55707ead385477b1d4ab71540a3fcbda.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Infrastructure & Technology – Part 2 CPS 181 s March 27, 2003
Infrastructure & Technology – Part 2 CPS 181 s March 27, 2003
 e. Commerce Enablers Page 86, Table 2. 6 2
e. Commerce Enablers Page 86, Table 2. 6 2
 Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology
Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology
 Seven Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology t. Ubiquity t. Global Reach t. Universal Standards t. Richness t. Interactivity t. Personalization/Customization t. Information Density 4
Seven Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology t. Ubiquity t. Global Reach t. Universal Standards t. Richness t. Interactivity t. Personalization/Customization t. Information Density 4
 Seven Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology t Ubiquity t Alters industry structure by creating new marketing channels and expanding size of overall market t Creates new efficiencies in industry operations and lowers cost of firms’ sales operations t Enables new differentiation strategies 5
Seven Unique Feature of e. Commerce Technology t Ubiquity t Alters industry structure by creating new marketing channels and expanding size of overall market t Creates new efficiencies in industry operations and lowers cost of firms’ sales operations t Enables new differentiation strategies 5
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Global Reach t Changes industry structure by lowering barriers to entry, but greatly expands market at the same time t Lowers cost of industry and firm operations through production and sales efficiencies t Enables competition on global scale 6
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Global Reach t Changes industry structure by lowering barriers to entry, but greatly expands market at the same time t Lowers cost of industry and firm operations through production and sales efficiencies t Enables competition on global scale 6
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Universal Standards t Changes industry structure by lowering barriers to entry and intensifying competition within an industry t Lowers costs of industry and firm operations by lowering computing and communications costs t Enables broad-scope strategies 7
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Universal Standards t Changes industry structure by lowering barriers to entry and intensifying competition within an industry t Lowers costs of industry and firm operations by lowering computing and communications costs t Enables broad-scope strategies 7
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Richness t Alters industry structure by reducing strength of powerful distribution channels t Change industry and firm operations costs by lessening reliance on sales force t Enhances post-sale support strategies 8
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Richness t Alters industry structure by reducing strength of powerful distribution channels t Change industry and firm operations costs by lessening reliance on sales force t Enhances post-sale support strategies 8
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Interactivity t Alters industry structure by reducing threat of substitutes through enhanced customization t Reduces industry and firm costs by lessening reliance on sales force t Enables differentiation strategies 9
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Interactivity t Alters industry structure by reducing threat of substitutes through enhanced customization t Reduces industry and firm costs by lessening reliance on sales force t Enables differentiation strategies 9
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Personalization/Customization t Alters industry structure by reducing threats of substitutes, raising barriers to entry t Reduces value chain costs in industry and firm by lessening reliance on sales forces 10
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Personalization/Customization t Alters industry structure by reducing threats of substitutes, raising barriers to entry t Reduces value chain costs in industry and firm by lessening reliance on sales forces 10
 Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Information Density t Changes industry structure by weakening powerful sales channels, shifting bargaining power to consumer t Reduces industry and firm operations costs by lowering costs of obtaining, processing, and distributing information about suppliers and consumers 11
Seven Unique Features of e. Commerce Technology t Information Density t Changes industry structure by weakening powerful sales channels, shifting bargaining power to consumer t Reduces industry and firm operations costs by lowering costs of obtaining, processing, and distributing information about suppliers and consumers 11
 How the Internet and the Web Change Business: Basic Business Concepts t Industry Value Chains t t t set of activities performed in an industry by suppliers, manufacturers, transporters, distributors, and retailers that transform raw inputs into final products and services reducing the cost of information and other transactional costs Firm Value Chains t t set of activities performed within an individual firm to create final products from raw inputs increasing operational efficiency 12
How the Internet and the Web Change Business: Basic Business Concepts t Industry Value Chains t t t set of activities performed in an industry by suppliers, manufacturers, transporters, distributors, and retailers that transform raw inputs into final products and services reducing the cost of information and other transactional costs Firm Value Chains t t set of activities performed within an individual firm to create final products from raw inputs increasing operational efficiency 12
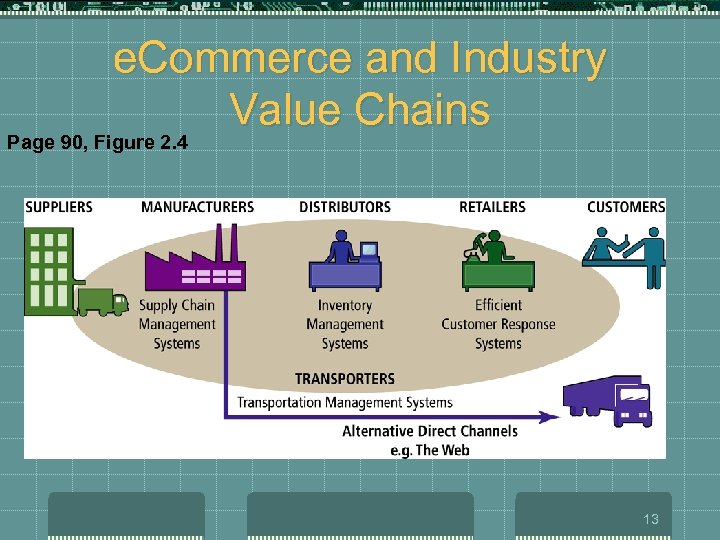 e. Commerce and Industry Value Chains Page 90, Figure 2. 4 13
e. Commerce and Industry Value Chains Page 90, Figure 2. 4 13
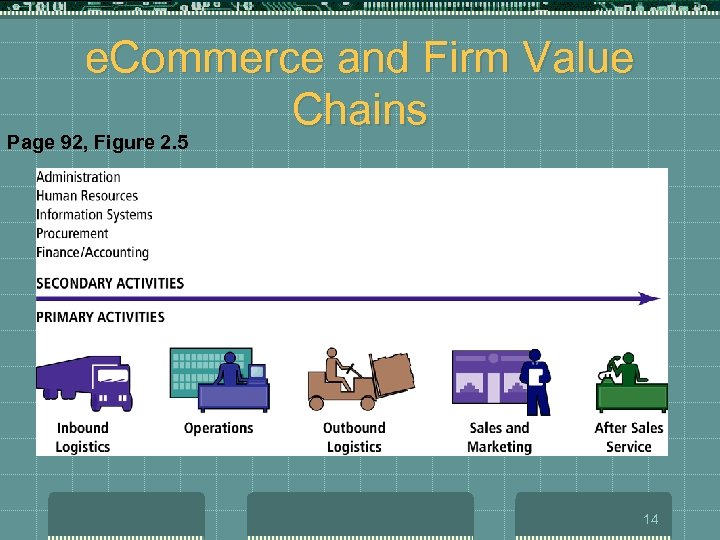 e. Commerce and Firm Value Chains Page 92, Figure 2. 5 14
e. Commerce and Firm Value Chains Page 92, Figure 2. 5 14
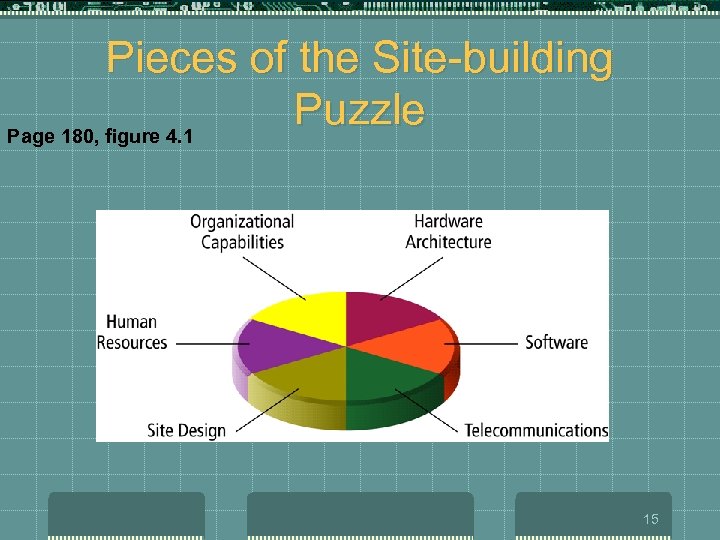 Pieces of the Site-building Puzzle Page 180, figure 4. 1 15
Pieces of the Site-building Puzzle Page 180, figure 4. 1 15
 Building an e. Commerce Web Site: A Systematic Approach t t t Planning: the systems development life cycle Systems analysis: identify business objectives, system functionality, and information requirements System design: hardware and software platforms Building the system: in-house vs. Outsourcing Testing the system Implementation and maintenance 16
Building an e. Commerce Web Site: A Systematic Approach t t t Planning: the systems development life cycle Systems analysis: identify business objectives, system functionality, and information requirements System design: hardware and software platforms Building the system: in-house vs. Outsourcing Testing the system Implementation and maintenance 16
 Systems Analysis: Identify Business Objectives, System Functionality, and Information Requirements t Business objectives t t System functionalities t t A list of capabilities you want your site to have A list of types of information systems capabilities you will need to achieve your business objectives Information requirements t The information elements that the system must produce in order to achieve the business objectives 17
Systems Analysis: Identify Business Objectives, System Functionality, and Information Requirements t Business objectives t t System functionalities t t A list of capabilities you want your site to have A list of types of information systems capabilities you will need to achieve your business objectives Information requirements t The information elements that the system must produce in order to achieve the business objectives 17
 System Design: Hardware and Software Platforms t System design specification t t Logical design t t t Description of the main components in a system and their relationship to one another Describes the flow of information at your e. Commerce site The processing functions that must be performed The databases that will be used The security and emergency backup procedures that will be instituted The controls that will be used in the system Physical design t Translates the logical design into physical components 18
System Design: Hardware and Software Platforms t System design specification t t Logical design t t t Description of the main components in a system and their relationship to one another Describes the flow of information at your e. Commerce site The processing functions that must be performed The databases that will be used The security and emergency backup procedures that will be instituted The controls that will be used in the system Physical design t Translates the logical design into physical components 18
 Merchant Server Software Packages (e. Commerce Suites) t t Offers an integrated environment that provides most or all of the functionality and capabilities needed to develop a sophisticated, customer-centric site. Key factors to consider t t t t t Functionality Support for different business models Business process modeling tools Visual site management tools and reporting Performance and scalability Connectivity to existing business systems Compliance to standards Global and multicultural capability Local sales tax and shipping rules 19
Merchant Server Software Packages (e. Commerce Suites) t t Offers an integrated environment that provides most or all of the functionality and capabilities needed to develop a sophisticated, customer-centric site. Key factors to consider t t t t t Functionality Support for different business models Business process modeling tools Visual site management tools and reporting Performance and scalability Connectivity to existing business systems Compliance to standards Global and multicultural capability Local sales tax and shipping rules 19
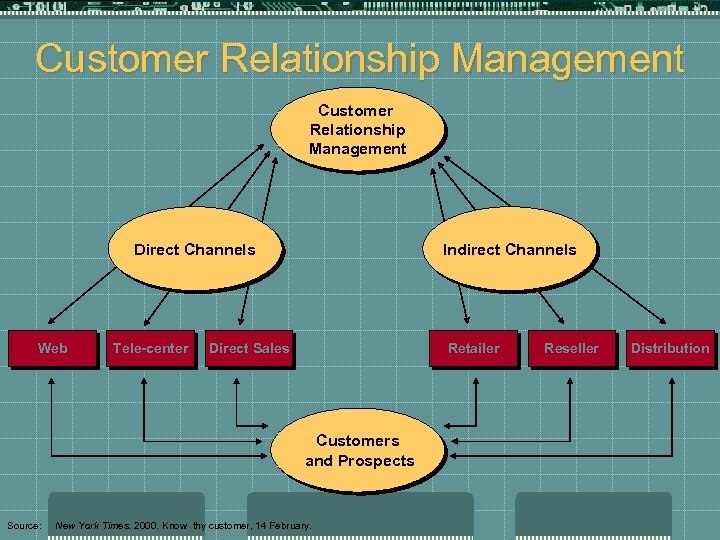
 Customer Relationship Management (CRM) t Customer relationship management, also called one-to-one marketing or permission marketing, enables a company to provide excellent customer service in real time by focusing on relationship development with each individual customer through the effective use of individual account information t Behavior patterns can help customers become lifetime customers t Goals of effective CRM are: t to achieve long-running customer dialogue across all customer access points t to provide more effective cross-sell and up-sell t to increase customer retention and loyalty t to increase customer profitability t to achieve higher responses to marketing campaigns t to provide extraordinary service and support
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) t Customer relationship management, also called one-to-one marketing or permission marketing, enables a company to provide excellent customer service in real time by focusing on relationship development with each individual customer through the effective use of individual account information t Behavior patterns can help customers become lifetime customers t Goals of effective CRM are: t to achieve long-running customer dialogue across all customer access points t to provide more effective cross-sell and up-sell t to increase customer retention and loyalty t to increase customer profitability t to achieve higher responses to marketing campaigns t to provide extraordinary service and support
 CRM. . . t Achieving Long-running Customer Dialogue Across All Customer Access Points: manage input through call centers, the Internet, or mail through a centralized database, 24 x 7, regardless of the sales channel t More Effective Cross-selling and Up-selling: profiles in databases and conversations allow for collaborative filtering and focusing t Increase Customer Retention and Loyalty: better understanding of behavior leads to increased sales and higher retention
CRM. . . t Achieving Long-running Customer Dialogue Across All Customer Access Points: manage input through call centers, the Internet, or mail through a centralized database, 24 x 7, regardless of the sales channel t More Effective Cross-selling and Up-selling: profiles in databases and conversations allow for collaborative filtering and focusing t Increase Customer Retention and Loyalty: better understanding of behavior leads to increased sales and higher retention
 CRM. . . t Achieving Higher Customer Profitability: CRM places a greater value on customers, in depth examination of those in the Pareto (Pareto Principle or 80/20 rule) range helps managers focus on the top tier t Achieving Higher Responses to Marketing Campaigns: integrated information from sales and service departments help increase overall sales and identify potential bottlenecks t Provide Extraordinary Service and Support: technology helps companies and their customer find information 24 x 7
CRM. . . t Achieving Higher Customer Profitability: CRM places a greater value on customers, in depth examination of those in the Pareto (Pareto Principle or 80/20 rule) range helps managers focus on the top tier t Achieving Higher Responses to Marketing Campaigns: integrated information from sales and service departments help increase overall sales and identify potential bottlenecks t Provide Extraordinary Service and Support: technology helps companies and their customer find information 24 x 7
 Customer Relationship Management Direct Channels Web Tele-center Indirect Channels Direct Sales Retailer Customers and Prospects Source: New York Times. 2000. Know thy customer, 14 February. Reseller Distribution
Customer Relationship Management Direct Channels Web Tele-center Indirect Channels Direct Sales Retailer Customers and Prospects Source: New York Times. 2000. Know thy customer, 14 February. Reseller Distribution
 How Will the Increased Use of the Internet Effect Public Policy and Politics? t Privacy t Cookies tracking every keystroke t Use of personal information t Issue of reliability of privacy statements and regulations t Taxation t Debates between federal, state, and local authorities t The 19 -member Advisory Commission of Electronic Commerce, created by Congress, voted to extend the tax moratorium for five years after it expires in October 2001, with divided interests t Patents t Amazon. com’s One-click ordering system have lead critics to complain that these software developments are rather trivial, and that much of software development is incremental, and that patent examiners do not do a good job at looking at similar existing software on the Internet
How Will the Increased Use of the Internet Effect Public Policy and Politics? t Privacy t Cookies tracking every keystroke t Use of personal information t Issue of reliability of privacy statements and regulations t Taxation t Debates between federal, state, and local authorities t The 19 -member Advisory Commission of Electronic Commerce, created by Congress, voted to extend the tax moratorium for five years after it expires in October 2001, with divided interests t Patents t Amazon. com’s One-click ordering system have lead critics to complain that these software developments are rather trivial, and that much of software development is incremental, and that patent examiners do not do a good job at looking at similar existing software on the Internet
 How Will the Increased Use of the Internet Effect Public Policy and Politics? . . . t Access t The entry price into the Internet is higher than a telephone, prompting a “wired and unwire” “haves and have-nots” society, prompting governments and organizations to make computers more accessible at public schools and libraries t Free Speech t Police fear Internet access provides disenchanted members of society an easier opportunity to communicate with one another and other disgruntled outcasts, building communities that runs counter to the public interest t Network Economics and Monopolies t Media convergence, both among media providers and information distributors, have raised issues of conflict of interest, antitrust, and concentration of media power such as AOL-Time Warner
How Will the Increased Use of the Internet Effect Public Policy and Politics? . . . t Access t The entry price into the Internet is higher than a telephone, prompting a “wired and unwire” “haves and have-nots” society, prompting governments and organizations to make computers more accessible at public schools and libraries t Free Speech t Police fear Internet access provides disenchanted members of society an easier opportunity to communicate with one another and other disgruntled outcasts, building communities that runs counter to the public interest t Network Economics and Monopolies t Media convergence, both among media providers and information distributors, have raised issues of conflict of interest, antitrust, and concentration of media power such as AOL-Time Warner


