Innovation and investments Week 9 What is innovation?





























lecture_week_9_ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Innovation and investments Week 9
Innovation and investments Week 9
 What is innovation? Innovation is a process of taking new ideas to satisfied customers. It is the conversion of new knowledge into new products and services. Innovation involves the whole process from opportunity identification, invention to development, production marketing and sales, while entrepreneurship only needs to involve commercialization
What is innovation? Innovation is a process of taking new ideas to satisfied customers. It is the conversion of new knowledge into new products and services. Innovation involves the whole process from opportunity identification, invention to development, production marketing and sales, while entrepreneurship only needs to involve commercialization
 Innovation is the multi-stage process whereby organizations transform ideas into new/improved products, service or processes, in order to advance, compete and differentiate themselves successfully in their marketplace. What is innovation?
Innovation is the multi-stage process whereby organizations transform ideas into new/improved products, service or processes, in order to advance, compete and differentiate themselves successfully in their marketplace. What is innovation?
 What is innovation? The capacity to quickly adapt by adopting new innovations (products, processes, strategies, organization, etc)
What is innovation? The capacity to quickly adapt by adopting new innovations (products, processes, strategies, organization, etc)
 Schumpeter and innovation Schumpeter identified innovation as the critical dimension of economic change. Economic change is around innovation, entrepreneurial activities and market power Innovation-originated market power could provide better results than the invisible hand & price competition. He argues that technological innovation often creates temporary monopolies, allowing abnormal profits that would soon be competed away by rivals and imitators. He said that these temporary monopolies were necessary to provide the incentive necessary for firms to develop new products and processes
Schumpeter and innovation Schumpeter identified innovation as the critical dimension of economic change. Economic change is around innovation, entrepreneurial activities and market power Innovation-originated market power could provide better results than the invisible hand & price competition. He argues that technological innovation often creates temporary monopolies, allowing abnormal profits that would soon be competed away by rivals and imitators. He said that these temporary monopolies were necessary to provide the incentive necessary for firms to develop new products and processes
 What is innovation? Schumpeter argued that innovation comes about through new combinations made by an entrepreneur, resulting in a new product, a new process, opening of new market, new way of organizing the business new sources of supply
What is innovation? Schumpeter argued that innovation comes about through new combinations made by an entrepreneur, resulting in a new product, a new process, opening of new market, new way of organizing the business new sources of supply
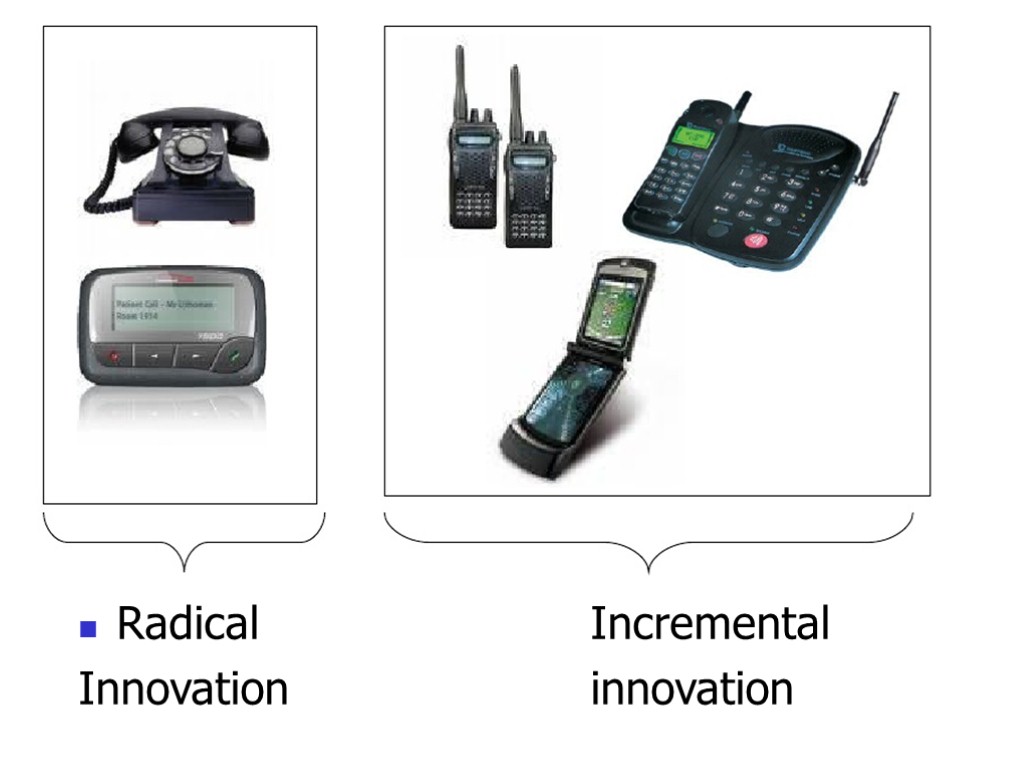
 Dimensions of innovation Process, product/service, strategy, which can vary in degree of newness: Incremental to radical
Dimensions of innovation Process, product/service, strategy, which can vary in degree of newness: Incremental to radical
 Radical Incremental Innovation innovation
Radical Incremental Innovation innovation
 Drivers for innovation Financial pressures to reduce costs, increase efficiency, do more with less, etc Increased competition Shorter product life cycles Stricter regulation Industry and community needs for sustainable development Demographic, social and market changes Rising customer expectations regarding service and quality Changing economy Greater availability of potentially useful technologies coupled with a need to exceed the competition in these technologies
Drivers for innovation Financial pressures to reduce costs, increase efficiency, do more with less, etc Increased competition Shorter product life cycles Stricter regulation Industry and community needs for sustainable development Demographic, social and market changes Rising customer expectations regarding service and quality Changing economy Greater availability of potentially useful technologies coupled with a need to exceed the competition in these technologies
 Innovation strategies Financial backing to innovation Give opportunities to employees Skillful recruitment policy Information from outside the organization Target being set for innovation Employees should be rewarded
Innovation strategies Financial backing to innovation Give opportunities to employees Skillful recruitment policy Information from outside the organization Target being set for innovation Employees should be rewarded
 Research findings 50-90% of innovation projects judged to have made little or no contribution to organizational goals. The impact of failure: loss of investment, loss of morale among employees, an increase in cynicism and even higher resistance to change in the future. Failure
Research findings 50-90% of innovation projects judged to have made little or no contribution to organizational goals. The impact of failure: loss of investment, loss of morale among employees, an increase in cynicism and even higher resistance to change in the future. Failure
 Causes of failure Some causes will be external to the organisation and outside its influence of control. Internal causes of failure can be divided into causes associated with the cultural infrastructure and causes associated with the innovation process itself. Poor Leadership Poor Organization Poor Communication Poor Empowerment Poor Knowledge Management
Causes of failure Some causes will be external to the organisation and outside its influence of control. Internal causes of failure can be divided into causes associated with the cultural infrastructure and causes associated with the innovation process itself. Poor Leadership Poor Organization Poor Communication Poor Empowerment Poor Knowledge Management
 Common causes of failure within the innovation process Poor goal definition Poor alignment of actions to goals Poor participation in teams Poor monitoring of results Poor communication and access to information
Common causes of failure within the innovation process Poor goal definition Poor alignment of actions to goals Poor participation in teams Poor monitoring of results Poor communication and access to information
 Measures There are two fundamentally different types of measures for innovation: the organizational level and the political level. The measure of innovation at the organizational level relates to individuals, team-level assessments, private companies from the smallest to the largest. Measure of innovation for organizations can be conducted by surveys, workshops, consultants or internal benchmarking.
Measures There are two fundamentally different types of measures for innovation: the organizational level and the political level. The measure of innovation at the organizational level relates to individuals, team-level assessments, private companies from the smallest to the largest. Measure of innovation for organizations can be conducted by surveys, workshops, consultants or internal benchmarking.
 The political level For the political level, measures of innovation are more focusing on a country or region competitive advantage through innovation. In this context, organizational capabilities can be evaluated through various evaluation frameworks, such as those of the European Foundation for Quality Management. The OECD Oslo Manual (1995) suggests standard guidelines on measuring technological product and process innovation. The new Oslo manual from 2005 takes a wider perspective to innovation, and includes marketing and organizational innovation. These standards are used for example in the European Community Innovation Surveys.
The political level For the political level, measures of innovation are more focusing on a country or region competitive advantage through innovation. In this context, organizational capabilities can be evaluated through various evaluation frameworks, such as those of the European Foundation for Quality Management. The OECD Oslo Manual (1995) suggests standard guidelines on measuring technological product and process innovation. The new Oslo manual from 2005 takes a wider perspective to innovation, and includes marketing and organizational innovation. These standards are used for example in the European Community Innovation Surveys.
 There are several international studies of the innovation performance of countries (above called the political level), Global Innovation Index being one. Richard Florida´s index for the Creative Class and the Innovation Capacity Index (ICI) published by a large number of international professors working in a collaborative fashion. The top scorers of ICI 2009-2010 being:1.Sweden 82.2, 2. Finland 77.8, 3. United States 3 77.5. The Global Innovation Index is a global index measuring the level of innovation of a country, produced jointly by The Boston Consulting Group (BCG), the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM), and The Manufacturing Institute (MI).
There are several international studies of the innovation performance of countries (above called the political level), Global Innovation Index being one. Richard Florida´s index for the Creative Class and the Innovation Capacity Index (ICI) published by a large number of international professors working in a collaborative fashion. The top scorers of ICI 2009-2010 being:1.Sweden 82.2, 2. Finland 77.8, 3. United States 3 77.5. The Global Innovation Index is a global index measuring the level of innovation of a country, produced jointly by The Boston Consulting Group (BCG), the National Association of Manufacturers (NAM), and The Manufacturing Institute (MI).
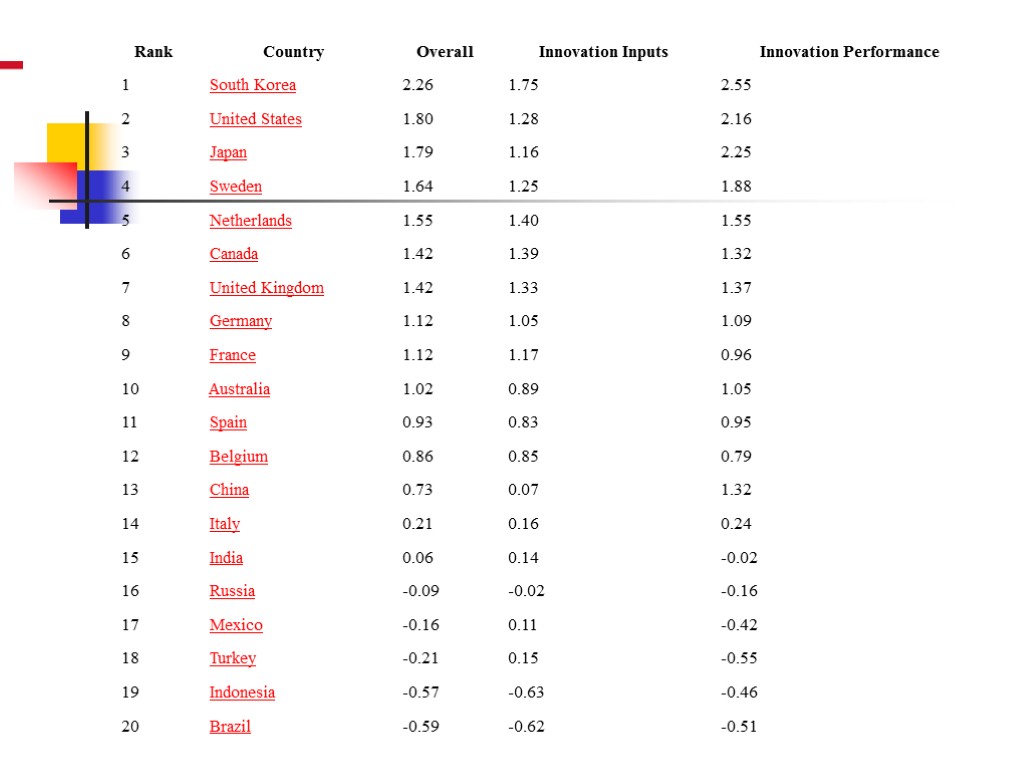
 The International Innovation Index The International Innovation Index is part of a large research study that looked at both the business outcomes of innovation and government's ability to encourage and support innovation through public policy. The report discusses not only country performance but also what companies are doing and should be doing to spur innovation. It looks at new policy indicators for innovation, including tax incentives and policies for immigration, education and intellectual property. The latest index was published in March 2009.To rank the countries, the study measured both innovation inputs and outputs. Innovation inputs: government and fiscal policy, education policy and the innovation environment. Outputs included patents, technology transfer, and other R&D results; business performance, such as labor productivity, and the impact of innovation on business migration and economic growth
The International Innovation Index The International Innovation Index is part of a large research study that looked at both the business outcomes of innovation and government's ability to encourage and support innovation through public policy. The report discusses not only country performance but also what companies are doing and should be doing to spur innovation. It looks at new policy indicators for innovation, including tax incentives and policies for immigration, education and intellectual property. The latest index was published in March 2009.To rank the countries, the study measured both innovation inputs and outputs. Innovation inputs: government and fiscal policy, education policy and the innovation environment. Outputs included patents, technology transfer, and other R&D results; business performance, such as labor productivity, and the impact of innovation on business migration and economic growth

 What is Investment? Investment is the commitment of money or capital to the purchase of financial instruments or other assets so as to gain profitable returns in the form of interest, income (dividend). In business, the purchase by a producer of a physical good, such as durable equipment or inventory, in the hope of improving future business, to save money and increase profit.
What is Investment? Investment is the commitment of money or capital to the purchase of financial instruments or other assets so as to gain profitable returns in the form of interest, income (dividend). In business, the purchase by a producer of a physical good, such as durable equipment or inventory, in the hope of improving future business, to save money and increase profit.
 Types of investment Real investment (new equipment, buying licenses and property) Portfolio investment (stocks of other enterprises, bonds
Types of investment Real investment (new equipment, buying licenses and property) Portfolio investment (stocks of other enterprises, bonds
 Investment process stages Defining the object Investing Monitoring
Investment process stages Defining the object Investing Monitoring
 Investment project The project life cycle – 3 stages: Pre-investment stage Investment stage Operational stage
Investment project The project life cycle – 3 stages: Pre-investment stage Investment stage Operational stage
 Pre-investment stage Setting investment goals on the basis of marketing research (0,8-5%) Consideration of alternative projects by costs and profits Defining methods of achieving the goals with taking into consideration economic, political, social and technical factors Contract phase – setting qualification requirements and selecting performers (investors, workers) The end of this stage – the detailed business plan of the investment project
Pre-investment stage Setting investment goals on the basis of marketing research (0,8-5%) Consideration of alternative projects by costs and profits Defining methods of achieving the goals with taking into consideration economic, political, social and technical factors Contract phase – setting qualification requirements and selecting performers (investors, workers) The end of this stage – the detailed business plan of the investment project
 Investment project efficiency Financial efficiency – considering financial impact on participants Budget efficiency – financial impact on budget Economic efficiency – money spent on the projects
Investment project efficiency Financial efficiency – considering financial impact on participants Budget efficiency – financial impact on budget Economic efficiency – money spent on the projects
 Sources of investment Enterprises’ budget State pension funds and other funds Banks Enterprises’ shares
Sources of investment Enterprises’ budget State pension funds and other funds Banks Enterprises’ shares
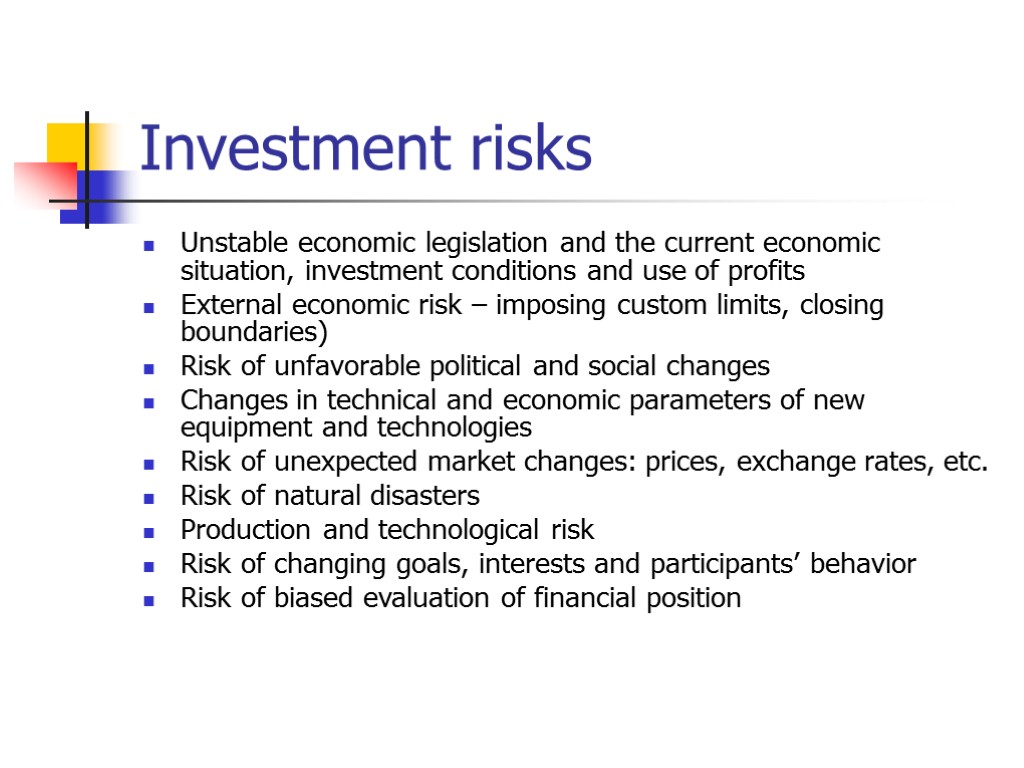
 Investment risks Unstable economic legislation and the current economic situation, investment conditions and use of profits External economic risk – imposing custom limits, closing boundaries) Risk of unfavorable political and social changes Changes in technical and economic parameters of new equipment and technologies Risk of unexpected market changes: prices, exchange rates, etc. Risk of natural disasters Production and technological risk Risk of changing goals, interests and participants’ behavior Risk of biased evaluation of financial position
Investment risks Unstable economic legislation and the current economic situation, investment conditions and use of profits External economic risk – imposing custom limits, closing boundaries) Risk of unfavorable political and social changes Changes in technical and economic parameters of new equipment and technologies Risk of unexpected market changes: prices, exchange rates, etc. Risk of natural disasters Production and technological risk Risk of changing goals, interests and participants’ behavior Risk of biased evaluation of financial position
 The strategy of industrial-innovative development One of the main directions of the state policy in the sphere of scientific-technical and innovative activities is formation of innovation infrastructure Technoparks Business incubators Venture companies Regional innovation funds
The strategy of industrial-innovative development One of the main directions of the state policy in the sphere of scientific-technical and innovative activities is formation of innovation infrastructure Technoparks Business incubators Venture companies Regional innovation funds
 Technoparks Scientific-production territorial complexes, the aim of which is to create favorable conditions for developing small and medium-sized innovative businesses.
Technoparks Scientific-production territorial complexes, the aim of which is to create favorable conditions for developing small and medium-sized innovative businesses.
 Business incubators Programs designed to support the successful development of entrepreneurial companies through business support resources and services, developed and managed by incubator management and offered both in the incubator and through its network of contacts.
Business incubators Programs designed to support the successful development of entrepreneurial companies through business support resources and services, developed and managed by incubator management and offered both in the incubator and through its network of contacts.
 Business incubators The National Business Incubation Association (NBIA) is the world’s leading organization advancing business incubation and entrepreneurship. Each year, it provides thousands of professionals with information, education, advocacy and networking resources to bring excellence to the process of assisting early-stage companies. An elected, voting board of directors representing the world's leading incubators governs the association. Source: http://www.nbia.org
Business incubators The National Business Incubation Association (NBIA) is the world’s leading organization advancing business incubation and entrepreneurship. Each year, it provides thousands of professionals with information, education, advocacy and networking resources to bring excellence to the process of assisting early-stage companies. An elected, voting board of directors representing the world's leading incubators governs the association. Source: http://www.nbia.org

