Session2_innovators_dilemma (1).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Innovation and Creativity Management Sessions 2 - 3 The Innovator’s. Dilemma and Solution by Clayton M. Christensen
Innovation and Creativity Management Sessions 2 - 3 The Innovator’s. Dilemma and Solution by Clayton M. Christensen
 Dilemma “Well-managed companies often fail because the very management practices that have allowed them to become industry leaders also make it extremely difficult for them to develop the disruptive technologies that ultimately steal away their markets. ” p. 265
Dilemma “Well-managed companies often fail because the very management practices that have allowed them to become industry leaders also make it extremely difficult for them to develop the disruptive technologies that ultimately steal away their markets. ” p. 265
 Overview Characteristics of goods companies Why they fail anyway Sustaining versus Disruptive Technologies Intersecting Performance Trajectories Market Need versus Technology Improvement Low-end versus high-end disruption
Overview Characteristics of goods companies Why they fail anyway Sustaining versus Disruptive Technologies Intersecting Performance Trajectories Market Need versus Technology Improvement Low-end versus high-end disruption
 What do good companies do well? ü ü Listen responsively to their customers Invest aggressively in the technology, products, and manufacturing capabilities that satisfied their customers’ future needs Seek higher margins Target larger markets rather than smaller ones
What do good companies do well? ü ü Listen responsively to their customers Invest aggressively in the technology, products, and manufacturing capabilities that satisfied their customers’ future needs Seek higher margins Target larger markets rather than smaller ones
 Why do good companies fail? Good management The Dilemma: The logical, competent decisions of management that are critical to the success of their companies are also the reasons why they lose their positions of leadership.
Why do good companies fail? Good management The Dilemma: The logical, competent decisions of management that are critical to the success of their companies are also the reasons why they lose their positions of leadership.
 Why good management can lead to failure 1 Reason 1 Lack of understanding the difference between sustaining and disruptive technologies
Why good management can lead to failure 1 Reason 1 Lack of understanding the difference between sustaining and disruptive technologies
 Two Types of Innovations Sustaining Improve performance of established products Meet demands of mainstream customers in major markets Vary in difficulty, cost, time, etc. Established firms Disruptive Generally underperform established products in mainstream markets Have new features that fringe / new customers value Cheaper, simpler, smaller, more convenient to use Entrant firms
Two Types of Innovations Sustaining Improve performance of established products Meet demands of mainstream customers in major markets Vary in difficulty, cost, time, etc. Established firms Disruptive Generally underperform established products in mainstream markets Have new features that fringe / new customers value Cheaper, simpler, smaller, more convenient to use Entrant firms
 Disruptive Technologies v. Rational Investments Disruptive products are simpler and cheaper, and promise lower margins Disruptive technologies are first commercialized in emerging or insignificant markets Most profitable current customers are not interested in the product
Disruptive Technologies v. Rational Investments Disruptive products are simpler and cheaper, and promise lower margins Disruptive technologies are first commercialized in emerging or insignificant markets Most profitable current customers are not interested in the product
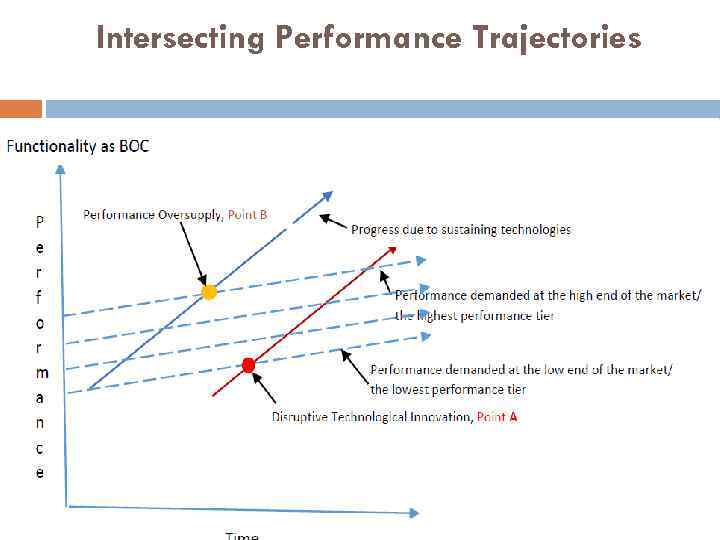 Intersecting Performance Trajectories
Intersecting Performance Trajectories
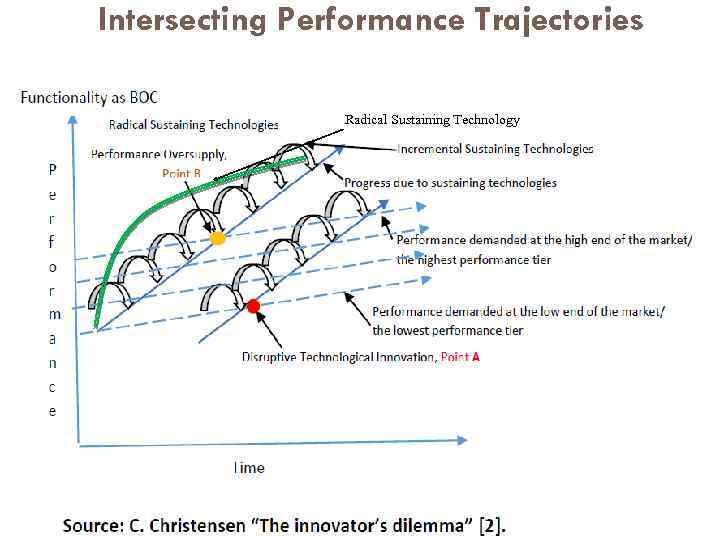 Intersecting Performance Trajectories Radical Sustaining Technology
Intersecting Performance Trajectories Radical Sustaining Technology
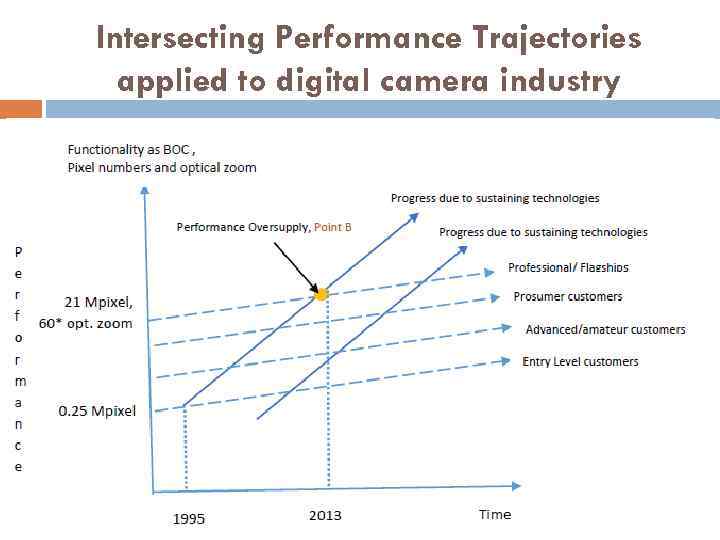 Intersecting Performance Trajectories applied to digital camera industry
Intersecting Performance Trajectories applied to digital camera industry
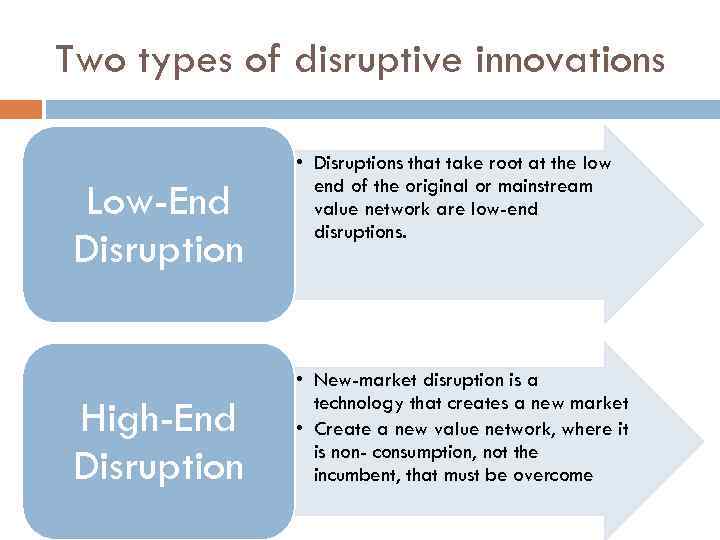 Two types of disruptive innovations Low-End Disruption High-End Disruption • Disruptions that take root at the low end of the original or mainstream value network are low-end disruptions. • New-market disruption is a technology that creates a new market • Create a new value network, where it is non- consumption, not the incumbent, that must be overcome
Two types of disruptive innovations Low-End Disruption High-End Disruption • Disruptions that take root at the low end of the original or mainstream value network are low-end disruptions. • New-market disruption is a technology that creates a new market • Create a new value network, where it is non- consumption, not the incumbent, that must be overcome
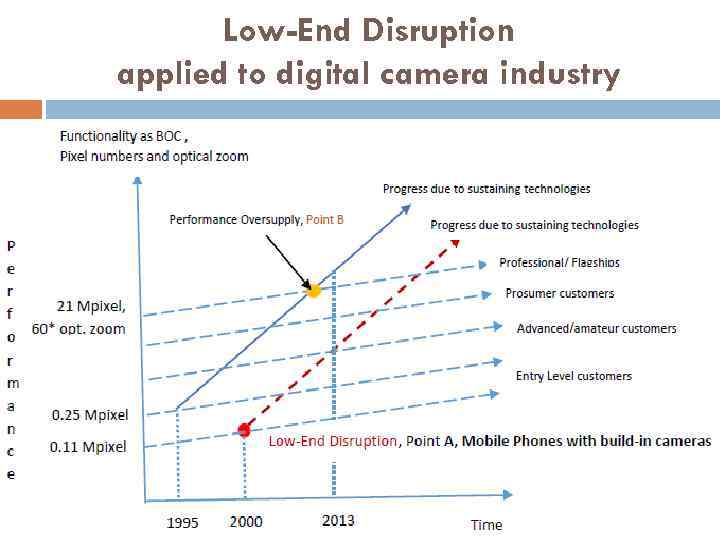 Low-End Disruption applied to digital camera industry
Low-End Disruption applied to digital camera industry
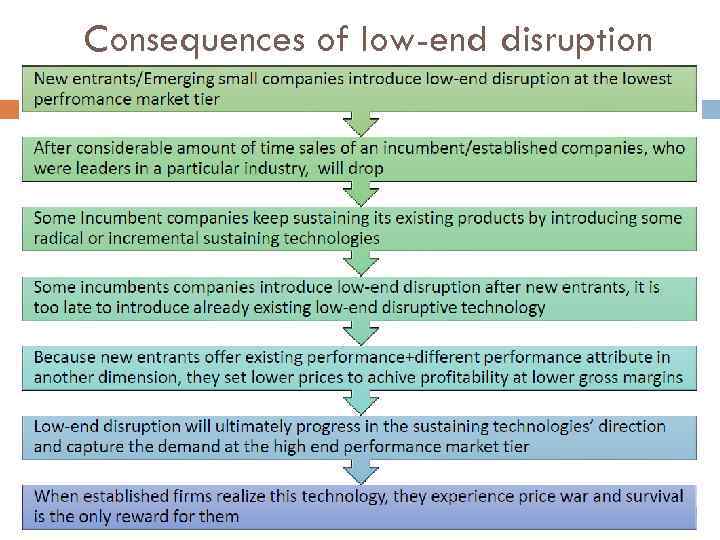 Consequences of low-end disruption
Consequences of low-end disruption
 Why good management can lead to failure 2 Reason 2 The pace of technological progress often outstrips the needs of the market.
Why good management can lead to failure 2 Reason 2 The pace of technological progress often outstrips the needs of the market.
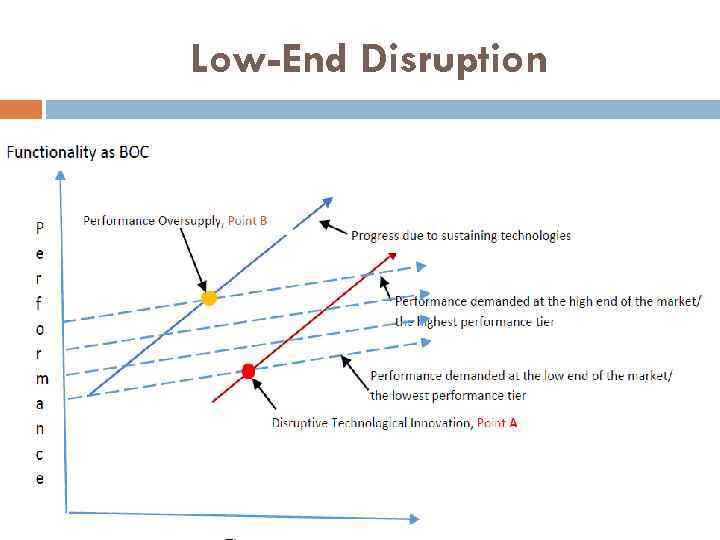 Low-End Disruption
Low-End Disruption
 Market Need v. Technology Improvement Technologies can progress faster than demand Suppliers give customers more than they need or are willing to pay Allows room for underperforming disruptive technologies
Market Need v. Technology Improvement Technologies can progress faster than demand Suppliers give customers more than they need or are willing to pay Allows room for underperforming disruptive technologies
 Why good management can lead to failure Reason 2 Customers and financial structures of successful companies heavily influence the types of investments that appear attractive.
Why good management can lead to failure Reason 2 Customers and financial structures of successful companies heavily influence the types of investments that appear attractive.
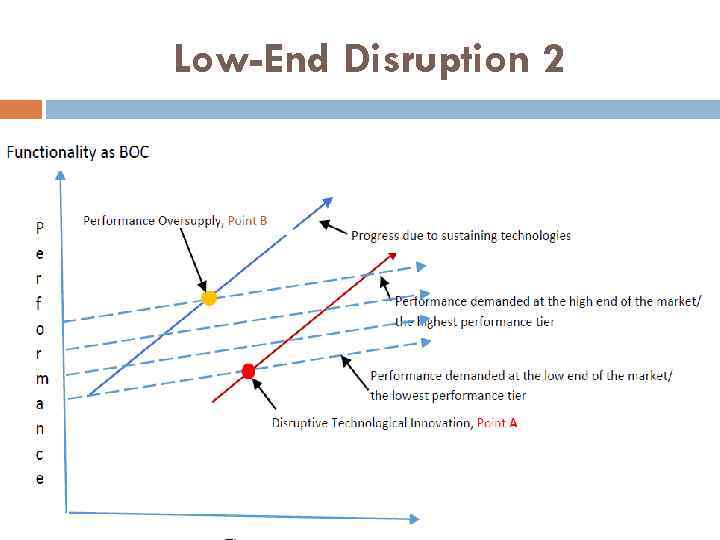 Low-End Disruption 2
Low-End Disruption 2
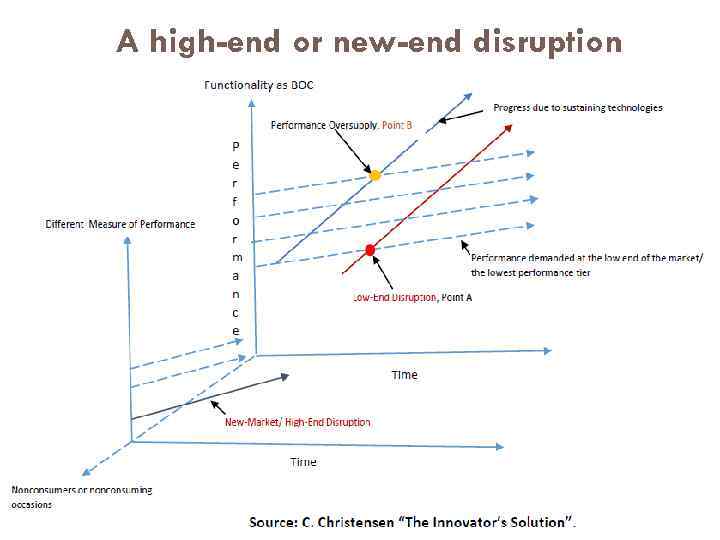 A high-end or new-end disruption
A high-end or new-end disruption
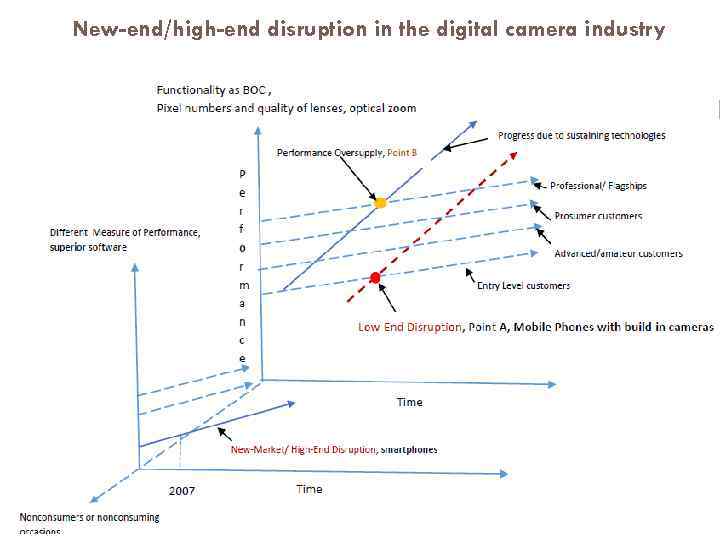 New-end/high-end disruption in the digital camera industry
New-end/high-end disruption in the digital camera industry
 The Innovator’s Solution Is there any solution for Innovator’s Dilemma? How is it possible to prevent low-end and high-end disruptive technologies/innovation for market leaders? “The Innovator’s Solution” by Clayton Christensen
The Innovator’s Solution Is there any solution for Innovator’s Dilemma? How is it possible to prevent low-end and high-end disruptive technologies/innovation for market leaders? “The Innovator’s Solution” by Clayton Christensen
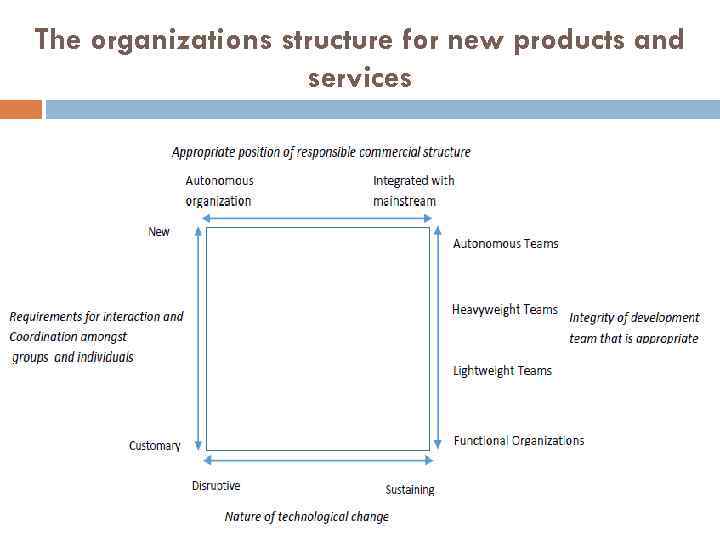 The organizations structure for new products and services
The organizations structure for new products and services
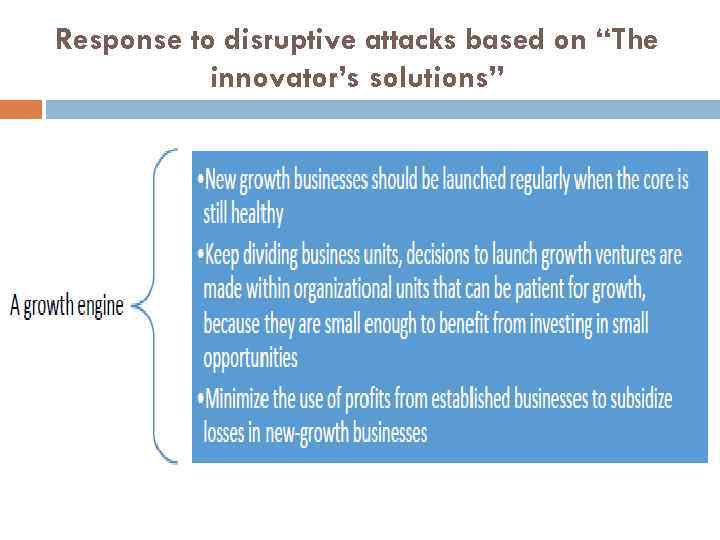 Response to disruptive attacks based on “The innovator’s solutions”
Response to disruptive attacks based on “The innovator’s solutions”
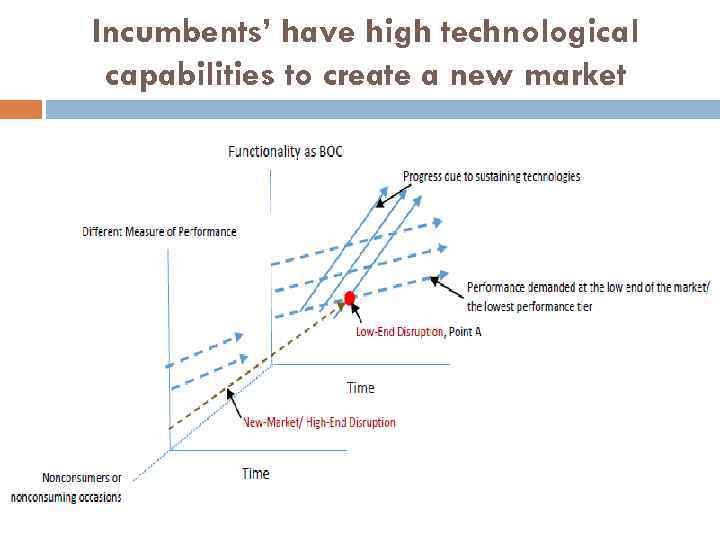 Incumbents’ have high technological capabilities to create a new market
Incumbents’ have high technological capabilities to create a new market
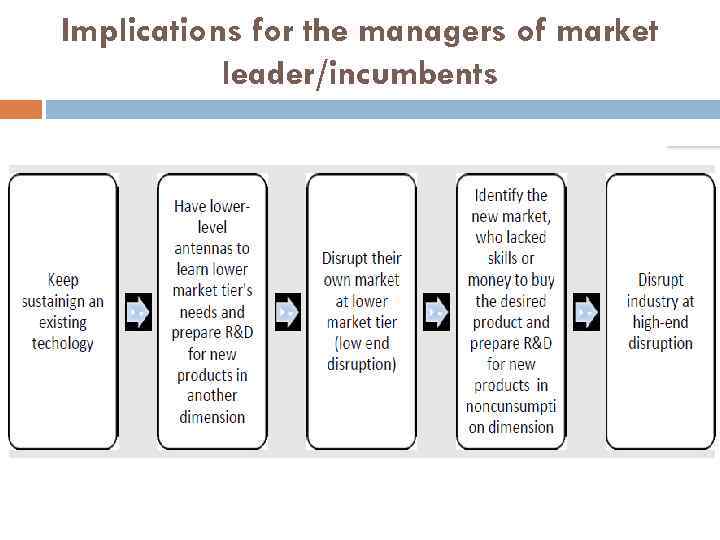 Implications for the managers of market leader/incumbents
Implications for the managers of market leader/incumbents
 Principles of disruptive innovation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Companies depend on customers and investors for resources Small markets don’t solve the growth needs of large companies Markets that do not exist cannot be analyzed An organization’s capabilities define its disabilities Technology supply may not equal market demand
Principles of disruptive innovation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Companies depend on customers and investors for resources Small markets don’t solve the growth needs of large companies Markets that do not exist cannot be analyzed An organization’s capabilities define its disabilities Technology supply may not equal market demand
 Thanks! Any Questions?
Thanks! Any Questions?


