874460c5c04cde19a47af3def2de137e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 INFSY 540 Information Resources in Management Lesson 3 Chapter 4 Operations and Transactions Copyright © 1998 by Jerry Post Introduction to MIS 1
INFSY 540 Information Resources in Management Lesson 3 Chapter 4 Operations and Transactions Copyright © 1998 by Jerry Post Introduction to MIS 1
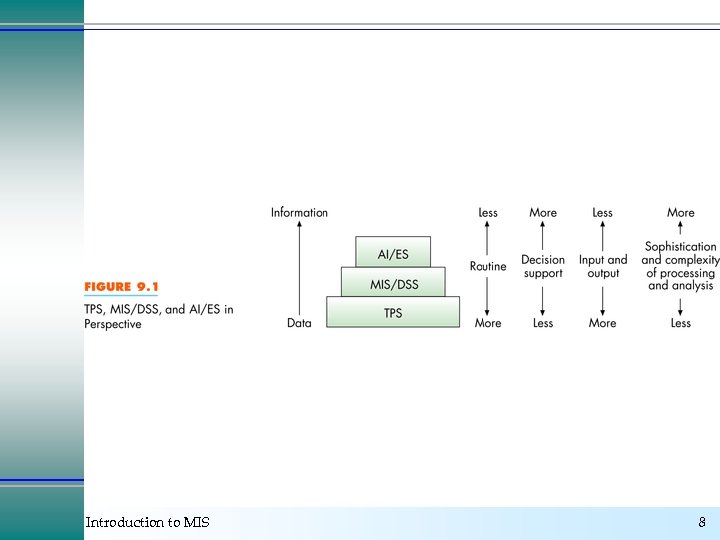
 Classes of Information Systems Ø Ø Ø Transaction processing systems Management information systems Decision support systems Expert systems Office automation systems Introduction to MIS 2
Classes of Information Systems Ø Ø Ø Transaction processing systems Management information systems Decision support systems Expert systems Office automation systems Introduction to MIS 2
 Transaction Processing Transaction processing systems are information system applications that capture and process data about business transactions. v Includes data maintenance, which provides for custodial updates to stored data. v Business process redesign (BPR) is the study, analysis, and redesign of fundamental business (transaction) processes to reduce costs and/or improve value added to the business. Introduction to MIS 3
Transaction Processing Transaction processing systems are information system applications that capture and process data about business transactions. v Includes data maintenance, which provides for custodial updates to stored data. v Business process redesign (BPR) is the study, analysis, and redesign of fundamental business (transaction) processes to reduce costs and/or improve value added to the business. Introduction to MIS 3
 Management Information Systems A management information system (MIS) is an information system application that provides for management-oriented reporting. These reports are usually generated on a predetermined schedule and appear in a prearranged format. Introduction to MIS 4
Management Information Systems A management information system (MIS) is an information system application that provides for management-oriented reporting. These reports are usually generated on a predetermined schedule and appear in a prearranged format. Introduction to MIS 4
 Decision Support Systems A decision support system (DSS) is an information system application that provides its users with decision-oriented information whenever a decision-making situation arises. When applied to executive managers, these systems are sometimes called executive information systems (EIS). v A data warehouse is a read-only, informational database that is populated with detailed, summary, and exception data and information generated by other transaction and management information systems. The data warehouse can then be accessed by end-users and managers with DSS tools that generate a virtually limitless variety of information in support of unstructured decisions. Introduction to MIS 5
Decision Support Systems A decision support system (DSS) is an information system application that provides its users with decision-oriented information whenever a decision-making situation arises. When applied to executive managers, these systems are sometimes called executive information systems (EIS). v A data warehouse is a read-only, informational database that is populated with detailed, summary, and exception data and information generated by other transaction and management information systems. The data warehouse can then be accessed by end-users and managers with DSS tools that generate a virtually limitless variety of information in support of unstructured decisions. Introduction to MIS 5
 Expert Systems An expert system is a programmed decision-making information system that captures and reproduces the knowledge and expertise of an expert problem solver or decision maker and then simulates the “thinking” or “actions” of that expert. v Expert systems are implemented with artificial intelligence technology that captures, stores, and provides access to the reasoning of the experts. Introduction to MIS 6
Expert Systems An expert system is a programmed decision-making information system that captures and reproduces the knowledge and expertise of an expert problem solver or decision maker and then simulates the “thinking” or “actions” of that expert. v Expert systems are implemented with artificial intelligence technology that captures, stores, and provides access to the reasoning of the experts. Introduction to MIS 6
 Office Automation Systems Office automation (OA) systems support the wide range of business office activities that provide for improved work flow and communications between workers, regardless of whether or not those workers are located in the same office. v v Personal information systems are those designed to meet the needs of a single user. They are designed to boost an individual’s productivity. Work group information systems are those designed to meet the needs of a work group. They are designed to boost the group’s productivity. Introduction to MIS 7
Office Automation Systems Office automation (OA) systems support the wide range of business office activities that provide for improved work flow and communications between workers, regardless of whether or not those workers are located in the same office. v v Personal information systems are those designed to meet the needs of a single user. They are designed to boost an individual’s productivity. Work group information systems are those designed to meet the needs of a work group. They are designed to boost the group’s productivity. Introduction to MIS 7
 Introduction to MIS 8
Introduction to MIS 8
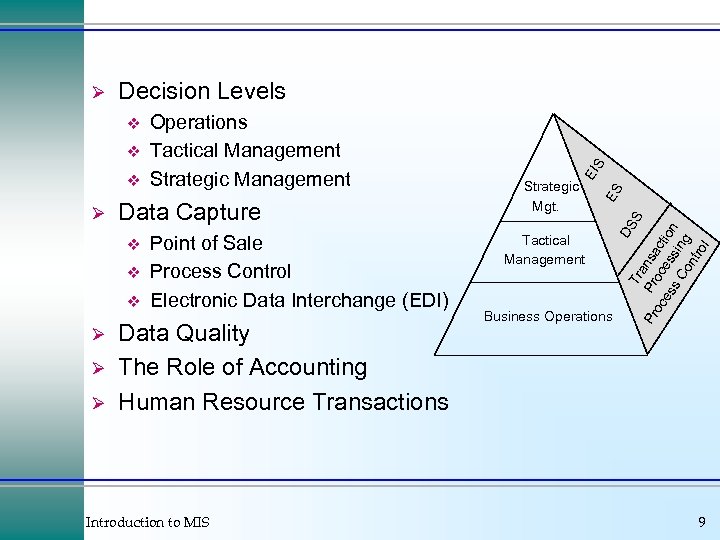 Ø Data Capture v v v Ø Ø Ø Point of Sale Process Control Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Data Quality The Role of Accounting Human Resource Transactions Introduction to MIS Strategic Mgt. Tactical Management Business Operations Tr S a Pr Pr nsa oc oc ct es es ion s C sin on g tro l v ES v Operations Tactical Management Strategic Management DS v S Decision Levels EI Ø 9
Ø Data Capture v v v Ø Ø Ø Point of Sale Process Control Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Data Quality The Role of Accounting Human Resource Transactions Introduction to MIS Strategic Mgt. Tactical Management Business Operations Tr S a Pr Pr nsa oc oc ct es es ion s C sin on g tro l v ES v Operations Tactical Management Strategic Management DS v S Decision Levels EI Ø 9
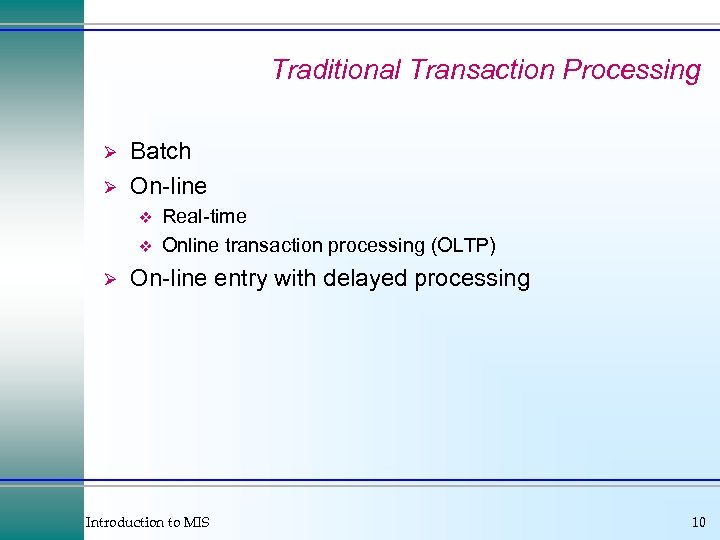 Traditional Transaction Processing Ø Ø Batch On-line v v Ø Real-time Online transaction processing (OLTP) On-line entry with delayed processing Introduction to MIS 10
Traditional Transaction Processing Ø Ø Batch On-line v v Ø Real-time Online transaction processing (OLTP) On-line entry with delayed processing Introduction to MIS 10
 Transaction Processing System Objectives Ø Ø Ø Ø Process data generated for and about transactions. Maintain a high degree of accuracy and integrity. Produce timely documents & reports Increase labor efficiency Help provide improved service Help build and maintain customer loyalty Achieve competitive advantage Introduction to MIS 11
Transaction Processing System Objectives Ø Ø Ø Ø Process data generated for and about transactions. Maintain a high degree of accuracy and integrity. Produce timely documents & reports Increase labor efficiency Help provide improved service Help build and maintain customer loyalty Achieve competitive advantage Introduction to MIS 11
 Control & Management Issues Ø Ø Business resumption planning Disaster recovery v v v Ø Backups Hot sites Cold sites Backups Introduction to MIS 12
Control & Management Issues Ø Ø Business resumption planning Disaster recovery v v v Ø Backups Hot sites Cold sites Backups Introduction to MIS 12
 Transaction Processing Audit v v v Does the system meet its business requirements? Are there procedures and controls? Are the procedures & controls properly used? Introduction to MIS 13
Transaction Processing Audit v v v Does the system meet its business requirements? Are there procedures and controls? Are the procedures & controls properly used? Introduction to MIS 13
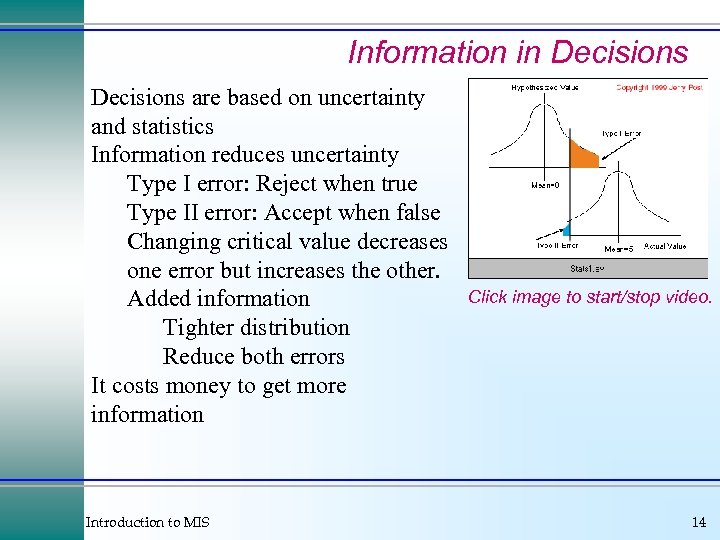 Information in Decisions are based on uncertainty and statistics Information reduces uncertainty Type I error: Reject when true Type II error: Accept when false Changing critical value decreases one error but increases the other. Added information Tighter distribution Reduce both errors It costs money to get more information Introduction to MIS Click image to start/stop video. 14
Information in Decisions are based on uncertainty and statistics Information reduces uncertainty Type I error: Reject when true Type II error: Accept when false Changing critical value decreases one error but increases the other. Added information Tighter distribution Reduce both errors It costs money to get more information Introduction to MIS Click image to start/stop video. 14
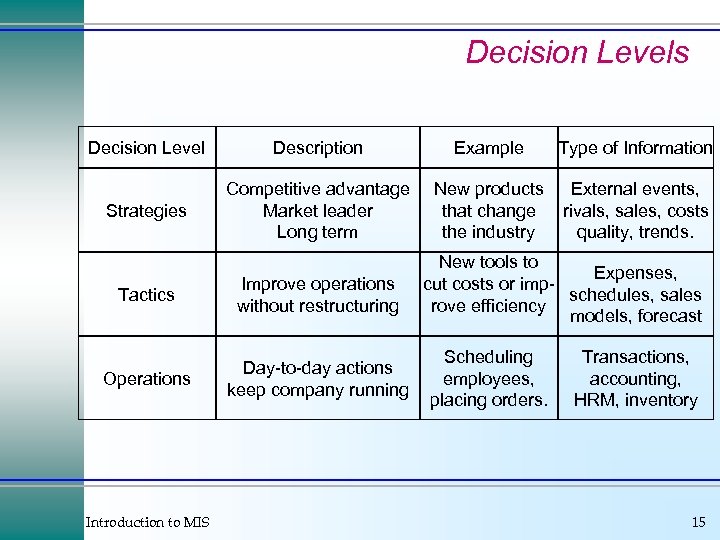 Decision Levels Decision Level Description Example Type of Information Strategies Competitive advantage Market leader Long term New products that change the industry External events, rivals, sales, costs quality, trends. Tactics Improve operations without restructuring Operations Day-to-day actions keep company running Introduction to MIS New tools to Expenses, cut costs or impschedules, sales rove efficiency models, forecast Scheduling employees, placing orders. Transactions, accounting, HRM, inventory 15
Decision Levels Decision Level Description Example Type of Information Strategies Competitive advantage Market leader Long term New products that change the industry External events, rivals, sales, costs quality, trends. Tactics Improve operations without restructuring Operations Day-to-day actions keep company running Introduction to MIS New tools to Expenses, cut costs or impschedules, sales rove efficiency models, forecast Scheduling employees, placing orders. Transactions, accounting, HRM, inventory 15
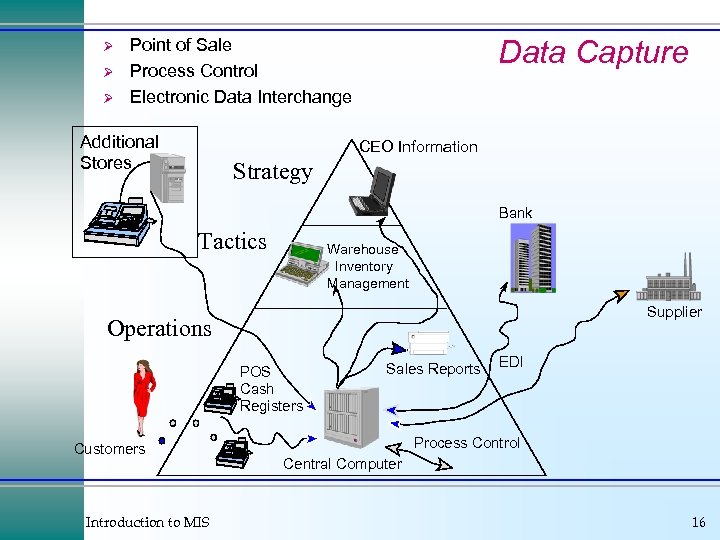 Ø Ø Ø Data Capture Point of Sale Process Control Electronic Data Interchange Additional Stores CEO Information Strategy Bank Tactics Warehouse Inventory Management Supplier Operations POS Cash Registers Customers Introduction to MIS Sales Reports EDI Process Control Central Computer 16
Ø Ø Ø Data Capture Point of Sale Process Control Electronic Data Interchange Additional Stores CEO Information Strategy Bank Tactics Warehouse Inventory Management Supplier Operations POS Cash Registers Customers Introduction to MIS Sales Reports EDI Process Control Central Computer 16
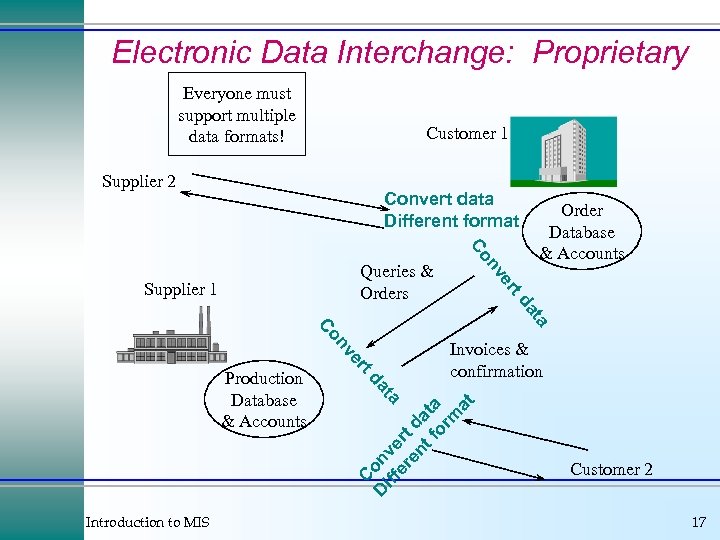 Electronic Data Interchange: Proprietary Everyone must support multiple data formats! Customer 1 Supplier 2 Convert data Different format D onv iff e er rt en d t f ata or m at C Introduction to MIS Invoices & confirmation ta da Production Database & Accounts rt e nv Co a at td er nv Supplier 1 Co Queries & Orders Order Database & Accounts Customer 2 17
Electronic Data Interchange: Proprietary Everyone must support multiple data formats! Customer 1 Supplier 2 Convert data Different format D onv iff e er rt en d t f ata or m at C Introduction to MIS Invoices & confirmation ta da Production Database & Accounts rt e nv Co a at td er nv Supplier 1 Co Queries & Orders Order Database & Accounts Customer 2 17
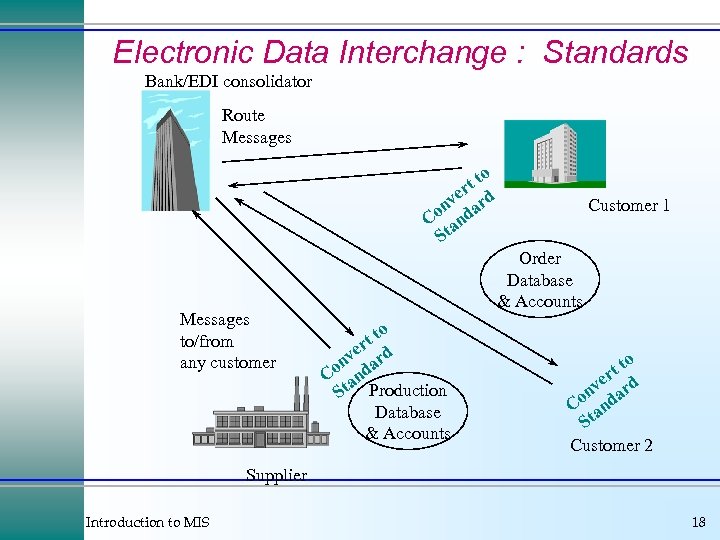 Electronic Data Interchange : Standards Bank/EDI consolidator Route Messages o tt r ve ard n Co and St Messages to/from any customer Customer 1 Order Database & Accounts o tt r ve ard n Co and St Production Database & Accounts o tt r ve ard on d C an St Customer 2 Supplier Introduction to MIS 18
Electronic Data Interchange : Standards Bank/EDI consolidator Route Messages o tt r ve ard n Co and St Messages to/from any customer Customer 1 Order Database & Accounts o tt r ve ard n Co and St Production Database & Accounts o tt r ve ard on d C an St Customer 2 Supplier Introduction to MIS 18
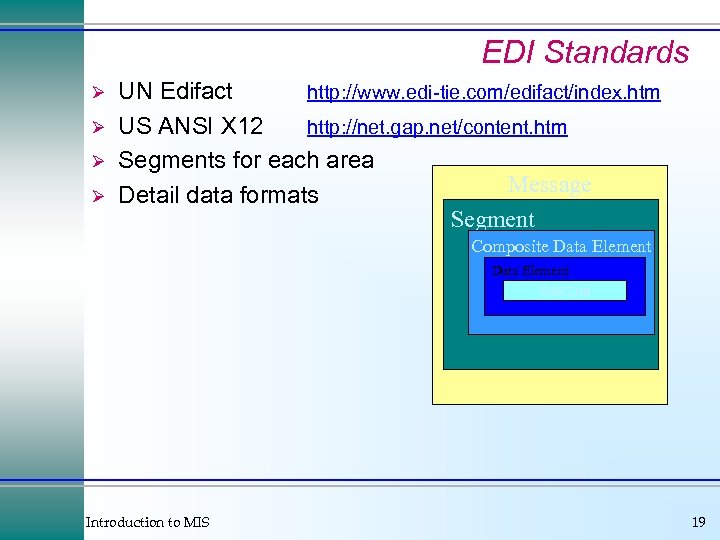 EDI Standards Ø Ø UN Edifact http: //www. edi-tie. com/edifact/index. htm US ANSI X 12 http: //net. gap. net/content. htm Segments for each area Message Detail data formats Segment Composite Data Element Code Lists Introduction to MIS 19
EDI Standards Ø Ø UN Edifact http: //www. edi-tie. com/edifact/index. htm US ANSI X 12 http: //net. gap. net/content. htm Segments for each area Message Detail data formats Segment Composite Data Element Code Lists Introduction to MIS 19
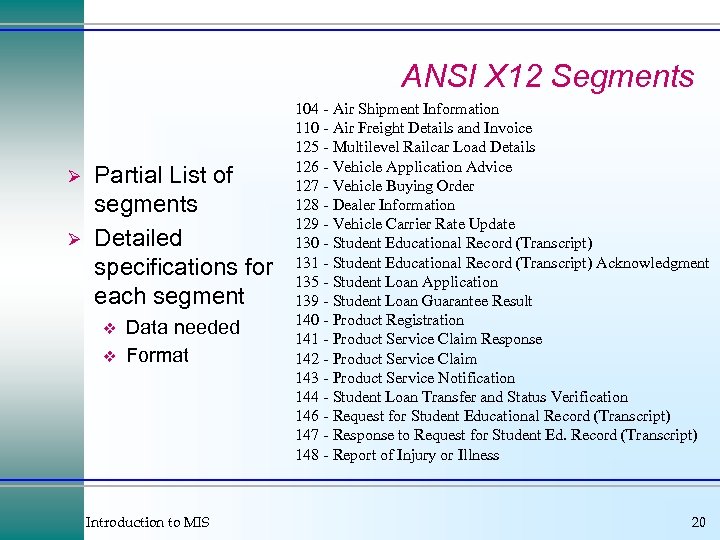 ANSI X 12 Segments Ø Ø Partial List of segments Detailed specifications for each segment v v Data needed Format Introduction to MIS 104 - Air Shipment Information 110 - Air Freight Details and Invoice 125 - Multilevel Railcar Load Details 126 - Vehicle Application Advice 127 - Vehicle Buying Order 128 - Dealer Information 129 - Vehicle Carrier Rate Update 130 - Student Educational Record (Transcript) 131 - Student Educational Record (Transcript) Acknowledgment 135 - Student Loan Application 139 - Student Loan Guarantee Result 140 - Product Registration 141 - Product Service Claim Response 142 - Product Service Claim 143 - Product Service Notification 144 - Student Loan Transfer and Status Verification 146 - Request for Student Educational Record (Transcript) 147 - Response to Request for Student Ed. Record (Transcript) 148 - Report of Injury or Illness 20
ANSI X 12 Segments Ø Ø Partial List of segments Detailed specifications for each segment v v Data needed Format Introduction to MIS 104 - Air Shipment Information 110 - Air Freight Details and Invoice 125 - Multilevel Railcar Load Details 126 - Vehicle Application Advice 127 - Vehicle Buying Order 128 - Dealer Information 129 - Vehicle Carrier Rate Update 130 - Student Educational Record (Transcript) 131 - Student Educational Record (Transcript) Acknowledgment 135 - Student Loan Application 139 - Student Loan Guarantee Result 140 - Product Registration 141 - Product Service Claim Response 142 - Product Service Claim 143 - Product Service Notification 144 - Student Loan Transfer and Status Verification 146 - Request for Student Educational Record (Transcript) 147 - Response to Request for Student Ed. Record (Transcript) 148 - Report of Injury or Illness 20
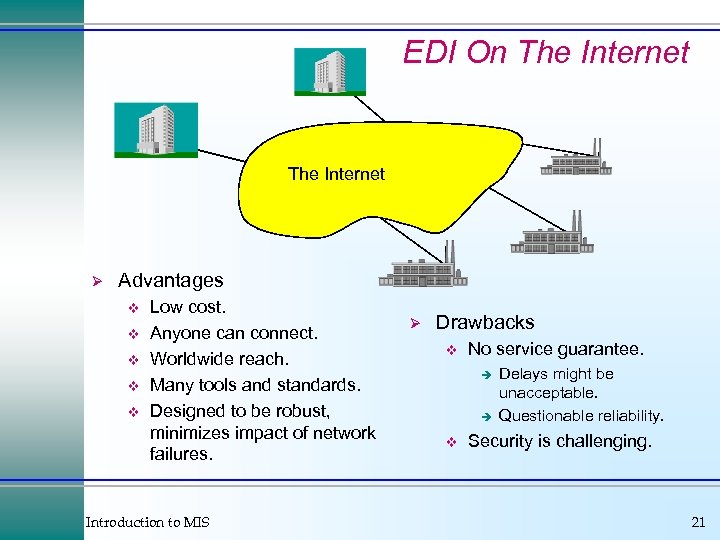 EDI On The Internet Ø Advantages v v v Low cost. Anyone can connect. Worldwide reach. Many tools and standards. Designed to be robust, minimizes impact of network failures. Introduction to MIS Ø Drawbacks v No service guarantee. è è v Delays might be unacceptable. Questionable reliability. Security is challenging. 21
EDI On The Internet Ø Advantages v v v Low cost. Anyone can connect. Worldwide reach. Many tools and standards. Designed to be robust, minimizes impact of network failures. Introduction to MIS Ø Drawbacks v No service guarantee. è è v Delays might be unacceptable. Questionable reliability. Security is challenging. 21
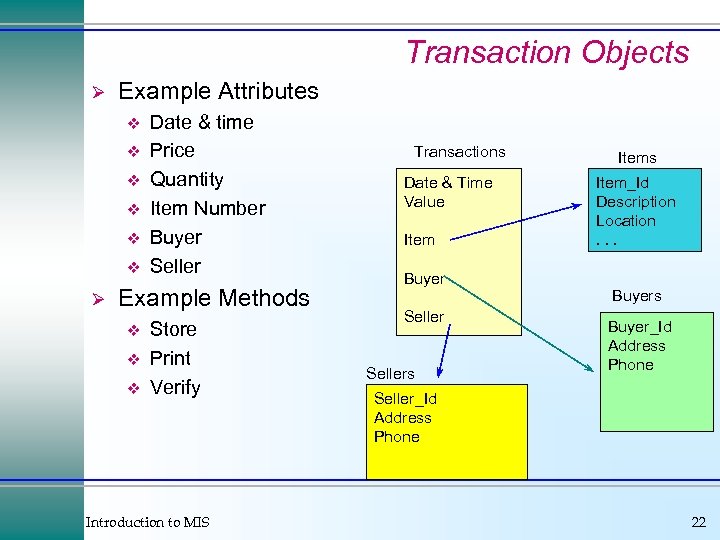 Transaction Objects Ø Example Attributes v v v Ø Date & time Price Quantity Item Number Buyer Seller Example Methods v v v Store Print Verify Introduction to MIS Transactions Date & Time Value Item Buyer Sellers Item_Id Description Location. . . Buyers Buyer_Id Address Phone Seller_Id Address Phone 22
Transaction Objects Ø Example Attributes v v v Ø Date & time Price Quantity Item Number Buyer Seller Example Methods v v v Store Print Verify Introduction to MIS Transactions Date & Time Value Item Buyer Sellers Item_Id Description Location. . . Buyers Buyer_Id Address Phone Seller_Id Address Phone 22
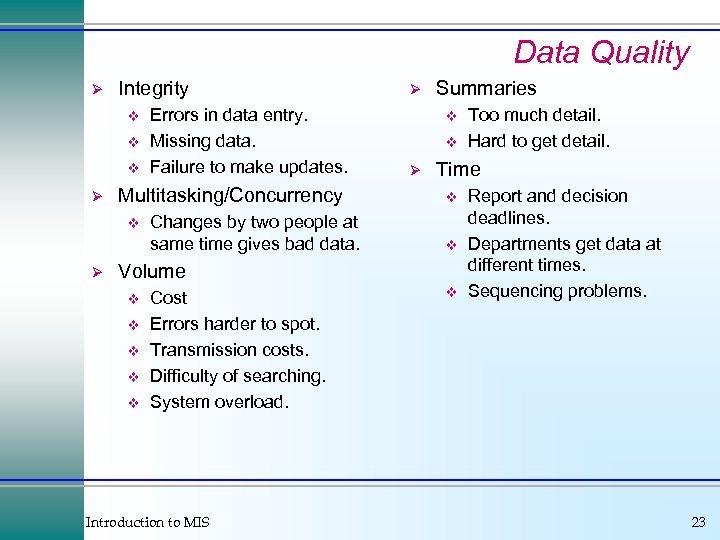 Data Quality Ø Integrity v v v Ø Multitasking/Concurrency v Ø Errors in data entry. Missing data. Failure to make updates. Changes by two people at same time gives bad data. Ø Summaries v v Ø Time v v Volume v v v Cost Errors harder to spot. Transmission costs. Difficulty of searching. System overload. Introduction to MIS Too much detail. Hard to get detail. v Report and decision deadlines. Departments get data at different times. Sequencing problems. 23
Data Quality Ø Integrity v v v Ø Multitasking/Concurrency v Ø Errors in data entry. Missing data. Failure to make updates. Changes by two people at same time gives bad data. Ø Summaries v v Ø Time v v Volume v v v Cost Errors harder to spot. Transmission costs. Difficulty of searching. System overload. Introduction to MIS Too much detail. Hard to get detail. v Report and decision deadlines. Departments get data at different times. Sequencing problems. 23
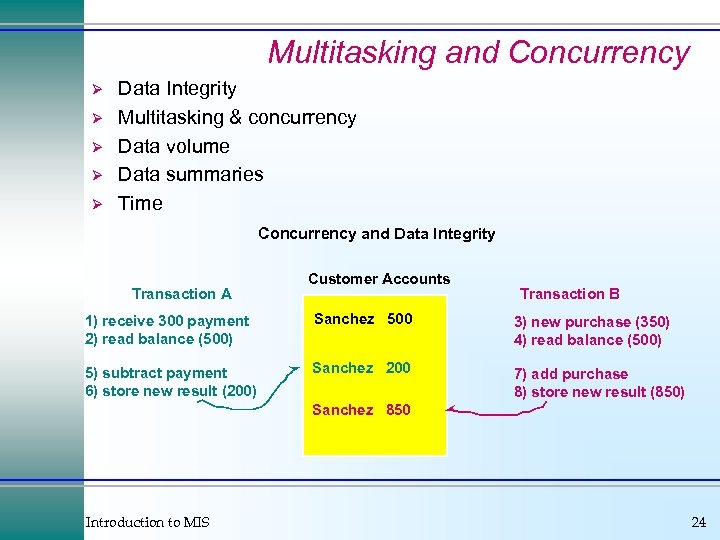 Multitasking and Concurrency Ø Ø Ø Data Integrity Multitasking & concurrency Data volume Data summaries Time Concurrency and Data Integrity Transaction A Customer Accounts Transaction B 1) receive 300 payment 2) read balance (500) Sanchez 500 3) new purchase (350) 4) read balance (500) 5) subtract payment 6) store new result (200) Sanchez 200 7) add purchase 8) store new result (850) Sanchez 850 Introduction to MIS 24
Multitasking and Concurrency Ø Ø Ø Data Integrity Multitasking & concurrency Data volume Data summaries Time Concurrency and Data Integrity Transaction A Customer Accounts Transaction B 1) receive 300 payment 2) read balance (500) Sanchez 500 3) new purchase (350) 4) read balance (500) 5) subtract payment 6) store new result (200) Sanchez 200 7) add purchase 8) store new result (850) Sanchez 850 Introduction to MIS 24
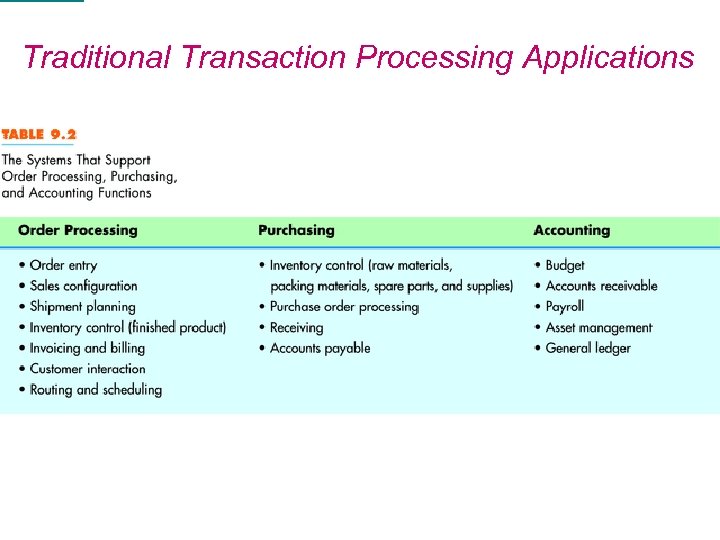 Traditional Transaction Processing Applications Introduction to MIS 25
Traditional Transaction Processing Applications Introduction to MIS 25
 Accounting Ø Ø Ø Financial data and reports What do things really cost? The accounting cycle Inventory Checks and balances v v v Double-entry Separation of duties Audit trails Introduction to MIS 26
Accounting Ø Ø Ø Financial data and reports What do things really cost? The accounting cycle Inventory Checks and balances v v v Double-entry Separation of duties Audit trails Introduction to MIS 26
 Accounting Software Ø General Ledger v v v v Ø Sample chart of accounts Automatic posting Automatic entry of vendors Fiscal years Keep past data books open Post to prior years Allocate department expenses Accounts Receivable v v v v Automatic early discounts Interest on late payments Multiple shipping addresses Sales tax Automatic reminder notices Automatic monthly fees Keep monthly details Introduction to MIS Ø Accounts payable v v v Ø Check reconciliation Automatic recurring entries Monitor payment discounts Select bills from screen Pay by item, not just total bill General Features v v v Printer support Use of preprinted forms Custom reports Custom queries Security controls Technical support costs 27
Accounting Software Ø General Ledger v v v v Ø Sample chart of accounts Automatic posting Automatic entry of vendors Fiscal years Keep past data books open Post to prior years Allocate department expenses Accounts Receivable v v v v Automatic early discounts Interest on late payments Multiple shipping addresses Sales tax Automatic reminder notices Automatic monthly fees Keep monthly details Introduction to MIS Ø Accounts payable v v v Ø Check reconciliation Automatic recurring entries Monitor payment discounts Select bills from screen Pay by item, not just total bill General Features v v v Printer support Use of preprinted forms Custom reports Custom queries Security controls Technical support costs 27
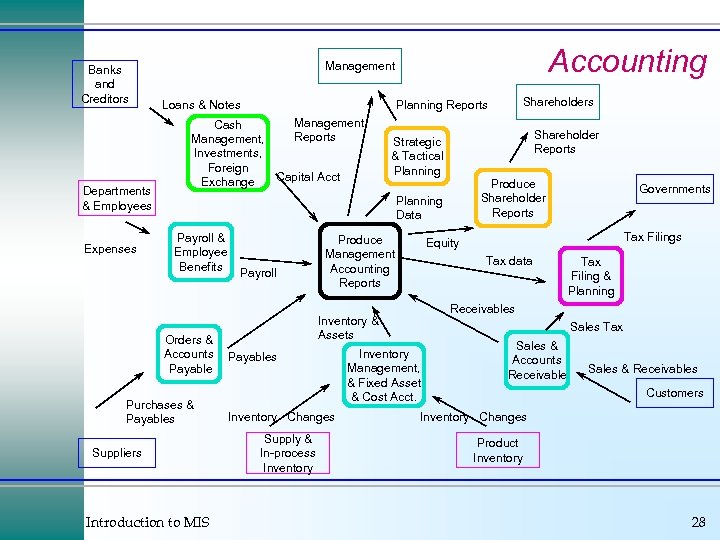 Banks and Creditors Departments & Employees Expenses Accounting Management Loans & Notes Management Cash Reports Management, Investments, Foreign Capital Acct Exchange Shareholder Reports Strategic & Tactical Planning Produce Shareholder Reports Planning Data Payroll & Employee Benefits Orders & Accounts Payable Purchases & Payables Suppliers Introduction to MIS Shareholders Planning Reports Payroll Produce Management Accounting Reports Inventory Changes Supply & In-process Inventory Tax Filings Equity Tax data Tax Filing & Planning Receivables Inventory & Assets Payables Governments Sales Tax Inventory Management, & Fixed Asset & Cost Acct. Sales & Accounts Receivable Sales & Receivables Customers Inventory Changes Product Inventory 28
Banks and Creditors Departments & Employees Expenses Accounting Management Loans & Notes Management Cash Reports Management, Investments, Foreign Capital Acct Exchange Shareholder Reports Strategic & Tactical Planning Produce Shareholder Reports Planning Data Payroll & Employee Benefits Orders & Accounts Payable Purchases & Payables Suppliers Introduction to MIS Shareholders Planning Reports Payroll Produce Management Accounting Reports Inventory Changes Supply & In-process Inventory Tax Filings Equity Tax data Tax Filing & Planning Receivables Inventory & Assets Payables Governments Sales Tax Inventory Management, & Fixed Asset & Cost Acct. Sales & Accounts Receivable Sales & Receivables Customers Inventory Changes Product Inventory 28
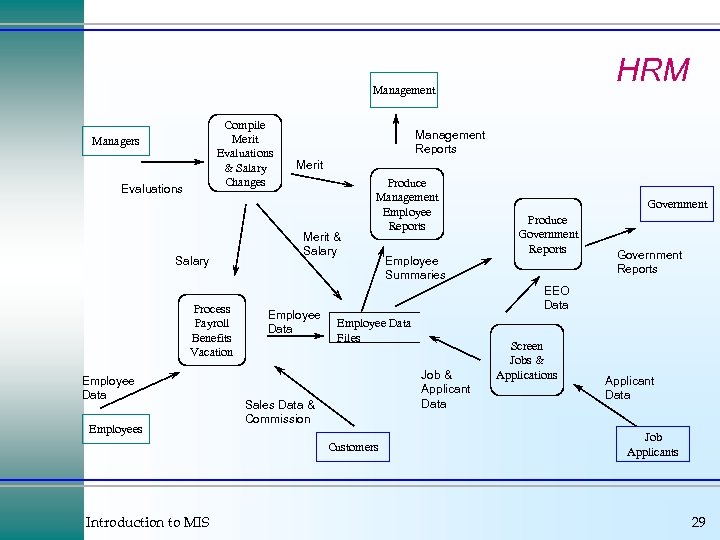 HRM Management Compile Merit Evaluations & Salary Changes Managers Evaluations Salary Process Payroll Benefits Vacation Employee Data Employees Management Reports Merit & Salary Employee Data Produce Management Employee Reports Government Reports EEO Data Employee Data Files Job & Applicant Data Sales Data & Commission Customers Introduction to MIS Employee Summaries Government Produce Government Reports Screen Jobs & Applications Applicant Data Job Applicants 29
HRM Management Compile Merit Evaluations & Salary Changes Managers Evaluations Salary Process Payroll Benefits Vacation Employee Data Employees Management Reports Merit & Salary Employee Data Produce Management Employee Reports Government Reports EEO Data Employee Data Files Job & Applicant Data Sales Data & Commission Customers Introduction to MIS Employee Summaries Government Produce Government Reports Screen Jobs & Applications Applicant Data Job Applicants 29
 Questions? Introduction to MIS 30
Questions? Introduction to MIS 30


