195880154346743c3e48852bae2c4b81.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Inkjet Printing by Brian Smith LRPS

Print Quality Factors • Colour Rendition – Colour Casts – Neutral Greys – Saturation – Smooth tones • Brightness & Contrast • Sharpness • Other Faults

Test Evaluation - colour • Rich Blues • Gradients • Skin colour and smoothness • Shadow separation • Sky Blue, and highlight detail • Natural hues • Bright Reds • Neutral monochrome • Sharpness • Texture in all colours
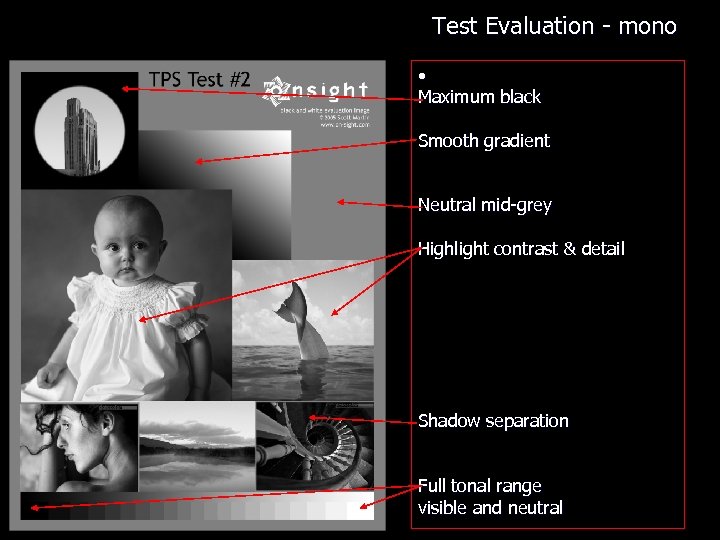
Test Evaluation - mono • Maximum black Smooth gradient Neutral mid-grey Highlight contrast & detail Shadow separation Full tonal range visible and neutral

Print Rendition • Causes of poor prints – Poor image – Printer faults – Wrong or incompatible paper & ink – Software

Printer Faults • Misaligned heads • Clogged nozzles • Depleted cartridge(s) • Mechanical malfunctions – Pizza wheel marks – Scratches (paper thickness? ) – Paper curl – Ink deposits from rollers

Papers & Inks • Paper type – – – Matte Glossy & Lustre/Pearl Swellable vs Micro-Porous Cotton Rag Baryta (Fibre) – – – Dye Pigment OEM vs Compatible • Inks

The need for coated paper Inkjet coating Base Paper PE coating Uncoated media – Uncontrolled ink spread – Bleed & strike-through due to porous substrate – Lower density due to absorption – Poor fade resistance – Cockle Coated media – Controlled ink spread – High resolution – Large colour gamut – Stays flat – Better fade resistance
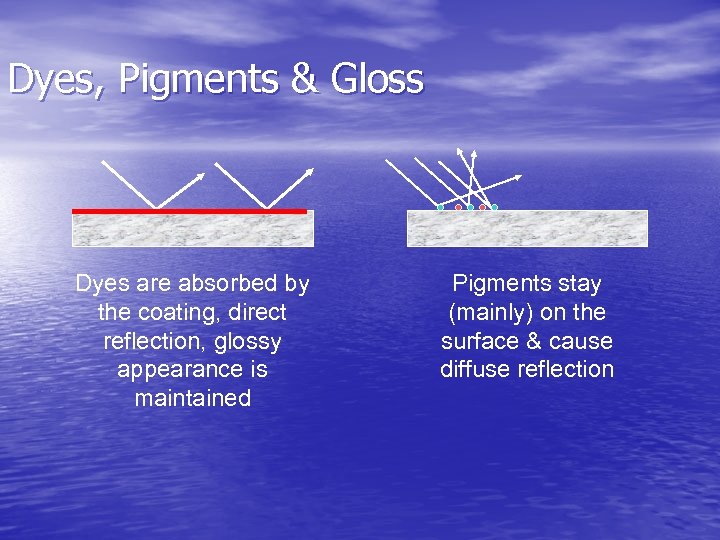
Dyes, Pigments & Gloss Dyes are absorbed by the coating, direct reflection, glossy appearance is maintained Pigments stay (mainly) on the surface & cause diffuse reflection

Inkjet Inks Generalities Dye based inks – Bright colours – Quicker fading – Sensitive to oxidizing – Glossy media available – Colours vary more with different papers – Low water resistance after printed Pigmented inks – Less bright colours – Fade resistant – Wide range of Matte surfaces – Fewer glossy options available – Good weather resistance

Paper vs Ink problems • Colour! – Wrong profile or driver setting? • Poor contrast (D-Max) • Banding • Metamarism • Blotching (slow drying) • Gloss differential • Bronzing

Why is monochrome so difficult? Because making grey by mixing C+M+Y is extremely difficult

Printer Ink Sets • C+M+Y+K – normal printing & consumer inkjets • C+M+Y+K+Lm+Lc - Photo inkjets • C+M+Y+PK+MK+Lm+Lc+Lk - HP Vivera • C+M+Y+K+Lm+Lc+Lk+Llk - Epson K 3 Ultrachrome • C+M+Y+K+Lm+Lc+Lk+Llk+Red+Blue – Canon Chroma. Life More inks deliver wider gamut

Ink Starts Two blacks Three blacks

What’s the solution? • Use the printer’s default monochrome settings • Use monochrome (low chroma) inks • Use special (extended grey) ICC colour profiles • Use “grey balancing” software • Use a RIP (raster image processor) • Use a printer that has 2 or 3 black inks

Printing Software Photo Editor Application Printer Driver PC/Operating System

Colour Management • Non-managed printing – Assumes s. RGB files – Colours controlled by driver • Colour Managed – – By driver OR printing software Double profiling typically gives a magenta cast Built-in profiles for manufacturers papers only Custom profiles are more accurate Demo: Print Drivers

Resolution • dpi – dots per inch (e. g. 2400: Canon, HP, 2880: Epson) - internal to printer • ppi – pixels per inch (e. g. 300, 360) – determines how large your print will be. • 300 ppi is an industry standard for commercial printing (e. g. magazines) • 240 ppi is easily sufficient for high quality inkjet printing

Print Size Consider a 6 MB image: 3000 x 2000 pixels • At 300 ppi -> 10” x 6. 6” print • At 200 ppi -> 15” x 10” print • If you actually want a 12” x 8” print, then print at 250 ppi. • In all cases, the image itself is unchanged.

What actually happens Photoshop/Elements Printer Driver PC/Operating System • Print 6 MB photo at 250 ppi • Resampled to internal resolution (600 ppi) • Data (35 MB) transmitted via USB connection • Outputs ink droplets at 2400 dpi

Resampling (upsizing) • Printers have a native resolution: – Epson = 720 ppi – Canon & HP = 600 ppi • Printing at exact multiples can give higher quality – – 180 or 360 for Epson 150 or 300 for HP, Canon • Resample: Photoshop, Genuine Fractals etc. • Use Qimage
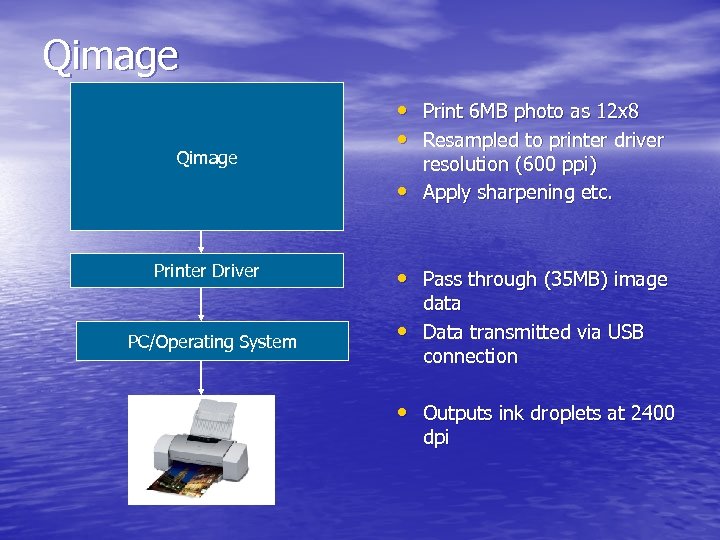
Qimage • Print 6 MB photo as 12 x 8 • Resampled to printer driver • Printer Driver PC/Operating System resolution (600 ppi) Apply sharpening etc. • Pass through (35 MB) image • data Data transmitted via USB connection • Outputs ink droplets at 2400 dpi

Sharpening • Images to be printed MUST be sharpened a little to compensate for ink diffusion • Over-sharpening is easily achieved, and harshly judged Demo: Examples

Summary Tips • If you find colour management complex, stick to an unmanaged workflow: – – – Use s. RGB colour space Use manufacturers papers and inks Find the right driver settings, and stick with them • Managed workflow offers more options, but more pitfalls – Limit the range of papers you use, and learn their characteristics – Have custom profiles made for non-OEM papers • Don’t keep changing your workflow – consistency in • • results comes from consistency in approach Do a nozzle check before an important print run Print a test image periodically…
195880154346743c3e48852bae2c4b81.ppt