9fd6f81ec4fbc0e157842e9c43064d2c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 INMM Nuclear Security and Physical Protection Technical Division PERFORMANCE TESTING TO VALIDATE SYSTEM EFFECTIVENESS
INMM Nuclear Security and Physical Protection Technical Division PERFORMANCE TESTING TO VALIDATE SYSTEM EFFECTIVENESS
 What is Effectiveness? Definition: Producing or capable of producing a desired effect. How do we derive to the desired effect? Regulations Vulnerability assessments Risk assessments Programmatic guidance Management decisions
What is Effectiveness? Definition: Producing or capable of producing a desired effect. How do we derive to the desired effect? Regulations Vulnerability assessments Risk assessments Programmatic guidance Management decisions
 What are the expectations of a security system? System will work when needed System will work to the level (effectiveness) needed How can we determine (with confidence) that our security systems will work as needed or required? Assessments/inspections Operator use and operator failure notifications Management oversight Testing
What are the expectations of a security system? System will work when needed System will work to the level (effectiveness) needed How can we determine (with confidence) that our security systems will work as needed or required? Assessments/inspections Operator use and operator failure notifications Management oversight Testing
 Testing provides the most reliable information about a system’s effectiveness When performed properly, testing: Continually challenges the protective system to reasonable levels Reports performance information to management and other stakeholders
Testing provides the most reliable information about a system’s effectiveness When performed properly, testing: Continually challenges the protective system to reasonable levels Reports performance information to management and other stakeholders
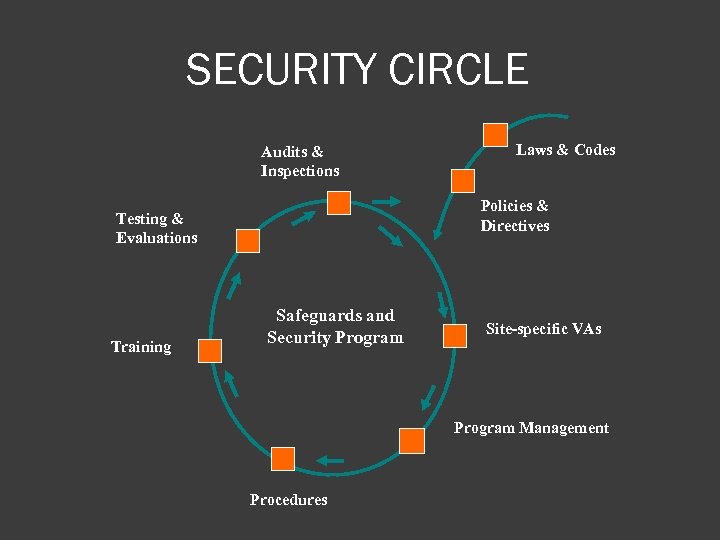 SECURITY CIRCLE Audits & Inspections Policies & Directives Testing & Evaluations Training Laws & Codes Safeguards and Security Program Site-specific VAs Program Management Procedures
SECURITY CIRCLE Audits & Inspections Policies & Directives Testing & Evaluations Training Laws & Codes Safeguards and Security Program Site-specific VAs Program Management Procedures
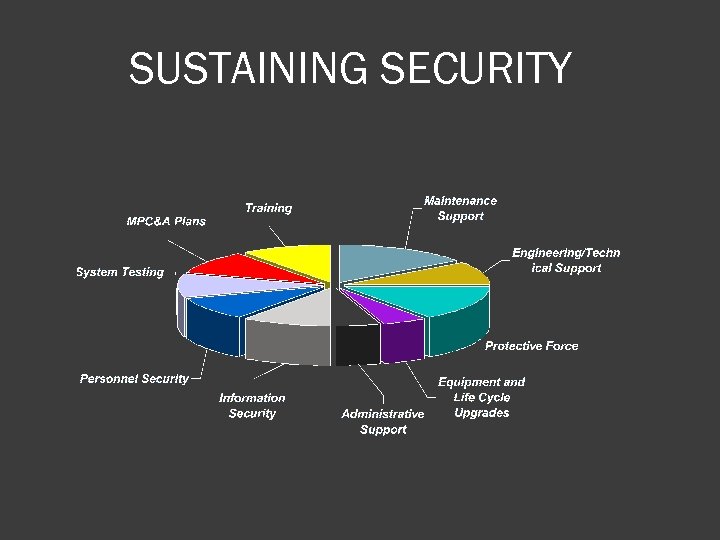 SUSTAINING SECURITY
SUSTAINING SECURITY
 Testing and data management can be very large and complex Test schedules Testing priorities Corrective action process Interfaces to other programs and sources of data Performance Assurance Program Plan
Testing and data management can be very large and complex Test schedules Testing priorities Corrective action process Interfaces to other programs and sources of data Performance Assurance Program Plan
 Performance Assurance Program A management program that provides assurances that protective systems are performing as required Program Objectives: ○ Develop a method to sustain the safeguards and security program ○ Implement a consistent and recurring evaluation process ○ Report information to decision makers
Performance Assurance Program A management program that provides assurances that protective systems are performing as required Program Objectives: ○ Develop a method to sustain the safeguards and security program ○ Implement a consistent and recurring evaluation process ○ Report information to decision makers
 What is a Performance Assurance Program? A performance assurance program continually challenges the safeguards and security systems to determine if those systems are functioning to established standards. The program also provides a systemic process to enhance the protection of assets. Contrast to Performance Testing A test to confirm the ability of an implemented and operating system element or total system to meet an established requirement.
What is a Performance Assurance Program? A performance assurance program continually challenges the safeguards and security systems to determine if those systems are functioning to established standards. The program also provides a systemic process to enhance the protection of assets. Contrast to Performance Testing A test to confirm the ability of an implemented and operating system element or total system to meet an established requirement.
 Benefits of a Performance Assurance Program Determines the effectiveness of the safeguards and security program elements Determines effectiveness of individual critical protection elements Identifies system strengths and weaknesses Validates vulnerability analysis Validates procedures Validates training effectiveness
Benefits of a Performance Assurance Program Determines the effectiveness of the safeguards and security program elements Determines effectiveness of individual critical protection elements Identifies system strengths and weaknesses Validates vulnerability analysis Validates procedures Validates training effectiveness
 Benefits of a Performance Assurance Program (con’t) Promotes continuous improvement of protection systems Produces data for lifecycle management Provides data for financial analysis for continued support/upgrades Promotes quality by supporting improvement initiatives Integrates MC&A and physical protection
Benefits of a Performance Assurance Program (con’t) Promotes continuous improvement of protection systems Produces data for lifecycle management Provides data for financial analysis for continued support/upgrades Promotes quality by supporting improvement initiatives Integrates MC&A and physical protection
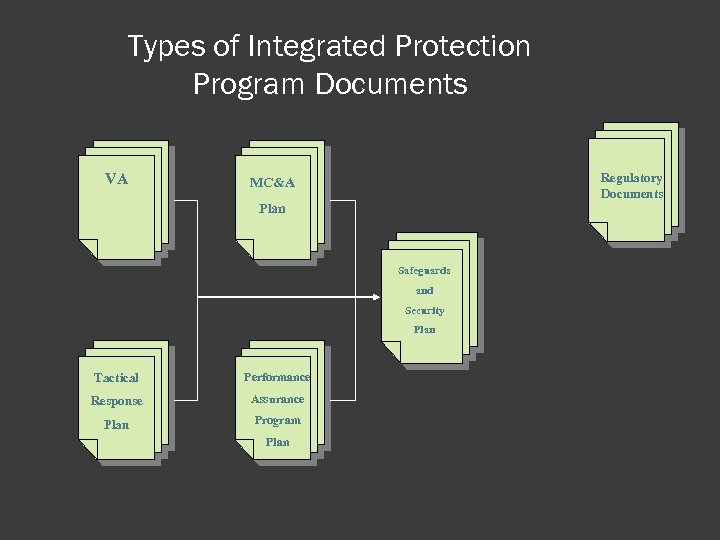 Types of Integrated Protection Program Documents VA Regulatory Documents MC&A Plan Safeguards and Security Plan Tactical Performance Response Assurance Plan Program Plan
Types of Integrated Protection Program Documents VA Regulatory Documents MC&A Plan Safeguards and Security Plan Tactical Performance Response Assurance Plan Program Plan
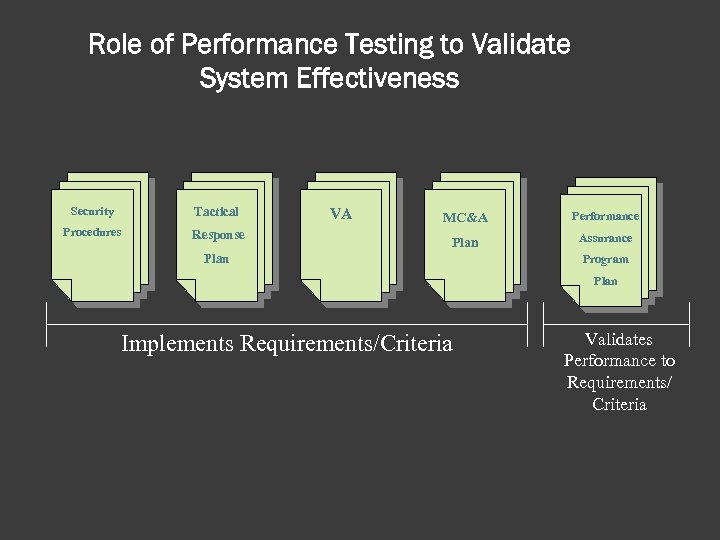 Role of Performance Testing to Validate System Effectiveness Security Tactical Procedures Response VA MC&A Performance Plan Assurance Plan Program Plan Implements Requirements/Criteria Validates Performance to Requirements/ Criteria
Role of Performance Testing to Validate System Effectiveness Security Tactical Procedures Response VA MC&A Performance Plan Assurance Plan Program Plan Implements Requirements/Criteria Validates Performance to Requirements/ Criteria
 How to decide what to test? Define those elements most critical to the protection of assets ○ Components ○ Sub-systems ○ Systems Critical protection element defined: A selected portion of a safeguards and security system that directly affects the ability of the system to perform a required function.
How to decide what to test? Define those elements most critical to the protection of assets ○ Components ○ Sub-systems ○ Systems Critical protection element defined: A selected portion of a safeguards and security system that directly affects the ability of the system to perform a required function.
 Critical Protection Elements typically fall into one of the following: Information security program Material control & accountability systems Personnel security program and Human Reliability Physical protection systems Protective forces Transportation systems Critical Infrastructure Cyber security program
Critical Protection Elements typically fall into one of the following: Information security program Material control & accountability systems Personnel security program and Human Reliability Physical protection systems Protective forces Transportation systems Critical Infrastructure Cyber security program
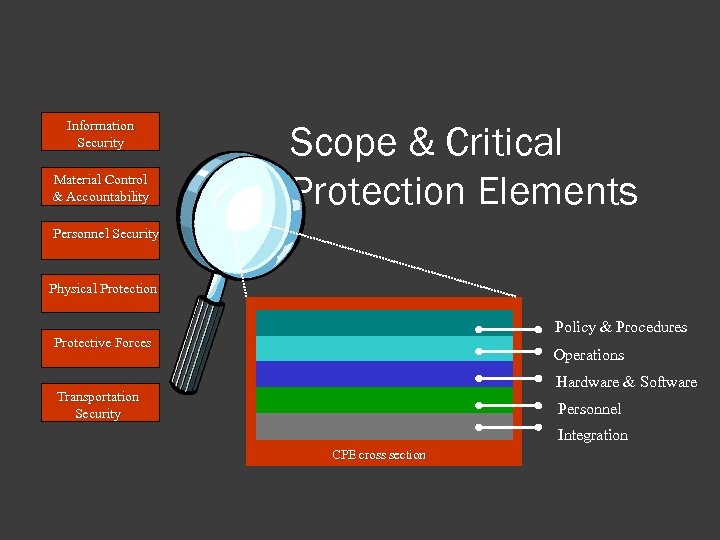 Information Security Material Control & Accountability Scope & Critical Protection Elements Personnel Security Physical Protection Policy & Procedures Protective Forces Operations Hardware & Software Transportation Security Personnel Integration CPE cross section
Information Security Material Control & Accountability Scope & Critical Protection Elements Personnel Security Physical Protection Policy & Procedures Protective Forces Operations Hardware & Software Transportation Security Personnel Integration CPE cross section
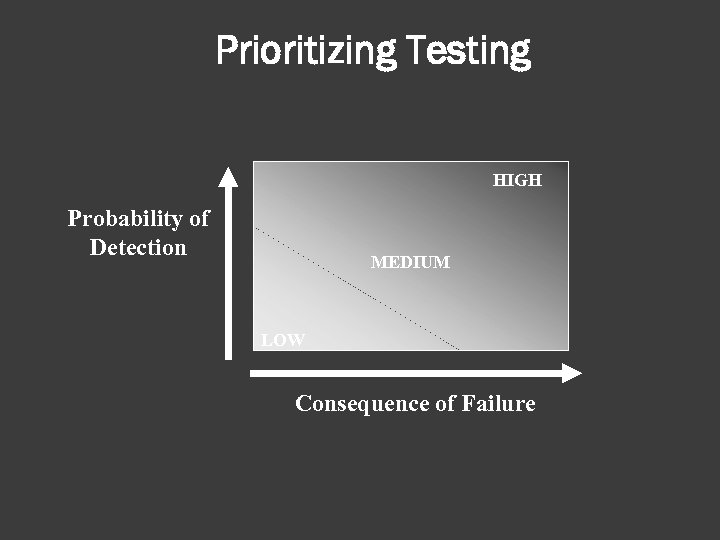
 The size of the protection system can be very large and complex. How do you prioritize testing functions? Graded safeguards Graded protection
The size of the protection system can be very large and complex. How do you prioritize testing functions? Graded safeguards Graded protection
 Graded Safeguards A system designed to provide varying degrees of physical protection, accountability, and material control consistent with the risks and consequences of threat scenarios. Based upon nuclear material: Type Physical form Chemical or isotopic composition
Graded Safeguards A system designed to provide varying degrees of physical protection, accountability, and material control consistent with the risks and consequences of threat scenarios. Based upon nuclear material: Type Physical form Chemical or isotopic composition
 Graded Protection The level of effort and magnitude of resources expended for a particular safeguards and security interest are commensurate with the interest’s importance or the impact of its loss, destruction, or misuse. Attractiveness of assets being protected Threats against the assets Results of vulnerability assessments
Graded Protection The level of effort and magnitude of resources expended for a particular safeguards and security interest are commensurate with the interest’s importance or the impact of its loss, destruction, or misuse. Attractiveness of assets being protected Threats against the assets Results of vulnerability assessments
 Testing Categories Four categories of performance tests are used Acceptance Testing ○ Performed if the element is new to the protection system, or ○ If there have been significant changes to the protection system Validation ○ Repeated testing to derive a level of performance confidence Effectiveness ○ Reveals how well the protection system works Operational (functional) ○ Typically answers the question “Does it work or not” without regard for how well it works. 20
Testing Categories Four categories of performance tests are used Acceptance Testing ○ Performed if the element is new to the protection system, or ○ If there have been significant changes to the protection system Validation ○ Repeated testing to derive a level of performance confidence Effectiveness ○ Reveals how well the protection system works Operational (functional) ○ Typically answers the question “Does it work or not” without regard for how well it works. 20
 Prioritizing Testing HIGH Probability of Detection MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure
Prioritizing Testing HIGH Probability of Detection MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure
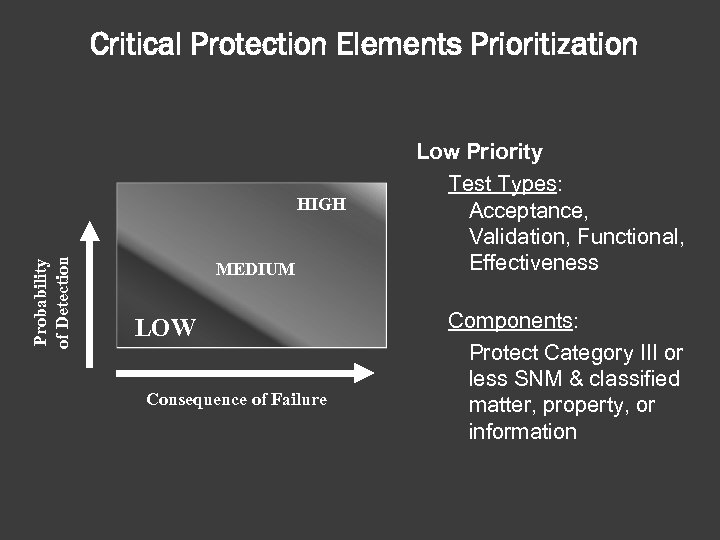 Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure Low Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Protect Category III or less SNM & classified matter, property, or information
Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure Low Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Protect Category III or less SNM & classified matter, property, or information
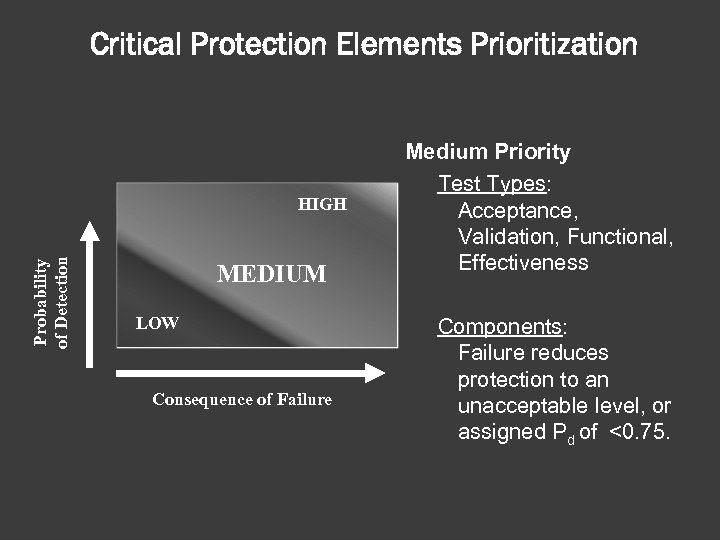 Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure Medium Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Failure reduces protection to an unacceptable level, or assigned Pd of <0. 75.
Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure Medium Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Failure reduces protection to an unacceptable level, or assigned Pd of <0. 75.
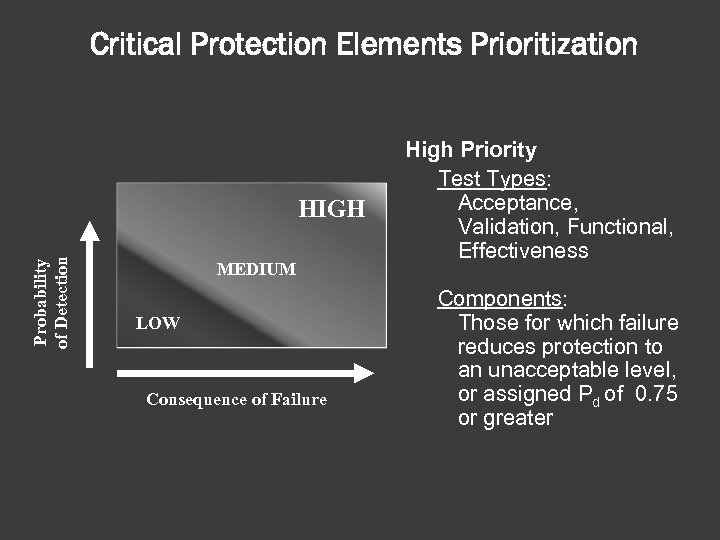 Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure High Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Those for which failure reduces protection to an unacceptable level, or assigned Pd of 0. 75 or greater
Critical Protection Elements Prioritization Probability of Detection HIGH MEDIUM LOW Consequence of Failure High Priority Test Types: Acceptance, Validation, Functional, Effectiveness Components: Those for which failure reduces protection to an unacceptable level, or assigned Pd of 0. 75 or greater
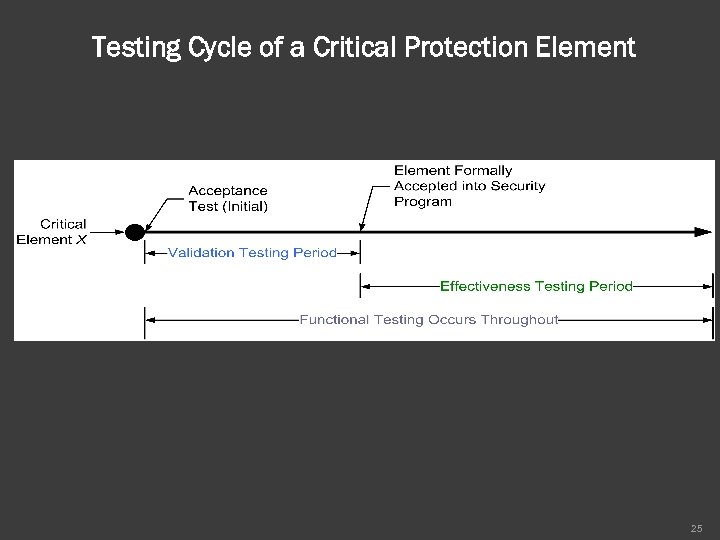 Testing Cycle of a Critical Protection Element 25
Testing Cycle of a Critical Protection Element 25
 A corrective action process is essential for continual improvement: Root cause analyses Compensatory measures Designation of high, medium, or low priority deficiencies May require performance tests to validate a corrected deficiency
A corrective action process is essential for continual improvement: Root cause analyses Compensatory measures Designation of high, medium, or low priority deficiencies May require performance tests to validate a corrected deficiency
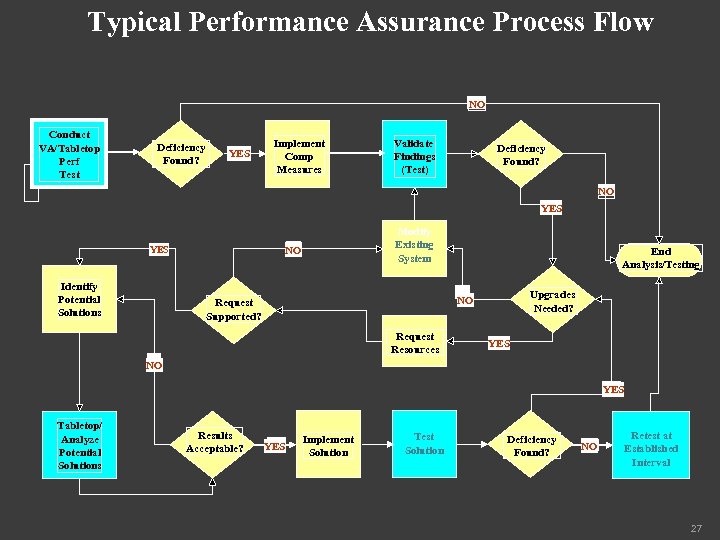 Typical Performance Assurance Process Flow NO Conduct VA/Tabletop Perf Test Deficiency Found? YES Implement Comp Measures Validate Findings (Test) Deficiency Found? NO YES Identify Potential Solutions Modify Existing System End Analysis/Testing Upgrades Needed? NO Request Supported? Request Resources YES NO YES Tabletop/ Analyze Potential Solutions Results Acceptable? YES Implement Solution Test Solution Deficiency Found? NO Retest at Established Interval 27
Typical Performance Assurance Process Flow NO Conduct VA/Tabletop Perf Test Deficiency Found? YES Implement Comp Measures Validate Findings (Test) Deficiency Found? NO YES Identify Potential Solutions Modify Existing System End Analysis/Testing Upgrades Needed? NO Request Supported? Request Resources YES NO YES Tabletop/ Analyze Potential Solutions Results Acceptable? YES Implement Solution Test Solution Deficiency Found? NO Retest at Established Interval 27
 Collecting and Analyzing Performance Test Data 28
Collecting and Analyzing Performance Test Data 28
 Data Collection Are there conditions that will affect the results? • Shift-to-shift differences • Environmental conditions - Day/Night - Rainy/Dry • Differences in security devices Testing should encompass all conditions that may affect the test outcomes 29
Data Collection Are there conditions that will affect the results? • Shift-to-shift differences • Environmental conditions - Day/Night - Rainy/Dry • Differences in security devices Testing should encompass all conditions that may affect the test outcomes 29
 Statistical Analysis What do I do with the data collected during performance testing? The collected data tells a story about the security component / system. 30
Statistical Analysis What do I do with the data collected during performance testing? The collected data tells a story about the security component / system. 30
 Statistical Analysis Many statistical tools are available to use in the management and tracking of performance-program data. 31
Statistical Analysis Many statistical tools are available to use in the management and tracking of performance-program data. 31
 Statistical Analysis Pareto Analysis • Ranks reasons that contribute to the problem Typically, relatively few reasons are responsible for the majority of the problems 32
Statistical Analysis Pareto Analysis • Ranks reasons that contribute to the problem Typically, relatively few reasons are responsible for the majority of the problems 32
 Statistical Analysis Regression Analysis • Determines the values of parameters for a function that cause the function to best fit a set of data observations provided For example, do day/night and building contribute to whether a motion sensor alarms? 33
Statistical Analysis Regression Analysis • Determines the values of parameters for a function that cause the function to best fit a set of data observations provided For example, do day/night and building contribute to whether a motion sensor alarms? 33
 Statistical Analysis Control Charts • Used to distinguish between normal and unusual variations in a system Some examples: - Physical Protection: monitoring the response of a walk-through metal detector - Material Control: assuring that scales used to weigh material are accurate 34
Statistical Analysis Control Charts • Used to distinguish between normal and unusual variations in a system Some examples: - Physical Protection: monitoring the response of a walk-through metal detector - Material Control: assuring that scales used to weigh material are accurate 34
 Statistical Analysis Experimental Design / Analysis of Variance • A planned approach to determine what factors affect a question of interest A well-designed experiment will provide the most information with the fewest possible tests conducted 35
Statistical Analysis Experimental Design / Analysis of Variance • A planned approach to determine what factors affect a question of interest A well-designed experiment will provide the most information with the fewest possible tests conducted 35
 Statistical Analysis These statistical tools: Are dependent upon the specific test objectives and type of data that is collected Are identified by factors that significantly affect test results Determine how many tests to conduct Assure randomized test runs Will allow proper analysis of test results 36
Statistical Analysis These statistical tools: Are dependent upon the specific test objectives and type of data that is collected Are identified by factors that significantly affect test results Determine how many tests to conduct Assure randomized test runs Will allow proper analysis of test results 36
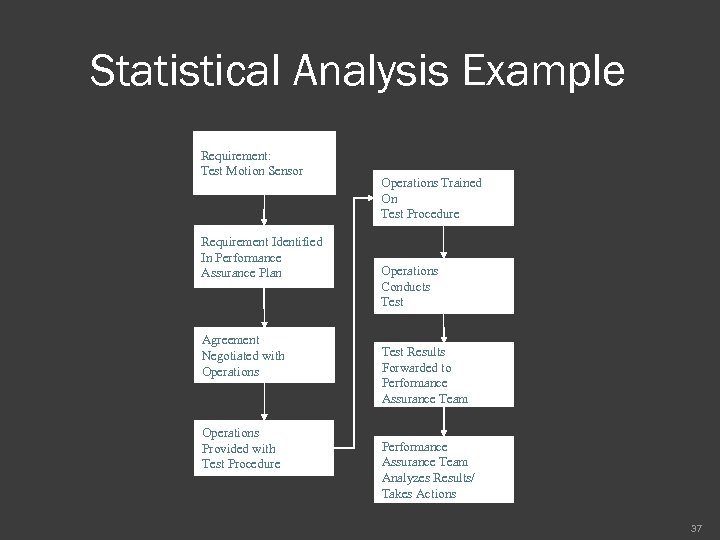 Statistical Analysis Example Requirement: Test Motion Sensor Requirement Identified In Performance Assurance Plan Agreement Negotiated with Operations Provided with Test Procedure Operations Trained On Test Procedure Operations Conducts Test Results Forwarded to Performance Assurance Team Analyzes Results/ Takes Actions 37
Statistical Analysis Example Requirement: Test Motion Sensor Requirement Identified In Performance Assurance Plan Agreement Negotiated with Operations Provided with Test Procedure Operations Trained On Test Procedure Operations Conducts Test Results Forwarded to Performance Assurance Team Analyzes Results/ Takes Actions 37
 Function Test of a Motion Sensor Once a week, each shift supervisor is required to test the motion sensor in his facility to determine its operability. The results of these test are reported to the Performance Program group monthly. 38
Function Test of a Motion Sensor Once a week, each shift supervisor is required to test the motion sensor in his facility to determine its operability. The results of these test are reported to the Performance Program group monthly. 38
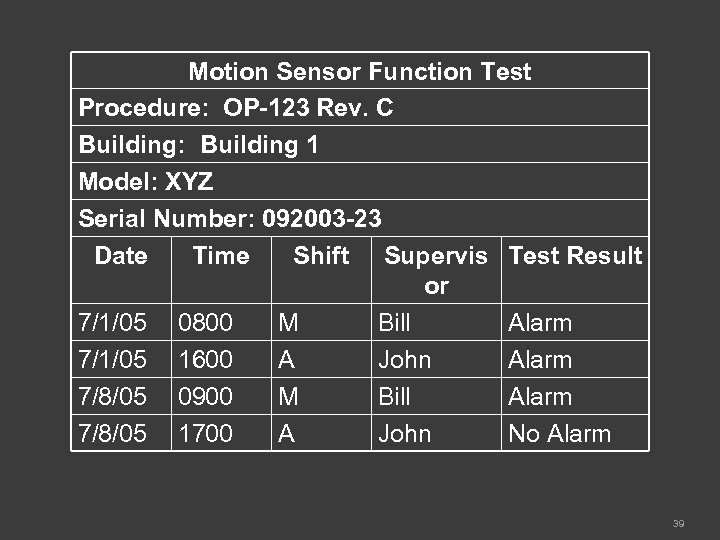 Motion Sensor Function Test Procedure: OP-123 Rev. C Building: Building 1 Model: XYZ Serial Number: 092003 -23 Date Time Shift Supervis Test Result or 7/1/05 0800 M Bill Alarm 7/1/05 1600 A John Alarm 7/8/05 0900 M Bill Alarm 7/8/05 1700 A John No Alarm 39
Motion Sensor Function Test Procedure: OP-123 Rev. C Building: Building 1 Model: XYZ Serial Number: 092003 -23 Date Time Shift Supervis Test Result or 7/1/05 0800 M Bill Alarm 7/1/05 1600 A John Alarm 7/8/05 0900 M Bill Alarm 7/8/05 1700 A John No Alarm 39
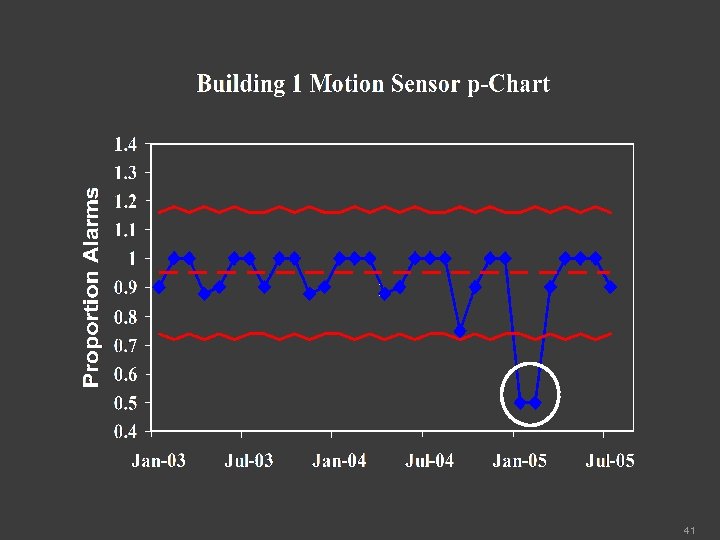
 Performance Program group uses a p-chart (control chart) to monitor the results of the motion sensor tests. 40
Performance Program group uses a p-chart (control chart) to monitor the results of the motion sensor tests. 40
 41
41
 The January and February 2005 data points were investigated because they were below the lower control limit The investigation revealed that a new supervisor was working in Building 1 and he was not following the motion sensor test procedure The supervisor was trained and began performing the test correctly 42
The January and February 2005 data points were investigated because they were below the lower control limit The investigation revealed that a new supervisor was working in Building 1 and he was not following the motion sensor test procedure The supervisor was trained and began performing the test correctly 42
 Statistical Analysis What data collection tools will be used? • Manual/Automated • Automated Are my test observers / data collectors properly trained and consistent? Is the test progressing as planned? If no, are changes being documented? 43
Statistical Analysis What data collection tools will be used? • Manual/Automated • Automated Are my test observers / data collectors properly trained and consistent? Is the test progressing as planned? If no, are changes being documented? 43
 System Performance Confidence Levels Performance tests are used to validate that a security component or system is performing at a desired level. How is the “desired” level selected? • Vulnerability assessment (VA) risk • Regulatory documents • Management decisions 44
System Performance Confidence Levels Performance tests are used to validate that a security component or system is performing at a desired level. How is the “desired” level selected? • Vulnerability assessment (VA) risk • Regulatory documents • Management decisions 44
 System Performance Confidence Levels Ultimately, the desired levels are management decisions. Management must determine if there adequate resources to meet the desired levels. 45
System Performance Confidence Levels Ultimately, the desired levels are management decisions. Management must determine if there adequate resources to meet the desired levels. 45
 System Performance Confidence Levels Suppose the VA risk levels are selected as a basis to conduct performance tests. An example: VA Risk Level Confidence Margin of Error Level High 95% 3% Medium 90% 10% Low 80% 20% A high confidence level and a small margin of error increases the sample size 46
System Performance Confidence Levels Suppose the VA risk levels are selected as a basis to conduct performance tests. An example: VA Risk Level Confidence Margin of Error Level High 95% 3% Medium 90% 10% Low 80% 20% A high confidence level and a small margin of error increases the sample size 46
 System Performance Confidence Levels For example: The VA requires a Pd of motion sensors in vaults to be 0. 95 Management has decided that they would like to be 90% confident in the test data that is produced Management has also decided that the acceptable margin of error can be no more than 5% Given this situation, how many motion sensors should be tested? 47
System Performance Confidence Levels For example: The VA requires a Pd of motion sensors in vaults to be 0. 95 Management has decided that they would like to be 90% confident in the test data that is produced Management has also decided that the acceptable margin of error can be no more than 5% Given this situation, how many motion sensors should be tested? 47
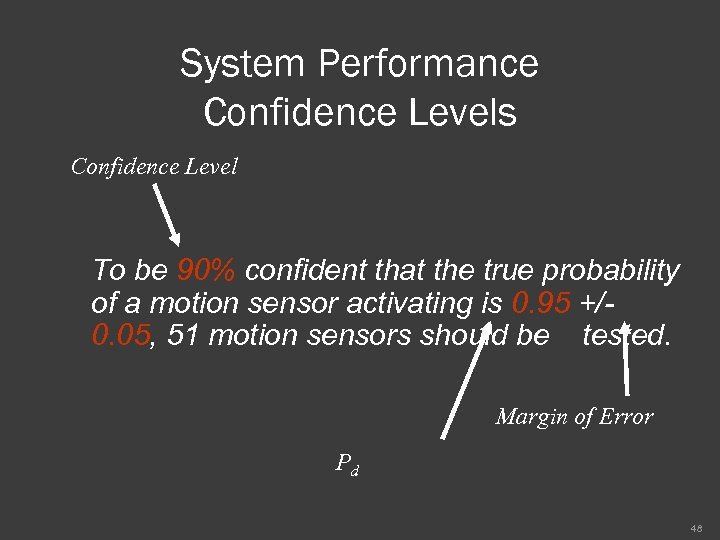 System Performance Confidence Levels Confidence Level To be 90% confident that the true probability of a motion sensor activating is 0. 95 +/0. 05, 51 motion sensors should be tested. Margin of Error Pd 48
System Performance Confidence Levels Confidence Level To be 90% confident that the true probability of a motion sensor activating is 0. 95 +/0. 05, 51 motion sensors should be tested. Margin of Error Pd 48
 System Performance Confidence Levels One of the most challenging aspects of conducting a performance test is to determine how many tests need to be conducted to characterize the performance of a system with some level of confidence. Performing one or two tests is not sufficient and conducting thousands of tests is probably not feasible. 49
System Performance Confidence Levels One of the most challenging aspects of conducting a performance test is to determine how many tests need to be conducted to characterize the performance of a system with some level of confidence. Performing one or two tests is not sufficient and conducting thousands of tests is probably not feasible. 49
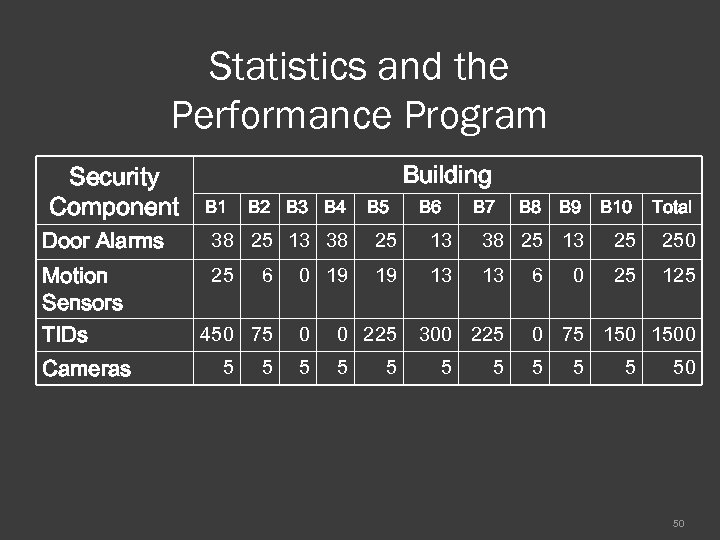 Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Building B 1 B 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 B 8 B 9 B 10 Total Door Alarms 38 25 13 25 250 Motion Sensors TIDs 25 19 13 13 25 125 Cameras 6 450 75 5 5 0 19 0 0 225 5 300 225 5 5 6 0 0 75 1500 5 50 50
Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Building B 1 B 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 B 8 B 9 B 10 Total Door Alarms 38 25 13 25 250 Motion Sensors TIDs 25 19 13 13 25 125 Cameras 6 450 75 5 5 0 19 0 0 225 5 300 225 5 5 6 0 0 75 1500 5 50 50
 Statistics and the Performance Program Normally Distributed Data • The number of tests to be conducted is determined prior to sampling • Two possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis • Parameters needed - Standard deviation of population of interest - Margin of error - Confidence level 51
Statistics and the Performance Program Normally Distributed Data • The number of tests to be conducted is determined prior to sampling • Two possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis • Parameters needed - Standard deviation of population of interest - Margin of error - Confidence level 51
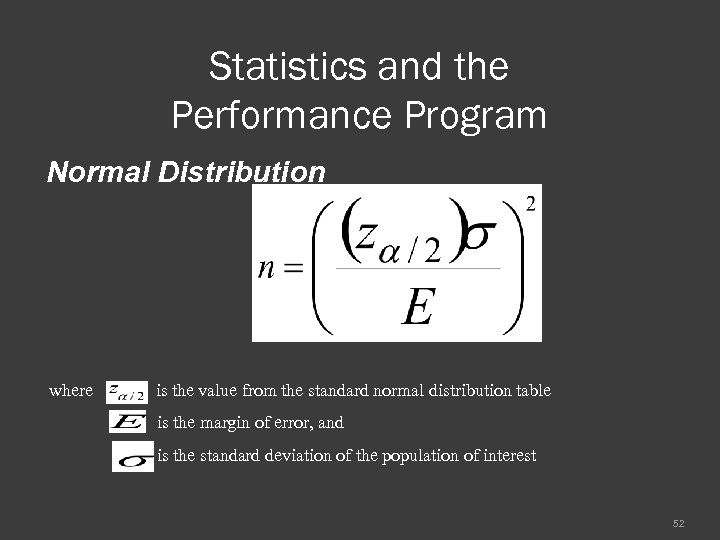 Statistics and the Performance Program Normal Distribution where is the value from the standard normal distribution table is the margin of error, and is the standard deviation of the population of interest 52
Statistics and the Performance Program Normal Distribution where is the value from the standard normal distribution table is the margin of error, and is the standard deviation of the population of interest 52
 Statistics and the Performance Program Sequential Sampling: • The number of tests to be conducted is undecided and is determined only by the sample observations as these are completed • Three possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis - Keep sampling or conclude that a decision cannot be made • Parameters needed: - The performance value - The minimally acceptable lower value - Confidence level 53
Statistics and the Performance Program Sequential Sampling: • The number of tests to be conducted is undecided and is determined only by the sample observations as these are completed • Three possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis - Keep sampling or conclude that a decision cannot be made • Parameters needed: - The performance value - The minimally acceptable lower value - Confidence level 53
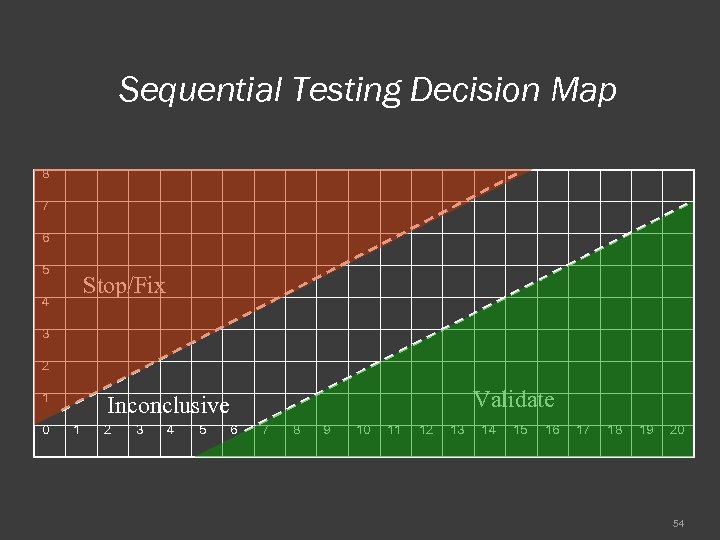 Sequential Testing Decision Map 8 7 6 5 Stop/Fix 4 3 2 1 0 Validate Inconclusive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 54
Sequential Testing Decision Map 8 7 6 5 Stop/Fix 4 3 2 1 0 Validate Inconclusive 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 54
 Statistics and the Performance Program Bernouilli Trials • The number of tests to be conducted is predetermined prior to sampling • Two possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis • Parameters needed - Proportion of interest (Pd) - Margin of error - Confidence level 55
Statistics and the Performance Program Bernouilli Trials • The number of tests to be conducted is predetermined prior to sampling • Two possible decisions: - Reject the hypothesis - Fail to reject the hypothesis • Parameters needed - Proportion of interest (Pd) - Margin of error - Confidence level 55
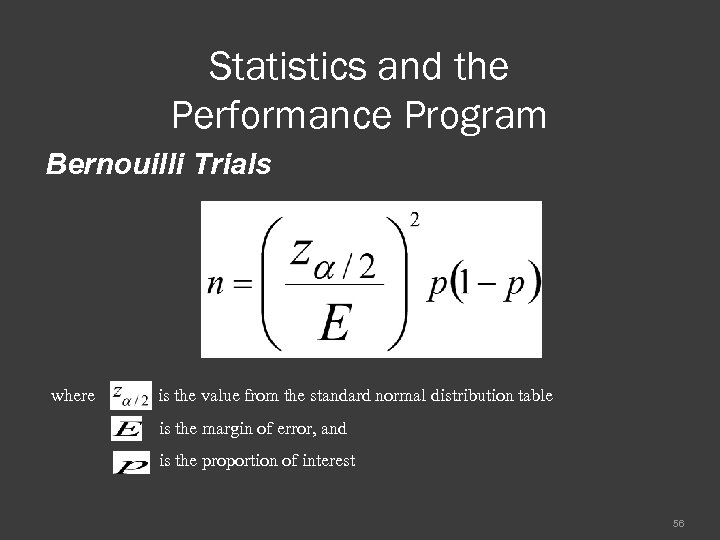 Statistics and the Performance Program Bernouilli Trials where is the value from the standard normal distribution table is the margin of error, and is the proportion of interest 56
Statistics and the Performance Program Bernouilli Trials where is the value from the standard normal distribution table is the margin of error, and is the proportion of interest 56
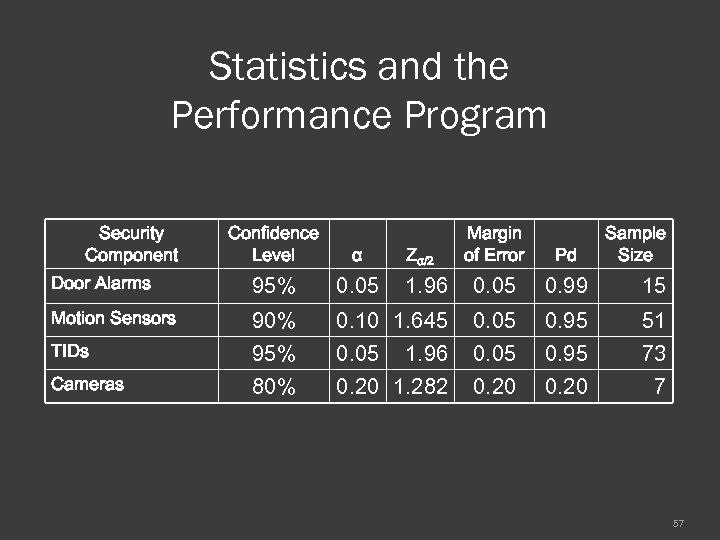 Statistics and the Performance Program Confidence Level Margin of Error α Pd Door Alarms 95% 0. 05 1. 96 0. 05 0. 99 15 Motion Sensors TIDs 90% 95% 0. 10 1. 645 0. 05 1. 96 0. 05 0. 95 51 73 Cameras 80% 0. 20 1. 282 0. 20 7 Security Component Zα/2 Sample Size 57
Statistics and the Performance Program Confidence Level Margin of Error α Pd Door Alarms 95% 0. 05 1. 96 0. 05 0. 99 15 Motion Sensors TIDs 90% 95% 0. 10 1. 645 0. 05 1. 96 0. 05 0. 95 51 73 Cameras 80% 0. 20 1. 282 0. 20 7 Security Component Zα/2 Sample Size 57
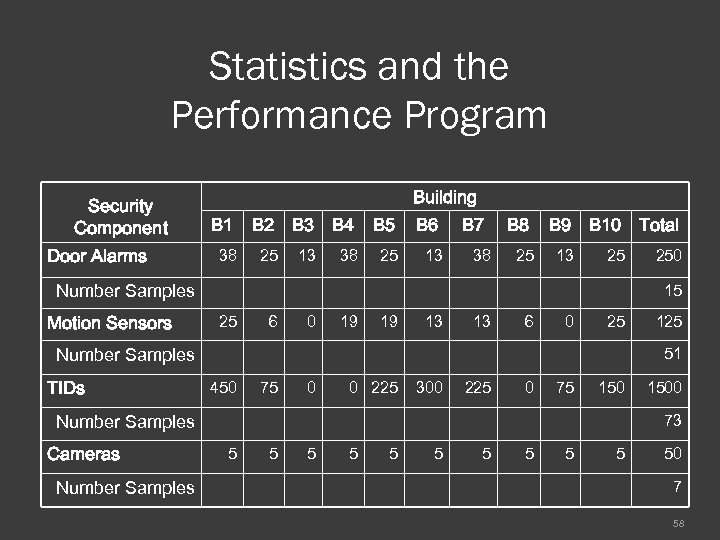 Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Door Alarms Building B 1 38 B 2 B 3 25 13 B 4 B 5 38 25 B 6 13 B 7 38 B 9 B 10 Total 25 13 25 250 Number Samples Motion Sensors 15 25 6 0 19 19 13 13 6 0 25 Number Samples TIDs 51 450 75 0 0 225 300 225 0 75 150 Number Samples Cameras Number Samples 125 1500 73 5 5 50 7 58
Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Door Alarms Building B 1 38 B 2 B 3 25 13 B 4 B 5 38 25 B 6 13 B 7 38 B 9 B 10 Total 25 13 25 250 Number Samples Motion Sensors 15 25 6 0 19 19 13 13 6 0 25 Number Samples TIDs 51 450 75 0 0 225 300 225 0 75 150 Number Samples Cameras Number Samples 125 1500 73 5 5 50 7 58
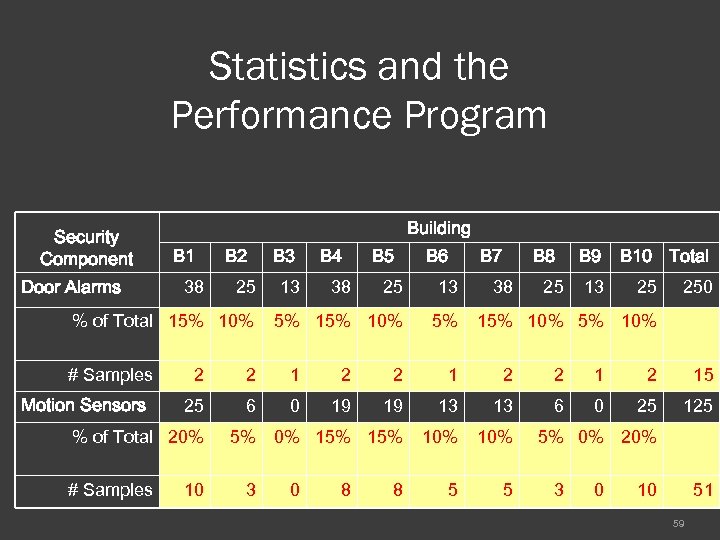 Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Door Alarms Building B 1 38 B 2 25 % of Total 15% 10% # Samples Motion Sensors 13 B 4 38 B 5 B 6 25 13 5% 10% 5% B 7 38 B 8 25 B 9 13 B 10 Total 25 250 15% 10% 2 2 15 25 6 0 19 19 13 13 6 0 25 125 5% 0% 15% 10% 5 5 % of Total 20% # Samples B 3 10 3 0 8 8 5% 0% 20% 3 0 10 51 59
Statistics and the Performance Program Security Component Door Alarms Building B 1 38 B 2 25 % of Total 15% 10% # Samples Motion Sensors 13 B 4 38 B 5 B 6 25 13 5% 10% 5% B 7 38 B 8 25 B 9 13 B 10 Total 25 250 15% 10% 2 2 15 25 6 0 19 19 13 13 6 0 25 125 5% 0% 15% 10% 5 5 % of Total 20% # Samples B 3 10 3 0 8 8 5% 0% 20% 3 0 10 51 59
 Statistics and the Performance Program Assumptions: Protection elements designed to perform a certain task and that are tested to the same standard are grouped together Randomly select elements or systems to test 60
Statistics and the Performance Program Assumptions: Protection elements designed to perform a certain task and that are tested to the same standard are grouped together Randomly select elements or systems to test 60
 Summary A well designed Performance Assurance Program serves as the vehicle to determine the health of the safeguards and security system. For each critical protection element, equipment, procedures, personnel and system integration must be considered. The performance assurance program is a continuous process.
Summary A well designed Performance Assurance Program serves as the vehicle to determine the health of the safeguards and security system. For each critical protection element, equipment, procedures, personnel and system integration must be considered. The performance assurance program is a continuous process.


