c6b0c4991a94735b6d5f23858e7e457a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 INNOVATION AND ON-LINE LEARNING: Insights and experience with on-line learning issues from research, policy, and practical perspectives. OECD-CMEC-CANADA Seminar David Fransen Associate Assistant Deputy Minister Spectrum, Information Technologies and Telecommunications Industry Canada April 2002 Canada
INNOVATION AND ON-LINE LEARNING: Insights and experience with on-line learning issues from research, policy, and practical perspectives. OECD-CMEC-CANADA Seminar David Fransen Associate Assistant Deputy Minister Spectrum, Information Technologies and Telecommunications Industry Canada April 2002 Canada
 The Innovation Vision “In the new global knowledge economy of the 21 st century prosperity depends on innovation which, in turn, depends on the investments that we make in the creativity and talents of our people. We must invest not only in technology and innovation but also, in the Canadian way, to create an environment of inclusion, in which all Canadians can take advantage of their talents, their skills and their ideas; in which imagination, skills and innovative capacity combine for maximum effect. ” The Right Honourable Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy 2
The Innovation Vision “In the new global knowledge economy of the 21 st century prosperity depends on innovation which, in turn, depends on the investments that we make in the creativity and talents of our people. We must invest not only in technology and innovation but also, in the Canadian way, to create an environment of inclusion, in which all Canadians can take advantage of their talents, their skills and their ideas; in which imagination, skills and innovative capacity combine for maximum effect. ” The Right Honourable Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy 2
 Canada’s Innovation Strategy Achieving Excellence I e i g i Pe e, K edge a d O i Knowledge Matters Ski a d Lea i g f Ca adia “Economic Success and Social Success go hand in hand” Prime Minister Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy February 12, 2002
Canada’s Innovation Strategy Achieving Excellence I e i g i Pe e, K edge a d O i Knowledge Matters Ski a d Lea i g f Ca adia “Economic Success and Social Success go hand in hand” Prime Minister Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy February 12, 2002
 Innovation: Context k k k Knowledge has become key driver of economic performance. Canada will secure its competitive advantage in the global KBE by maximizing its capacity to innovate. Canada’s goal is to be recognized as one of the most innovative countries in the world. We must improve Canada’s innovation performance to ensure a high standard of living and quality of life. The private sector is at the centre of innovation. Governments and academia have a supportive role in three areas: knowledge performance, skills, and the innovation environment.
Innovation: Context k k k Knowledge has become key driver of economic performance. Canada will secure its competitive advantage in the global KBE by maximizing its capacity to innovate. Canada’s goal is to be recognized as one of the most innovative countries in the world. We must improve Canada’s innovation performance to ensure a high standard of living and quality of life. The private sector is at the centre of innovation. Governments and academia have a supportive role in three areas: knowledge performance, skills, and the innovation environment.
 Canada’s Innovation Strategy Canada’s Innovation Challenges: k k k The Knowledge Performance Challenge Knowledge Matters ! Create and use knowledge strategically to benefit Canadians The Skills Challenge - Achieving Excellence ! Increase the supply of highly qualified people The Innovation Environment Challenge ! Work towards a better innovation environment
Canada’s Innovation Strategy Canada’s Innovation Challenges: k k k The Knowledge Performance Challenge Knowledge Matters ! Create and use knowledge strategically to benefit Canadians The Skills Challenge - Achieving Excellence ! Increase the supply of highly qualified people The Innovation Environment Challenge ! Work towards a better innovation environment
 Knowledge Matters: Literacy Redefined k k k Literacy 3 Rs and a D Need for collaborative approach for defining and tracking digital literacy “(Digital)/ICT literacy is using digital technology, communications tools, and/or networks to access, manage, integrate, evaluate, and create information in order to function in a knowledge society. ” All young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 6
Knowledge Matters: Literacy Redefined k k k Literacy 3 Rs and a D Need for collaborative approach for defining and tracking digital literacy “(Digital)/ICT literacy is using digital technology, communications tools, and/or networks to access, manage, integrate, evaluate, and create information in order to function in a knowledge society. ” All young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 6
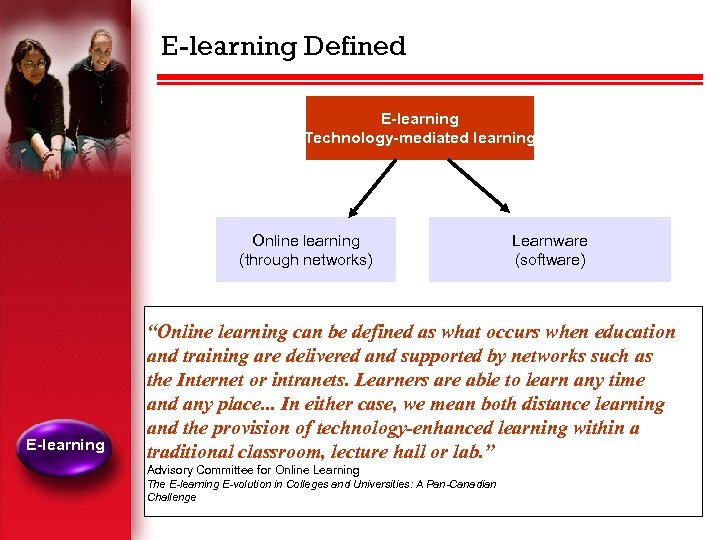 E-learning Defined E-learning Technology-mediated learning Online learning (through networks) E-learning Learnware (software) “Online learning can be defined as what occurs when education and training are delivered and supported by networks such as the Internet or intranets. Learners are able to learn any time and any place. . . In either case, we mean both distance learning and the provision of technology-enhanced learning within a traditional classroom, lecture hall or lab. ” Advisory Committee for Online Learning The E-learning E-volution in Colleges and Universities: A Pan-Canadian Challenge 7
E-learning Defined E-learning Technology-mediated learning Online learning (through networks) E-learning Learnware (software) “Online learning can be defined as what occurs when education and training are delivered and supported by networks such as the Internet or intranets. Learners are able to learn any time and any place. . . In either case, we mean both distance learning and the provision of technology-enhanced learning within a traditional classroom, lecture hall or lab. ” Advisory Committee for Online Learning The E-learning E-volution in Colleges and Universities: A Pan-Canadian Challenge 7
 E-learning is Key to Canada’s Innovation Strategy E-learning offers the opportunity to: k k increase the number of adults pursuing learning opportunities k E-learning develop the most skilled and talented labour force in the world increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers k k stimulate Canadian educational content address the Digital Divide 8
E-learning is Key to Canada’s Innovation Strategy E-learning offers the opportunity to: k k increase the number of adults pursuing learning opportunities k E-learning develop the most skilled and talented labour force in the world increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers k k stimulate Canadian educational content address the Digital Divide 8
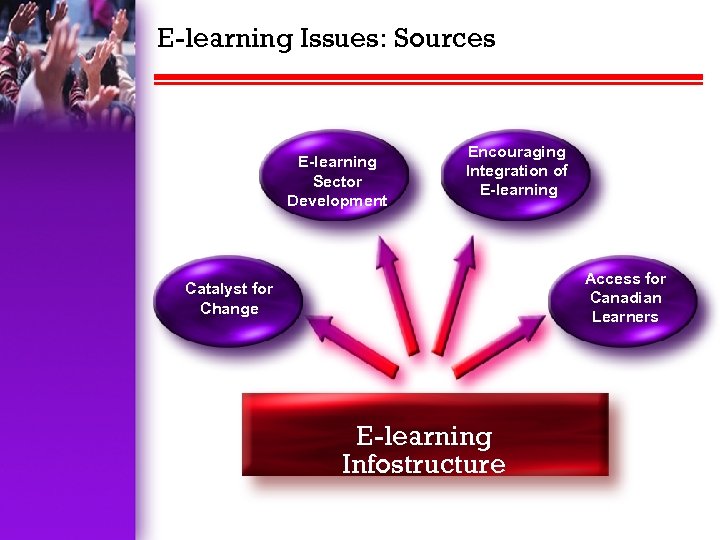 E-learning Issues: Sources E-learning Sector Development Encouraging Integration of E-learning Access for Canadian Learners Catalyst for Change E-learning Infostructure
E-learning Issues: Sources E-learning Sector Development Encouraging Integration of E-learning Access for Canadian Learners Catalyst for Change E-learning Infostructure
 Learning in Canada: Context k k k In Canada, education is the responsibility of each province and territory Provincial and territorial Ministers responsible for education set curriculum and educational context They also established the Council of Ministers of Education, Canada (CMEC) k The federal government focuses on the integration of ICT into learning k Industry Canada focuses on helping to establish the networks and applications that facilitate the delivery of on-learning and content. Catalyst 10
Learning in Canada: Context k k k In Canada, education is the responsibility of each province and territory Provincial and territorial Ministers responsible for education set curriculum and educational context They also established the Council of Ministers of Education, Canada (CMEC) k The federal government focuses on the integration of ICT into learning k Industry Canada focuses on helping to establish the networks and applications that facilitate the delivery of on-learning and content. Catalyst 10
 Catalyst for Innovation and National Leadership School. Net National Advisory Board k k k Fosters national consensus and action about technology in education and guides the development and implementation of Canada’s School. Net Members: Deputy Ministers and Assistant Deputy Ministers of Education, CMEC and education associations Identifies e-learning issues related to K-12 Catalyst 11
Catalyst for Innovation and National Leadership School. Net National Advisory Board k k k Fosters national consensus and action about technology in education and guides the development and implementation of Canada’s School. Net Members: Deputy Ministers and Assistant Deputy Ministers of Education, CMEC and education associations Identifies e-learning issues related to K-12 Catalyst 11
 School. Net National Advisory Board k. The 5 strategic priorities that capture selected K -12 e-learning issues are: k advancing and sharing of innovative k k practices in networked-based learning; research on the impact of ICT; facilitating development and sharing of content; human resource capacity building; and broadband connectivity. Catalyst 12
School. Net National Advisory Board k. The 5 strategic priorities that capture selected K -12 e-learning issues are: k advancing and sharing of innovative k k practices in networked-based learning; research on the impact of ICT; facilitating development and sharing of content; human resource capacity building; and broadband connectivity. Catalyst 12
 Catalyst for Innovation and National Leadership Advisory Committee for Online Learning Catalyst • Leaders in post-secondary and business identified postsecondary e-learning issues to CMEC and Industry Canada. • Recommended a coordinated approach for governments, universities, colleges, and the private sector to integrate on-line delivery in post-secondary education. Recommendations included: k Broadband accessibility; k Pan-Canadian online learning service; k Copyright and intellectual property laws; k Increased theoretical and applied learning R&D; k Ensure online materials meet the needs of persons with disabilities; and k Increase the development of learnware applications. 13
Catalyst for Innovation and National Leadership Advisory Committee for Online Learning Catalyst • Leaders in post-secondary and business identified postsecondary e-learning issues to CMEC and Industry Canada. • Recommended a coordinated approach for governments, universities, colleges, and the private sector to integrate on-line delivery in post-secondary education. Recommendations included: k Broadband accessibility; k Pan-Canadian online learning service; k Copyright and intellectual property laws; k Increased theoretical and applied learning R&D; k Ensure online materials meet the needs of persons with disabilities; and k Increase the development of learnware applications. 13
 Advisory Committee for Online Learning k. The Committee identified the following three issues as falling under the purview of Industry Canada: k k k infrastructure; research; and learnware applications development. Canada needs more people completing education through college, university, & apprenticeship learning. Catalyst Knowledge Matters 14
Advisory Committee for Online Learning k. The Committee identified the following three issues as falling under the purview of Industry Canada: k k k infrastructure; research; and learnware applications development. Canada needs more people completing education through college, university, & apprenticeship learning. Catalyst Knowledge Matters 14
 E-learning Sector Development School. Net Multimedia Learnware Fund Matched funds to develop online learning products and public access applications and foster new alliances between large distributors and SMEs involved in production E-learning Sector Over the next five years, increase the number of adults pursuing learning opportunities by 1 million and increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers. Achieving Excellence 15
E-learning Sector Development School. Net Multimedia Learnware Fund Matched funds to develop online learning products and public access applications and foster new alliances between large distributors and SMEs involved in production E-learning Sector Over the next five years, increase the number of adults pursuing learning opportunities by 1 million and increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers. Achieving Excellence 15
 E-learning Sector Development Canada’s Campus Connection k k k began in 1999 as a portal to the on-line courses of 50 participating universities and colleges 2, 300 online courses; 75 Canadian university and college participants significant enhancements to student mobility Edu. Specs k k E-learning Sector Representing Canada on international e-learning bodies (including the IMS Global Learning Consortium) Informing the Canadian e-learning community of Canadian and international activities Facilitate mobility and access to PSE for adult learners and students. Knowledge Matters 16
E-learning Sector Development Canada’s Campus Connection k k k began in 1999 as a portal to the on-line courses of 50 participating universities and colleges 2, 300 online courses; 75 Canadian university and college participants significant enhancements to student mobility Edu. Specs k k E-learning Sector Representing Canada on international e-learning bodies (including the IMS Global Learning Consortium) Informing the Canadian e-learning community of Canadian and international activities Facilitate mobility and access to PSE for adult learners and students. Knowledge Matters 16
 Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Providing Access to Quality Online Content and E-tools School. Net E-learning Portal k 4, 500 teacher-vetted and indexed online educational resources k Link to federal government online learning resources Canada’s Digital Collections k k Integration One of the largest Canadian cultural and historical online resources Over 400 collections online Increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers Achieving Excellence 17
Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Providing Access to Quality Online Content and E-tools School. Net E-learning Portal k 4, 500 teacher-vetted and indexed online educational resources k Link to federal government online learning resources Canada’s Digital Collections k k Integration One of the largest Canadian cultural and historical online resources Over 400 collections online Increase the supply of highly qualified people with the skills required by employers Achieving Excellence 17
 Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Fostering local content development and ICT skills School. Net Grassroots k Integration Over 21, 000 collaborative online learning projects developed by teachers and students All young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 18
Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Fostering local content development and ICT skills School. Net Grassroots k Integration Over 21, 000 collaborative online learning projects developed by teachers and students All young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 18
 Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Showcasing Best Practices Prime Ministers Awards for Teaching Excellence k Recognition of over 950 outstanding educators providing their schools with over $1. 9 million worth of financial awards School. Network of Innovative Schools k 85 schools promoting and sharing ICT best practices Smart Communities k k Integration 12 Smart Communities Demonstration projects New model for community development All students who graduate from high school achieve a level of literacy sufficient to participate in the knowledge economy and all young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 19
Encouraging Integration of E-learning. . . Showcasing Best Practices Prime Ministers Awards for Teaching Excellence k Recognition of over 950 outstanding educators providing their schools with over $1. 9 million worth of financial awards School. Network of Innovative Schools k 85 schools promoting and sharing ICT best practices Smart Communities k k Integration 12 Smart Communities Demonstration projects New model for community development All students who graduate from high school achieve a level of literacy sufficient to participate in the knowledge economy and all young Canadians are computer and Internet literate by grade school graduation. Knowledge Matters 19
 Promoting Access to E-learning Opportunities First Nations School. Net k Direct support for connectivity (infrastructure and service) for all First Nations schools under federal jurisdiction Community Access Program k Access 8, 800 Community Access sites providing Canadians in 3, 832 communities affordable access to the Internet Work with partners to find ways of improving First Nations’ education outcomes in on-reserve schools. Knowledge Matters 20
Promoting Access to E-learning Opportunities First Nations School. Net k Direct support for connectivity (infrastructure and service) for all First Nations schools under federal jurisdiction Community Access Program k Access 8, 800 Community Access sites providing Canadians in 3, 832 communities affordable access to the Internet Work with partners to find ways of improving First Nations’ education outcomes in on-reserve schools. Knowledge Matters 20
 Promoting Access to E-learning Opportunities Computers for Schools k over 300, 000 recycled computers provided to schools and libraries Francommunautés virtuelles k k 74 Francommunautés virtuelles projects to help Canada's Francophone and Acadian communities take full advantage of information and communications technologies. increase content, applications and services in French on the Internet and to promote networking among these communities Access Develop the most skilled and talented labour force in the world Achieving Excellence 21
Promoting Access to E-learning Opportunities Computers for Schools k over 300, 000 recycled computers provided to schools and libraries Francommunautés virtuelles k k 74 Francommunautés virtuelles projects to help Canada's Francophone and Acadian communities take full advantage of information and communications technologies. increase content, applications and services in French on the Internet and to promote networking among these communities Access Develop the most skilled and talented labour force in the world Achieving Excellence 21
 Success through Shared Vision and Strategy k k Partnerships with range of stakeholders to lever resources k Shared Vision and Strategy Recognized federal government’s role as catalyst, facilitator and co-investor Promotion and support for innovation and best practices k Responding to a need in the community 22
Success through Shared Vision and Strategy k k Partnerships with range of stakeholders to lever resources k Shared Vision and Strategy Recognized federal government’s role as catalyst, facilitator and co-investor Promotion and support for innovation and best practices k Responding to a need in the community 22
 The Innovation Goal “ The Canadian way. . . entails an abiding national commitment to sharing prosperity and opportunity; to the belief that economic success and social success go hand in hand; and that all Canadians should be afforded the means and the chance to fulfill their individual potential and to contribute to building a higher Canadian standard of living and a better quality of life. ” The Right Honourable Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy 23
The Innovation Goal “ The Canadian way. . . entails an abiding national commitment to sharing prosperity and opportunity; to the belief that economic success and social success go hand in hand; and that all Canadians should be afforded the means and the chance to fulfill their individual potential and to contribute to building a higher Canadian standard of living and a better quality of life. ” The Right Honourable Jean Chrétien Canada’s Innovation Strategy 23
 For a copy of this presentation, please contact: e-mail: mongrain. susan@ic. gc. ca tel: 613 -941 -9806 Canada
For a copy of this presentation, please contact: e-mail: mongrain. susan@ic. gc. ca tel: 613 -941 -9806 Canada


