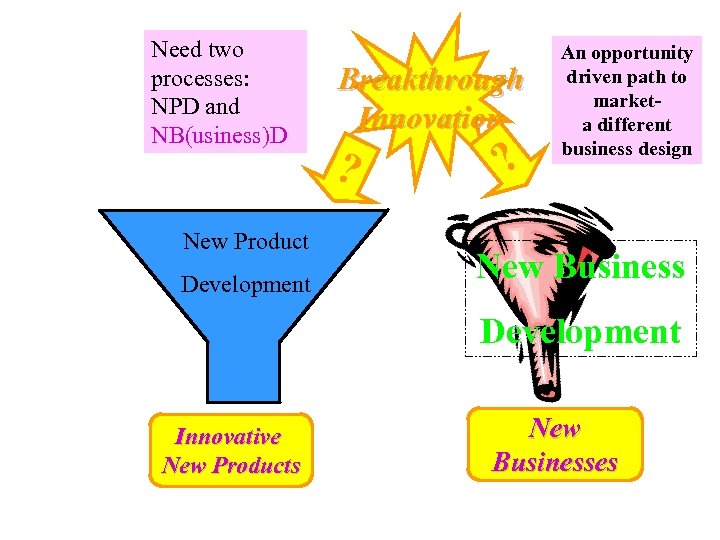
Need two processes: NPD and NB(usiness)D New Product Development Breakthrough Innovation ? ? An opportunity driven path to marketa different business design New Business Development Innovative New Products New Businesses
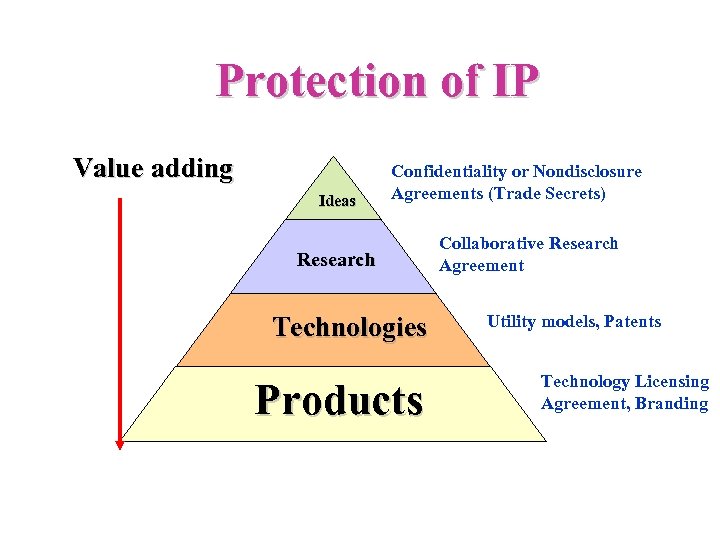
Protection of IP Value adding Ideas Confidentiality or Nondisclosure Agreements (Trade Secrets) Research Technologies Products Collaborative Research Agreement Utility models, Patents Technology Licensing Agreement, Branding

Thank You
c5b06a36e7ae923ab7aa20581c6fc6cc.ppt