de54067e5a2a32b8c2da347fdcb740a3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Innovation in Western Canada ISRN Policy Workshop, 2004 J. Adam Holbrook, P. Eng. , Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology, Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC 1 CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Innovation in Western Canada ISRN Policy Workshop, 2004 J. Adam Holbrook, P. Eng. , Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology, Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC 1 CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 What are the objectives for innovation policy • To identify who are the innovators and what are the innovations • To differentiate between inventors, innovators and implementers • To establish public sector infrastructure to support innovation CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
What are the objectives for innovation policy • To identify who are the innovators and what are the innovations • To differentiate between inventors, innovators and implementers • To establish public sector infrastructure to support innovation CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 Innovation in Western Canada • Studies of innovation have been carried out at the national level, but : • Industrial demographics skew results towards Ontario and Quebec, and towards major population centres in other provinces, tending to mask regional effects • Studies of innovation are usually tied to areas, “poles”, where there are significant levels of industrial activity. But what happens in areas where manufacturing is not the predominant sector? • For example, BC is moving from a resource-based economy directly to a services-based economy; outside the Lower Mainland the key actors are SMEs, federal laboratories and CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY community colleges 05/14/99 2 Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Innovation in Western Canada • Studies of innovation have been carried out at the national level, but : • Industrial demographics skew results towards Ontario and Quebec, and towards major population centres in other provinces, tending to mask regional effects • Studies of innovation are usually tied to areas, “poles”, where there are significant levels of industrial activity. But what happens in areas where manufacturing is not the predominant sector? • For example, BC is moving from a resource-based economy directly to a services-based economy; outside the Lower Mainland the key actors are SMEs, federal laboratories and CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY community colleges 05/14/99 2 Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 Our regional policy challenges • How to apply current scholarship to regional economies and specific clusters that are rooted in resource industries and/or are based on lifestyle considerations? • Is it possible for an economy to move from a resource-based, labour intensive economy, to a services-based, knowledge based economy? • Are western Canadian economies and societies measurably different from those in eastern Canada? Are OECD studies and surveys relevant? CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY • What is the role of Canada in the Pacific Rim? Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Our regional policy challenges • How to apply current scholarship to regional economies and specific clusters that are rooted in resource industries and/or are based on lifestyle considerations? • Is it possible for an economy to move from a resource-based, labour intensive economy, to a services-based, knowledge based economy? • Are western Canadian economies and societies measurably different from those in eastern Canada? Are OECD studies and surveys relevant? CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY • What is the role of Canada in the Pacific Rim? Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 Factors affecting innovation in a resource-based economy • From CPROST studies, high-tech firms tended to view in-house R&D, customers and marketing as important sources of innovation. • Resource-based firms tended to regard suppliers, management and production departments as more sources of innovation, possibly reflecting their interest in improving processes rather than products. • Innovative firms have common characteristics regardless of industrial sector (e. g. training programs). • Availability of financing was not seen as a hindrance to innovation (confirming an. FRASER UNIVERSITY CPROST SIMON earlier Stat. Can result). Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Factors affecting innovation in a resource-based economy • From CPROST studies, high-tech firms tended to view in-house R&D, customers and marketing as important sources of innovation. • Resource-based firms tended to regard suppliers, management and production departments as more sources of innovation, possibly reflecting their interest in improving processes rather than products. • Innovative firms have common characteristics regardless of industrial sector (e. g. training programs). • Availability of financing was not seen as a hindrance to innovation (confirming an. FRASER UNIVERSITY CPROST SIMON earlier Stat. Can result). Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 Necessary vs. Sufficient Cluster Conditions • What are the necessary and sufficient conditions that support the formation of a cluster in Canada? Are these region specific? • Necessary (common features): university, labs, government agencies, private firms, human capital (? ) • Sufficient (conditions for continued existence): at least one private firm with a global reach (Porter), manufacturing resources, active/interventionist public sector (? ) • Potential test – Catastrophic loss of a node/actor CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY can a cluster survive without certain nodes? Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Necessary vs. Sufficient Cluster Conditions • What are the necessary and sufficient conditions that support the formation of a cluster in Canada? Are these region specific? • Necessary (common features): university, labs, government agencies, private firms, human capital (? ) • Sufficient (conditions for continued existence): at least one private firm with a global reach (Porter), manufacturing resources, active/interventionist public sector (? ) • Potential test – Catastrophic loss of a node/actor CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY can a cluster survive without certain nodes? Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
 Selected initial results • Clusters in Canada have a large public-sector institution at the centre • High-tech clusters in the west often produce IP rather than manufactured products: biotech, new media; Vancouver has a higher number of biotech “stars” than Montreal or Toronto • Biotech in Saskatoon is different: much of the knowledge required for innovation and production is acquired through straightforward market transactions. • Major differences in labour structure between CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY primary wood products sector and secondary wood products Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Selected initial results • Clusters in Canada have a large public-sector institution at the centre • High-tech clusters in the west often produce IP rather than manufactured products: biotech, new media; Vancouver has a higher number of biotech “stars” than Montreal or Toronto • Biotech in Saskatoon is different: much of the knowledge required for innovation and production is acquired through straightforward market transactions. • Major differences in labour structure between CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY primary wood products sector and secondary wood products Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
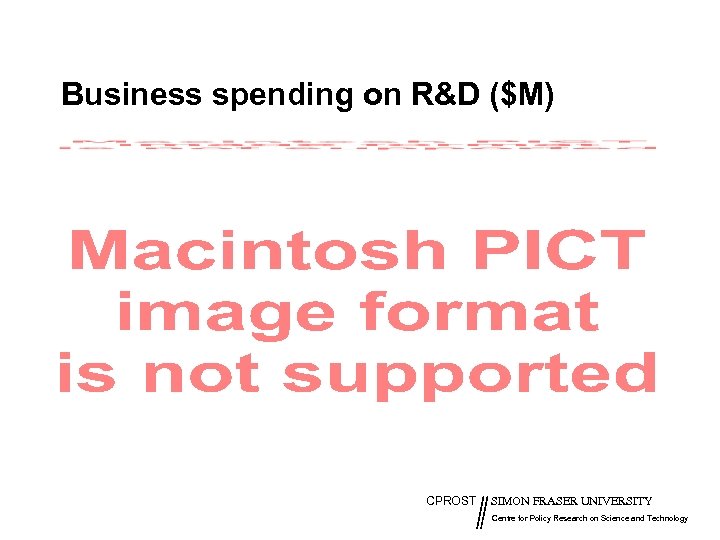 Business spending on R&D ($M) CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Business spending on R&D ($M) CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
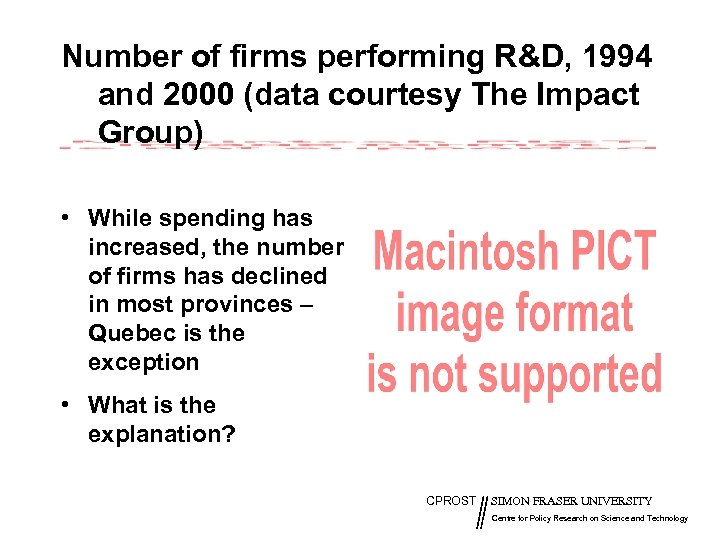 Number of firms performing R&D, 1994 and 2000 (data courtesy The Impact Group) • While spending has increased, the number of firms has declined in most provinces – Quebec is the exception • What is the explanation? CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
Number of firms performing R&D, 1994 and 2000 (data courtesy The Impact Group) • While spending has increased, the number of firms has declined in most provinces – Quebec is the exception • What is the explanation? CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
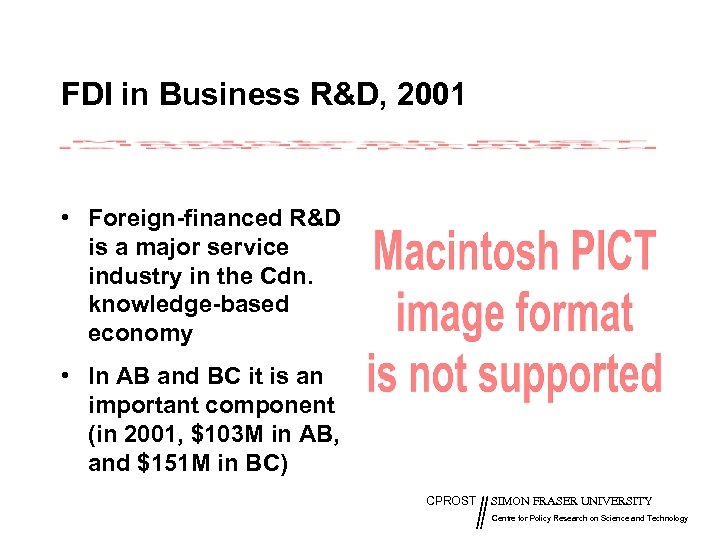 FDI in Business R&D, 2001 • Foreign-financed R&D is a major service industry in the Cdn. knowledge-based economy • In AB and BC it is an important component (in 2001, $103 M in AB, and $151 M in BC) CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology
FDI in Business R&D, 2001 • Foreign-financed R&D is a major service industry in the Cdn. knowledge-based economy • In AB and BC it is an important component (in 2001, $103 M in AB, and $151 M in BC) CPROST SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Centre for Policy Research on Science and Technology


