cdb0f971e22088b17c966ea9e10de1b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Innovation Management: an overview innovation Dr Paul Trott, Reader in Innovation Management, University of Portsmouth. Professor of Innovation & Entrepreneurship, TU Delft, The Netherlands. P Trott January 2009 Slide 1
Innovation Management: an overview innovation Dr Paul Trott, Reader in Innovation Management, University of Portsmouth. Professor of Innovation & Entrepreneurship, TU Delft, The Netherlands. P Trott January 2009 Slide 1
 PAUL TROTT INNOVATION MANAGEMENT AND NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 4 th Edition innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 2
PAUL TROTT INNOVATION MANAGEMENT AND NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT 4 th Edition innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 2
 Management of Innovation: an overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Introduction Can we manage innovation? Models of understanding of innovation management Factors that influence the innovation process A framework for innovation management Conclusions innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 3
Management of Innovation: an overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Introduction Can we manage innovation? Models of understanding of innovation management Factors that influence the innovation process A framework for innovation management Conclusions innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 3
 Popular view of innovation: innovation. . . the lone inventor/mad professor. P Trott January 2009 Slide 4
Popular view of innovation: innovation. . . the lone inventor/mad professor. P Trott January 2009 Slide 4
 Table 1: World’s most innovative companies Company Margin Growth Stock Returns 1995 -2005 % 1 Apple 7. 1 24. 6 2 Google NA** 3 3 M 3. 4 11. 2 4 Toyota 10. 7 11. 8 5 Microsoft 2. 0 18. 5 6 General Electric 5. 7 13. 4 7 Procter & Gamble 4. 4 12. 6 8 Nokia 0. 0 34. 6 9 Starbucks 2. 2 27. 6 10 IBM -0. 7 14. 4 2006 Rank innovation Source: Business Week April 24, (2006) P Trott January 2009 Slide 5
Table 1: World’s most innovative companies Company Margin Growth Stock Returns 1995 -2005 % 1 Apple 7. 1 24. 6 2 Google NA** 3 3 M 3. 4 11. 2 4 Toyota 10. 7 11. 8 5 Microsoft 2. 0 18. 5 6 General Electric 5. 7 13. 4 7 Procter & Gamble 4. 4 12. 6 8 Nokia 0. 0 34. 6 9 Starbucks 2. 2 27. 6 10 IBM -0. 7 14. 4 2006 Rank innovation Source: Business Week April 24, (2006) P Trott January 2009 Slide 5
 Overview of the innovation process Scientific & technological developments inevitably lead to knowledge inputs. { Creative individuals Firms operating functions & activities innovation { Firms architecture & external linkages Firm’s develop knowledge, processes & products. Societal changes & market needs lead to demands & opportunities. P Trott January 2009 Slide 6
Overview of the innovation process Scientific & technological developments inevitably lead to knowledge inputs. { Creative individuals Firms operating functions & activities innovation { Firms architecture & external linkages Firm’s develop knowledge, processes & products. Societal changes & market needs lead to demands & opportunities. P Trott January 2009 Slide 6
 2. What is innovation ? Invention & innovation Innovation = conception + invention + exploitation innovation Source: Henry & Walker (1991) Innovation is not a single action but a total process of interrelated sub processes. It is not just the conception of a new idea, nor the invention of a new device, nor the development of a new market. The process is all these things acting in an integrated fashion . . . ' Myers and Marquis (1969). P Trott January 2009 Slide 7
2. What is innovation ? Invention & innovation Innovation = conception + invention + exploitation innovation Source: Henry & Walker (1991) Innovation is not a single action but a total process of interrelated sub processes. It is not just the conception of a new idea, nor the invention of a new device, nor the development of a new market. The process is all these things acting in an integrated fashion . . . ' Myers and Marquis (1969). P Trott January 2009 Slide 7
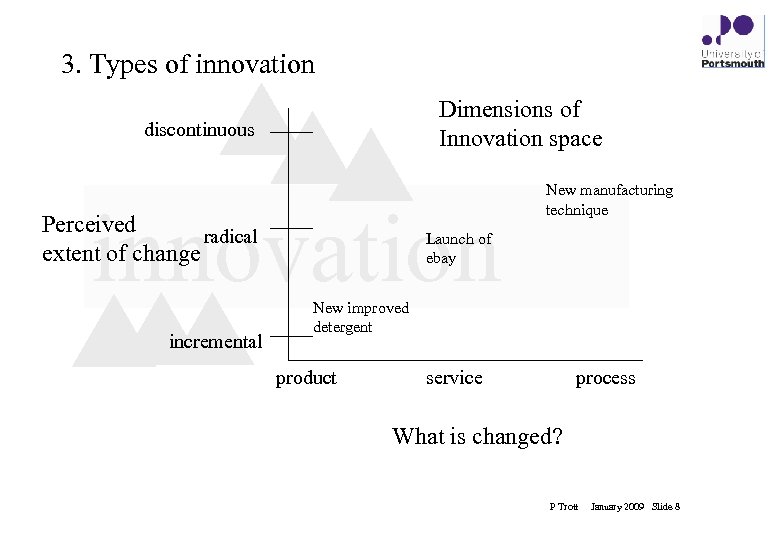 3. Types of innovation Dimensions of Innovation space discontinuous innovation Perceived radical extent of change incremental New manufacturing technique Launch of ebay New improved detergent product service process What is changed? P Trott January 2009 Slide 8
3. Types of innovation Dimensions of Innovation space discontinuous innovation Perceived radical extent of change incremental New manufacturing technique Launch of ebay New improved detergent product service process What is changed? P Trott January 2009 Slide 8
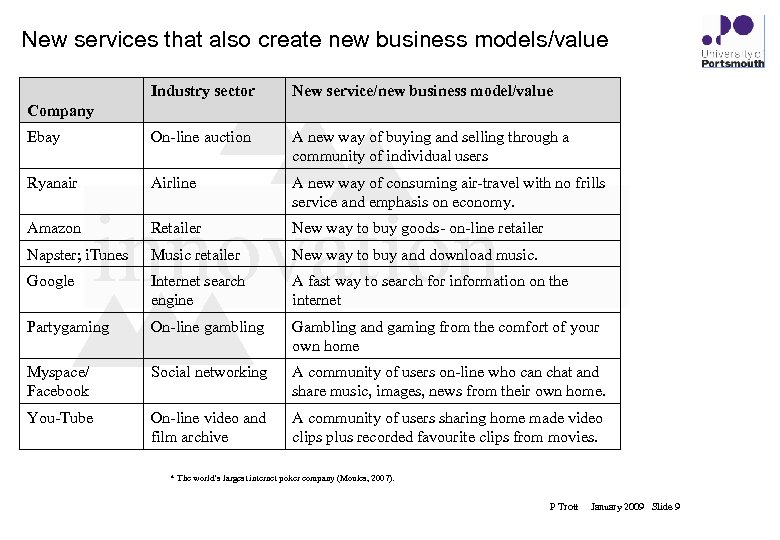 New services that also create new business models/value Industry sector New service/new business model/value Ebay On-line auction A new way of buying and selling through a community of individual users Ryanair Airline A new way of consuming air-travel with no frills service and emphasis on economy. Company Amazon innovation Retailer New way to buy goods- on-line retailer Napster; i. Tunes Music retailer New way to buy and download music. Google Internet search engine A fast way to search for information on the internet Partygaming On-line gambling Gambling and gaming from the comfort of your own home Myspace/ Facebook Social networking A community of users on-line who can chat and share music, images, news from their own home. You-Tube On-line video and film archive A community of users sharing home made video clips plus recorded favourite clips from movies. * The world’s largest internet poker company (Moules, 2007). P Trott January 2009 Slide 9
New services that also create new business models/value Industry sector New service/new business model/value Ebay On-line auction A new way of buying and selling through a community of individual users Ryanair Airline A new way of consuming air-travel with no frills service and emphasis on economy. Company Amazon innovation Retailer New way to buy goods- on-line retailer Napster; i. Tunes Music retailer New way to buy and download music. Google Internet search engine A fast way to search for information on the internet Partygaming On-line gambling Gambling and gaming from the comfort of your own home Myspace/ Facebook Social networking A community of users on-line who can chat and share music, images, news from their own home. You-Tube On-line video and film archive A community of users sharing home made video clips plus recorded favourite clips from movies. * The world’s largest internet poker company (Moules, 2007). P Trott January 2009 Slide 9
 Disruptive innovations • Research by Utterback (1994) & Christensen (2000) suggests many firms find it difficult to manage disruptive innovations; • e. g. IBM, Hoover, UK Banks, etc. innovation • Incumbents in an industry do not respond well to dramatic shifts in behaviour • How do firms manage both continuous change and discontinuous change? P Trott January 2009 Slide 10
Disruptive innovations • Research by Utterback (1994) & Christensen (2000) suggests many firms find it difficult to manage disruptive innovations; • e. g. IBM, Hoover, UK Banks, etc. innovation • Incumbents in an industry do not respond well to dramatic shifts in behaviour • How do firms manage both continuous change and discontinuous change? P Trott January 2009 Slide 10
 5 studies of innovation management Studies of Innovation management 1. Carter & Williams 2. Project Hindsight- TRACES (Isensen) 3. Wealth from knowledge (Langrish et al. ) 4. Project Sappho 1957 1968 5. Minnesota Studies (van de van) 6. Rothwell 7. Sources of innovation (Wheelwright & Clark) 8. MIT studies (Utterback) 9. Project NEWPROD (Cooper) 1989 1992 10. Radical innovation (Leifer) 2000 1972 1974 Industry & technical progress Historical reviews of US gvt funded defence industry Queens Awards for tech innov Success & failure factors in chemical industry 14 case studies of innovations 25 yr review of studies innovation 1992 1994 Different levels of user involvement 5 major industry-level cases Longditudinal survey of success & failure in new products Review of mature businesses P Trott January 2009 Slide 11
5 studies of innovation management Studies of Innovation management 1. Carter & Williams 2. Project Hindsight- TRACES (Isensen) 3. Wealth from knowledge (Langrish et al. ) 4. Project Sappho 1957 1968 5. Minnesota Studies (van de van) 6. Rothwell 7. Sources of innovation (Wheelwright & Clark) 8. MIT studies (Utterback) 9. Project NEWPROD (Cooper) 1989 1992 10. Radical innovation (Leifer) 2000 1972 1974 Industry & technical progress Historical reviews of US gvt funded defence industry Queens Awards for tech innov Success & failure factors in chemical industry 14 case studies of innovations 25 yr review of studies innovation 1992 1994 Different levels of user involvement 5 major industry-level cases Longditudinal survey of success & failure in new products Review of mature businesses P Trott January 2009 Slide 11
 Factors that affect innovation Firm related factors: Organisational heritage Experience R&D team Strategy towards Innovation Organisational structure R&D intensity innovation Project related factors: Complementarity Management style Top management support Technological viability Successful marketable product Product related factors: Relative price Relative quality Uniqueness Technologically advanced Commercial viability Market related factors: Concentration of Target market Timing of market entry Competitive pressure Marketing P Trott January 2009 Slide 12
Factors that affect innovation Firm related factors: Organisational heritage Experience R&D team Strategy towards Innovation Organisational structure R&D intensity innovation Project related factors: Complementarity Management style Top management support Technological viability Successful marketable product Product related factors: Relative price Relative quality Uniqueness Technologically advanced Commercial viability Market related factors: Concentration of Target market Timing of market entry Competitive pressure Marketing P Trott January 2009 Slide 12
 Linear models of innovation management innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 13
Linear models of innovation management innovation P Trott January 2009 Slide 13
 Interactive model of innovation TECHNOLOGY PUSH latest science and technology advances in society innovation idea MARKET PULL R&D Manufacturing Marketing commercial product needs of society and the market place Source: Rothwell & Zegweld (1985) P Trott January 2009 Slide 14
Interactive model of innovation TECHNOLOGY PUSH latest science and technology advances in society innovation idea MARKET PULL R&D Manufacturing Marketing commercial product needs of society and the market place Source: Rothwell & Zegweld (1985) P Trott January 2009 Slide 14
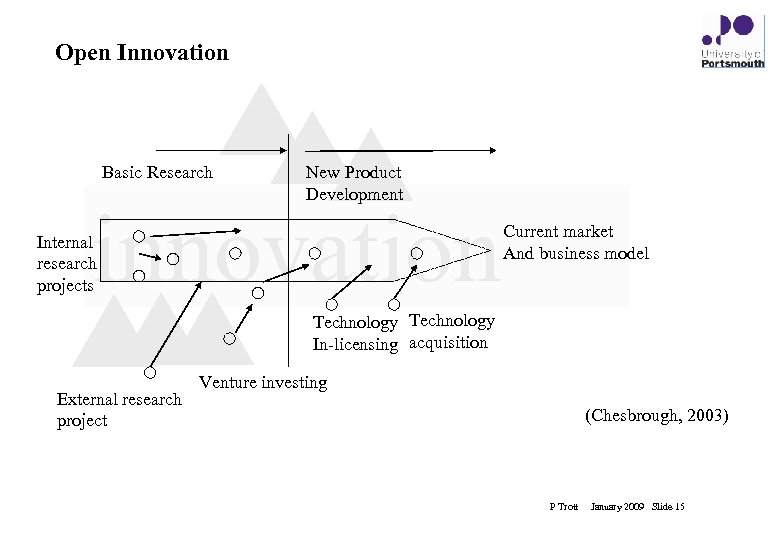 Open Innovation Basic Research New Product Development innovation Internal research projects Current market And business model Technology In-licensing acquisition External research project Venture investing (Chesbrough, 2003) P Trott January 2009 Slide 15
Open Innovation Basic Research New Product Development innovation Internal research projects Current market And business model Technology In-licensing acquisition External research project Venture investing (Chesbrough, 2003) P Trott January 2009 Slide 15
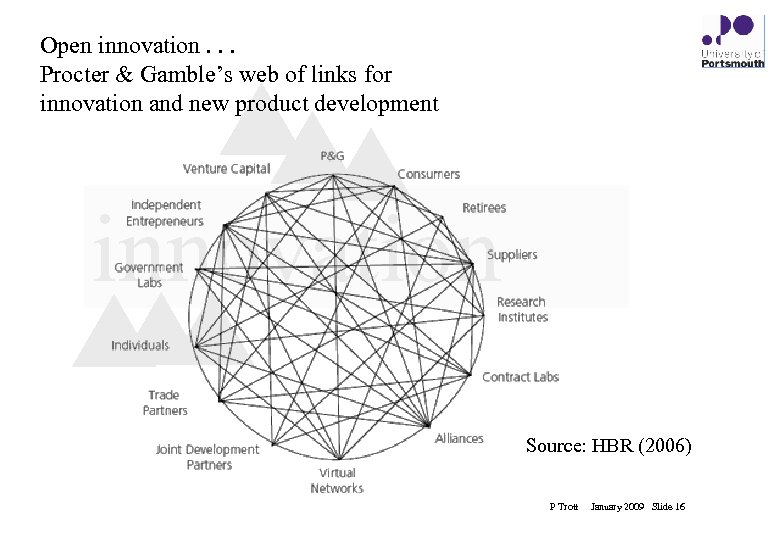 Open innovation. . . Procter & Gamble’s web of links for innovation and new product development innovation Source: HBR (2006) P Trott January 2009 Slide 16
Open innovation. . . Procter & Gamble’s web of links for innovation and new product development innovation Source: HBR (2006) P Trott January 2009 Slide 16
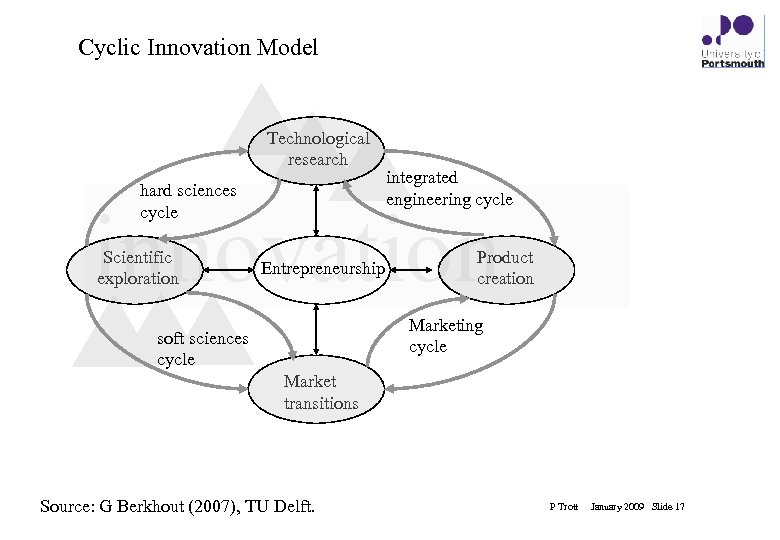 Cyclic Innovation Model Technological research hard sciences cycle integrated engineering cycle innovation Scientific exploration Entrepreneurship Product creation Marketing cycle soft sciences cycle Market transitions Source: G Berkhout (2007), TU Delft. P Trott January 2009 Slide 17
Cyclic Innovation Model Technological research hard sciences cycle integrated engineering cycle innovation Scientific exploration Entrepreneurship Product creation Marketing cycle soft sciences cycle Market transitions Source: G Berkhout (2007), TU Delft. P Trott January 2009 Slide 17
 The end innovation Thank you For listening P Trott January 2009 Slide 18
The end innovation Thank you For listening P Trott January 2009 Slide 18


