e0e321de10f51878a535a32256dcb592.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

Innovation and Good Practice in Selection: Job Analysis Project and Progress 2011 Mary O’Reilly, Leicester Programme, Co Chair of Selection Working Party

Background to the Project: The Lancaster Programme 2001: published results of first job analysis, funded by Clearing House. Authors: Phillips, Gray and Hatton from Lancaster Programme 2005: Lancaster begin using the competencies established using written task, interview and presentation to collect evidence for competencies 2006: Lancaster begins to use a written task to screen candidates instead of application forms 2007: Clearing House funded research into use of application forms and written test as first sift of applicants. Report in 2008. Published 2010 (Simpson and Hemmings)

Background to the Project: other programmes 2005/6 Leicester Programme fund an occupational psychologist to develop competencies and design an assessment centre approach to selection based on these 2007 Leicester begin screening using a written task 2009 Surrey commence using written test for screening, Salomons join forces for 2011 Shrops/Staffs use written test for screening

Background: National work 2006: Working party founded by Roth, Wang, & Reynolds. › Fast Stream civil service email in tray task demonstrated at GTi. CP › http: //faststream. civilservice. gov. uk/How-do-Iapply/Example-e-Tray-Excercise/ › Prohibitive costs to develop this for our use 2009: Results of Clearing House survey of all UK programmes to look at whethere is a will to move to national screening: 54% express interest 2009: Selection sub group of GTi. CP formed and in 2010 a bid is made for funding to develop a more up to date set of trainee competencies, for use at the point of selection

Successful bid in November 2010 Helen Baron, Independent Consultant and selection specialist engaged to undertake the work Steering group for the project: Mary O’Reilly, Leicester Cathy Amor, Lancaster Laura Simonds, Surrey Matthew Jones -Chesters, UEL Linda Hammond, Salomons Shrops/Staffs Rep (Helena Priest)invited to join us in 2011
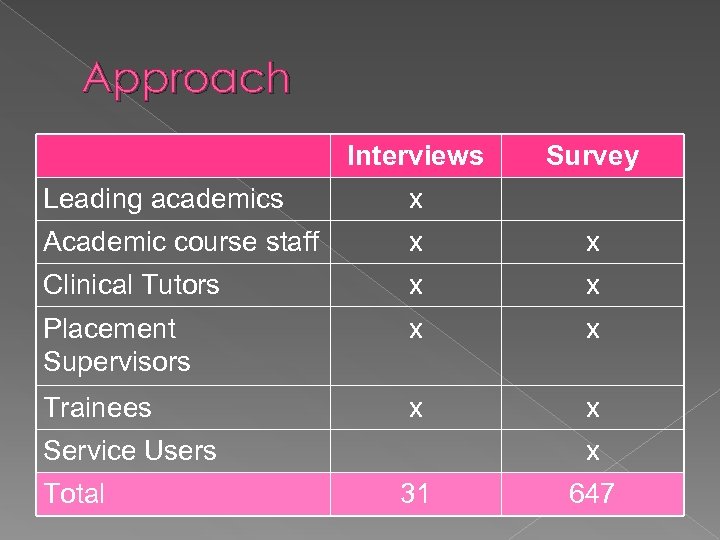
Approach Interviews Survey Leading academics x Academic course staff x x Clinical Tutors x x Placement Supervisors x x Trainees x x Service Users Total x 31 647
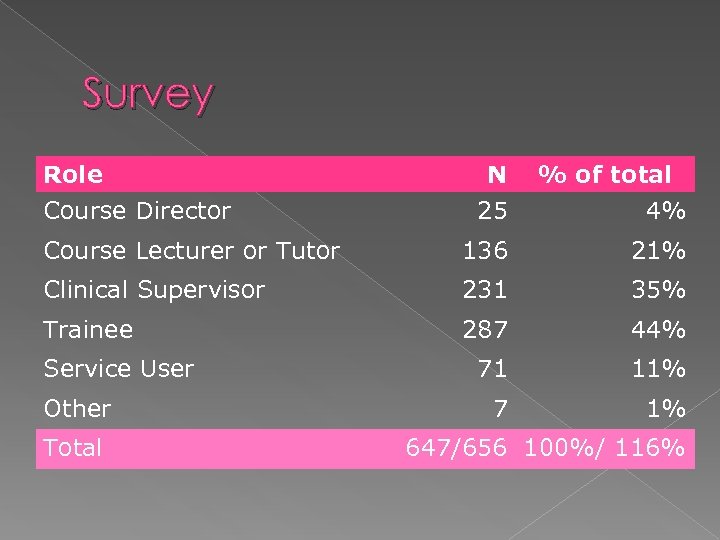
Survey Role Course Director N 25 % of total 4% Course Lecturer or Tutor 136 21% Clinical Supervisor 231 35% Trainee 287 44% 71 11% 7 1% Service User Other Total 647/656 100%/ 116%

CP Model Intellectual Ability Communication Skills Self Aware and Open to Learning Personal Maturity Warmth and Empathy Resilience Organised Autonomy and Initiative Motivation and Application Contextual Awareness
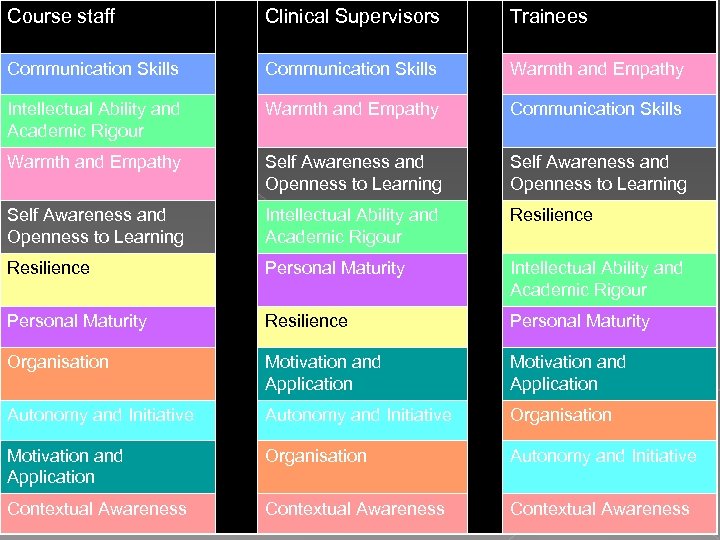
Course staff Clinical Supervisors Trainees Communication Skills Warmth and Empathy Intellectual Ability and Academic Rigour Warmth and Empathy Communication Skills Warmth and Empathy Self Awareness and Openness to Learning Intellectual Ability and Academic Rigour Resilience Personal Maturity Intellectual Ability and Academic Rigour Personal Maturity Resilience Personal Maturity Organisation Motivation and Application Autonomy and Initiative Organisation Motivation and Application Organisation Autonomy and Initiative Contextual Awareness
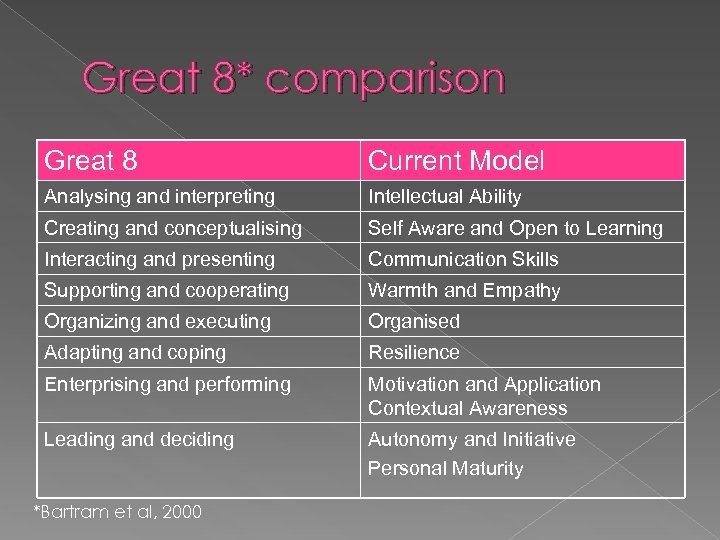
Great 8* comparison Great 8 Current Model Analysing and interpreting Intellectual Ability Creating and conceptualising Self Aware and Open to Learning Interacting and presenting Communication Skills Supporting and cooperating Warmth and Empathy Organizing and executing Organised Adapting and coping Resilience Enterprising and performing Motivation and Application Contextual Awareness Leading and deciding Autonomy and Initiative Personal Maturity *Bartram et al, 2000

Attitudes to a National Shortlisting Tool Sub-sample from Survey engaged in selection 86 respondents › › 23 course directors 45 other course staff 13 clinical supervisors 5 trainees
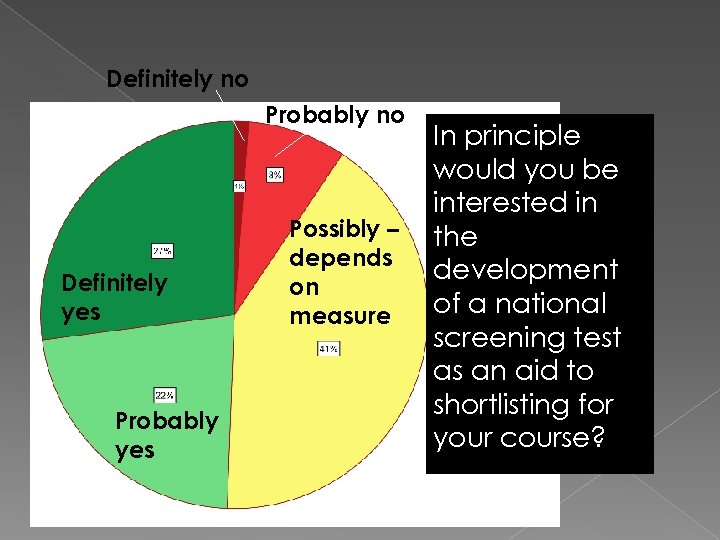
Definitely no Probably no Definitely yes Probably yes Possibly – depends on measure In principle would you be interested in the development of a national screening test as an aid to shortlisting for your course?

How appropriate do you consider each of the following measures? Test of Research Comprehension Situational Judgement Test of writing skills Verbal Reasoning Measure Test of English Language and Grammar Cognitive Ability Tests Personality Questionnaire % appropriate or somewhat appropriate 94% 85% 82% 82% 70% 54%

Survey Conclusions Most courses interested in national shortlisting Over half interested in pilot Many willing to share costs with students Variety of assessment options seen as appropriate › Critical Reasoning and other cognitive measures › Situational Judgement › English Language skills

Options appraisal at June conference Three options presented › No change › Limited pilot › Wholesale adoption of screening Five groups looked at differing issues › › › What competencies to measure Development process Evaluation process Logistics and liaising with clearing house Mandate and accountability

Key messages In 2011 there were 2000 of 3500 applicants not shortlisted by any course › think of the opportunity costs on staff time (HEI and NHS) of this duplication. Local decision-making needs to be retained Current off-the-shelf-measures the preferred way forward › an up-front fee per use that can be known, vs resources needed to develop and scrutinise bespoke measures being the decider There needs to be proper transparency and accountability (at local programme level and national GTi. CP/DCP level) It is crucial to work closely with the Clearing House on any forward planning

For Screening Time savings within courses especially with high applicant numbers Potential to reduce duplication of effort across courses Addresses double tick applicants Mapped to competence model Based on sound selection practice Capable of empirical study to check validity etc.

For ‘status quo’ Many courses involve clinicians and service users at the ‘screening by form information’ stage Feeling that if it isn’t broke don’t fix it Concern about costs of development

Evidence of effectiveness of screening tests in use Lancs: › Daiches and Amor (2006) › Simpson et al (2011) Leics: GTi. CP conference 2007 Surrey/Salomons: GTi. CP conference 2009

The scope for a common screening task To date, 5 programmes are using a screening task This is a written task Two programmes have collaborated to use the same task and process (and are reported as one)

Comparisons across 4 programmes • Completed – At the University: all programmes – On computer: 3 programmes – By hand: 1 programme • Marked – By computer: 1 programme – By hand: 3 programmes • Past papers – 2 programmes make these available on-line, 2 do not

Comparisons across 4 programmes • Length of exercise – 30 mins to 1 hour (Mean 49 mins) • Number of questions – 7 -14 (mean = 9) • 2 programmes allow flexibility in order of answering questions 2 programmes ask only about quantitative research 2 programmes give equal emphasis to quantitative and qualitative methods No psychological knowledge beyond undergraduate is assumed Cut off score – 1 programme has a cut off score (50%), 3 rank order
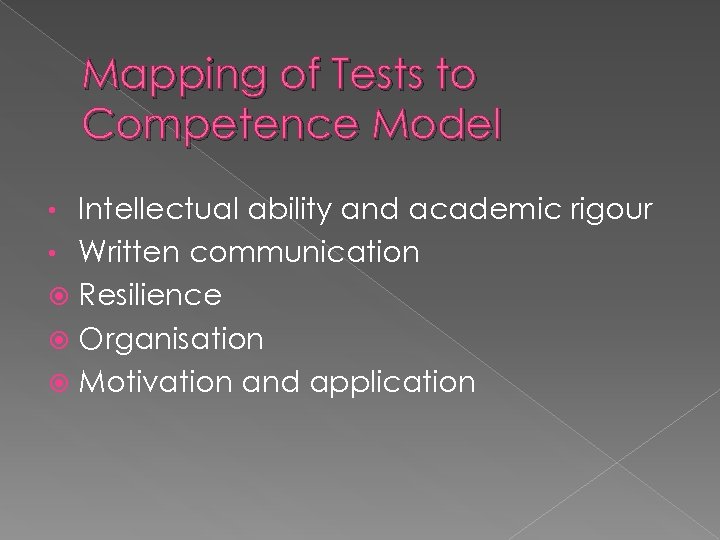
Mapping of Tests to Competence Model Intellectual ability and academic rigour • Written communication Resilience Organisation Motivation and application •

Intellectual ability and academic rigour Analyses and integrates complex/contradictory material › 2/4 Synthesises ideas from a variety of sources › 2/4 Solves problems creatively › 3/4 Critically evaluates information › 4/4 Shows good academic and research skills › 4/4 All other indicators in this area endorsed by one programme or other

Written communication All competences under written communication Precise, well expressed and clear › 4/4 Well organised and grammatical › 4/4 Adapted to purpose and reader › 2/4 Coherently argued › 4/4

Resilience, Copes well with pressure › 4/4 Tolerates anxiety and uncertainty › 4/4 Shows flexibility when required › 2/4 Shows confidence in own ability to deal with multiple demands › 2/4

Organisation Is punctual and reliable › 3/4 Prioritises tasks and uses time effectively › 3/4

Motivation and application Is committed to completing tasks as well as possible Invests additional effort willingly Is dedicated to career as clinical psychologist This competency area mapped by just one course, however, arguably applies to all test takers!

Double Tick Multi-stage selection process can manage all double tick candidates All those who meet essential criteria are invited to sit the screening test Need to set a cut off score below which no candidate can be progressed to next stage › Eg minimum of 60% › Ranking of candidates not accepted under double tick All double tick applicants above cut score then invited to next stage

A mandate to continue Directors have said ‘go on’, and want to take more ownership of the project Steering group made up of directors across regional areas Working group Terms of reference to be drawn up by Malcolm Adams

Current working group ideas Proposal to Pilot use of a common measure for 2013 intake Requesting further funding for development of a common test › Perhaps one course centre to take lead under the steering group Initial ideas: One day (Saturday) › One test (form and content) › Computer administration › Scoring options available machine scored for all but many centres will hand mark

Logistics Advance notice in Clearing House course entries One common test vs one common form and different content One testing day vs several Regional/area testing centres All applicants to the ‘opted in’ programmes attend one centre for test No charge to candidates during pilot
The Future Competencies Screening National Screening ?
e0e321de10f51878a535a32256dcb592.ppt